Loading
Journal of Experimental Neurology
ISSN: 2692-2819


Hooshang Lahooti
University of Sydney, Australia
Featured Article
Protein Citrullination in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases

Featured Article
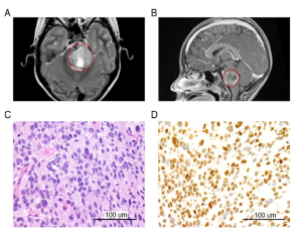
A Protocol for the Generation of Treatment-naïve Biopsy-derived Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma and Diffuse Midline Glioma Models
Featured Article
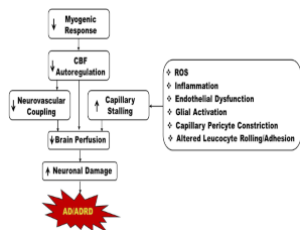
Capillary Stalling: A Mechanism of Decreased Cerebral Blood Flow in AD/ADRD
About this Journal
Journal of Experimental Neurology is an international publication primarily dedicated to publish original research and novel findings in the neuroscience field. This journal offers a great opportunity to the neuroscientists to discuss and exchange their ideas and major advances in clinical and experimental neurology. The journal publishes original articles, reviews, editorials, letters, and short communications in all major concepts of experimental neurology.
Articles
Integrating Psychotherapy into Clinical Care for Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease
Psychotherapy has historically played a limited role in Parkinson’s disease (PD) care, despite the high prevalence of neuropsychiatric and psychological conditions in this population. With sporadic evidence for the benefits of psychotherapy in PD, a clear pathway for psychotherapeutic intervention is still in development.
A Commentary on “Suppressive Effect of Topical Moxifloxacin on Imiquimod-Induced Model of Psoriasis in Mice”
The Journal of Experimental Neurology frequently highlights studies that bridge the gap between neurological disorders and systemic conditions, particularly those with an immunological component. The recent article, "Suppressive Effect of Topical Moxifloxacin on Imiquimod-Induced Model of Psoriasis in Mice," by Abbas et al., presents intriguing data suggesting a potential role for the fluoroquinolone antibiotic moxifloxacin in the treatment of psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory skin disorder.
From Atmospheric Forecasting to Neurological Inspiration: The Emerging Role of Brain Emotional Learning in Environmental Modeling
The intersection of computational neuroscience and environmental modeling has birthed novel algorithms that emulate brain-inspired emotional learning. One such contribution is the BELBFM (Brain Emotional Learning Based on Basic and Functional Memories) model, recently proposed for dual-height wind speed forecasting. While designed for meteorological applications, the structure and function of BELBFM echo principles long studied in neurobiology.
Extraforaminal Spinal Nerve Stimulation: A Practical Surgical Guide Based on Clinical Experience
Extraforaminal spinal nerve stimulation (SNS) is an emerging neuromodulation technique for treating neuropathic pain. Targeting the spinal nerve distal to the intervertebral foramen enables anatomically precise stimulation, distinguishing it from conventional spinal cord or dorsal root ganglion stimulation. This article provides the first comprehensive description of the extraforaminal SNS approach, including technical refinements, anatomical insights, and clinical experience.
Hypoplastic Internal Carotid Artery in a Young Stroke Patient
Hypoplastic internal carotid artery (HICA) is a rare congenital vascular anomaly, typically asymptomatic due to collateral circulation. However, in certain cases, it may present with ischemic stroke. We report a 17-year-old male with a history of smoking and illicit drug use who presented with acute left-sided weakness. Imaging revealed an infarct in the right middle cerebral artery territory and a hypoplastic right internal carotid artery.
Capillary Stalling: A Mechanism of Decreased Cerebral Blood Flow in AD/ADRD
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) and Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Dementias (ADRD) are debilitating conditions that are highly associated with aging populations, especially those with comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertension.
Impact of Cellular Senescence on Neurodegenerative Diseases during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Suitable Targets Required to Eliminate Cellular Senescence
We recently reviewed the scientific literature that elucidates the impact of cellular senescence on COVID-19 complications.
Differential Fecal Microbiome Dysbiosis after Equivalent Traumatic Brain Injury in Aged Versus Young Adult Mice
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) has a bimodal age distribution with peak incidence at age 24 and age 65 with worse outcomes developing in aged populations
Combined Antiseizure Efficacy of Cannabidiol and Clonazepam in a Conditional Mouse Model of Dravet Syndrome
Dravet syndrome (DS) is an intractable childhood epilepsy disorder affecting one in 15,000 to 20,000 births [1]. It is caused by de novo heterozygous lossof- function mutations in the SCN1A gene encoding the brain type-I voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.1
Comparing Contrast Agent Enhancement: The Value of Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) work by shortening the T1, T2, and T2* relaxation time constants of adjacent water protons in tissues.
Inhalational Anaesthetics: An Update on Mechanisms of Action and Toxicity
Inhalational anaesthetics have been used for induction and maintenance of general anaesthesia for more than 150 years. In human medicine desflurane, sevoflurane, and isoflurane are commonly used.
Capillary Stalling: A Mechanism of Decreased Cerebral Blood Flow in AD/ADRD
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) and Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Dementias (ADRD) are debilitating conditions that are highly associated with aging populations, especially those with comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertension.
The Spread of Spectrin in Ataxia and Neurodegenerative Disease
Experimental and hereditary defects in the ubiquitous scaffolding proteins of the spectrin gene family cause an array of neuropathologies
Differential Fecal Microbiome Dysbiosis after Equivalent Traumatic Brain Injury in Aged Versus Young Adult Mice
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) has a bimodal age distribution with peak incidence at age 24 and age 65 with worse outcomes developing in aged populations
Combined Antiseizure Efficacy of Cannabidiol and Clonazepam in a Conditional Mouse Model of Dravet Syndrome
Dravet syndrome (DS) is an intractable childhood epilepsy disorder affecting one in 15,000 to 20,000 births [1]. It is caused by de novo heterozygous lossof- function mutations in the SCN1A gene encoding the brain type-I voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.1
Inhalational Anaesthetics: An Update on Mechanisms of Action and Toxicity
Inhalational anaesthetics have been used for induction and maintenance of general anaesthesia for more than 150 years. In human medicine desflurane, sevoflurane, and isoflurane are commonly used.
Glutaminergic Signaling in the Nucleus Accumbens Modulates the Behavioral Response to Acute and Chronic Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate (MPD) is a psychostimulant that is widely used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and is being increasingly misused as a recreational drug and cognitive enhancer
Testing the Efficacy of Minocycline Treatment in an Awake, Female Rat Model of Repetitive Mild Head Injury
Minocycline is being tested in clinical trials for the treatment of stroke and traumatic brain injury. As an antibiotic it reduces microglia activation. Can minocycline be used to treat mild repetitive head injury? To that end, minocycline was tested in a novel, closed-head, momentum exchange model of repetitive mild head injury in female rats impacted while fully awake. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed there was no brain damage or contusion attesting to the mild nature of the head impacts in this model.
Capillary Stalling: A Mechanism of Decreased Cerebral Blood Flow in AD/ADRD
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) and Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Dementias (ADRD) are debilitating conditions that are highly associated with aging populations, especially those with comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertension.
Body Iron Overload is a Determining Factor in Brain Damage in Acute Ischemic Stroke
Stroke is the second largest cause of death worldwide, with a world annual mortality incidence of about 5.5 million people, and it is also the leading cause of disability worldwide with 50% of survivors being chronically disabled.
Discovery of New Candidate Genes for Anorexia Nervosa through Integration of eQTLs with Summary Statistics
Anorexia nervosa (AN) is a neuropsychic syndrome characterized by restriction of energy intake relative to requirements, abnormally low body weight and fear of weight gain, resulting in extreme emaciation and even death [1].
A Rodent Lumbosacral Spinal Cord Injury Model Reflecting Neurological and Urological Deficits of Humans
Spinal cord injury (SCI) to the terminal segments of the spinal cord causes severe disruption of the neural circuitry of the bladder, resulting in neurogenic underactive bladder (nUAB). We developed a rodent lumbosacral injury model to investigate the effects of bladder function and structure.
In the Mind of the US Olympic Athletes; Longevity Advantage and Its Relation to Nervous System Disorders and Mental Illness
In a recent study of 8124 US Olympic athletes, Antero et al. [1] found that the US Olympic athletes live 5 years longer than their general counterparts.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
