Loading
Journal of Clinical Haematology
ISSN: 2766-4686

Fa-Chyi Lee
Professor of Hematology
The University of California, Irvine, USA
Featured Article
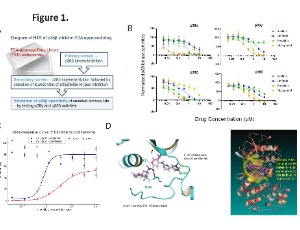
Repurposing Nilotinib as a Selective P38β Inhibitor in Hematopoietic Malignancies: Clinical Evidence and Mechanistic Insights
Featured Article
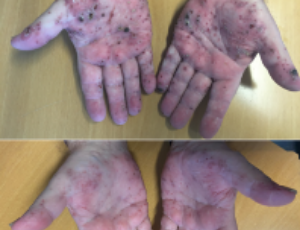
Concomitant Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis and Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukaemia Responding to 5-azacitidine
Featured Article
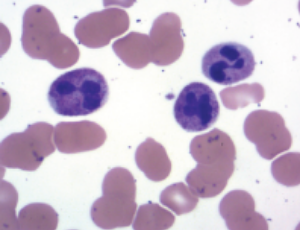
Multiple Myeloma with Neutrophilia: Two Etiologic Pathways for a Rare Presentation of a Common Diagnosis
About this Journal
Journal of Clinical Haematology is a highly reputed international journal dedicated to publish outstanding advances in vascular biology and haematology. Blood disorders and anomalies have adverse impact on human health thus making haematology research highly impactful and influential in the field of advanced medical research. Modern haematology research had contributed not only in basic research but it has revolutionised the treatment of various blood disorders such as blood cancers, thrombotic disorders, clotting diseases and so on
Articles
Diagnostic and Prognostic Challenges in Cytology for Multiple Myeloma: A Case Series in a Resource-limited Setting
Background: Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignancy of plasma cells characterized by clonal proliferation in the bone marrow and associated organ damage. In resource-limited settings, advanced diagnostic tools are often inaccessible, making conventional cytology a critical first-line diagnostic approach. Objectives: To assess the advantages and limitations of using bone marrow cytology as the primary diagnostic method for MM in a resource-constrained environment.
The Effect of Food on the Pharmacokinetics of Unesbulin in Patients with Advanced Leiomyosarcoma
Unesbulin is an orally bioavailable small molecule binding to the colchicine-binding site of tubulin and impeding tubulin polymerization and microtubule formation. It has been investigated as a monotherapy and in combination with other medications for the treatment of cancer, including leiomyosarcoma. This study investigated the effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of unesbulin. In total, eight leiomyosarcoma (LMS) patients (four males and four females) were enrolled in the food effect study during the phase 1b clinical study (NCT03761095).
How to Provide a Sufficient Supply of Safe, Effective and Quality-assured Blood and Blood Components in Emergency Situations
Background: Emergency situations can be personal and medical but also external and humanitarian (armed conflicts). In each situation a preparedness plan consisting of a risk assessment and gap analysis, emergency preparedness protocol, response and recovery protocol are needed. Objective: To discuss the question “how to provide a sufficient supply of safe, effective and quality blood and blood components in emergency situations?’”
Lymphoid Blast Crisis in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Transformation to B cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Background: Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is driven by the BCR-ABL1 fusion oncoprotein and is usually controllable with first- and second-generation tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKIs). However, ~5–7 % of patients eventually develop blast crisis, and a minority of these transform to B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL-B), a biologically aggressive state with a median overall survival of only 6–12 months despite therapy.
Reduced Intensity Therapy for Primary Central Nervous System Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders is Associated with Preserved Survival Outcomes: A Twenty-Year Single-Institutional Experience
Primary central nervous system post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders (PCNS-PTLD) are rare complications of transplantation. Due to PCNS-PTLD’s scarcity, optimal treatments, risk factors, and outcomes are poorly characterized. By retrospective analysis of 20 patients treated at the University of Wisconsin between the years 2000–2022, we aimed to describe patient/disease characteristics, therapies received, and survival outcomes of PCNS-PTLD. Three separate clinical and pathological databases were reviewed to identify cases, with all patients having at least 2 years of long-term follow-up.
Repurposing Nilotinib as a Selective P38β Inhibitor in Hematopoietic Malignancies: Clinical Evidence and Mechanistic Insights
Background: Cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) is an incurable cancer characterized by elevated p38β and p38γ and downregulated tumor-suppressive p38α. Objectives: We aimed to identify selective p38β inhibitors and investigate their mechanisms and therapeutic implications in hematologic malignancies. Methods: A high-throughput screen of Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved compounds was conducted to identify p38β inhibitors. In vitro kinase assays, Western blots, scRNA-seq, synergy tests, and mass spectrometry were used. Clinical trial and public datasets were analyzed.
Flavopiridol (Alvocidib), a Cyclin-dependent Kinases (CDKs) Inhibitor, Found Synergy Effects with Niclosamide in Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma
Flavopiridol (FVP; alvocidib), an FDA-approved orphan drug, has been studied in clinical trials under both single treatment and combination scenarios; several singleagent Phase I and Phase II clinical trials against leukemia, lymphomas, and solid tumors are active. To date, there have been more than 50 clinical trials involving FVP in the United States. Unfortunately, almost half of patients on FVP clinical trials showed serious adverse effects, implicating appropriate dosages need to be found and an alternative way to circumvent the toxicity of FVP with synergistic agents.
Chemotherapy Promotes Release of Exosomes Which Upregulate Cholesterol Synthesis and Chemoresistance in AML Blasts
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are emerging as a key mediator of intercellular communication as well as a major mechanism of functional reprogramming of cells in disease. All cells produce EVs, which freely circulate and are found in all body fluids. EVs are heterogenous, consisting of subsets of vesicles with different sizes, distinct origins, and various functions (Figure 1). They mediate a broad variety of biological events ranging from cellular activation, inflammation, blood coagulation, angiogenesis, cellular transport, and others.
Lower 24-Month Relative Survival among Black Patients with Non- Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: An Analysis of the SEER Data 1997-2015
Recent progress in the therapies used for patients with Non- Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) has improved survival. In 2020, 77,240 people were diagnosed with NHL. Although it accounts for 4% of all cancers, the incidence has been reported to be decreasing in the last few years. About 26% of people will expire from NHL (15% males and 11% females).Non-Hodgkin lymphoma arises from the clonal expansion of B, T, and natural killer (NK) cells. There is a significant degree of heterogeneity in NHL and this is likely related to different degrees of differentiation and maturation of these cells. These hematological malignancies exhibit different tumor behavior and are responsive to different chemotherapy agents which impacts clinical outcomes. There are patients who can be cured with current regimens; however, subtypes such as indolent and some aggressive lymphomas remain incurable necessitating treatment with new therapies including immunotherapy, targeted therapy, CAR T cells, and hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
Second Generation Platelet Concentrates - L-PRF (Fibrin Rich in Platelets and Leukocytes) and Its Derivatives (A-PRF, I-PRF)-: Morphological Characteristics to be Used in Modern Regenerative Surgery. Experimental Research
Platelet preparations (PDPs) have gained success, mainly due to their high concentrations of biologically active molecules, such as growth factors and cytokines, which play an important role in tissue repair and reconstruction. Recent knowledge shows that platelets can play a new role in tissue reproduction and vascular restoration, as well as being the protagonists of inflammatory processes and immune system responses. They release bio-active proteins and other active ingredients that can affect a number of phenomena that promote cell consumption, growth and transformation (growth factors).
Anticancer Activity of S-Glycosylated Quinazoline Derivatives
Breast cancer is the most frequent malignancy in females. Due to its major impact on the population, this disease represents a critical public health problem that requires further research at the molecular level to define its prognosis and specific treatment. Basic research is required to accomplish this task and this involves cell lines as they can be widely used in many aspects of laboratory research and, particularly, as in vitro models in cancer research. MCF-7 is a commonly used breast cancer cell line, that has been promoted for more than 40 years by multiple research groups but its characteristics have never been gathered in a consistent review article.
Management of Diagnostic and Treatment Centers in the Second Wave of COVID-19
COVID-19 has challenged global health and affected many countries. The disease had infected more than 16 million people and killed over 650,000 ones by the end of July 2020. According to Sahu et al., COVID-19 epidemic is the third most common coronavirus in the 21st century, resulting in numerous deaths all over the world. It has caused severe psychological stress and increased hospital visits along with increased tiredness and burnout of medical staff. The disease has also raised many problems for the management of hospitals and diagnostic-treatment centers, so that many of them have no capacity to receive patients.
Physiology, Coagulation Cascade: Inherited Disorders, and the Molecular Phenomenon of Alterations in Hemostasis
The physiology of coagulation routes and paths is a cascade of several molecular phenomena and biological events which was classified into two categories based on their phenomena i.e., intrinsic and extrinsic, originated separately, consisting of various factors and features such as fibrinogen, prothrombin, plasma thromboplastin, Hageman factor, Christmas factor, and Stuart-Prower factor, participate in its physiology
Flavopiridol (Alvocidib), a Cyclin-dependent Kinases (CDKs) Inhibitor, Found Synergy Effects with Niclosamide in Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma
Flavopiridol (FVP; alvocidib), an FDA-approved orphan drug, has been studied in clinical trials under both single treatment and combination scenarios; several singleagent Phase I and Phase II clinical trials against leukemia, lymphomas, and solid tumors are active. To date, there have been more than 50 clinical trials involving FVP in the United States. Unfortunately, almost half of patients on FVP clinical trials showed serious adverse effects, implicating appropriate dosages need to be found and an alternative way to circumvent the toxicity of FVP with synergistic agents.
Lower 24-Month Relative Survival among Black Patients with Non- Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: An Analysis of the SEER Data 1997-2015
Recent progress in the therapies used for patients with Non- Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) has improved survival. In 2020, 77,240 people were diagnosed with NHL. Although it accounts for 4% of all cancers, the incidence has been reported to be decreasing in the last few years. About 26% of people will expire from NHL (15% males and 11% females).Non-Hodgkin lymphoma arises from the clonal expansion of B, T, and natural killer (NK) cells. There is a significant degree of heterogeneity in NHL and this is likely related to different degrees of differentiation and maturation of these cells. These hematological malignancies exhibit different tumor behavior and are responsive to different chemotherapy agents which impacts clinical outcomes. There are patients who can be cured with current regimens; however, subtypes such as indolent and some aggressive lymphomas remain incurable necessitating treatment with new therapies including immunotherapy, targeted therapy, CAR T cells, and hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
Gemcitabine in the Era of Cancer Immunotherapy
Gemcitabine is a synthetic pyrimidine nucleoside analogue which is administered intravenously as a chemotherapeutic to treat numerous cancers. Gemcitabine requires transport into cells and activation by phosphorylation, the resulting gemcitabine triphosphate is incorporated into newly synthesized DNA during cell division, inhibiting further DNA synthesis and causing cell death. Gemcitabine is used to treat cancers including those of the pancreas, lung, breast, colon, and ovary either as first or second line treatments as a single agent or in combination.
Citius, Altius, Fortius: Performance in a Bottle for CAR T-Cells
The renewed interest in understanding how activated T cells alter their metabolism to support their growth and differentiation has led to several innovative advances in synthetic biology; culminating in a number of genetic and pharmacologic approaches aimed at improving the antitumor function of adoptively transferred T cells. Indeed, the growing field of immunometabolism has accelerated rapidly giving rise to exciting discoveries and exploratory studies revealing how T cells balance metabolic adaptations in response to intrinsic and extrinsic regulatory cues. Central to this body of work, we showed how chimeric antigen receptors (CAR)-induced metabolic reprogramming is an important determinant of efficacy and clinical outcome in blood-based malignancies.
Second Generation Platelet Concentrates - L-PRF (Fibrin Rich in Platelets and Leukocytes) and Its Derivatives (A-PRF, I-PRF)-: Morphological Characteristics to be Used in Modern Regenerative Surgery. Experimental Research
Platelet preparations (PDPs) have gained success, mainly due to their high concentrations of biologically active molecules, such as growth factors and cytokines, which play an important role in tissue repair and reconstruction. Recent knowledge shows that platelets can play a new role in tissue reproduction and vascular restoration, as well as being the protagonists of inflammatory processes and immune system responses. They release bio-active proteins and other active ingredients that can affect a number of phenomena that promote cell consumption, growth and transformation (growth factors).
Repurposing Nilotinib as a Selective P38β Inhibitor in Hematopoietic Malignancies: Clinical Evidence and Mechanistic Insights
Background: Cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) is an incurable cancer characterized by elevated p38β and p38γ and downregulated tumor-suppressive p38α. Objectives: We aimed to identify selective p38β inhibitors and investigate their mechanisms and therapeutic implications in hematologic malignancies. Methods: A high-throughput screen of Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved compounds was conducted to identify p38β inhibitors. In vitro kinase assays, Western blots, scRNA-seq, synergy tests, and mass spectrometry were used. Clinical trial and public datasets were analyzed.
Toward Precision Medicine for Patients with Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), the second most common hematologic malignancy, is a plasma cell neoplasm that arises from a precursor, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), which may or may not be previously diagnosed. Smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM), another precursor of MM, lacks myeloma-defining events and end-organ damage that are diagnostic of MM in the appropriate clinical settings. Newly diagnosed MM (NDMM) is highly heterogeneous genetically and clinically with very variable survival outcomes ranging from a few months to over a decade.
Concomitant Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis and Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukaemia Responding to 5-azacitidine
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is a rare, clonal, haematological disease of myeloid origin involving infiltration of neoplastic cells resembling Langerhans cells in various tissues. LCH cells express normal Langerhans cell markers such as CD1a, Langerin (CD207), and S100.
Multiple Myeloma with Neutrophilia: Two Etiologic Pathways for a Rare Presentation of a Common Diagnosis
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a common hematologic malignancy, with 32,110 new cases diagnosed in the United States in 2019, resulting in 12,960 deaths. While neutrophilia
is also a common entity, it most often arises secondary to other etiologies, such as infection or inflammatory processes.
Flavopiridol (Alvocidib), a Cyclin-dependent Kinases (CDKs) Inhibitor, Found Synergy Effects with Niclosamide in Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma
Flavopiridol (FVP; alvocidib), an FDA-approved orphan drug, has been studied in clinical trials under both single treatment and combination scenarios; several singleagent Phase I and Phase II clinical trials against leukemia, lymphomas, and solid tumors are active. To date, there have been more than 50 clinical trials involving FVP in the United States. Unfortunately, almost half of patients on FVP clinical trials showed serious adverse effects, implicating appropriate dosages need to be found and an alternative way to circumvent the toxicity of FVP with synergistic agents.
Lower 24-Month Relative Survival among Black Patients with Non- Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: An Analysis of the SEER Data 1997-2015
Recent progress in the therapies used for patients with Non- Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) has improved survival. In 2020, 77,240 people were diagnosed with NHL. Although it accounts for 4% of all cancers, the incidence has been reported to be decreasing in the last few years. About 26% of people will expire from NHL (15% males and 11% females).Non-Hodgkin lymphoma arises from the clonal expansion of B, T, and natural killer (NK) cells. There is a significant degree of heterogeneity in NHL and this is likely related to different degrees of differentiation and maturation of these cells. These hematological malignancies exhibit different tumor behavior and are responsive to different chemotherapy agents which impacts clinical outcomes. There are patients who can be cured with current regimens; however, subtypes such as indolent and some aggressive lymphomas remain incurable necessitating treatment with new therapies including immunotherapy, targeted therapy, CAR T cells, and hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
