Loading
Journal of Cellular Immunology
ISSN: 2689-2812
All Articles
Deubiquitinase as Potential Targets for Cancer Immunotherapy
Xiaoping Xie
During the last few decades, immunotherapy is considered to be an important approach to help our immune system to fight various kinds of diseases, such as tumor. Sometimes, it works very well for some types of cancers, for example: bladder cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer and lymphoma.
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.001
What Can Go Wrong When Applying Immune Modulation Therapies to Target Persistent Bacterial Infections
Sofiya Micheva-Viteva, Elizabeth Hong-Geller
Antibiotics can treat the acute phase of a disease, but often do not completely clear the etiologic agent, allowing the pathogen to establish persistent infection that can revive the disease in a frustrating recurrence of infection. The mechanisms that control chronic bacterial infections are complex and involve pathogen adaptations that favor survival from both host immune responses and antibiotic bactericidal activity.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p1-5 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.011
Sticky Interactions in Lupus Nephritis
Radha Nune, Rajalakshmy Ayilam Ramachandran, Jessica Castillo, Chandra Mohan
Cell adhesion molecules (CAM) mediate cell to cell interactions in various body systems including the immune system. The four major families of CAMs include immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily, cadherins, integrins, and selectins. Most interestingly, several CAMs have emerged in recent years as leading biomarkers of lupus nephritis (LN) based on comprehensive proteomic screens of urine. Proteins belonging to all four families of CAMs have been reported to be upregulated in LN urine.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p1-5 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.126
Intracellular Hyaluronan Synthesis Impairs Hematopoiesis in Diabetes that can be Prevented by Heparin
Andrew Jun Wang, Vincent Charles Hascall
Hyperglycemia in diabetes induces impairment of hematopoiesis, an important consequence in bone marrow (BM) that contributes to chronic complications in advanced diabetes. The alterations to blood cells associated with diabetes mellitus (DM) pathologies have been carefully and extensively documented, but the underlying mechanism(s) is still unclear. Our recent publication indicates that aberrant intracellular synthesis of hyaluronan (HA) by hyperglycemic dividing BM progenitors is the central mechanism involved.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p1-6 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.155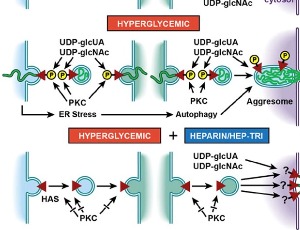
Guardians of Intestinal Homeostasis: Focus on Intestinal Epithelial Cells
Maha M. Elbrashy, Hozaifa Metwally, Tadamitsu Kishimoto
The intestinal epithelium not only facilitates the absorption of nutrients, but also plays a pivotal role in guarding intestinal homeostasis and preventing opportunistic gut microbiome invasions. The intestinal epithelial cells have diverse and coordinated regulatory networks that provide intricate lines of defense, in order to maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p1-6 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.186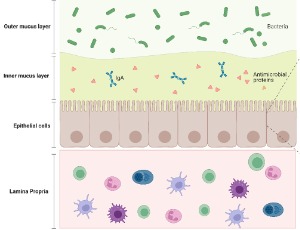
A Review of the Possibility of Nafamostat Mesylate in COVID-19 Treatment
Ji-Young Rhee
Nafamostat mesylate is a synthetic serine protease inhibitor, which inhibits various enzyme systems such as coagulation and fibrinolytic systems, the kallikrein–kinin system, the complement system, and the activation of protease-activated receptors. It also inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production, apoptosis, and interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 levels in cultured human trophoblasts.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p1-7 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.069
A Novel Guardian of Telomeres: RIOK2 Regulates Telomerase Activity Through TRiC and Dyskerin Complexes
Merve Akyol, Shrestha Ghosh
Telomeres are repetitive DNA sequences located at chromosomal ends that are crucial for maintaining genomic stability. Telomere lengths are tightly regulated under physiological conditions, disruption of which results in telomere shortening that ultimately leads to telomere biology disorders, such as Dyskeratosis congenita (DC), bone marrow failure syndromes, and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF), amongst others. Progressive telomere shortening is also a well-recognized feature of aging.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p1-8 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.216
The Endothelium: Global Integrator of Vascular-Immune Interactions
Daniel Bergey
Endothelial cells (ECs) are mesodermally-derived modified simple squamous epithelial cells that collectively form the vascular endothelium–the vast living shield that lines the luminal surface of all blood vessels, the lymphatic circuit, and heart. Endothelial cell phenotypes vary among different organs and tissues with regard to specific barrier characteristics, and can be altered by environmental stimuli
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p4-11 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.002
Is Platelet Desialylation a Novel Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Immune Thrombocytopenia?
June Li, Jade A. Sullivan, Heyu Ni
Immune thrombocytopenia is an autoimmune disease predominantly caused by autoantibody mediated platelet and megakaryocyte destruction and or dysfunction, which leads to low platelet counts and risk of bleeding. Currently prognostic biomarkers are underdeveloped and there lacks a gold-standard for therapeutics, which leaves an inexplicable refractory subset of patients which are clinically challenging.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p6-14 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.012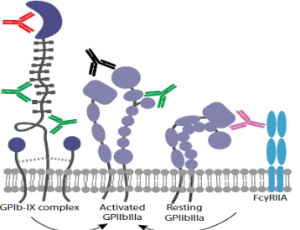
Towards a Better Understanding of Staphylococcus aureus Skin Infections-The Interactions with Dendritic Cells
Aizat Iman Abdul Hamid, Elisabeth Billard, Pascale Gueirard
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is the leading cause of skin and soft tissue infections in humans. Additionally, local infections further lead to dissemination and colonization of secondary infections sites including the lungs, heart valves and even medical prostheses. It is well known that this bacterial species is capable of altering host immune responses and that long-term protection against S. aureus is not completely effective.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p6-14 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.127
Role of Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) in Immune Regulation and Neuroprotection
John Dumbuya, Howard Prentice, Jang-Yen Wu
Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) has been in clinical use for over two decades to enhance hematopoiesis and granulopoiesis to increase the numbers of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells in patients with neutropenia and patients involved in bone marrow transplantation. G-CSF protein or G-CSF gene therapy has also been shown to have both neuroprotective and neurogenesis function and is quite effective in improving neurological functions in Parkinson’s disease [1], stroke [2-4] and Alzheimer’s disease [5].
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p7-9 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.156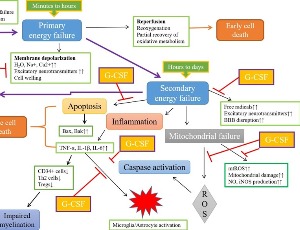
Hair Follicle Stem Cells: the Signaling Hub of the Skin
Yongci Tan, Haocai Chang
Hair follicle stem cells (HFSCs) are recognized as multipotential stem cells with exceptional proliferative capacity. Their regulatory effect on skin homeostasis is orchestrated through intricate signaling pathways, including Wnt/β-catenin, transforming growth factor-β/bone morphogenetic protein (TGFβ/BMP), Notch, and Hedgehog.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p7-14 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.187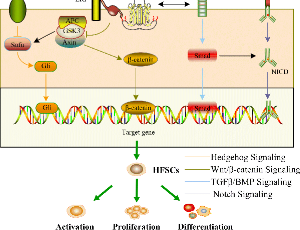
Gene Knock-in Strategy for Engineered T-cell Therapy
Qianqian Gao, Renpeng Ding, Cheng-Chi Chao
Genetically engineered T-cell therapy holds great potential for the curative treatment across a series of cancers. However, drug-related safety concerns need to be addressed in the emerging medicine of the future. T cells are engineered through conventional methods like lentivirus, retrovirus or transposon, which randomly integrate exogenous gene cassette into T cell genome, accompanied by the risks of transcriptional silencing, oncogenesis, and variegated transgene expression.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p8-11 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.070
GRP78: A Multifaceted Role in Cancer Progression and Infectious Disease Transmission
Akane Sato, Etsuro Ito
The 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein GRP78, also known as HSPA5 or BiP, is a heat shock protein 70 family member that promotes functions of the endoplasmic reticulum, such as protein folding and assembly, prevention of aggregation of misfolded proteins, translocation of secreted proteins, and initiation of the unfolded protein response. GRP78 may also be a cancer marker. When small extracellular vesicles containing GRP78 are released from cancer cells, recipient cells exhibit enhanced malignant progression and angiogenesis.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p9-13 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.217
Importance of Ultrasensitive ELISA in Cancer Research
Daiki Makioka, Kanako Iha, Etsuro Ito
The ultrasensitive ELISA method developed by Watanabe and Ito combines sandwich ELISA and thio-NAD cycling to enable the quantitation of trace amounts of proteins. The ultra-traceability provided by this method makes it possible to quantify extremely small amounts of proteins in small extracellular vesicles called exosomes as well as in urine.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p10-13 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.157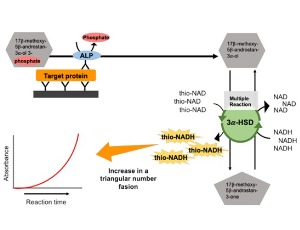
Progression of Autoantibodies Anti-Gad and Anti-IA2 in Type 1A Diabetics Aged 5 to 21 Years in Cote d’Ivoire
Aïssé Florence Judith Trébissou, Pascal Sibailly, Amos Ankotché, Mamadou Sanogo, Dinard Kouassi, Marie Thérèse Kouassi, Hatem Masmoudi, Adou Francis Yapo
Type 1A diabetes is an autoimmune disease, the final consequence of a slow and gradual process of ß-cell destruction of pancreatic islet Langerhans cells leading to ketoacidosis in the absence of treatment. This destruction of the β cells, responsible for the production of insulin, begins with the initiation of the autoimmune reaction triggered by certain environmental factors and, after several years of evolution, leads to the clinical signs of the disease when the mass of ß cells
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p12-15 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.003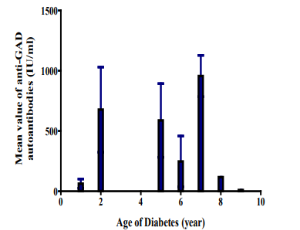
Role of BCG in Reduction of the Spread and Severity of COVID-19
Amit Raj Sharma, Ankita Semwal, Gitika Batra, Mukesh Kumar, Manisha Prajapat, Ashutosh Singh, Rahul Soloman Singh, Bikash Medhi
The COVID-19 has started from China and spread to all countries within a very short period. The severity of the disease varies from one patient to another as well as one country to another. It depends on the immune status of individuals simultaneously on the quality of the environment and customs of a particular country.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p12-19 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.071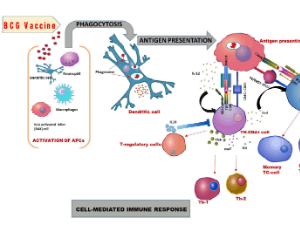
Commentary on “Epigenetically Altered T Cells Contribute to Lupus Flares”
Bruce Richardson
The recently published manuscript entitled “Epigenetically Altered T Cells Contribute to Lupus Flares” summarizes recent advances in our understanding of how the environment alters the immune system to cause flares of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in genetically predisposed people, and why it affects women approximately 9 times more often than men
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p13-14 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.004
From Lipase Elevation to Diabetes – Pancreatic Involvement during Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
Sonja C. S. Simon, Jochen S. Utikal
Nowadays, as a standard of care treatment of several cancers, immune checkpoint inhibitors have changed the field of oncology. However, their empowerment of T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity bears the risk for injury of various organs as a side effect.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p14-18 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.158
Urinary Borrelia Peptides Correlate with the General Symptom Questionnaire (GSQ-30) Scores in Symptomatic Patients with Suspicion of Tick-borne Illness
Sindhu Datla, Sumaiya Irfan, Nicole Trumbull, Rocio Cornero, Ahana Byne, Ghaliah Alluhaibi, Claudius Mueller, Ruben Magni, Weidong Zhou, Barbara Birkaya, Lance Liotta, Alessandra Luchini, Hope McIntyre
Lyme disease, or Lyme Borreliosis, is the most prevalent tick-borne illness in the Northern Hemisphere. It is caused by bacteria in the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato (s.l.) complex, which are transmitted to humans through the bite of infected hard bodied ticks, or Ixodes ticks. Post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome (PTLDS) is a significant complication of Lyme disease, characterized by persistent or recurrent symptoms, such as fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, and cognitive issues, which can lead to functional decline.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p14-25 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.218
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
A Novel Class of RIP1 or RIP3 Dual Inhibitors
Ting Zhou, Bo Liu
Necroptosis is a form of programed necrosis mediated by receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 (RIP1) and RIP3 and the subsequent phosphorylation of mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL). Necroptosis has been implicated in multiple human diseases such as myocardial infarction, atherosclerosis, and abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs). Levels of RIP3 are elevated in the human tissues affected by these diseases.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p15-17 | DOI: 10.33696/2689-2812.2.013
Glucose Metabolism is a Better Marker for Predicting Clinical Alzheimer’s Disease than Amyloid or Tau
Tyler C. Hammond, Ai-Ling Lin
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) research has long been dominated with communications regarding the amyloid hypothesis and targeting amyloid clearance through pharmacological therapies from the brain. Unfortunately, this research strategy has yielded only one new FDA-accelerated approved therapeutic for early AD, and its clinical benefit still needs to be verified. It may be time to employ a new strategy in AD therapeutics research. Hammond et al. reported that diminished uptake of glucose in the brain is a better marker for classifying AD than beta-amyloid (Aβ) or phosphorylated tau deposition.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p15-18 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.128
Design of a Peptide Against the Interaction Between Immune Response Protein TRAF5 and the Oncoprotein E6 from HPV
Santos GT, Oliveira LN, Moraes D, Araujo DS, Assuncao LP, de Curcio JS, Silva MG, Silva CTX, Barbosa AM, Silva KSF
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the human papillomavirus (HPV) affects more than 600 million people worldwide, being the most common sexually transmitted disease (STD). There were over 250,000 deaths due to cervical cancer worldwide and most of them took place in developing countries (WHO). There are more than 80 HPV types and more than 40 infect the genital tract
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p15-24 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.005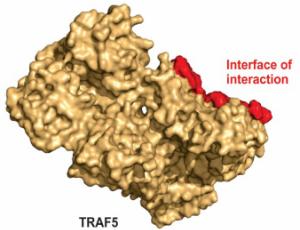
Personalized Neoantigen DNA Cancer Vaccines: Current Status and Future Perspectives
Nadia Viborg, Daniela Kleine-Kohlbrecher, Birgitte Rønø
Tumor mutation-derived neoantigens are considered promising targets for cancer immunotherapy. Personalized vaccines have emerged as an approach to deliver neoantigens and thereby trigger the induction of specific T-cell responses that can find and eliminate tumor cells based on the cell-surface presence of neoantigens. To this end, several neoantigen vaccine formats have provided encouraging results in clinical trials, resulting in neoantigen immunogenicity and clinical benefit.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p15-24 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.188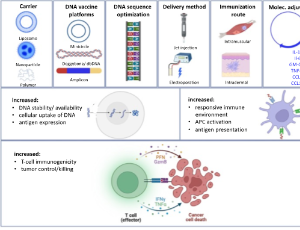
Recent Advances Show That Abnormal T-Regulatory Cell Function Perpetuates Chronic Inflammatory Arthritis
Charles J. Malemud
The principal mechanism governing immune central tolerance is regulated by T-cells that reside in a pathway wherein the death of immature T-cells is coupled to the development of CD4+ regulatory T (Treg) cells. In that regard, Treg cells undergo development in the thymus or peripheral tissues upon recognition of self-antigens.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p18-22 | DOI: 10.33696/2689-2812.2.014
Towards a Chemo-immunotherapy to Improve Breast Cancer Immunotherapy
Xia Li, Lixin Ma, Yunhong Hu
Chemo-immunotherapy has shown great promise as a next-generation treatment strategy for established solid tumors. Cheng et al. first developed the PD-L1- and CD44-responsive multifunctional nanoparticles (MNPs) utilizing a polymer complex of polyethyleneimine and oleic acid (PEI-OA) and loaded with two chemotherapeutic drugs (paclitaxel and chloroquine), an antigen (ovalbumin), an immunopotentiator (CpG), and an immune checkpoint inhibitor (anti-PD-L1 antibody).
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p19-21 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.159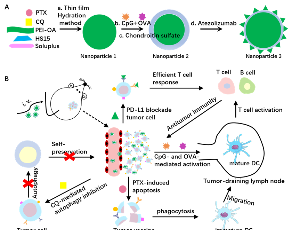
Comparison of Gene Editing versus a Neutrophil Elastase Inhibitor as Potential Therapies for ELANE Neutropenia
Vahagn Makaryan, Merideth Kelley, Breanna Fletcher, Isabella Archibald, Tanoya Poulsen, David Dale
Heterozygous mutations in ELANE, the gene for neutrophil elastase, cause cyclic and congenital neutropenia through the programed cell death of neutrophil progenitors in the bone marrow. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor is an effective therapy for these diseases, but alternative therapies are needed, especially for patients who do not respond well or are at high risk of developing myeloid malignancies. We developed an HL60 cell model for ELANE neutropenia and previously demonstrated that transient and regulated expression of mutant ELANE causes cell death by accelerated apoptosis.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p19-28 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.129
COVID-19, the Immune System, and Neurological Damage
Sayed Ausim Azizi
The Germ Theory of Disease was solidified in the 19th century by Louise Pasteur and Robert Koch. They systematically visualized, isolated, and quantified microscopic pathogens as causative agents of diseases and epidemics. Viruses are submicroscopic; therefore, they were discovered later as pathogens by indirect methods.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p20-25 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.072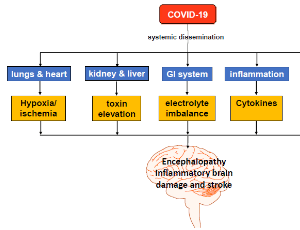
IL-1 in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
Jessica Millar, Elias Nasser, Gorav Ailawadi, Morgan Salmon
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA) remain a clinically devastating disease with no effective medical treatment therapy. AAAs are characterized by immune cell infiltration, smooth muscle cell apoptosis, and extracellular matrix degradation. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) has been shown to play role in AAA associated inflammation through immune cell recruitment and activation,
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 2, p22-31 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.163
Tenofovir at the Crossroad of the Therapy and Prophylaxis of HIV and HBV Infections
Erik De Clercq
Tenofovir, alias (R)-PMPA, was first divulged as an anti- HIV agent in 1993 [1]. That it would in 2012, become the first antiretroviral agent, approved by the US FDA (Food and Drug Administration) to prevent HIV infection, could have been predicted from the findings of Tsai et al.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p23-30 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.015
Proteomic Functional Signatures during the Priming of Human Th17 Cells
Mohd Moin Khan, Robert Moulder, Riitta Lahesmaa
A combination of regulated responses toward pathogens and minimized autoimmune reactions is needed for the balanced function of the immune system. Amongst the immunologically important CD4+ lymphocytes, T helper 17 (Th17) cells help maintain homeostasis and provide protection against pathogens of fungal or bacterial origins
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p25-28 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.006
Essentials of CAR-T Therapy and Associated Microbial Challenges in Long Run Immunotherapy
Muhammad Kalim, Rui Jing, Xin Li, Zhiwu Jiang, Ningbo Zheng, Ziyu Wang, Guo Wei, Yong Lu
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy has shown potential in improving outcomes for individuals with hematological malignancies. However, achieving long-term full remission for blood cancer remains challenging due to severe life-threatening toxicities such as limited anti-tumor efficacy, antigen escape, trafficking restrictions, and limited tumor invasion. Furthermore, the interactions between CAR-T cells and their host tumor microenvironments have a significant impact on CAR-T function.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p25-50 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.189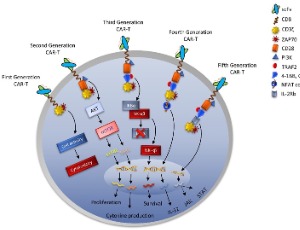
The Interplay between Transcription Factor SALL4 and Histone Modifiers in Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells
Hiro Tatetsu, Daniel G. Tenen, Li Chai
Currently, there is a growing need for culturing hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs) ex vivo for various clinical applications such as HSPC transplantation and gene therapy. For many patients with hematologic, genetic, and immune diseases, HSPC transplants can be a life-saving treatment. There are over 20,000 patients in the US receiving HSPC transplantation yearly.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p26-30 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.073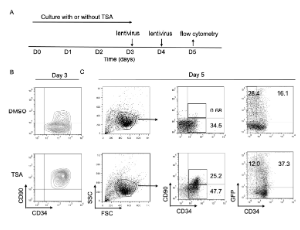
The Long-COVID Syndrome: Neoantigens as Driving Force for the Onset of Autoimmune Diseases
Rolf Marschalek
In the fifth year of the pandemic, SARS-CoV-2 variants continue to unveil new insights into particular mechanism of human immunology but also new clues on the interaction of SARS-CoV-2 proteins with host proteins. Nearly all yet known SARS-CoV-2 variants had the ability to cause a post-infection disease termed the Long COVID (LC) syndrome
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p26-31 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.219
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Commentary: Experimental Mouse Models of Invasive Candidiasis Caused by Candida auris and Other Medically Important Candida Species
Hong Xin
The study “Experimental Mouse Models of Disseminated Candida auris Infection” provides the first insight into the critical role of C5 in the host antimicrobial defense to disseminated candidiasis caused by C. auris. This study also establishes an inbred A/J mouse model of systemic C. auris infection without drug-induced immunosuppression. C. auris has become the first fungal pathogen causing global public health threat due to its multidrug resistance (MDR) and persistence in hospital and nursing home settings.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p29-33 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.130
TNFAIP8: Inflammation, Immunity and Human Diseases
Suryakant Niture, John Moore, Deepak Kumar
Inflammation can be caused by various environmental factors, including microbial infection and toxic chemical exposure. In response to inflammation, immune cells like macrophages, B and T lymphocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and various stromal cells secrete soluble polypeptide cytokine Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF?)
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p29-34 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.007
The Role of Quantification of Glucocorticoid-associated Toxicity in Severe Asthma
PJ McDowell, JH Stone, LG Heaney
Until recently, oral glucocorticoid (GC) therapies were the mainstay of treatment for uncontrolled inflammatory disease across many body systems. The last 30 years, however, have witnessed a transformation in the management of many diseases due to the development of targeted biological agents leading to a reduction, albeit not a removal, of the dependence on oral GCs.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p31-35 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.074
CAR-T cell Goes on a Mathematical Model
Luciana Rodrigues Carvalho Barros, Brendon de Jesus Rodrigues, Regina C Almeida
CAR-T cell immunotherapy is a great advance in hematological cancers treatment. New CARs and therapy schemes are being developed and a mathematical model could contribute to a rational design of treatment. Here we comment and show new results with previously published models of CAR-T cell therapy, emphasizing the contribution of initial tumor load, the proliferation of CAR-T cell and inhibition of CAR-T cell activity by the tumor resulting in different scenarios as tumor escape, equilibrium (stable disease) and tumor elimination.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p31-37 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.016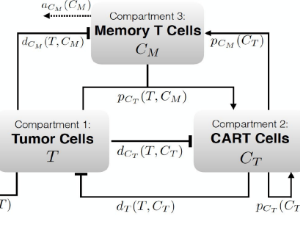
Is Interstitial Macrophage Mainly Responsible for Lung Injury in SARS-CoV-2 Infection?
José Guillermo Cabanillas López
The course of the COVID-19 pandemic has led to high mortality rates worldwide, which justifies the development of various research studies aimed at elucidating the physiopathological mechanisms involved in the development of lung injury associated with this disease. The angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 2, p32-35 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.165
Spatial Architecture of the Tumor Microenvironment in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor–Induced Hyper Progressive Bladder Cancer
Ryoichi Maenosono, Kazuki Nishimura, Kensuke Hirosuna, Moritoshi Sakamoto, Masahiko Ajiro, Kazumasa Komura, Haruhito Azuma, Akihide Yoshimi
Muscle invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) is associated with high recurrence and life-threating metastasis. Although the standard therapy for MIBC is a radical cystectomy to prevent metastasis, this approach has been associated with distant recurrence in 75 % of cases and local recurrence in 25 % of cases with a median time to recurrence of 12 months, leading to adverse impact on quality of life
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p32-36 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.220
SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The Viral Arms Race and Pattern- Recognition Receptors
Qi Liu, Sensen Chi, Shuai Tan
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARSCoV-2), the causative agent of COVID-19 respiratory disease, was first identified on 7 December 2019, and quickly spread worldwide. The SARS-CoV-2 belongs to Coronaviridea family, enveloped single-stranded RNA viruses. The family is divided into two subfamilies, the Coronavirinae and the Torovirinae, distinguished by the shape of their nucleocapsids . Virions are roughly spherical and are notable for the large spike (S) glycoprotein that mediate viral entry to the host cell. The subfamily Coronavirinae consists of four genera, the alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and delta-coronaviruses. There are seven coronaviruses that can infect people – four of them causing a common cold (229E, NL63, OC43, HKU1), and three are associated with potentially severe respiratory conditions, namely severe syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), and the emerging type of SARS-CoV-2, which has 79% sequence homology with SARS-CoV.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 2, p34-49
The Role of NETosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Ryan Salemme, Lauren N. Peralta, Sri Harika Meka, Nivetha Pushpanathan, Jessy J Alexander
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a devastating autoimmune disease that affects women to men at a ratio of 9:1 and is predominant in those of African ancestry. In SLE, the presence of autoantigens results in aberrant immune activation leading to systemic inflammation that predominantly affects the brain, kidneys, blood, and skin. Current guidelines recommend treatment with immunosuppressive drugs like prednisone, cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, and even some antimalarial drugs
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p35-44 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.008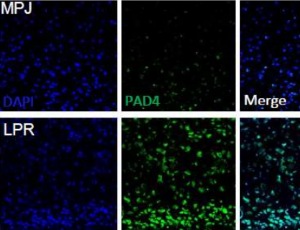
Exploring the Potential of Probiotics in Boosting the Immune System's Response to Reduce the Severity of Malaria
Bamgbose Timothy, José de la Fuente
Malaria, caused by various strains of malaria parasites such as Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium ovale, Plasmodium malariae, and Plasmodium knowlesi, is a major threat to human health worldwide. It is estimated that around 3.3 billion people are at risk of developing this disease [1]. Recent research on the human microbiome has revealed a link between resident microbial communities and the risk of blood parasites, offering potential for microbialbased disease treatments such as probiotics [2].
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 2, p36-40 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.166
Prospects of JAK Inhibition in the Framework of Bone Loss
Susanne Adam, Georg Schett, Silke Frey
Cytokine receptors may possess an intrinsic capability for the transduction of signals upon engagement by the respective cytokine ligand. However, if they lack an own intracellular signaling entity, they rely on other signaling machineries. One of the key intracellular signaling molecules mediating cytokine effects on immune cells are Janus kinases (JAKs),
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p36-41 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.075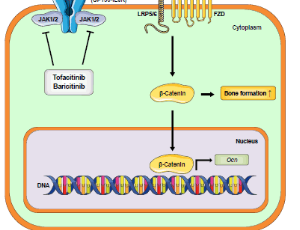
Inflammation and Aging: The Skin Inflammasome in the Context of Longevity Science
Ekta Yadav, MD, MBA, MS
The skin inflammasome is a critical component of the immune system, pivotal not only in responding to acute threats but also in contributing to the chronic inflammation associated with aging. This review provides an in-depth examination of the molecular mechanisms of the skin inflammasome, detailing its role in dermatological conditions like acne, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and hyperpigmentation, as well as its impact on systemic aging
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 2, p37-42 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.221
A New Window onto the Pacemaker of the Heart, the Sinus Node, Provided by Quantitative Proteomics and Single- Nucleus Transcriptomics
Mark Boyett, Alicia Lundby
Hypothesis-driven research has dominated biomedical science for at least the past century. There are many papers and grant applications that will have been rejected because they are not hypothesis-driven. For example, Haufe reports that the NIH guidelines for RO1 grants states that “A strong grant application is driven by a strong, solid hypothesis with clear research objectives”.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p38-41 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.017
Sharing Weal and Woe: A Commentary on “Gasdermin E Regulates the Stability and Activation of EGFR in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells”
Limei Xu, Xiangguo Liu
Abnormal activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) promotes the development of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells (NSCLC). Chemoresistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), which is elicited by EGFR mutations, is a key challenge for NSCLC treatment. In the present study, we demonstrate a critical role of gasdermin E (GSDME), an important protein for pyroptosis, in the maintenance of EGFR stability and activation.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 2, p41-44 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.167
The Role of Myeloid Populations during Perinatal Liver Injury and Repair
Anas Alkhani, Sarah Mohamedaly, Amar Nijagal
Perinatal liver inflammation can have life-threatening consequences, particularly in infants and young children. An example of a hepatic inflammatory disease during infancy is biliary atresia (BA), an obliterative cholangiopathy that rapidly progresses to hepatic fibrosis and liver failure.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p42-45 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.076
Naltrexone as a Novel Therapeutic for Diabetic Corneal Complications
Patricia J. McLaughlin, Joseph W. Sassani, Ian S. Zagon
Diabetes is a widespread autoimmune disorder that affects nearly 10% of the adult population in the United States. In addition to the primary disease, there are numerous complications associated with inflammation including abnormalities of the heart, visual system, and peripheral nervous system. More than half of the individuals with diabetes will have one or more ocular related complications such as dry eye disease (DED), keratopathy, or retinopathy.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p42-46 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.018
Anti-inflammatory Activity of the Aqueous Extract of the Mixture of Gossypium hirsutum L. (Malvaceae) and Terminalia catappa L. (Combretaceae)
Aïssé Florence Judith Trebissou, Okpo Jean-Noël Okogni, Adou Francis Yapo
Inflammation is a natural defense response of higher organisms to various external aggressors, such as physicochemical factors or microbial infections. The objective of this work is to enhance a medicinal formula derived from a mixture of Gossypium hirsutum L. and Terminalia catappa L. by evaluating and improving its anti-inflammatory activity. The two plant species selected for this study are Gossypium hirsutum L. and Terminalia catappa L. by evaluating and improving its anti-inflammatory activity
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 2, p43-48 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.223
Dual Expression of GARP in Immune and Glioma Cells: Yet Another Mechanism of Cancer Immune Escape
Emily Trzeciak, Niklas Zimmer, Ella Kim, Jonathan Schupp, Bettina Sprang, Petra Leukel, Fatemeh Khafaji, Florian Ringel, Clemens Sommer, Jochen Tuettenberg, Andrea Tuettenberg
Glioblastomas (GB) are amongst the most lethal human tumors exhibiting a highly aggressive behavior manifested by tumor cell infiltration into surrounding tissue. Furthermore, GBs are notorious for their high degree of resistance to cytotoxic treatments [1-3].
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p45-49 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.009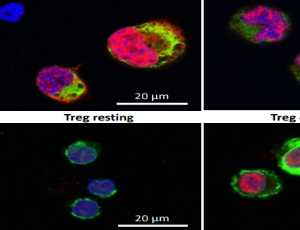
Dysregulated CXCL12 Expression in Osteoblasts Promotes B-lymphocytes Preferentially Homing to the Bone Marrow in MRL/lpr Mice
Wenjuan Zheng, Yu Tang, Mengwei Cheng, Cui Ma, Xiaoming Fei, Wei Shi
Peripheral circulating B-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes in the bone marrow (BM) show different responses to lymphotoxic or immunosuppressive agents. We explored the existence of a dysregulated distribution of B-lymphocytes between peripheral and BM compartments and the underlying mechanisms. The percentage of CXC chemokine receptor 4+ B (CXCR4+ B) cells was decreased in the peripheral blood (PB) and increased in the BM of MRL/lpr mice and SLE patients.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 2, p45-56 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.168
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Insulin-like Growth Factor 2: Beyond its Role in Hippocampal-dependent Memory
Paulina Troncoso-Escudero, Rene L. Vidal
The insulin-like peptides family is composed of insulin, insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1), and insulin-like growth factor (IGF2), together with IGF binding proteins (IGFBP1- IGFBP6). IGF2 is a single-chain secreted protein of 67 amino acids with important functions in fetal growth and development. IGF2 is the less characterized member of this family, and in mice and rats its expression in the brain occurs during embryonic development and adulthood but declines during aging.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p46-52 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.077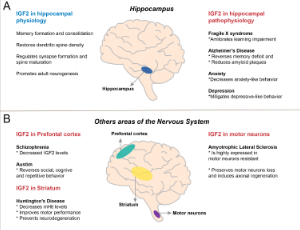
Autism – A Potential Autoimmune Disease Neurodegeneration-Induced Autoantibodies against Neural Proteins
Mohamed B. Abou-Donia
We hypothesize that maternal neurodegeneration, resulting from a chemical, infectious or physical brain injury event, can be causative in the development of autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Following a maternal brain injury event before or during gestation, maternal neural proteins escape the breached blood brain barrier (BBB), triggering the formation of IgG autoantibodies.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p47-54 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.019
Identification of Septic Shock Subgroups for Fluid Strategy Formulation: A Multi-Omics Integrated Approach
Xiong Lei, Zhongheng Zhang
Septic shock is characterized by systemic inflammation, vasodilation, and organ hypoperfusion, often necessitating aggressive fluid resuscitation to restore intravascular volume and improve tissue perfusion. However, the administration of intravenous fluids is a double-edged sword. While it can improve hemodynamics, excessive fluid administration can lead to complications such as fluid overload, pulmonary edema, and dilutional coagulopathy.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 2, p49-51 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.224
Targeting "Do Not Eat Me" Signal CD47 in Cancer Immunotherapy
Sachin Kumar Deshmukh
Cells of the innate and adaptive arm of the immune system including macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells, neutrophils, T cells, and B cells, etc. are crucial for the maintenance of the body’s homeostatic balance and prevention of multiple diseases including cancer.
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p50-52 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.010
Inulin Supplementation Mitigates Gut Dysbiosis and Brain Impairment Induced by Mild Traumatic Brain Injury during Chronic Phase
Lucille M. Yanckello, Brian Fanelli, Scott McCulloch, Xin Xing, McKenna Sun, Tyler C. Hammond, Rita Colwell, Zezong Gu, Aaron C. Ericsson, Ya-Hsuan Chang, Adam D. Bachstetter, Ai-Ling Lin
Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) has been shown to acutely alter the gut microbiome diversity and composition, known as dysbiosis, which can further exacerbate metabolic and vascular changes in the brain in both humans and rodents. However, it remains unknown how mTBI affects the gut microbiome in the chronic phase recovery (past one week post injury). It is also unknown if injury recovery can be improved by mitigating dysbiosis. The goal of the study is to fill the knowledge gap.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 2, p50-64 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.132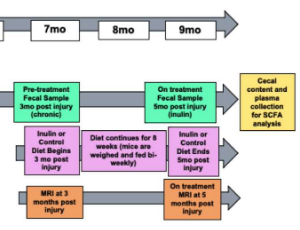
Mechanism, Challenges, and Progresses of Chimeric Antigen Receptors T-cell Cancer Therapy
Adem Hussein, Bedaso Mammo
Cancer is a deadly disease and affects everyone at any level of age. Many people lose hope once they are diagnosed with cancer. This is because there is no effective treatment for it. Till the end of the 19th century, researchers across the world were eager to design effective remedies for this decapitating phenomenon and designed so many interventions even though nothing is compensatory for a malignant tumor; in some cases, the side effects overwhelm the benefits.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p51-63 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.190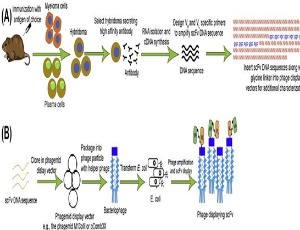
The Ability of Neonatal Mice to Develop Immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis Shows Sex Differences, with Females Displaying Evidence of an Enhanced Immune Response
Mrinal K. Ghosh, Ameae M. Walker
Using four core genotypes (FCG) mice, we have previously shown a larger number of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in the spleens of female mice, a sex difference that develops by postnatal day 7 and is retained through adulthood. This difference in splenic T cell number is a consequence of reduced thymic egress and reduced splenic seeding in male mice, caused in part by the male-specific perinatal surge of testosterone, and in part by Sry, which is overexpressed in this model.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 2, p52-63 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.225
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Role of Perforin-2 in Regulating Type I Interferon Signaling
Gregory V Plano, Noula Shembade
Sepsis is a systemic inflammatory response caused by a harmful host immune reaction that is activated in response to microbial infections. Infection-induced type I interferons (IFNs) play critical roles during septic shock. Type I IFNs initiate their biological effects by binding to their transmembrane interferon receptors and initiating the phosphorylation and activation of tyrosine kinases TYK2 and JAK1, which promote phosphorylation and activation of STAT molecules.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p53-60 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.078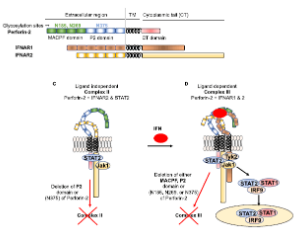
Multiple Roles of the Interleukin IL-17 Members in Breast Cancer and Beyond
Stephane Potteaux, Jacqueline Lehmann-Che, Armand Bensussan, Richard Le Naour, Yacine Merrouche
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) family proteins are involved in the control of infections. When unrestrained, these cytokines contribute to the development of chronic inflammatory diseases. The IL-17 family contains 6 members: IL-17A to F. In this review, we outline the current knowledge on the roles of each IL-17 member on breast cancer.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p55-64 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.020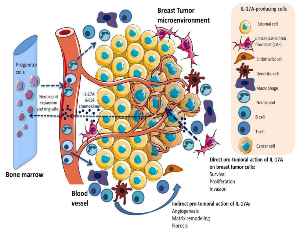
The Regulation Impact of Naringenin-loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles on Succinate Dehydrogenase Activity in Cancer Cells
Eman M. Ragab, Abeer A. Khamis, Doaa M. El Gamal, Tarek M. Mohamed
Oxidative phosphorylation dysregulation (OXPHOS) has been demonstrated to be essential for the development of cancer. Therefore, it may be argued that chaperone and deacetylase activities modulate OXPHOS activity. For instance, a complicated network of interactions connects a cell’s bioenergetic features and neoplastic potential through the imbalance of sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) and succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) enzymatic activity in mitochondria.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 3, p57-64 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.169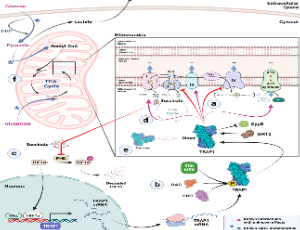
Teledermatology Before, During, and After COVID-19: A Vital Tool to Improve Access and Equity in Specialty Care
Bina Kassamali, Alice J. Tan, Ellen B. Franciosi, Mehdi Rashighi, Avery LaChance
Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine has rapidly expanded across the nation as medical systems have had to shift to providing care through virtual modalities to ensure the safety of patients and staff. Teledermatology, in particular, is wellsuited for telemedicine, with literature supporting its efficacy, equitable quality and accuracy, and cost-effectiveness in comparison to in-person visits.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p61-67 | DOI: doi.org/10.33696/immunology.3.079
Sepsis: A Molecular Odyssey from Infection to Organ Failure
Tamer A. Addissouky
Background: Sepsis arises when an uncontrolled systemic immune response to infection leads to life-threatening organ dysfunction. Despite available therapies, sepsis remains a major global health challenge with high mortality. Further research into molecular mechanisms, diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, and novel treatments is critical to improve outcomes.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 2, p64-73 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.226
The Natural History of Post-Chikungunya Viral Arthritis Disease Activity and T-cell Immunology: A Cohort Study
Aileen Yu-hen Chang, Alfonso Sucerquia Hernández, Jose Forero-Mejía, Sarah Renee Tritsch, Evelyn Mendoza-Torres, Liliana Encinales, Andres Cadena Bonfanti, Abigale Marie Proctor, Gary Leonard Simon, Samuel Joseph Simmens, Gary Steven Firestein
Background: Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) is an alphavirus spread by mosquitos that causes arthralgias and arthritis that may last for years. The objective of this study was to describe the arthritis progression and T cell immunology over a two-year period. Methods: A cohort of 40 cases of serologically confirmed CHIKV from Magdalena and Atlántico, Colombia were followed in 2019 and again in 2021. Arthritis disease severity, disability, pain, stiffness, physical function, mobility, fatigue, anxiety, sleep disturbances and depression were assessed.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 2, p64-75 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.191
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Targeting Mesothelin in Pancreatic Ductal Adeno- Carcinoma PDAC
Christopher Montemagno, Gilles Pagès
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) represents 90% of all pancreatic malignancies. To date, PDAC is the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death and its incidence is rising to become the second one in the next decade. Two major public health problems, obesity and type 2 diabetes, are important etiology factors involved in PDAC development.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p65-67 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.021
Evolution of the RNA Cleavage Subunit C11/RPC10, and Recycling by RNA Polymerase III
Saurabh Mishra, Richard J. Maraia
All cellular RNAs are synthesized by evolutionary related DNAdependent multisubunit RNA polymerases (Pols). Bacteria and archaea each use a single Pol to synthesize all their RNAs whereas a hallmark of eukaryotes is three homologous Pols, I, II and III and the associated Pol-specific transcription factors (TFs) to regulate synthesis of different class RNAs. The Pol III system produces high molar amounts of tRNAs and other small ncRNAs by the efficient reuse of its stable transcription complexes after formation on the promoters of its target genes, and the recycling of Pol III itself.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 2, p65-71 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.133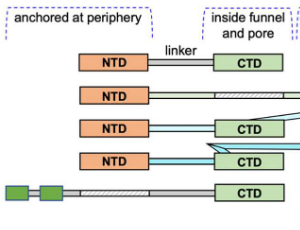
Immunologic Implications for Stroke Recovery: Unveiling the Role of the Immune System in Pathogenesis, Neurorepair, and Rehabilitation
Grace Hey, Siya Bhutani, Maxwell G. Woolridge, Aashay Patel, Anna Walls, Brandon Lucke-Wold
Stroke is a debilitating neurologic condition characterized by an interruption or complete blockage of blood flow to certain areas of the brain. While the primary injury occurs at the time of the initial ischemic event or hemorrhage, secondary injury mechanisms contribute to neuroinflammation, disruption of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), excitotoxicity, and cerebral edema in the days and hours after stroke.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 3, p65-81 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.170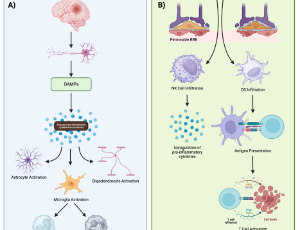
Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/NFkB Axis in Ovarian Cancer
Alia Ghoneum, Ammar Yasser Abdulfattah, Neveen Said
Ovarian cancer stands as the most lethal gynecologic malignancy and remains the fifth most common gynecologic cancer. Poor prognosis and low five-year survival rate are attributed to nonspecific symptoms at early phases along with a lack of effective treatment at advanced stages. It is thus paramount, that ovarian carcinoma be viewed through several lenses in order to gain a thorough comprehension of its molecular pathogenesis, epidemiology, histological subtypes, hereditary factors, diagnostic approaches, and methods of treatment.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p68-73 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.022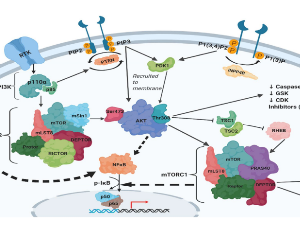
Review of the COVID-19 Risk in Multiple Sclerosis
Farhan Chaudhry, Cristina Jageka, Phillip D. Levy, Mirela Cerghet, Robert P Lisak
The ongoing pandemic of the novel coronavirus of 2019 (COVID-19) has resulted in over 1 million deaths, primarily affecting older patients with chronic ailments. Multiple sclerosis (MS) patients have been deemed particularly vulnerable given their high rates of disability and increased susceptibility to infections. There have also been concerns regarding disease-modifying therapy (DMT) during the pandemic as many DMTs may increase the risk of infection due to some of their immunosuppressive properties.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p68-77 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.080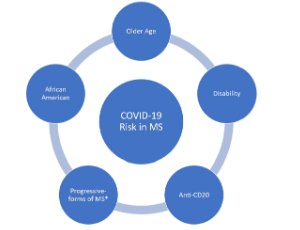
LncZFAS1 Inhibit MPP+-Induced Neuroinflammation Through TXNIP/MIB1 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase/NLRP3 Axis
Peiling Huang MM, Weijun Gong MD
Neuroinflammation is associated with the occurrence and progression of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Nucleotide-binding domain-like receptor protein-3 (NLRP3) is closely related to pyroptosis in PD-related cells and animal models, such as microglia and SH-SY5Y cells. The novel lncRNA ZFAS1 (LncZFAS1) regulates a variety of signaling pathways and participates in the inflammatory response in various diseases.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 2, p72-78 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.134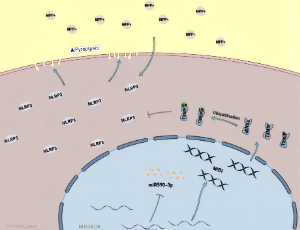
MicroRNA Signature Targeting Transient Receptor Potential Channels in the Prognosis and Therapy of Cancer
Giorgio Santoni, Consuelo Amantini, Massimo Nabissi, Federica Maggi, Maria Beatrice Morelli
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that modulate protein-coding mRNAs. Numerous miRNAs are expressed in human and 50% of human miRNAs are associated with carcinogenesis. Specific miRNAs are expressed in different cancer tissues and modulation of their expression is associated to different tumor stages and clinical outcomes.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p74-79 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.023
Inflammatory, Functional, and Compositional Changes of the Uterine Immune Microenvironment in a Lymphangioleiomyomatosis Mouse Model
Danielle S. Stiene, Andrew R. Osterburg, Lori B. Corsarie, Nick R. Balzarini, Mario Medvedovic, Michael T. Borchers
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) is a rare, female-dominated pulmonary cystic disease. Cysts that develop in LAM are characterized by the presence of smooth muscle-like (LAMCore) cells in the periphery. These cells harbor mutations in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex 1 or 2 (TSC1/2), driving uncontrolled proliferation through the mTORC1 pathway. LAMCore cells originate from an extrapulmonary source. Published data supports the uterine origin of LAMCore cells that metastasize from the uterus to precipitate pulmonary function destruction. Immune evasion is hypothesized to occur to allow seeding of the lungs from the uterus. This evasion specifically involves dysfunctional NK cells to allow aberrant proliferation and migration from the tissue.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 3, p74-97 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.227
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
A Natural Metabolite and Inhibitor of the NLRP3 Inflammasome: 4-hydroxynonenal
Jinmin Zhang, Bradford C. Berk, Chia George Hsu
The NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome, crucial in the innate immune response, is linked to various human diseases. However, the effect of endogenous metabolites, like 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE), on NLRP3 inflammasome activity remains underexplored. Recent research highlights HNE's inhibitory role in NLRP3 inflammasome activation, shedding light on its potential as an endogenous regulator of inflammatory responses.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 2, p76-81 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.192
Syncytiotrophoblast Extracellular Microvesicles in Preeclampsia
Chirag Ram, Robert W. Hu, Laxminarayana Korutla, Andreas Habertheuer, Prashanth Vallabhajosyula
Preeclampsia, a placental disease, is typically characterized by hypertension and proteinuria in pregnant mothers. There is a need for improved noninvasive detection and diagnosis of this condition. Extracellular microvesicles (EVs), including exosomes, are tissue specific nanoparticles released by many tissue types including the placenta into peripheral circulation.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p78-84 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.081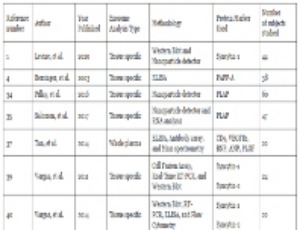
BIOMODULINA T® Modulates Lymphocyte Compartments in Institutionalized Cuban Geriatric Patients
Imilla Casado Hernandez, Vianed Marsán Suárez, Elizabeth Hernandez Ramos, Yenisey Triana Marrero, Gabriela Diaz Dominguez, Yaneisy Duarte Pérez, Mary Carmen Reyes Zamora, Sahily Estradé Fernandez, Consuelo Amantini, Luis Felipe Heredia Guerra
BIOMODULINA T® is a biological immunomodulator of natural origin, not blood derived, which promises to be a strategy for immune restoration in the elderly, in the midst of the worldwide epidemiological crisis due to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. This research aimed to determine the changes induced by BT in the distribution of lymphocyte compartments of institutionalized Cuban geriatric patients.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 2, p79-91 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.135
Trade-off and Cardiotonic Steroid Signaling: Natriuresis Maintains Sodium Balance at The Expense of Cardiac Fibrosis
Steven T. Haller, Joseph I. Shapiro
The pivotal work by Zijian Xie provided groundbreaking insights describing that the Na/K-ATPase (NKA), in addition to being an essential ion pump, also functions as a signal transducer with the capability to interact with multiple signaling partners. As an extension of this, our work along with a large body of work from the laboratories of Blaustein and Hamlyn as well as Bagrov and Fedorova, demonstrated that there were two major classes of endogenous NKA ligands or cardiotonic steroids (CTS), those from the cardenolide class such as ouabain and those which were bufadienolide such as marinobufagenin.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p80-83 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.024
Breast Implant-associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: A Review with Emphasis on the Role of Brentuximab Vedotin
Anthony Stack, Nadia Ali, Nadia Khan
Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma is a recently recognized complication of textured breast implants. It typically presents as unilateral peri-implant swelling approximately 7-10 years after implantation. While the course is usually indolent, breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma may form a locally invasive mass and metastasize to regional lymph nodes or beyond to distant sites.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p80-89 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.025
Non-reducing End of Heparin Tri-saccharide is a Scavenger Tool to Detoxify the Glucose Toxicity in Diabetes
Andrew Jun Wang, Aimin Wang, Vincent Charles Hascall
Heparin is a highly sulfated, hence highly polyanionic, glycosaminoglycan with a repeating disaccharide that contains a hexuronic acid, and it has been used as an anticoagulant clinically for more than half a century. Daily IP injections of small amounts of heparin in the STZ diabetic rat prevented these pathological responses even though the animals sustained hyperglycemic levels of glucose throughout.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 3, p82-86 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.171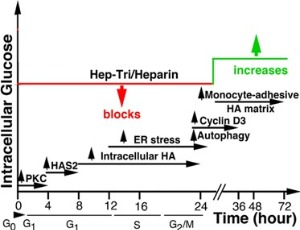
Can Molecular Biomarkers be Utilized to Determine Appropriate Adjuvant Therapy in Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)?
Prashanth Ashok Kumar, Alina Basnet, Stephen Graziano
Early-stage NSCLC, encompassing resectable stage I-III are curable, and represents 25% of all lung cancers. The management of non-metastatic NSCLC is a rapidly changing area of clinical oncology, where utilization of molecular biomarkers has become a cornerstone in informing appropriate management. In current clinical practice, adjuvant chemotherapy is recommended after surgical resection for tumors ≥ 4 cms in size (AJCC 7th stage IB, AJCC 8th stage IIA, and higher stage groups thereafter).
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 2, p82-86 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.193
Immunomodulatory Effects of Cell Therapy after Myocardial Infarction
Joseph B Moore 4th, Marcin Wysoczynski
Myocardial infarction (MI) due to coronary artery stenosis compromises vascular endothelial integrity and increases vascular permeability. Concurrently, ensuing myocardial tissue death and necrosis results in the release of danger associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), cytokines, chemokines, bioactive lipids, as well as activation of the complement cascade.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p85-90 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.082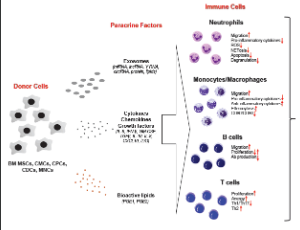
Fluoxetine is Antimicrobial and Modulates the Antibiotic Resistance Status of Bacteria
Alison M Mackay
The ability of mobile genetic elements to transfer drug resistance between bacteria can cause the rapid establishment of multi-drug resistance (MDR) [1,2], and human infection caused by multi-resistant, rather than susceptible organisms increases the likelihood of death [3].
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 3, p87-91 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.172
T cell-Intrinsic Peripheral Tolerance: A Checkpoint Target to Treat Autoimmunity
Nasser Gholijani, Gholamreza Daryabor, Fatemeh Rezaei Kahmini
Recent advances highlight the importance of intrinsic peripheral tolerance in the maintenance of a steady state. Peripheral tolerance is tightly regulated and any alteration in its biological process contributes to the breakdown of immune tolerance and induction of autoimmunity. Recent evidence related to T cell tolerance mechanisms inspired researchers to treat autoimmunity via modulation of tolerant checkpoints that are involved in intrinsic T-cell tolerance such as ignorance, anergy, exhaustion, and senescence.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 2, p87-97 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.194
IL-10 Responsiveness and Anti-TNF Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Felicia M. Bloemendaal, Charlotte P. Peters, Anje A. te Velde, Cyriel Y. Ponsioen, Gijs R. van den Brink, Manon E. Wildenberg, Pim J. Koelink
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a multifactorial disease in which both genetic and environmental factors play an important role, although the precise cause remains obscure. It is clear that both the innate and adaptive immunity are involved in acquiring mucosal immune homeostasis in the intestine, which is dysregulated in IBD.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p91-96 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.083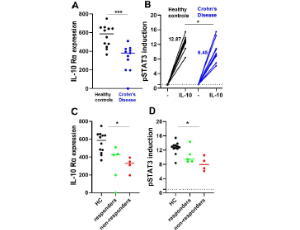
A Nonagenarian’s View of Dietary Impacts on Cellular Immunology
Bill Lands
Fatty acids and their esters bind to proteins and lipids rather than being solvated molecules like most metabolites. Some selective lipid-protein interactions can override expected lipidlipid interactions of cell membrane “fluidity” in determining cell physiology.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 3, p92-94 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.136
Would It be Possible for a SARS-CoV-2 Infection to Affect the Male Reproductive System?
Kaveh Rahimi, Akram Ebrahimifar, Mehri Rahimi
The male reproductive system may be affected by the systemic infections of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The precise mechanisms of male reproductive impairment are not well known. There are two possible mechanisms for the effect of SARS-CoV-2 on the male reproductive system either directly through the impact of the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 3, p92-96 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.173
A novel therapeutic strategy for antifibrotic based on a new gene NS5ATP9
Jing Zhao, Jun Cheng
In this article, we introduced a screening of anti-fibrotic drugs focused on new genes. More precisely, we screened and cloned 127 new genes, reporting on a potential target gene and two promising drugs for fibrosis. Among 127 genes, hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A transactivated protein 9 (NS5ATP9), which expression is significantly upregulated by tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF)/tenofovir alafenamide fumarate (TAF), suppresses hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and HFL1 cells (lung fibroblasts) activation.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p94-101 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.027
M1 Macrophages are More Susceptible to Necroptosis
Qin Hao, Steven Idell, Hua Tang
Macrophages play a crucial role in host innate immune defense against infection and tissue injury. Although macrophage activation and polarization has been well studied, we know less regarding the role of macrophage activation/polarization in inflammationassociated necrotic cell death. By using bone marrow-derived macrophages, we have recently demonstrated that M1 macrophages are much more susceptible than M0 and M2 subtypes of macrophages to necrotic cell death.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p97-102 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.084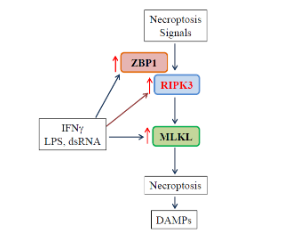
Designing Anti-Viral Vaccines that Harness Intrastructural Help from Prior BCG Vaccination
Tony W. Ng, Steven A. Porcelli
Vaccines are among the most effective tools for combatting the impact and spread of infectious diseases. However, the effectiveness of a vaccine can be diminished by vaccine inequality, particularly during severe outbreaks of infectious diseases in resource-poor areas. As seen in many developing countries that lack adequate healthcare infrastructure and economic resources, the acquisition and distribution of potentially life-saving vaccines may be limited, leading to prolonged suffering and increased deaths.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 4, p97-102 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.174
Advances of Immune Cells in the Pathogenesis and Targeted Therapy of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Junyue Fang, Li Lin, Xiaoyun Xiao, Jingwei Tian, Meng Zhang, Phei Er Saw
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a heterogeneous autoimmune disease reflecting an imbalance between regulatory and effector immune responses. With the rapid development of molecular biology and multi-omics, the pathogenesis of SLE has been gradually elucidated. In particular, imbalances and abnormalities in immune cell function have been shown to play an important role in the development of SLE. Understanding the specific pathogenesis of SLE is the basis for targeted therapy against specific targets.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 2, p98-112 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.195
Modeling TCIRG1 Neutropenia by Utilizing Patient Derived Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Vahagn Makaryan, Merideth Kelley, Audrey Anna Bolyard, Chris Cavanaugh, Jennifer Hesson, Julie Mathieu, Michael J. Lenaeus, David C. Dale
Congenital neutropenia is characterized by a reduced neutrophil count, decreased innate immunity and increased susceptibility to recurrent infections. While congenital neutropenia has various genetic causes, recent studies have linked TCIRG1 mutations to this condition. TCIRG1, a key component of the vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase) complex, is essential for osteoclast function, but its role in hematopoiesis remains unclear. We previously identified heterozygous TCIRG1 mutations, including R736S, R736C, R736P, and E722D, in individuals with congenital neutropenia.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 3, p98-112 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.228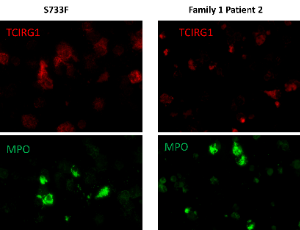
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Friend or Foe? Opposing Functions of O-GlcNAc in Regulating Inflammation
Miranda Machacek, Chad Slawson, Patricia J. McLaughlin
Effector CD4+ T cells (i.e. Th1, Th2, Th17) are essential in the adaptive immune system’s specific elimination of different classes of pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, and parasites, while regulatory T cells shut these inflammatory responses off once a pathogen has been cleared. Interestingly, effector T cells preferentially utilize
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p102-107 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.028
Structural Consequences of Variation in SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7
David A. Ostrov
New globally circulating SARS-CoV-2 strains are causing concern about evolution of virus transmissibility, fitness and immune evasion mechanisms. A variant emerging from the United Kingdom called SARS-CoV-2 VUI 202012/01, or B.1.1.7, is thought to exhibit increased transmissibility that results from replication 4-10 times faster than the original Wuhan virus (Wuhan-Hu-1).
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p103-108 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.085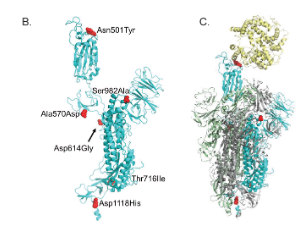
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis in Lymphoma by Chemotherapy Regimen
Kamen W. Kossow, Joseph G. Bennett, Marc S Hoffmann
Treatment of lymphomas involves a wide variety of chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted-agents tailored to disease biology and patient characteristics. Each of these regimens carry their own risk of opportunistic infections in an immunocompromised population. In addition to the treatment associated immunosuppression, lymphoma itself is immunosuppressive. Lymphoma associated immunosuppression is secondary to increased production of abnormal lymphocytes
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 4, p103-115 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.175
Commentary on the Clinicopathological Characteristics Prognosis and Immune Microenvironment Mapping in MSI-H/ MMR-D Endometrial Carcinomas
Yu-e Guo, Guofang Chen
TME contains various cell types (malignant cells, immune cells, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, etc.) and extracellular components (cytokines, growth factors, hormones, extracellular matrix, etc.). Tumor heterogeneity, characterized by each tumor’s distinct TME cellular composition and states and the interplay between these components, may play a critical role in tumor initiation, progression, therapeutic efficacy, and patient survival.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 3, p107-110 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.137
M1 and M2 Macrophages Polarization via mTORC1 Influences Innate Immunity and Outcome of Ehrlichia Infection
Ibrahim Ahmed, Nahed Ismail
Human monocytic ehrlichiosis (HME) is an emerging life-threatening tick-borne disease caused by the obligate intracellular bacterium Ehrlichia chaffeensis. HME is often presented as a nonspecific flu-like illness characterized by presence of fever, headache, malaise, and myalgia. However, in some cases the disease can evolve to a severe form, which is commonly marked by acute liver injury followed by multi-organ failure and toxic shock-like syndrome.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p108-115 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.029
Pregnancy Specific Glycoproteins: A Possible Mediator of Immune Tolerance of Cancers
Junfei Zhao, Raul Rabadan, Arnold J. Levine
Cancer immunotherapy relies upon the immune system recognizing and killing cancer cells. Tumors can elude recognition by readapting existing mechanisms of immune control and suppression. Here we explore the hypothesis that cancers repurpose the immune suppression employed during pregnancy to protect the allogeneic fetus. Those mechanisms are reviewed and shown to be employed both in pregnancy and by tumors.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p109-117 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.086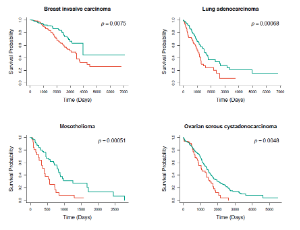
FLIP-expressing myeloid cells as driver of systemic immune disorders
Alberto Atanasio, Davide Rizzini, Stefano Ugel
The role of FLIP as a moonlighting protein is becoming progressively evident since this protein is often involved in various processes correlated to aberrant immunological responses independently from its function as master anti-apoptotic regulator. It has been uncovered that FLIP drives the acquisition of immunosuppression and inflammation-associated pathways in myeloid cells.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 3, p111-116 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.138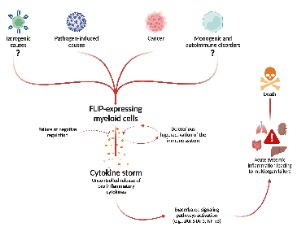
Neuroimmunopathology in Coenurosis: A Mini Review
Eman Mohamed Emara, Asmaa Hassan Bedair, Omnia Mostafa Elaafy, Alyaa Atef Abd ElRazik, Donia Sobhy Mohammed Bishr, Omar Ashraf Aladawy, Hamdy Ahmed Shahin, Saeed El-Ashram
Coenurosis is a socioeconomically significant zoonotic disease. The neuroimmunopathology of this disease is complex, involving a dynamic interplay between the parasite and immune system dynamics of several hosts. Although current diagnostic and treatment approaches remain inadequate, there is some solace in the recent investigations leading to proper prevention and control mechanisms of coenurosis with the One Health philosophy, integrating veterinary medicine, parasitology, immunology, community medicine, and public health—while also addressing other neglected trematode pathogens.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 3, p113-115 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.229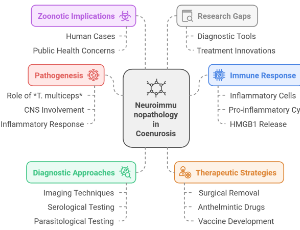
Targeting Monocyte Abnormalities in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus through Omics-Based Drug Repurposing
Panagiotis Garantziotis, Dimitrios Nikolakis, Eleni Frangou, George Bertsias, Dimitrios T. Boumpas
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a complex disease marked by extensive immune system dysfunction, culminating in a diverse spectrum of clinical phenotypes of varying severity. Despite the significant advancements in elucidating the pathogenesis of the disease, the management of SLE remains largely empirical with attainment of low disease activity and remission targets being an infrequent outcome among patients.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 3, p113-116 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.196
Commentary on Updated Insight into the Role of Th2-Associated Immunity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Xinyue Hou, Jinjin Chu, Shuhao Liu, Shuyu Jin, Jiamei Sun, Hui Wang, Haibo Li, Wei Liu, Chunxiang Chai, Sue Zhang, Donghua Xu
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a common autoimmune disease caused by multiple factors. The pathogenesis of SLE remains unclear. Helper T cell 2 (Th2 cell) is essential for humoral immunity, which participates in regulating type 2 immune response by producing typical cytokines of interleukin (IL)-4, IL-5, and IL-13. It is well known that Th2-associated immunity plays a vital role in autoimmune diseases, including SLE.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 4, p116-119 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.176
The Role of Innate Immune System: A Crosstalk between Invertebrates and Humans
Camile Dias Avelino, Yorran Hardman Araújo Montenegro
Innate immunity is the oldest form in evolution and is present in all multicellular organisms, including vertebrates and invertebrates. Although humans are the most recent evolutionary phylum, there is abundant evidence of a genetic inheritance shared between invertebrates and humans. There is correspondence between molecular pathways associated with the recognition systems of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) via pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) and Peptidoglycan recognition proteins (PGRPs).
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 3, p116-121 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.230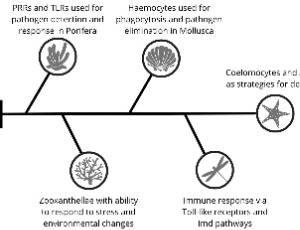
CD146-Positive Tumors are Associated with Venous Thromboembolism
A. Joshkon, J. Stalin, W. Traboulsi, L. Vivancos-Stalin, M. Nollet, R. Lacroix, R.Bachelier, F. Dignat-George, A. Bertaud, A.S. Leroyer, H. Fayyad-Kazan, N. Bardin, M.Blot-Chabaud
The role of CD146 and its soluble form have been intensely reviewed in the processes of cancer and inflammation. However, how CD146 is linked to coagulation and thrombotic events remains unclear. The aim of this paper is to shed light on this topic and clarify the contribution of CD146 as a procoagulant factor.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p116-123 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.030
Microbial Resistance to Photodynamic Therapy
Alison M Mackay
Microbial resistance to antibiotics has become a major area of research having caused over a million human deaths in 2019. At present, lower respiratory infection is the most burdensome disease. Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) is regularly reported not to cause resistance in any pathogen, and to eradicate both microbes that are susceptible to antibiotics and those that are resistant.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 3, p117-120 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.139
Homology-Independent Targeted Insertion (HITI) for Therapeutic T-Cell Engineering
Vimal Keerthi, Hyatt Balke-Want, Ramya Tunuguntla, Steven Feldman
In this commentary we discuss our recent work on delivering an anti-GD2 CAR (chimeric antigen receptor) via homology independent targeted insertion (HITI) using the CRISPR/Cas9 technology. HITI relies on Non-Homologous End Joining (NHEJ) that is predominantly exploited by both dividing and non-dividing cells to repair double stranded DNA breaks (DSBs). We explore considerations when using HITI based strategies. Furthermore, we discuss a method for post-HITI CRISPR EnrichMENT (CEMENT) within the context of large-scale clinical manufacturing of non-viral CAR-T cells.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 3, p117-120 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.197
IL-22-mediates Cross-talk between Tumor Cells and Immune Cells Associated with Favorable Prognosis in Human Colorectal Cancer
Raoul André Droeser, Giandomenica Iezzi
The positive prognostic role of the immune environment in colorectal cancer is widely accepted. However, there are few data about the prognostic significance of interleukin-22 in human colorectal cancer which is still debated.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p118-121 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.087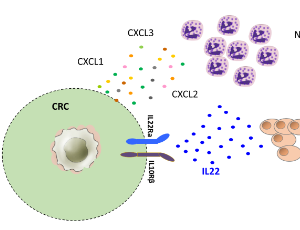
Type 1 Diabetes: A Disorder of the Exocrine and Endocrine Pancreas
Brittany S. Bruggeman, Desmond A. Schatz
Type 1 diabetes has historically been described as an endocrine (β-cell) specific autoimmune disease. However, a substantial reduction (20-50%) in pancreas organ size and subclinical to symptomatic exocrine pancreatic insufficiency are present at diagnosis and may begin even prior to the development of islet autoimmunity. The mechanisms of exocrine loss in type 1 diabetes are not well understood, but leading hypotheses include developmental defects, β-cell loss resulting in exocrine atrophy, or autoimmune or inflammatory destruction of exocrine cells.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 4, p120-126 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.177
The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor as a Possible Novel Immunotherapy Target in Myeloma
Olivia Kerekes, Paloma Gonzalez, Don M Benson Jr, Abdullah Khan
Epidemiologic studies have demonstrated a possible association between exposure to environmental aromatic hydrocarbons and the development of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) and multiple myeloma (MM). These aromatic hydrocarbons bind the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) expressed by plasma cells that seem to promote development and survival of malignant cells.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 3, p121-124 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.198
Persistence, Pathogenicity and Plasticity: The Role of IL-23 in Th17 Fate
Jens C. Kleiner, Christian F. Krebs
For a long time Th1 cells were considered the key players in the induction of inflammation and progression of disease in autoimmune diseases. With the discovery of IL-17-producing CD4+ T cells (Th17) being abundant at inflammation sites, this soon changed. Investigating this new T helper subset, it became clear that in comparison to Th1 and Th2 cells, Th17 cells have an increased tendency to change their phenotype and therefore become either more pathogenic or immunoregulatory.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 4, p121-130 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.140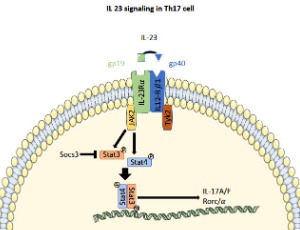
From Bench to Body: Protective Candida-specific Monoclonal Antibodies Show In vivo and Translational Potential
Hong Xin
Candida auris is a multidrug-resistant fungal pathogen that presents a growing global health challenge, particularly due to its ability to cause invasive bloodstream and deep-seated infections in vulnerable patients. Monoclonal antibody (mAb)-based immunotherapy offers a novel and targeted approach to overcoming the limitations of current antifungal treatments. This commentary highlights the protective efficacy of Candida-specific mAbs, C3.1, 6H1, and 9F2, in in vivo mouse models of disseminated candidiasis.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 3, p122-126 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.231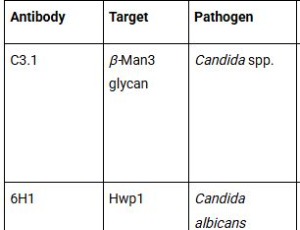
Understanding the Role of the Scabies Mite Microbiota in the Development of Novel Control Strategies
Sara Taylor, Katja Fischer
With a global prevalence of approximately 300 million people, scabies is one of the most common dermatological infectious diseases worldwide, and was recognised as a neglected tropical disease in 2017 by the World Health Organisation. Scabies is especially prevalent in economically disadvantaged communities and disproportionately affects children in poor and overcrowded living conditions.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p122-127 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.088
Basophil Activation Tests BAT: Degranulation, Cytometry and Chemotaxis in Drug Allergy
Maria de Lourdes Irigoyen Coria, María Isabel Rojo Gutierrez, David Solís Hernández, Ruben Humberto Meyer Gómez, Isabel Leyva Carmona, Jaime Mellado Abrego, Gloria Castillo Narváez, Isabel Guerrero Vargas
To Increase the knowledge on Drugs Hypersensitivity Reactions (DHRs); activation, development of reliable diagnostic tests for better: selection of studies, diagnosis, identification of risk groups, prevention, cross-reactions, severs skin drug reactions and alternative therapeutics.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p124-142 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.031
Evolution of the Classification and Management of Smoldering Multiple Myeloma
Dennis D. Lee, Faith E. Davies, Gareth J. Morgan
The evolving molecular landscape of Smoldering Multiple Myeloma (SMM) has underscored its complex nature and the urgent need for more refined diagnostic and treatment strategies. With an increased risk of progression to Multiple Myeloma (MM), it has become important to identify patients at the highest risk of progression for interception strategies. Risk evaluation has been a constantly moving target with rapidly changing approaches to classification being based predominantly based on imaging and biochemical data thus far.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 3, p125-139 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.199
Estrogen Receptor Alpha Contributes to Intestinal Inflammation in a Murine Model of Ileitis
Alyssia V. Broncano, Wendy A. Goodman
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are inflammatory conditions characterized by chronic and recurrent intestinal inflammation. IBD affects nearly five million people worldwide, with an estimated prevalence of 245.3 cases per 100,000 people in the United States alone. The incidence of IBD is steadily increasing in industrialized countries and is appearing more often developing countries, contributing to its rise as a global disease burden.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 4, p127-132 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.232
Can Vaccines Stop Cancer Before It Starts? Assessing the Promise of Prophylactic Immunization Against High-Risk Preneoplastic Lesions
Tamer A. Addissouky, Ibrahim El Tantawy El Sayed, Majeed M. A. Ali, Yuliang Wang, Ayman El Baz, Ahmed A. Khalil, Naglaa Elarabany
Background: Cancer remains a leading cause of mortality with modest declines, highlighting the need for more efficacious prevention strategies like early immunological intervention against premalignant disease.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 4, p127-140 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.178
The First Viral Expression Model in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells to Observe Enteroviral Infections In vitro
Stefan Peischard, Huyen Tran Ho, Nathalie Strutz-Seebohm, Guiscard Seebohm
Viruses recently caused global outbreaks of potentially severe diseases. The newly recognized corona virus, which is causing SARS-CoV-2 is the most recent example for this scenario. Potentially severe but not as prominent as the corona virus is the Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3), which can cause fatal outcomes of myocarditis, meningitis, encephalitis and diabetes type 1 due to chronical infections of the heart, the brain, and the pancreas.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p128-131 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.089
CAR Therapy for T-cell Malignancies
Andrew Cinquina, Jia Feng, Hongyu Zhang, Yupo Ma
The introduction of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) immunotherapy has been revolutionary in the treatment of hematological malignancies.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 4, p131-133 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.141
Salivary Lymphocyte Phenotypes Differ from Blood and Serve as a Model for Other Mucosal Fluids
Muruganantham Lillimary Eniya, Shervin Dokht Sadeghi Nasab, Albert Judith, Frederick Clasen, David Moyes, Saeed Shoaie, Newell Johnson, Priya Kannian, Stephen Challacombe
The oral cavity is part of the mucosal immune system of the body, embracing all mucosae including lungs, gut and nose. The oral mucosa is the gateway for a plethora of gastrointestinal and respiratory antigens and is capable of mounting a very strong mucosal immune response. Mucosal immunity is structurally and functionally similar in all mucosae and, soluble mediators including cytokines, chemokines, immunoglobulins and other proteins have been well studied in many diseases.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 4, p133-138 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.233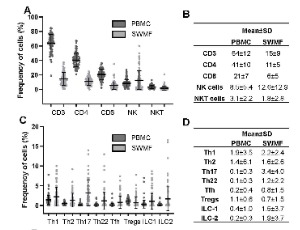
Efferocytosis and Anthrax: Implications for Bacterial Sepsis?
Joshua S. Mytych, Zijian Pan, A. Darise Farris
Bacillus anthracis (Ba) is a gram-positive, rod-shaped, spore- and toxin-forming bacterium. While mainly an herbivore pathogen, human infection with Ba spores can occur through a number of routes including cutaneous, gastrointestinal, injectional, or inhalational. The deadliest form of anthrax exposure is through inhalation of Ba spores, leading to systemic dissemination of the bacteria, with mortality ranging from 45% to 90%.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p133-139 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.090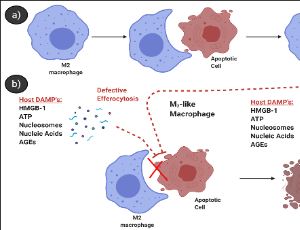
Serum Cytokines During Acute Respiratory Infection and Relationship to Age
Aanya Gupta, Holden T. Maecker
Influenza and other seasonal respiratory viruses affect millions annually. While age is generally known to be correlated with risk and outcome, the mechanisms underlying thesedifferences, especially in the infected, have been poorly defined. Previous studies have focused primarily on cell-subset shifts in older adults, leaving a gap in understanding of how cytokine responses vary across the full age spectrum.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 4, p139-145 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.234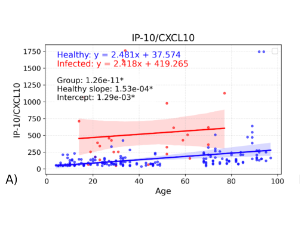
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Association of Smoking and Crohn's Disease: An Update
Alejandro Mínguez, Pilar Nos
The relationship between smoking and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which has been widely studied for years, is complex and different in Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). The negative effect on CD, not only on disease progression and post-surgical recurrence, but also on post-surgical complications after intestinal resection, on its influence on the reservoir and on the modification of the natural evolution of CD towards fistulizing and stenosing forms, makes a proper approach to the problem imperative.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 3, p140-147 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.200
Examining the Relationship between SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Type 1 Diabetes: A Reanalysis of Recent Findings
Yongxin Zhang, Ying Wang
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), an autoimmune disease mediated by T cells, has long been associated with various viral infections [1-4]. Among these infections, enterovirus infection [5-7] was more consistently reported to contribute to the development of T1D
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 5, p141-142 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.179
PD-L1 as a Novel Mediator of Lung Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Transition
Xia Guo, Guoqing Qian
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is an incurable disease that affects approximately 3 million people worldwide. Although two drugs (nintedanib and pirfenidone) have been approved for treatment of IPF, currently there is a lack of effective pharmacotherapy that could stop the progression or offer a cure for this devasting disease.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 4, p141-144 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.142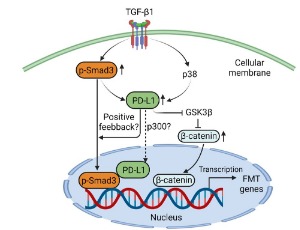
CRISPR Taking the Front Seat in Immunotherapy
Saad S. Kenderian, Andrew D. Badley
CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) technology has dramatically simplified genome editing and is widely applicable in both basic research and therapeutic areas. The basic principle of CRISPR relies on the use of guide RNA which is designed to bind to the DNA sequence of interest along with a CRISPR-associated (Cas) endonuclease which introduces a double-stranded DNA break (DSB) at that site.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p143-148 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.032
Expansion of Proteome-wide Coxiella burnetii Comparative T-cell Epitope Prediction to Include Small Ruminant Hosts
Paige C. Grossman, David A. Schneider, Robert Kirkpatrick, Stephen N. White, Lindsay M.W. Piel
Coxiella burnetii is the causative agent of Q fever, a human disease that can be acquired from livestock. Diseases caused by this organism have caused great losses in livestock and human health. No vaccine is approved for use in the United States, and formalininactivated whole-cell vaccines pose a significant manufacturing risk for biocontainment.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 5, p143-161 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.180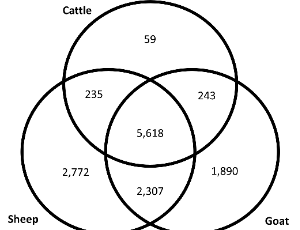
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinases in Leukemia Development
Changhao Cui, Chen Wang, Min Cao, Xunlei Kang
Ca2+/ calmodulin (CaM) signaling is important for a wide range of cellular functions. It is not surprised the role of this signaling has been recognized in tumor progressions, such as proliferation, invasion, and migration. However, its role in leukemia has not been well appreciated. The multifunctional Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinases (CaMKs) are critical intermediates of this signaling and play key roles in cancer development.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p144-150 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.091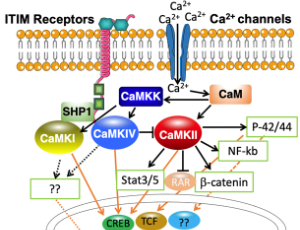
Improvement of the Specificity of the Indirect BAT for the Diagnosis of Peanut Allergy; the BA(Blocking Antibodies)-BAT
Janneke Ruinemans-Koerts, Monique van Uum-Otters, Don van Baar, Joost van Neerven, Judit Wesseling
The direct and indirect Basophil Activation Test (BAT) are well known for their capacity to predict the presence of an IgEmediated peanut allergy resulting in a reduction of expensive and time-consuming oral food challenge (OFC) tests. Although the BAT is a promising test, false-positive and false-negative outcomes are observed .
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 4, p145-148 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.143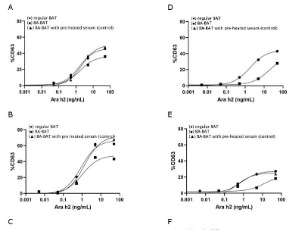
Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies to Overcome Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Resistance in Melanoma, Head and Neck, and Triple-Negative Breast Cancers
Iryna Voloshyna, Apoorvi Tyagi, Stanzin Idga, Nicole Wang, Tazrif Amin, Madonna Hanna, Adil Mukhtar, Francesca Torres, Farah Kabir, Dominic Florian, Chloe Wang, Yury Patskovsky, Michelle Krogsgaard
Immunotherapy, particularly immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), has revolutionized cancer treatment by harnessing the host immune system to target malignancies. Melanoma, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) were among the first solid tumors to gain regulatory approval for ICIs due to their immunogenicity and unmet clinical needs. Melanoma exemplifies the success of ICI therapy, with durable responses driven by its high mutation burden and neoantigen landscape, yet both primary and acquired resistance remain major challenges.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 4, p146-172 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.235
T lymphocytes in Aging: CD38 as a Novel Contributor between Inflammaging and Immunosenescence
Wendolaine Santiago-Cruz, Fabio García-García
CD38 is a transmembrane protein expressed in immune and non-immune cells involved in nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) consumption, cyclic Adenosine Diphosphate Ribose (cADPR) generation, and calcium mobilization by its enzymatic activity. It also promotes an activated and pro-inflammatory phenotype in immune cells. Senescence is a cellular state of cell growth arrest accompanied by senescent-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) products.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 4, p148-162 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.201
Lung-targeted SERCA2a Gene Therapy: From Discovery to Therapeutic Application in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis
Malik Bisserier, Lahouaria Hadri
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is an interstitial lung disease characterized by an accumulation of scar tissue within the lungs and the common presence of usual interstitial pneumonia. Unfortunately, only a few FDA-approved therapeutic options are currently available for the treatment of IPF and IPF remains associated with poor prognosis. Therefore, the identification of new pharmacological targets and strategies are critical for the treatment of IPF.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p149-156 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.033
Manufacturing of Human T-lymphoid Progenitors from Two Different Hematopoietic Stem Cell Sources and Perspective for New Immunotherapies
Pierre Gaudeaux, Ranjita Devi Moirangthem, Pauline Rault, Hanem Sadek, Francesco Carbone, Marieke Lavaert, Akshay Joshi, Tom Taghon, Isabelle André, Olivier Nègre, Tayebeh-Shabi Soheili
The adaptive immune system depends on the efficient response of lymphocytes, protecting the organism from infection or malignant diseases. T-cell immunodeficiency, innate or acquired, put the patient at risk for developing opportunistic infections and cancers.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 4, p149-157 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.144
Promoter Reporter Systems for Imaging of Cells Transplanted into Post-infarcted Heart
Katarzyna Fiedorowicz, Maciej Kurpisz
Molecular imaging has been a rapidly developing field of molecular biology. Specific sophisticated approaches have been pursued to effectively monitor the fate of transplanted cells in the body, i.e. retention in target organ, migration routes and cell survival up to their final destination. One of the strategies involves direct or indirect labeling of target cells.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p151-155 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.092
Duration of SARS-CoV-2 Infectivity
Seitz Tamara, Kelani Hasan, Wenisch Christoph, Laferl Hermann
After infection with SARS-CoV-2 prolonged SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding was reported for several weeks. However, the duration of actual infectivity depends on the severity of disease and the immune status of the affected individual. Infectivity is highly unlikely nine days after symptom onset in immunocompetent individuals with a mild course of COVID-19.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p156-163 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.093
TNF-alpha Inhibitors and Neutropenia: Current State of Art
Emmanuel Andres, Noel Lorenzo Villalba, Abrar-Ahmad Zulfiqar, Yasmine Maouche, Khalid Serraj, Jacques-Eric Gottenberg
To date, neutropenia and agranulocytosis related to TNF-α inhibitors have been discussed infrequently in the literature. In the current paper, a narrative review of the literature was performed on anti-TNF-α inhibitors, including infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept, golimumab, and certolizumab, using the PubMed database of the US National Library of Medicine. The review was restricted to autoimmune and auto-inflammatory diseases or other orphan diseases.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p157-164 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.034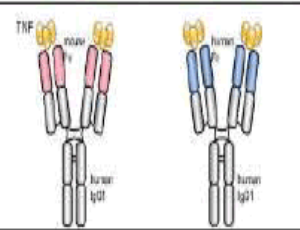
Sialyllactose Prevents Cartilage Damages via M0 Macrophage Maintenance in Yucatan Mini-Pig Osteoarthritis Model
Kyung-Tai Kim, Young-Kyu Kim, Mi-Jin Yang, Min-Young Kim, Lila Kim, Jeong Ho Hwang
Sialyllactose, known to be abundant in human breast milk, has anti-inflammatory properties, but its preventive effect on osteoarthritis remain unclear. Here, we demonstrated the efficacy of 3’ sialyllactose (3’ SL) and 6’ sialyllactose (6’ SL) in preventing osteoarthritis in Yucatan mini-pigs. Twelve female Yucatan mini-pigs were administered 0, 200, 400 mg 3’ SL or a combination of 200 mg 3’ SL + 200 mg 6’ SL for 12 weeks (4weeks before and 8 weeks after surgery); then, osteoarthritis was induced in the left knee by anterior cruciate ligament transection surgery.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 5, p158-166 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.145
Role of Regulatory T cells in Prognosis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Kidney Transplant Recipients
Katyayani Bejugama, Swarnalatha Guditi
The major issue in kidney transplantation remains the suppression of allograft rejection. Immunosuppressant decrease both donor-specific responsiveness and the risk of rejection in the months after transplantation and are maintained. The current immunosuppressant medications, although potent against short-time graft complications including acute renal rejection but are still less effective to ensure long-term graft survival.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 5, p162-167 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.181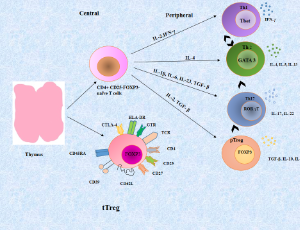
Cytoreductive Nephrectomy Following Immunotherapy: Evolution, Pearls, and Pitfalls of Treatment
Laura E. Davis, Adam Calaway, Eric A. Singer, Shawn Dason
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) is among the most frequently diagnosed malignancies in both genders with over 81,000 estimated cases in 2024. Despite increasing incidence of renal cell carcinomas <4 cm, up to 1/3 of patients diagnosed with RCC exhibit metastatic disease (mRCC) at time of diagnosis. Cytoreductive nephrectomy (CN), a procedure which encompasses the surgical removal of the primary tumor in patients with metastatic disease
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 4, p163-170 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.202
Unconventional Approaches to Direct Detection of Borreliosis and Other Tick Borne Illnesses: A Path Forward
Lance Liotta, Alessandra Luchini
The current COVID-19 pandemic has brought to public attention the conceptual difference between a test for COVID-19 derived RNA or proteins indicating the presence of an active infection, versus COVID-19 serology testing indicating pathogen infection. Only the former test for molecules derived from COVID-19 provides reliable evidence of a current active infection.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p164-172 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.094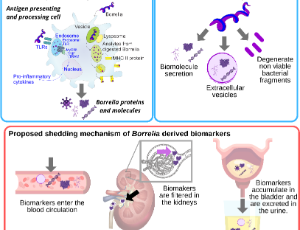
Autoantibodies in Overlapping Systemic Sclerosis and Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Autoimmune Diseases
Manuel M. Valdivia
Anticentromere antibodies (ACA) are considered an important diagnostic marker of scleroderma or systemic sclerosis (SSc), being CENP-B the major centromere auto-antigen recognized by sera from SSc patients. However, ACA can also be detected in patients with other connective tissue diseases. Significantly the prevalence of organ-specific antibodies in SSc patients is relatively high.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p165-167 | DOI: 10.33696//immunology.2.035
The Issue of Monocyte Activation in ASD: Troubles with Translation
P Ashwood, R.J. Moreno
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) prevalence has increased year on year for the past two decades and currently affects 1 in 44 individuals in the US. An increasing number of studies have pointed to increased immune activation as both an etiological agent and also involved in the ongoing pathological process of ASD. Both adaptive and innate immune responses have been implicated. Evidence of innate dysregulation has so far included increased production of innate inflammatory cytokines, increased cell numbers, and altered activation in monocytes in the blood and microglia in the brain.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 5, p167-170 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.146
Sex Differences in Clinical Characteristics and Platelet Activation in Respiratory Syncytial Virus Bronchiolitis
Isabella Tarissi De Jacobis, Rosa Vona, Elisabetta Straface, Lucrezia Gambardella, Giulia Ceglie, Francesca de Gennaro, Ilenia Pontini, Anna Chiara Vittucci, Alessandra Carè, Camilla Cittadini, Alberto Villani, Donatella Pietraforte
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the most common cause of bronchiolitis. It is a single-stranded RNA virus of the Paramyxoviridae family that is transmitted through nasopharyngeal or conjunctival mucosa from infected individuals. The incubation period ranges from 2 to 8 days. Two antigenically different RSV subtypes exist, A and B.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p168-170 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.036
The High Fat Diet Impacts the Plasticity between Fresh and Aged Neutrophils
Andrea Baragetti, Giuseppe Danilo Norata
Metabolic alterations induced by unhealthy lifestyles, including obesity and insulin resistance are often associated with increased innate immune response and chronic inflammation. Cholesterol has been identified as a key metabolite driving the activation of the inflammasome and the “epigenetic memory” in long-term living hematopoietic stem cells.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 5, p168-173 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.182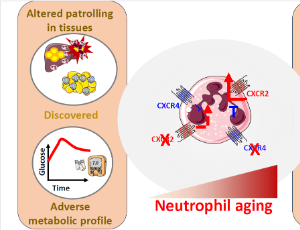
The status of Regulatory Cells/Molecules in Psoriatic Skin
Vadasz Zahava
In normal non-inflamed skin, the balance between the expression of pro-inflammatory cells/cytokines and regulatory/protective functions are extremely important for the maintenance of healthy skin. Normal skin T cells (mostly Th1 memory effector cells) have a remarkably diverse TCR repertoire and express high levels of CCR4, CCR6 and CCR8.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p171-174 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.037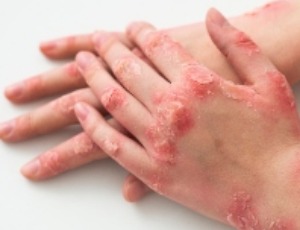
Profiling Proteasome Activities in Peripheral Blood – A Novel Biomarker Approach
Laylan Bramasole, Silke Meiners
The proteasome system in the cell degrades the majority of intracellular proteins. The broad nature of its substrates makes proteasome activity crucial for many cellular functions, such as protein quality control, transcription, apoptosis, immune responses, cell signaling and differentiation. The proteasome system is thus an effective therapeutic target for malignant and non-malignant diseases.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 5, p171-179 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.147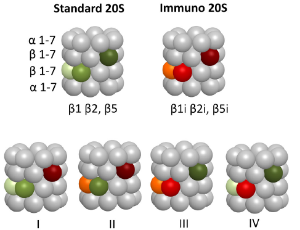
Chemokines and Their Receptors in Hepatitis B Virus Infection: A Comprehensive Review
Jiezuan Yang, Dan Cao, Ruiqi Tang, Xuefen Li
Chemokines, a group of small cytokines, play a central role in the pathogenesis of viral hepatitis by regulating the migration, proliferation, and activation of lymphocytes. These chemotactic factors of immune cells are directly involved in various cellular biological activities, including cell adhesion, angiogenesis, and diffusion. The aberrant expression of lymphocyte chemokines and their receptors is closely related to the biological behavior of host immune cells as well as the specific and non-specific immune responses to viral infections and may influence the prognosis of viral diseases.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 4, p171-181 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.203
Increased Binding Affinity of Furin to D614G Mutant S-glycoprotein May Augment Infectivity of the Predominating SARS-CoV-2 Variant
Sardar Sindhu, Rasheed Ahmad, Fahd Al-Mulla
COVID-19 pandemic has inflicted serious challenges to both global health and economy. The disease is caused by a +ssRNA zoonotic coronavirus named SARS-CoV-2, known to have four structural proteins named spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M), and nucleocapsid (N). Given the critical role in host immunity and virus attachment to ACE2 receptors on target cells, S-glycoprotein mutations are of significant concern.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p173-176 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.095
Risk Factors of Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria with COVID-19 Vaccination: A Cross-Sectional Study
Hossein Esmaeilzadeh, Mohammad Amin Gholami, Negar Mortazavi, Mohammad Reza Yousefi, Mohebat Vali
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria (CSU) is a multifactorial disease with an incompletely understood etiology. COVID-19 vaccines can influence the immune system. This study evaluates the risk factors and comorbidities associated with CSU in patients who developed CSU following COVID-19 vaccination or infection.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 4, p173-180 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.236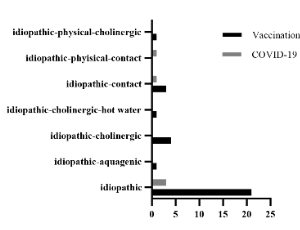
Molecular Pathways in Sepsis Pathogenesis: Recent Advances and Therapeutic Avenues
Tamer A. Addissouky, Ibrahim El Tantawy El Sayed, Majeed M. A. Ali, Yuliang Wang, Ayman El Baz, Ahmed A. Khalil, Naglaa Elarabany
Background: Sepsis remains a critical global health challenge with high mortality. This review summarizes current understanding of the intricate molecular mechanisms governing sepsis pathogenesis and highlights emerging therapeutic approaches.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 6, p174-183 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.183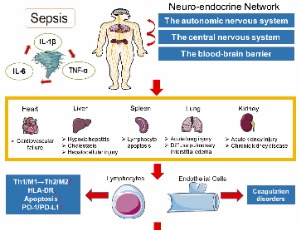
Are Cysteine-lipases Involved in the Immune System?
Qi Wu, Manfred T. Reetz
Lipases, esterases and proteases constitute superfamilies of hydrolases not only play an important role in the immune system, but also as catalysts in biotechnology and organic chemistry. Mechanistically, they all involve a similar catalytic triad.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p175-177 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.038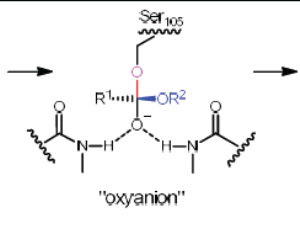
Murine Models of Alcohol Consumption: Imperfect but Still Potential Source of Novel Biomarkers and Therapeutic Drug Discovery for Alcoholic Liver Disease
Khaled Alharshawi, Costica Aloman
Improving our knowledge regarding the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying murine models of alcoholic liver injury should enhance the management and therapies of alcoholic liver disease (ALD) seen in humans [1]. Although none of the animal models available reproduce all main aspects of human ALD, they still provide very
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p177-181 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.096
Allicin as an Adjunct Immunotherapy against Tuberculosis
Samreen Fatima, Ved Prakash Dwivedi
Allicin (diallylthiosulfinate) is a volatile, oxygenated, sulphur-containing compound, extracted from garlic (Allium sativum). It is responsible for the characteristic odor of garlic. Allicin is known to exert its effects as an antipathogenic agent mainly by targeting the thiol-containing proteins or enzymes in different microorganisms and also by regulating the key genes responsible for the virulence of the microorganism.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p178-182 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.039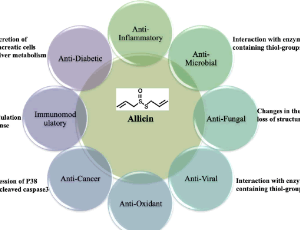
Establishment of an Indirect Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay for Detection of the NS4 Protein of Bluetongue Virus
Ji Ma, Xianping Ma, Rang Wang, Fang Li, Tingjun Hu, Huashan Yi
An indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (iELISA) was established to detect the serological prevalence of bluetongue virus (BTV) infection in ruminant populations. A recombinant NS4 (rNS4) protein was used as the encapsulated antigen. Optimization of the iELISA included the encapsulated antigen, serum dilution, blocking solution, and working concentration of a horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled secondary antibody (Ab) by the square-matrix titration test.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 5, p180-184 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.148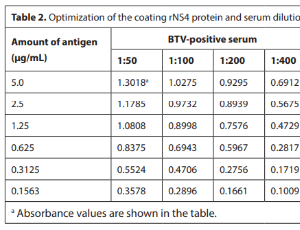
HMGB3: A Potential Immunotherapeutic Target in Glioblastoma Multiforme—Current Strengths, Existing Limitations, and Future Perspectives
Xing-Long Li, Feng-Yi Mai, Xin-Yu Li, Jie Guo, Chen-Guang Li
A key strength of Wang et al.’s study lies in its rigorous integration of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and bulk RNA-seq, which overcomes the inherent limitations of each technology alone. ScRNA-seq dissects GBM cellular heterogeneity to identify 21 cell clusters and 1,150 cell-type-specific markers, while bulk RNA-seq captures transcriptomic patterns across large cohorts.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 5, p181-184 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.237
Clinical Case Report of CAR-T Therapy of Patient with Refractory Burkitt's Lymphoma
Tatiana Mikhailovna Doroshenko, Olga Alexandrovna Kalenik, Ihar Mikhalaevich Seviaryn, Kataryna Yureuna Zharkova, Denis Alexandrovich Davydov, Anna Sergeevna Portyanko, Alena Vladimirovna Sukalinskaya, Sergey Lvovich Polyakov, Natalia Eugenevna Konoplya
Approximately 20% of adult patients with Burkitt's lymphoma (BL) have relapsed/refractory disease, which is characterized by poor overall survival (OS) and virtually no therapeutic options after failure of two lines of chemotherapy, due in part to the peculiarities of tumor cell biology. Improved treatment strategies are an unmet need for these patients. There have been individual attempts to use chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T therapy in this patient population using anti-CD19, CD20, and CD22 cells.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 4, p182-187 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.204
The Variable Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Potential Treatment with Combination IL-15 and IL-21
Stephen William Wilz
SARS-Cov-2 is the virus that causes the disease COVID-19. While most patients who contract the disease experience mild symptoms, a significant percentage has severe symptoms, sometimes leading to death. In this paper, the immune response to SARS-Cov-2 infection is reviewed, highlighting differences between patients with severe disease and patients with mild disease.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p182-190 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.097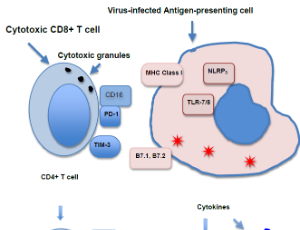
Cytokines (IL-1 β, IL-6, IL-18, TNF-α) in Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid in Neonatal Hypoxia/Ischemia)
Darinka Šumanovi?-Glamuzina, Marjana Jerkovi?-Raguž
Perinatal brain injury is an important clinical and socioeconomic entity. It is a syndrome of impaired brain function in the early days of life, and it is a consequence of inadequate brain oxygenation before, during or shortly after birth, with high mortality rates and early and late morbidity rates.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p183-187 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.040
Macrophages in Bone and Synovial Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Mobina Jalalvand, Shaghayegh Khanmohammadi, Maryam Akhtari, Elham Farhadi, Ahmadreza Jamshidi, Mahdi Mahmoudi
Macrophages are members of the innate immune system; that originate from monocyte cells from the myeloid stem cells. In response to the tissue environment, monocytes differentiate into two subtypes of macrophages, M1, or M2. The M1 or classically activated macrophages (CAM) aggravate immune responses by releasing reactive oxygen species (ROS), and pro-inflammatory cytokines.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 6, p184-192 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.184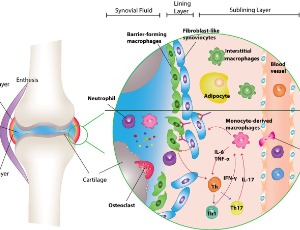
18F-FDG PET/CT in the Diagnostic Workup of Fever and Inflammatory Syndromes of Unknown Origin in the Elderly: A Valuable Tool with a Need for Clinical Finesse
Emmanuel Andres, Alessio Imperiale, Thierry Lavigne, Noel Lorenzo Villalba
Fever and inflammatory syndromes of unknown origin (FUO and IUO) represent some of the most challenging diagnostic entities in clinical medicine. These conditions often trigger extensive investigations, prolonged hospitalizations, and sometimes empirical treatments with limited benefit. The diagnostic complexity is even greater in the elderly, where clinical presentations are frequently atypical, underlying conditions are numerous, and physiological responses to illness are blunted or masked.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 5, p185-187 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.238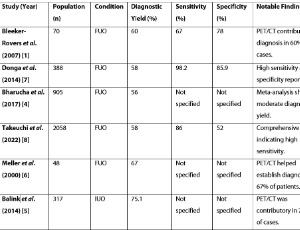
Going above and Beyond: Using an Attenuated Herpes Viral Vaccine Vector to Elicit Protective Immune Responses Through Neutralizing and Non-neutralizing Functions of Antibodies
Katherine E. Kaugars, Angelo R. Retamal-Diaz, Anna Paula de Oliveira, Pablo A. Gonzalez, William R. Jacobs Jr.
The COVID-19 pandemic has made the development of novel vaccines a high priority for public health. While many vaccines have focused on the generation of neutralizing antibodies, we have discovered a novel herpes simplex virus (HSV) vaccine candidate, designated ΔgD-2, that can preferentially elicit non-neutralizing antibodies that function through Fcγ receptor (FcγR) activation
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 5, p185-193 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.149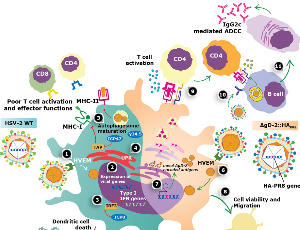
The Considerable Conundrum of NSAID-induced Melt
Basil Rigas, Wei Huang, Robert A. Honkanen
Over 20 years after the first description of NSAIDinduced Corneal Melt (NICM), a rare but potentially devastating visual complication induced by a topically applied medication, the optimal prevention and treatment for this condition remain unknown creating a clinical conundrum for eye care professionals and challenge for eye researchers.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p188-191 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.041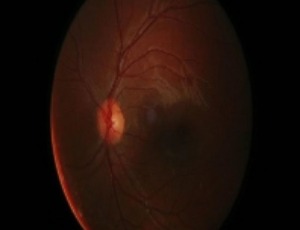
Revisiting Vaccine Innovation: A Critique of the “Generation Gold Standard” Initiative
Yongxin Zhang
The “Generation Gold Standard” (GGS) initiative, announced by NIH and BARDA, aims to develop universal vaccines for influenza and coronaviruses using β-propiolactone (BPL)–inactivated whole-virus technology. This approach, historically used in vaccines like Sinovac’s CoronaVac, is praised for its scalability but has faced scrutiny for limited durability and cross-protection. As the world seeks robust pandemic preparedness post-COVID-19, GGS’s reliance on an established platform raises questions about its transformative potential.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 5, p188-191 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.239
Upregulated Gene Expression of Histone Deacetylases (HDAC) 1, 2, and 11 in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
Samaneh Enayati, Mozhgan Moharamoghli, Ali Farazmand, Vahideh Hassan-Zadeh, Shiva Poursani, Elham Madreseh, Maryam Akhtari, Masoumeh Akhlaghi, Elham Farhadi, Asghar Hajiabbasi, Ahmadreza Jamshidi, Mahdi Mahmoudi
The histone deacetylase (HDAC) family consists of epigenetic modifiers that demonstrate anti-inflammatory activities, and hence they might have a substantial role in auto-inflammatory disorders including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Therefore, the aim of this study is to investigate the expression of HDAC1, HDAC2, and HDAC11 genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of RA cases compared to healthy controls.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 4, p188-195 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.205
Sleep Disturbances are a Significant Predictor of Chikungunya Arthritis Flare Severity
Sarah Renee Tritsch, Richard Amdur, Liliana Encinales, Andres Cadena Bonfanti, Paige Fierbaugh, Geraldine Avendaño, Carlos Andres Herrera Gomez, Karol Suchowiecki, Evelyn Mendoza-Torres, Wendy Rosales, Dennys Jimenez, Carlos Alberto Perez Hernandez, Alfonso Sucerquia Hernández, Paula Bruges Silvera, Yerlenis Galvis Crespo, Alberto David Cabana Jimenez, Jennifer Carolina Martinez Zapata, Christopher N. Mores, Gary Steven Firestein, Gary Leonard Simon, Aileen Yu-hen Chang
The primary objective of this research was to explore the link between sleep and flare pain associated with chikungunya virus (CHIKV) infection. The secondary objective was to investigate if cytokines and T regulatory (Treg) cells have an influence on this relationship.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p191-197 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.098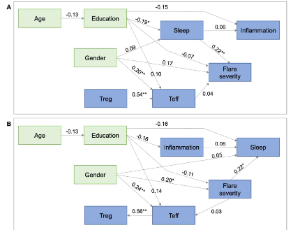
A Commentary on USP50 and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation: Revisiting Experimental Rigor with ASC-Deficient RAW264.7 Cells
Jing-Rong Liang, Jie Guo, Feng-Yi Mai, Ai-Guo Xue, Chen-Guang Li
The recent study by Zhao et al. in Frontiers in Immunology reported that bile acids induce USP50 expression in macrophages, which then deubiquitinates ASC to promote NLRP3 inflammasome activation and HMGB1 release, ultimately driving gastric cancer progression through PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways. These findings provide valuable insights into the potential role of bile reflux-driven inflammation in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer. In general, this is an insightful piece of research.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 5, p192-196 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.240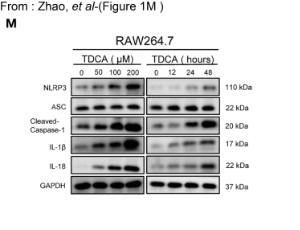
Current Advances in CAR T Cell Therapy for Malignant Mesothelioma
Astero Klampatsa, Steven M. Albelda
Malignant mesothelioma is a relatively rare malignancy arising in the body’s serosal surfaces, with malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) being the most common type. It is characterized by local spread within the thorax, poor prognosis and resistance to treatment. The development of various immunotherapeutic options has provided a new way- and hope- in treating cancer patients. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy has been proven very successful in treating hematological cancers, like leukemias and lymphomas, and its use is now being tested in solid tumors.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p192-200 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.042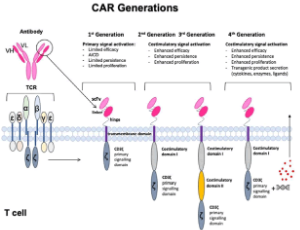
Commentary on “Osteosarcoma from the Unknown to the Use of Exosomes as a Versatile and Dynamic Therapeutic Approach”
Ana Figueiras
This commentary mentions to our published article that intends to describe the properties that turn exosomes (Exo) into an efficient, as well as safe nanovesicle for drug delivery and treatment of osteosarcoma (OS). Nowadays, the results of conventional treatments are still unsatisfactory, mainly, in patients with recurrent disease or metastatic.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 6, p193-194 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.185
The Importance of C5aR2 in Neutrophil Function and Its Impact on Neutrophil-mediated Diseases
Daniel Leonard Seiler, Marie Kleingarn, Syeda Zoela Gilani, Paula Emily Reichel, Jörg Köhl, Christian Marcel Karsten
C5aR2 serves as the second receptor for the anaphylatoxin C5a. It was identified about 10 years after identification of the first cognate receptor, C5aR1. Initially, C5aR2 was considered a mere decoy receptor for C5a. According to this view, its function was to scavenge excess C5a from C5aR1 and thereby exert anti-inflammatory effects. However, this initial view of C5aR2 had been oversimplified.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 6, p194-201 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.150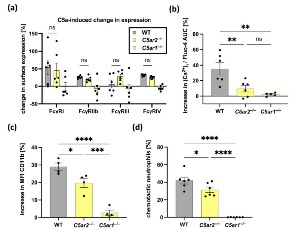
Polyamines: Key Players in Immunometabolism and Immune Regulation
Shanmuga S. Mahalingam, Pushpa Pandiyan
Polyamines are small organic molecules ubiquitously present in all living organisms and function as crucial regulators of biological processes ranging from fundamental cellular metabolism to immune regulation. Dysregulation of polyamine metabolism has been implicated in numerous diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders, inflammatory conditions, autoimmune diseases, and cancer. This review provides an overview of pathophysiology of these conditions, highlighting polyamines’ role in immunometabolic alterations in the context of immune regulation.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 5, p196-208 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.206
Diversity and Evolutionary Adaptations of the IMD Signaling Pathway in Hemipteran Innate Immunity against Bacterial Infections
Mario Henry Rodríguez, Eduardo Daniel Rodriguez-Aguilar
Insects conform large numbers of parasites and pathogens in diverse habitats. Cuticular structures on their body surfaces and secreted membranes in their digestive tracts are the first defensive barriers to prevent entry of invading organisms. Across the extended range of genera and species, insects acquired common first front defensive mechanisms.
J Cell Immunol, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 5, p197-203 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.7.241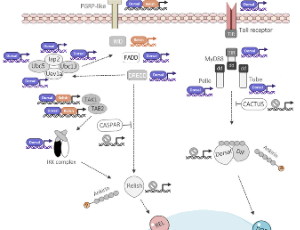
The Potential of Combination Therapies and Patient Stratification to Improve CCR2 Inhibition Therapeutics
Jason E. Duex, Dan Theodorescu
Chemokines and their receptors are the communication mechanism used by cells of the immune system, allowing them to identify and eliminate pathogens and cancerous cells. However, it is becoming clear that chemokines and their receptors are also playing a role in tumor progression and metastasis. An example of such coopting is the CCL2-CCR2 axis.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p198-200 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.099
Is Cellular Senescence of Dopaminergic Neurons the Cause of Local Inflammation in the Midbrain Observed in Parkinson’s Disease?
Markus Riessland
Current research investigating the pathomechanisms of neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system (CNS), such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), or Parkinson’s disease (PD), led to the understanding that these diseases have to be seen in the context of immune responses. In other words, inflammation plays a central role in neurodegenerative disorders of the CNS.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 5, p201-204 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.043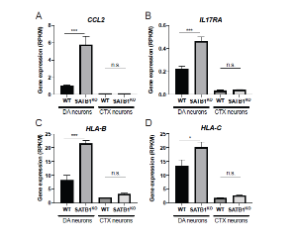
Efficacy of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange Alone or in Combination with Ruxolitinib for the Treatment of Penn Class 3 and 4 Cytokine Release Syndrome Complicating COVID-19
W. Larry Gluck, Wesley M. Smith, Sean P. Callahan, Robert A. Brevetta, Antine E. Stenbit, Julie C. Martin, Anna V. Blenda, Sergio Arce, W. Jeffery Edenfield
This study was conducted to validate the efficacy of therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE) in reducing the excessive cytokine load complicating a subset of patients with severe COVID-19 and respiratory compromise. Additionally, this trial explored molecular signals of potential benefit by the addition of JAK inhibition to TPE. Findings included an improvement in cytokine excess and oxygenation along with incremental benefit in cytokine reduction with the addition of ruxolitinib.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p201-206 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.100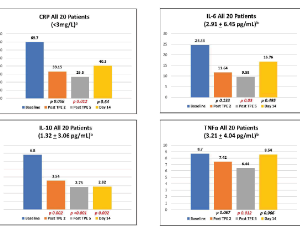
Ubiquitin-Dependent Regulation of Treg Function and Plasticity
Yikui Li, Ping Wei, Fan Pan
Delicately, our immune system eliminates exogenous and endogenous threats and prevents harmful immune responses against the host. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are indispensable in controlling immune responses and inducing immune tolerance; thus, immune homeostasis is maintained [1]. As a subset of CD4+ T cells, Tregs have been extensively studied for decades. They are best known for their ability to suppress immune responses, induce self-tolerance and help tumor cells escape immune surveillance [2-5]. Tregs mediate immune suppression via several mechanisms: They constitutively express cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4), which competes with the costimulatory molecule CD28 for binding CD80/86 to downregulate T cell activation [6].
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 6, p202-210 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.151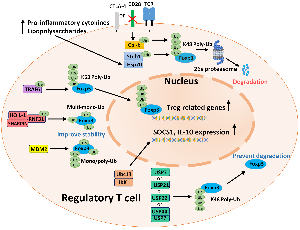
The Yin and the Yang of STAT1 Downstream of TLR4 Endocytosis: STAT1 beyond Interferon Signaling
Hozaifa Metwally, Tadamitsu Kishimoto
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)–induced toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) endocytosis has emerged as a key step for the production of interferon (IFN)-β, which activates the transcription of antiviral response genes through Janus kinase (JAK)/pTyr701 signal transducer and activator 1 (STAT1) signaling. TLR4 endocytosis also promotes proinflammatory cytokines production, at least in part through mediating a late-phase of nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 5, p205-210 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.044
The Importance of miRNA Identification During Respiratory Viral Infections
Ivan Martinez-Espinoza, Ma Del Rocio Banos-Lara, Antonieta Guerrero-Plata
The expression of small non-coding RNA MicroRNAs (miRNAs) during respiratory viral infections is of critical importance as they are implicated in the viral replication, immune responses and severity of disease pathogenesis. Respiratory viral infections have an extensive impact on human health across the globe. For that is essential to understand the factors that regulate the host response against infections.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p207-214 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.101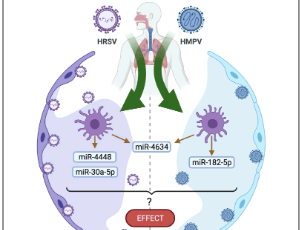
Telling Your Research Story
Houmam Araj
It is impossible for a person to begin to learn what he thinks he already knows. That's what Epictetus, the Greek Stoic philosopher, taught us two millennia ago. Yet somehow that lesson never made it to some of us – myself included. Rather, we have to learn it on our own and pay the appropriate price
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 5, p209-210 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.207
Preliminary Evidence of Differentially Induced Immune Responses by Microparticle-adsorbed LPS in Patients with Crohn’s Disease
P Ashwood
Inorganic microparticles are ubiquitous in the modern Western diet present as food additives and are actively scavenged by microfold (M) cells overlying human intestinal lymphoid aggregates. In Crohn’s disease (CD), inflammation is caused by the inability of the intestinal mucosa to sustain tolerance to gut luminal factors including bacteria and their by-products.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 6, p211-218 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.152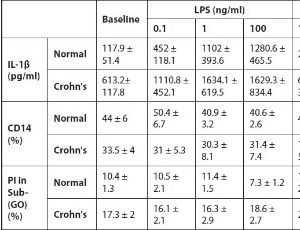
Evaluation of Neutrophil Elastase Inhibitors as Potential Therapies for ELANE Associated Neutropenia
Vahagn Makaryan, Merideth Kelley, Audrey Anna Bolyard, Gobind Chugh, David C. Dale
Neutrophil elastase (ELANE) mutations are the most common cause of cyclic (CyN) and congenital neutropenia (SCN), two autosomal dominant disorders causing recurrent infections due to impaired neutrophil production. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) corrects neutropenia but has adverse effects, including bone pain and in some cases, an increased risk of myelodysplasia (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is an alternative but is limited by its complications and donor availability. Alternative therapies are needed, particularly for patients with poor responses to G-CSF and those at higher risk of MDS/AML.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 5, p211-218 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.208
Updates of Recent Vinpocetine Research in Treating Cardiovascular Diseases
Chongyang Zhang, Chen Yan
Vinpocetine is a derivative of vincamine. It has been used to prevent and treat cerebrovascular disorders such as stoke and dementia, and remains widely available in dietary supplements that often marketed as nootropics. Due to its excellent safety profile at therapeutic dose regimen, vinpocetine has raised research interest in its new applications in various experimental disease models.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 5, p211-219 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.045
Environmental Enrichment and Its Benefits for Migraine: Dendritic Cell Extracellular Vesicles as an Effective Mimetic
Kae Myriam Pusic, Lisa Won, Richard Paul Kraig, Aya Darinka Pusic
Environmental enrichment produces beneficial effects in the brain at genetic, molecular, cellular and behavior levels, and has long been studied as a therapeutic intervention for a wide variety of neurological disorders. However, the complexity of applying a robust environmental enrichment paradigm makes clinical use difficult. Accordingly, there has been increased interest in developing environmental enrichment mimetics, also known as enviromimetics.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p215-225 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.102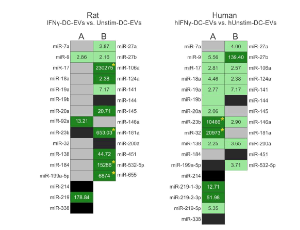
Computational and Mutational Hotspot Analysis of Mycobacterial Inorganic Pyrophosphatase and Virtual Screening of Natural Compounds to Discover Potential Therapeutics
Shivangi, Laxman S. Meena
Mycobacterial inorganic pyrophosphatase (Mt-PPa) plays an essential role in Mycobacterium tuberculosis survival both in vitro and in vivo. This enzyme family hydrolyzes inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi) to release inorganic phosphate (Pi), thereby preventing pyrophosphate toxicity. The M. tuberculosis gene Rv3628 encodes a type I inorganic pyrophosphatase that exhibits metal-ion-dependent catalytic activity.
J Cell Immunol, Volume 7, Issue 6, p216-233
Vγ2+ γδ T Cells and Their Regulatory Potential in Skin Allograft Survival
Shilpi Giri, Girdhari Lal
Our recently published research article “Vγ2+ γδ T cells in the presence of anti-CD40L control surgical inflammation and promote skin allograft survival” revealed that the Vγ2+ subset of γδ T cells, which otherwise are known primarily for its proinflammatory function, regulate the survival of skin allografts in the presence of anti-CD40L.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 6, p219-222 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.153
Epidemiology, Symptoms and Pathophysiology of Long Covid Complications
Chongyang Zhang, Chiung-Yu Hung, Chia George Hsu
Long COVID, or post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection, reports to affect a significant proportion of COVID-19 survivors, leading to persistent and multi-organ complications. This review examines the epidemiology, symptoms of long COVID complications, including cardiac, hematological, vascular, pulmonary, neuropsychiatric, renal, gastrointestinal, musculoskeletal, immune dysregulation, and dermatological issues
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 5, p219-230 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.209
Control of CD4 Helper and CD8 Cytotoxic T cell Differentiation
Vibhuti P Dave
Engagement of mature T cell receptor (TCR), a multiprotein complex consisting of an αβ heterodimer associated with invariant CD3 signaling proteins, on CD4+CD8+ double positive (DP) thymocytes by selfpeptide/ self-MHC complex on thymic stromal cells results in negative selection of thymocytes expressing strong affinity TCRs and positive selection of thymocytes expressing weak affinity TCRs.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 5, p220-226 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.046
Is Omicron Variant of COVID-19 Threatening Health Like Other Variants?
Mousa Ghelichi-Ghojogh, Hamed Ghasemloo, Hamid Hosseinpour, Rohollah Valizadeh, Tella Sadighpour
World health organization (WHO) designated the variant B.1.1.529 a variant of concern, named Omicron, as a fastspreading SARS-CoV-2 variant, on 26 November 2021 which started from Southern Africa. In addition to the new mutations (more than 30 mutations in the spike protein), Omicron also carries mutations similar to the alpha, beta, gamma, and delta variants of coronavirus, and is collectively known as the fifth most disturbing variant.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 6, p223-224 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.154
Immunotherapy for Dogs: Still Running Behind Humans
Hans Klingemann
Despite all good intentions, dogs are still running behind humans in effective cancer immunotherapies. The more effective treatments in humans, like infusions of CAR-T and NK-cells are not broadly pursued for canines due to significant costs, the rather complicated logistics and the lack of targetable surface antigens. Monoclonal antibodies are challenging to develop considering the limited knowledge about canine target antigens and about their mode of action.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p226-233 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.103
Pro-survival Bcl-2 Proteins are Modifiers of MYC-VX-680 Synthetic Lethality
Jing Zhang, Shenqiu Zhang, Qiong Shi, Dun Yang, Thaddeus D. Allen
The transcription factor encoded by the myelocytomatosis oncogene (MYC) is deregulated by distinct means in different human cancers. Aberrations include chromosomal translocation, amplification, mutation, enhancer activation and post-translational mechanisms that lead to MYC protein accumulation. It is perhaps the most commonly deregulated oncoprotein and is linked to most of the hallmarks of cancer.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 5, p227-232 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.047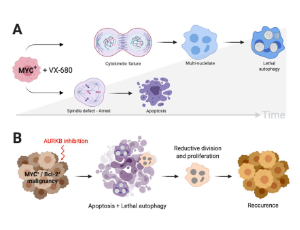
Innate Immune Sensors Spying Microbial Hideouts! OAS1 - ‘Stalwart Defender’ or ‘Hidden Enemy’?
Suparna Dhar, Sourish Ghosh
OAS1 plays a critical role in host-pathogen interactions by balancing translational shutdown to limit microbial replication while producing antimicrobial components. Host RNA sensors detect microbial nucleic acids, initiating an interferon-mediated innate immune response that induces ISGs to inhibit replication and shape adaptive immunity. OAS1 enhances the translation of selective mRNAs, producing proteins with antimicrobial properties.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 5, p231-235 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.210
Culture nTAD: A New Avenue for Research in Late-stage Human Lung Development and Perinatal Lung Disease
Hongmei Mou
Primary cell culture is a laboratory process that has been practiced for more than a century by which the cells of interest are isolated from tissues and grown under the appropriate conditions to achieve a certain cell number. In conducting airway, basal cells function as stem cells that self-renew and differentiate to maintain tissue homeostasis and to regenerate after injuries.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 5, p232-236 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.048
Body Mass Index and COVID-19: Likely Causes for Obesity and Undernutrition Correlation with Disease Severity
Nicolas Vitale
Very early on clinicians around the world reported that in addition to aging and various heart pathologies, excess of body weight, especially obesity is a major risk factor for the severity of COVID-19 infection. The multitude of symptoms that have been described from human patients likely arises from the broad distribution of ACE2, a member of the angiotensin receptor family, the receptor for SARS-CoV-2, among which adipose tissue is a prominent one.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p234-239 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.104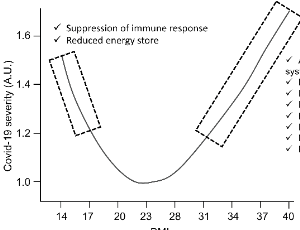
Development of a Chikungunya Arthritis Disease Activity Score (CHIK-DAS) Based on a Prospective Cohort Study
Aileen Yu-hen Chang, Samuel Joseph Simmens, Hugh Watson, Richard L. Amdur, André Siqueira, Abigale Marie Proctor, Sarah Renee Tritsch, Carlos Andres Herrera Gomez, Liliana Encinales, Alfonso Sucerquia Hernández, Jose Forero-Mejía, Alejandro Jaller, Juan Jose Jaller, J. Kennedy Amaral, Ilana Heckler, Gary Leonard Simon, Larry Moreland, Andres Cadena Bonfanti, Gary Steven Firestein
Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) is an alphavirus spread by mosquitos, primarily Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus, that causes a debilitating febrile illness called chikungunya fever (CHIKF). CHIKF usually presents in two phases, starting as an acute illness, characterized by high fever, polyarthralgia and polyarthritis, headache, maculopapular skin rash, sometimes pruritic, and severe fatigue, commonly accompanied by anorexia, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. This first phase usually resolves within 5-14 days.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 6, p236-246 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.211
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Cyclosporine Broadens the Therapeutic Potential of Lenalidomide in Myeloid Malignancies
Aixia Dou, Jing Fang
The immunomodulatory drug lenalidomide is used for the treatment of certain hematologic malignancies, including myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Lenalidomide interacts with cereblon (CRBN), a component of the CRL4CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, leading to ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of substrates, such as transcription factor Ikaros (Ikaros family zinc finger 1, IKZF1).
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 5, p237-244 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.049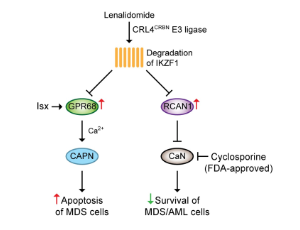
Novel Combination Treatments for AML
Montserrat Estruch, Camilla Vittori, Teresa Muñoz-Montesinos, Kristian Reckzeh, Kim Theilgaard-Mönch
Drug resistance of cancer patients toward chemotherapy remains a major problem in the clinic. Hence, understanding the intrinsic and acquired molecular mechanisms of drug resistance in cancer patients is paramount to identify relevant targets for therapeutic interventions that enhance chemotherapy response, and ultimately improve clinical outcome.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p240-245 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.105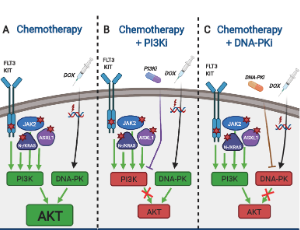
Hypomagnesemia and Outcomes in Hematologic Malignancies
Jennifer Gile, Joy Heimgartner, Gordon Ruan, M. Molly McMahon, Thomas Witzig
Magnesium, the fourth most abundant mineral in the human body, has several critically important functions in the body including cell growth, energy production and function of the immune system. There is an increasing interest in the role of magnesium in the pathology of different diseases including diabetes, cardiovascular disease and malignancies.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 5, p245-249 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.050
Expression of Pu.1, C/Ebpα and Bach1 Transcription in Immune Cells in Patients with Cancer
Gulnur K. Zakiryanova, Elena Kustova, Nataliya T. Urazalieva, Emile T. Baimukhametov, Valeriy A. Makarov, Galina V. Shurin, Narymzhan N. Nakisbekov, Michael R. Shurin
Dysfunction and abnormal differentiation of immune cells and hematopoietic precursors are well described in patients with cancer, although the role of transcription factors in these defects is not well established. Here, we evaluated expression of C/EBPa, PU.1 and BACH1 transcription factors in lymphoid and myeloid cells, including NK cells, T cells, neutrophils and monocytes, isolated from healthy donors and cancer patients.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p246-257 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.106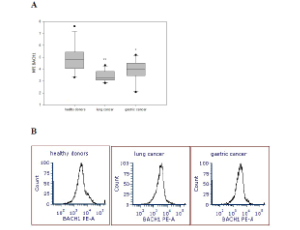
Medicinal Plant Use in Post-chikungunya Viral Arthritis Disease Patients in Brazil: A Cross-sectional Study
Ramão Luciano Nogueira Hayd, Tiago Matos Dourado, Jose Forero-Mejía, Jose Gabriel Lara-Amador, Aileen Yu-hen Chang
Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) is an alphavirus spread by mosquitoes that is endemic to the Amazon region of Brazil. One significant outbreak of CHIKV occurred between 2014 and 2018 In Roraima, Brazil, with 5,928 reported cases of chikungunya, of which 3,719 were confirmed in Boa Vista after phylogenetic analysis showed that the ECSA strain of the virus caused the outbreak in 2017. In a cross-sectional study of participants affected by this CHIKV outbreak in Roraima, the most common symptoms reported in the initial infection period were fever, joint pain, headache, myalgia, and eye pain.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 6, p247-254 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.212
Emerging Functions of ICAM-1 in Macrophage Efferocytosis and Wound Healing
Prarthana J. Dalal, Ronen Sumagin
ICAM-1 is a transmembrane, cell surface glycoprotein expressed by a variety of cells, but has been best-studied in vascular endothelium. Structurally, ICAM-1 is composed of five extracellular IgG- like domains to help facilitate cell-cell interactions and has a short cytoplasmic tail anchored to the cytoskeleton to facilitate intracellular signal transduction.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 5, p250-253 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.051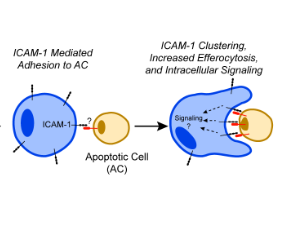
CALHM6: Expression Level in SARS-CoV-2 Patients and Its Trend as the Infection Progresses
Ali Zalan, Kehkshan Jabeen, Wajid Hussain, Bushra Khan, Wafa Omer, Saman Noor, Muhammad Usman, Aneela Javed
This study investigates the role of Calcium Homeostasis Modulator 6 (CALHM6) in immune regulation during SARS-CoV-2 infection, with the aim of exploring its potential as a prognostic marker. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from 42 SARS-CoV-2 positive patients and 19 healthy controls were analyzed for CALHM6 expression. Clinical data were collected from patients admitted with low oxygen saturation (≤90%) and severe symptoms, and RNA was extracted at admission.
J Cell Immunol, Volume 7, Issue 6, p250-262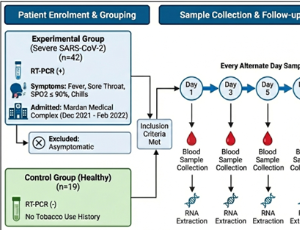
Juvenile-onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Accompanied by Secondary Thrombotic Microangiopathy
Eriko Tanaka, Tomoya Kaneda, Yuko Akutsu, Toru Kanamori, Mariko Mouri, Masaaki Mori
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects multiple organ systems. Juvenile-onset SLE (jSLE) accounts for up to 20% of all SLE patients. Compared to adult-onset SLE, jSLE patients tend to show different manifestations of SLE and are often difficult to diagnose promptly. JSLE patients show severe disease conditions, and intensive treatments are therefore required to control disease activity.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 5, p254-258 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.052
Evaluating the Role of the Renin-angiotensin System in COVID-19: Implications for ACE Inhibitor and ARB Use During SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Sarah Renee Tritsch, Evelyn Mendoza-Torres, Mónica Gómez-Pulido, Jairo Castellar-López, Rebecca Lynch, Carlos Andres Herrera Gomez, Hana Akselrod, Adrienne Poon, Samuel Joseph Simmens, Christopher N. Mores, Gary Leonard Simon, Lauren C. Ray, Sarah Conway, Aileen Yu-hen Chang
This study aimed to investigate the role of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) in COVID-19, particularly focusing on key components such as ACE, ACE2, and their related peptides, angiotensin-(1-7) and angiotensin-(1-9). Using serum samples from healthy controls and both non-severe and severe COVID-19 patients, ELISA assays revealed no significant differences in these RAS components between the groups.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 6, p255-265 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.213
Neurological Manifestations Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Invasion of the Autonomous Nervous System
Erwan Poivet, Matthieu Daniel, Fernando A. Bozza, Tarek Sharshar, Pierre-Marie Lledo
Although pneumonia and acute respiratory failure are the most frequent and severe complications of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, many of them also develop neurological signs and symptoms. From sickness behavior to coma, neurological disorders are associated with impairment of consciousness and dysautonomia, resulting from brainstem dysfunction.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p258-277 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.107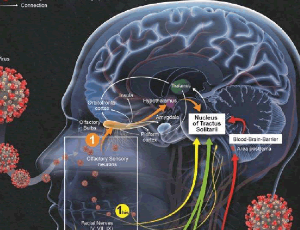
Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir/Voxilaprevir for Previously DAA-treated Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C?
Llaneras J, Riveiro-Barciela M, Esteban R, Buti M
Chronic hepatitis C infection is a global public health problem affecting more than 71 million people. Treatment of hepatitis C virus (HCV) has rapidly advanced with the introduction of oral direct-acting antivirals (DAAs). Interferon-free DAA combinations have changed the treatment paradigm in HCV, with elimination of the infection in more than 95% of cases.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 5, p259-264 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.053
Autoimmune Diseases Primarily Mediated by Cellular Immunity Mechanisms and Recent Treatment Advances
Yongxin Zhang
Autoimmune diseases primarily mediated by cellular immunity, classified as type IV hypersensitivity disorders, are driven by dysregulated T cell responses resulting in targeted tissue destruction. Unlike antibody-dominant autoimmune conditions, these disorders involve autoreactive CD4+ and CD8+ T cells that infiltrate tissues, amplify inflammatory cascades, and promote chronic organ damage through cytokine release and direct cytotoxicity.
J Cell Immunol, Volume 7, Issue 6, p263-267
The Hippo Pathway, Immunity, and Cancer: An update
Helena J. Janse van Rensbur, Zaid Taha
The Hippo pathway has well-established roles in physiology and pathology. However, functions for the Hippo pathway in modulating interactions with the immune system have only recently been elucidated. In this review, we provide a brief update on our previous summary of the field. More specifically, we highlight literature that demonstrates a role for the Hippo pathway in modulating the antitumour immune response, primarily through acting on PD-L1.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 6, p265-275 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.054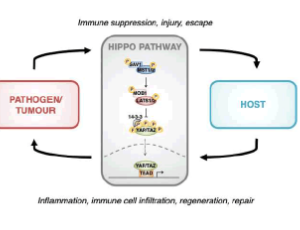
Immunotherapy in the Management of Hodgkin Lymphoma: Time for Immunotherapy for All?
Coen J. Lap, Joseph L. Roswarski
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a lymphoid malignancy of germinal center B cell origin. Conventional chemotherapy with or without radiation induces high cure rates but these treatments can have relevant long-term toxic side effects. As a result, there remains a lot of debate about the optimal management of these patients, especially for limited-stage disease. The last two decades have resulted in a greater understanding of the underlying biology of HL, including the presence of an aberrant phenotype on the tumor cells and the necessity of immune escape.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 6, p266-281 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.214
Influenza A Virus Infection Induces White Adipose Tissue Browning: A Metabolic Adaptation to Infection?
Johanna Barthelemy, Isabelle Wolowczuk
We recently reported that influenza infection is associated with drastic, depot-specific changes in white adipose tissue (WAT), notably the occurrence of thermogenic brown-like adipocytes within the subcutaneous depot, a process referred to as WAT browning. In mammals, induction of the thermogenic circuit increases heat production and consumes energy, consequently improving host’s metabolism.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 6, p276-283 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.055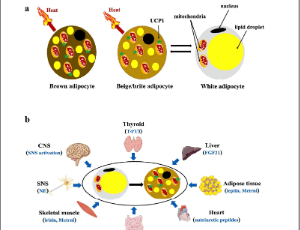
Risk of Venous Thrombotic Events in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: Genetic Insights
Maria I. Zervou, George N. Goulielmos
Various studies have reported a strong association between different autoimmune diseases or infection-mediated disorders and an increased risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE). Particularly, patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) have been found to be associated with VTE. The aforementioned studies posed an intriguing question concerning the putative role of a shared genetic background as regards with the co-occurrence of VTE with RA, AS or PsA.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 6, p282-286 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.215
Single-cell Approach to Generate Functional TCR-Ts: A Potential Accelerator of TCR-T Cell Therapy for Infectious Diseases
Qumiao Xu, Ziyi Li, Fei Wang, Zhenkun Zhuang, Yanling Liang, Qianqian Gao, Xuan Dong, Linnan Zhu
T cell-mediated immune response is essential for host defense against viruses, including the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) which has caused a global pandemic. Genetically engineered T cells with antigen-specific T cell receptors (TCR-Ts) are redirected to eliminate target cells via TCRs recognizing peptides bound with major histocompatibility complexes (MHCs).
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 6, p284-288 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.056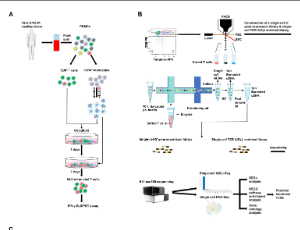
Use of Sysmex Hematology Analyzer based Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell (XN-HPC) Count in Allogeneic Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplant Setting; Is It Substantially Reliable?
Aisha Jamal, Ali Salim, Tahir Shamsi
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation remains the only curative option for various benign and malignant hematological disorders. The procedure of allogeneic stem cell transplantation entails the administration of adequate doses of hematopoietic progenitor cells, aiming for complete and sustained hematopoietic reconstitution. Hematopoietic progenitors are obtained either through a bone marrow harvest or from GCSF-mobilized peripheral blood of the identified donor.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 6, p289-293 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.057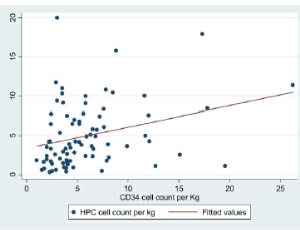
Commentary on “A Vaccine for Photodynamic Immunogenic Cell Death: Tumor Cell Caged b y Cellular Disulfide–Thiol Exchange for Immunotherapy”
Jie Zang, Haiqing Dong
Tumor immunotherapy, including monoclonal antibody of immune checkpoint blockade, therapeutic antibody, cancer vaccine and cell therapy, etc., is to restart and maintain the tumor immune cycle, restore the normal antitumor immune response of the body, so as to control and eliminate the tumor. Among them, tumor vaccine, which can elicit robust immune response and produce sustained immune memory effect, is particularly favored in the treatment and prevention of tumor recurrence.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p294-295 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.109
The Mammalian Gut Microbiome, Immune Responses and Disease: From Observational to Causal Relationships
Ulrich Desselberge
The gut is a major organ for the production of immune responses and is colonized by a large variety of microbes. The composition of microbes in the gut influences immune responses qualitatively and quantitatively and is also observationally correlated with enteric and extra-intestinal infectious and non-infectious diseases. Animal models have been extremely useful to unravel the relationships of the gut microbiome with immune responses and various diseases.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 6, p294-300 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.058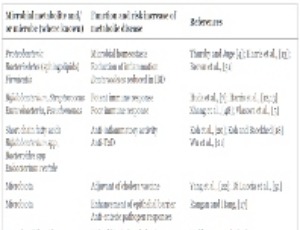
Short and Sweet: Viral 5`-UTR as a Canonical and Non-Canonical Translation Initiation Switch
Brandon M. Trainor, Natalia Shcherbik
The replication of viruses requires host cell functions, specifically for protein synthesis, as viruses lack their own translational machinery. Failure to translate viral mRNAs and generate viral proteins would affect the propagation and evolution of a virus. Thus, independently of their size, complexity, and genomes, viruses evolved sophisticated molecular mechanisms to hijack the translational apparatus of a host in order to recruit ribosomes for efficient protein production.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 5, p296-304 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.110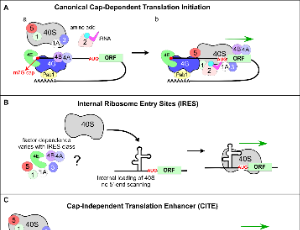
A Native 51 kDa Leishmania Membrane Protein Revealed as a Novel Antigenic Candidate for Immuno-Diagnosis of Human VL and PKDL diseases
Mohd Kamran, Sarfaraz Ahmad Ejazi, Anirban Bhattacharyya, Nicky Didwania, Nadia Ali
Visceral leishmaniasis (VL), a potentially devastating neglected tropical disease is a major health concern. Despite recent advances made in diagnosis of VL, an accurate and a reliable diagnostic biomarker is still needed.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 6, p301-307 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.059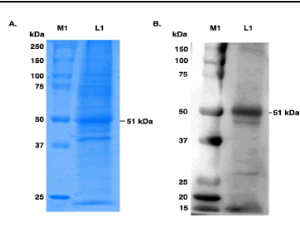
Exploring and Targeting the Tumor Immune Microenvironment of Neuroblastoma
Katherine E. Masih, Jun S. Wei, David Milewski, Javed Khan
Neuroblastoma is derived from the developing sympathetic nervous system and is the most common extracranial solid tumor of childhood.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 5, p305-316 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.111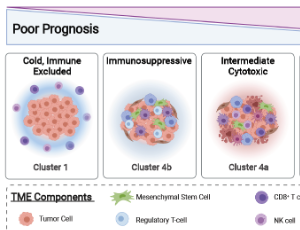
Role of Irreversible Post-Translational Modifications of Autoantigens in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: LL37 as a Model Autoantigen
Loredana Frasca, Roberto Lande
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a devastating disease, which affects several organs and with poor therapeutic options. Cathelicin LL37 is an antimicrobial peptide (AMP) with pleiotropic functions on immune cells and parenchymal cells, which can be implicated in inflammatory pathways and in immune regulation. LL37, a stimulator of both the innate and the adaptive immune responses in psoriasis and related psoriatic arthritis (PsA), can represent a relevant model autoantigen to study the effect of irreversible post-translational modifications (PTM) in SLE, as compared to psoriasis and PsA
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 6, p308-314 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.060
Maternal Diet Alters Trained Immunity in the Pathogenesis of Pediatric NAFLD
Karen R. Jonscher, Jesse Abrams, Jacob E. Friedman
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a spectrum of pathologies ranging from simple steatosis to fibrosis and cirrhosis, is the most common cause of chronic liver disease, affecting over 80% of adults with obesity, one third of obese children ages 3-18 in North America [2] and ~10% of the general pediatric population.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 6, p315-325 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.061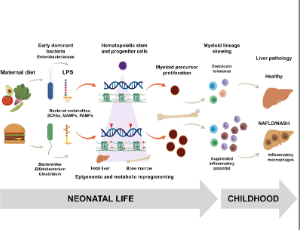
COVID-19 Clinical Outcomes and Vaccine Efficacy among Patients with Hematologic Malignancies
Sarah Gillaspie, Marc S Hoffmann
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic places the treating hematologist in a quandary: how best to protect patients with hematologic malignancies from potentially deadly COVID-19 infection while also providing the best therapy for their disease and maximizing opportunities for cure. Cancer patients as a whole trend toward more severe infection and increased mortality from COVID-19 infection.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 5, p317-320 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.112
Guanylate Binding Proteins promote anti-Leishmania Host Cell Defense
Arun Kumar Haldar
For their survival, many intracellular pathogens build and retain pathogen-containing vacuoles (PVs) to hide from the cytosolic host defense systems. Among the several PV-resident human pathogens are the obligate intracellular protozoa parasites Leishmania donovani and Toxoplasma gondii. The proinflammatory cytokine IFNγ, a key player in cellular immunity, can orchestrate a variety of defensive functions that destroy or prevent these intravacuolar pathogens from replicating inside host.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 5, p321-325 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.113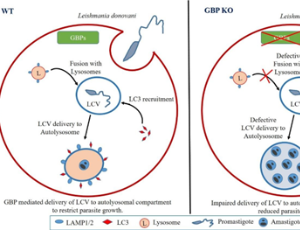
High Throughput Image Analysis for Cardiotoxicity Study using Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes
Lu Cao, Andries van der Meer, Robert Passier, Fons J. Verbeek
Cardiotoxicity is a well-known side-effect for the patients who are treated with different classes of anticancer drugs. In order to prevent potential drug-induced adverse effects, it is crucial to develop predictable human-based models and assays for drug screening. To that end, human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) are becoming promising and important for disease modeling and drug-induced toxicity screening.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 6, p326-332 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.062
Using Immune Cell/Adipocyte Co-Culture Models to Identify Inflammatory Paracrine Signaling Mechanisms: A Process Attenuated by Long-Chain N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
Jennifer M. Monk, Amber L. Hutchinson, Jamie L.A. Martin, Lindsay E. Robinson
Obese adipose tissue (AT) is characterized by increased recruitment and infiltration of multiple immune cell populations, in particular T cells (CD4+ or CD8+ subsets) and macrophages, that interact with adipocytes through paracrine signaling (i.e., cross-talk). Adipocyte/ immune cell cross-talk results in increased inflammatory and chemoattractant mediator production that contributes to local (i.e., AT) and systemic metabolic dysfunction.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 5, p326-335 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.114
Potentials of Interferons and Hydroxychloroquine for the Prophylaxis and Early Treatment of COVID-19
Alexander Yang, Lakshmi S. Guduguntla, Bing Yang
The symptoms of the COVID-19 range from asymptomatic or mild disease to severe disease that results in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and eventually death. Understanding the molecular mechanisms responsible for the progression from mild to severe disease is the key to decreasing the mortality of COVID-19. Compared to mild cases, severe cases of the COVID-19 have decreased interferon (IFN) a, ß, λ production. Type I (IFN a/ß) and III IFNs (λ) work coordinately to induce inhibition of viral reproduction through the stimulation of interferon stimulated genes (ISGs).
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 6, p333-340 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.063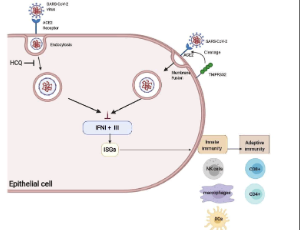
Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3) Regulation of Inhibitory Coreceptor Expression in T-cell Immunity
Mark E. Issa, Christopher E. Rudd
The serine/threonine kinase, glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) has been implicated in immune cell activation and function. Our recent studies have shown that the abrogation of GSK-3 activity down-regulates the expression of key inhibitory receptors PD-1 and LAG-3. It also regulates the expression of the transcription factor NFAT which, in turn, is responsible for inhibiting PD-1/ LAG-3 transcription as well as activating the expression of cytolytic effector proteins such as perforin and granzyme B.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 5, p336-342 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.115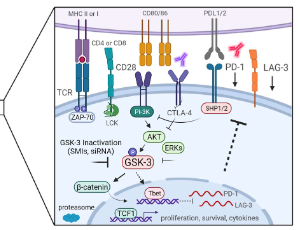
Newly Identified Function of Caspase-6 in ZBP1-mediated Innate Immune Responses, NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation, PANoptosis, and Host Defense
Min Zheng, Thirumala-Devi Kanneganti
Caspase-6 was discovered decades ago, but its roles in biological processes remain largely unknown. Recently, we have demonstrated that caspase-6 plays a critical role in influenza A virus (IAV)-induced cell death and innate immune responses. During IAV infection, Z-DNA binding protein 1 (ZBP1) initiates ZBP1-PANoptosome assembly to drive inflammasome activation and cell death, and we showed that caspase-6 interacts with RIPK3 to enhance the interaction between RIPK3 and ZBP1, thus promoting PANoptosome assembly.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 6, p341-347 | DOI: https://doi.org/10.33696/immunology.2.064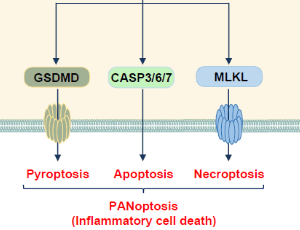
Immune Cells and Transcriptional Signatures Revealed Novel Regulators and Predict Clinical Response to Biologic Therapy in Ulcerative Colitis
Suzana D. Savkovic
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), which includes Crohn’s Disease (CD) and Ulcerative Colitis (UC), has a heterogeneous pathogenesis underlined by genetic predisposition, intestinal barrier dysfunction, impaired immune response, and microbiota imbalance. This proceeds to aberrant immune cells presence and function in the affected tissue, activation of signaling pathways, and expression of regulators that subsequently drive inflammation.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 5, p343-347 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.116
Resilience in Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases
Robert Passier, Federica Maggi, Francesca Romana Spinelli, Cristina Iannuccelli, Fabrizio Conti
Chronic conditions such as rheumatic diseases often carry a great burden, with pain, disability, and mood disorders ultimately leading to a poor quality of life. Resilience, defined as the skill to positively cope with stressful and critical events, could mediate the influence of rheumatic disease on patients’ life and may have a role in withstanding it. While resilience could be in some cases an innate ability, it can also be acquired through a dynamic process.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 5, p348-354 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.117
Cancer Immunoediting in Gliomas: Recent Advances and Implications for Immunotherapy
Parth V. Shah, Víctor A. Arrieta, Catalina Lee-Chang, Adam M Sonabend
Gliomas are an aggressive class of primary brain tumors with high rates of recurrence and a dismal overall survival. While existing therapeutic strategies provide some benefit, their effects are variable, and no curative modalities exist. The poor prognosis of these patients largely stems from the heterogenous molecular profile of these tumors and their tumor immune microenvironment (TIME).
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 6, p352-358 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.066
Joint Health Markers in Hemophilia: The State of the Art
E.D.P. van Bergen, S.C. Mastbergen, F.P.J.G. Lafeber, R.E.G. Schutgens, L.F.D. van Vulpen
Recurrent joint bleeds in hemophilia lead to (irreversible) joint damage, so-called hemophilic arthropathy causing major morbidity amongst hemophilia patients. Progression of arthropathy is monitored by clinical examination and imaging, but sensitive joint outcome measurements detecting early and subclinical joint damage are lacking. Biochemical markers reflecting joint tissue turnover can potentially provide this significant information about the joint status.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 6, p355-363 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.124
Molecular Tools for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Characterization
Radhashree Maitra, Elisha Fogel, Ruwan Parakrama, Sanjay Goel
In our recent publication, we have explored at the molecular level the consequences of reovirus administration to patients with KRAS mutated colorectal cancer (CRC). This was the first reported study where transcriptome assay was performed on KRAS mutated CRC patients receiving reovirus (pelareorep) therapy. Using peripheral mononuclear cells as a tumor surrogate, we have identified several hundred genes that were significantly altered in a transcriptome assay of patients receiving pelareorep serving as their own controls (pre and post reovirus administration) and compared to untreated controls.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 6, p359-363 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.067
Megalin-Mediated Trafficking of Mitochondrial Intracrines: Relevance to Signaling and Metabolism
David Sheikh-Hamad, Michael Holliday, Qingtian Li
The multi-ligand binding protein megalin (LRP2) is ubiquitously expressed and facilitates cell uptake of hormones, nutrients and vitamins. We have recently shown megalin is present in the mitochondria of cultured epithelial and mesenchymal cells, as well as many organs and tissues. Mitochondrial megalin associates with stanniocalcin-1 and SIRT3; two proteins that promote anti-oxidant defenses.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 6, p364-369 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.118
The Return of Tocilizumab for Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia
Kathy Tin, DO, Annamarie Fernandes, MD, Roderick Go, DO
The COVID-19 pandemic has been devastating for many for over one year. Vaccination has helped decrease the number of cases, but there are still multiple challenges to end the pandemic, such as the advent of variants, vaccine hesitancy, access to vaccines, and the impaired efficacy of vaccines in immunocompromised persons. Due to the hyperinflammatory state of SARS-COV-2 infections, research has been done on treatments that curtail the hyperinflammation.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 6, p370-374 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.119
Proteome-wide Epitope Prediction: Leveraging Bioinformatic Technologies in Rational Vaccine Design
Lindsay M.W. Piel, Stephen N. White
Artificial intelligence-based prediction technologies have allowed definition of T-cell epitopes presented by Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) molecules with allele-specificity of presentation. While some have utilized these technologies on a smaller scale, recent work has expanded the workable proteome size, leveraged both classes of Major Histocompatibility (MHC) molecules, extended the range of host species assessed during comparative analysis, and incorporated pathogen genetic diversity to highlight broadly useful epitopes.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 6, p375-379 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.120
Application of Mucosal Immune-related Molecular Adjuvants CCL19 and CCL28 in Enhancing the Function of HSV-2 gD DNA Vaccine
Yan Yan, Xu Wang, Renfang Chen
Herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) develops an annual incidence of 2.3 million people worldwide, which can lead to life-long latent infections, asymptomatic and reactivations, and with occasional symptomatic episodes causing ulcerative lesions in the genitalia and naus. The most serious complications are the long-term neurological sequelae and death of newborns during pregnancy.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 6, p380-386 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.121
Targeting Ovarian Cancer with IL-2 Cytokine/Antibody Complexes: A Summary and Recent Advances
Yilun Deng, Ryan M Reyes, Chenghao Zhang, José Conejo-Garcia, Tyler J. Curiel
Interleukin (IL)-2 was first identified as a potent T cell growth factor in 1976 and cloned in 1983. In the late 1990s, IL-2 gained further attention as the first immunotherapy demonstrating clinical efficacy against metastatic cancer, as high dose IL-2 was approved by the United States Food & Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma in 1992 and metastatic melanoma in 1998.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 6, p387-396 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.122
Human Gray and White Matter Metabolomics to Differentiate APOE and Stage Dependent Changes in Alzheimer’s Disease
Tyler C. Hammond, Xin Xing, Lucy M. Yanckello, Arnold Stromberg, Ya-Hsuan Chang, Peter T. Nelson, Ai-Ling Lin
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia with hallmarks of ß-amyloid (Aß) plaques, tau tangles, and neurodegeneration. Studies have shown that neurodegeneration components, especially brain metabolic deficits, are more predictable for AD severity than Aß and tau. However, detailed knowledge of the biochemical composition of AD brain tissue vs. normal brain tissue remains unclear.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 6, p397-412 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.123
Rethinking Radiation Dose-Fractionation in the Immuno- Oncology Era
Joseph Sia, Nicole M. Haynes
Leveraging the immunomodulatory effects of radiation therapy (RT) for synergy with immunotherapeutic agents for the treatment of cancer is an area of immense interest. A pressing deficiency in the translation of this strategy into the clinic is the lack of clarity on the impact of radiation dose-fractionation on host anti-cancer immune defences.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 6, p413-418 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.125
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
