Loading
Journal of Cellular Signaling
ISSN: 2692-0638
All Articles
Flow Cytometric Characterization of Accidental Cell Death Highlights Connections to Regulated Cell Death
Gary Warnes
Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs) are known by their nature to cause inflammatory responses in numerous disease states from cancer, trauma to age related diseases (e.g. atherosclerosis, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases), these molecules are released by cells undergoing cell death.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.001
The Outcome of Tumor Ablation Therapies is Determined by Stress Signaling Networks
Mladen Korbelik
Increasingly prominent roles in interventional oncology are held by various tumor ablation therapies performed by direct applications of local acute trauma-inducing insult to the targeted lesion aiming for its rapid in situ destruction. These therapies include treatments based on various forms of thermal energy delivery (photothermal, cryoablation, microwave ablation, radiofrequency ablation), non-thermal illumination (photodynamic therapy), electric field exposure, or high hydrostatic pressure
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p1-4 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.062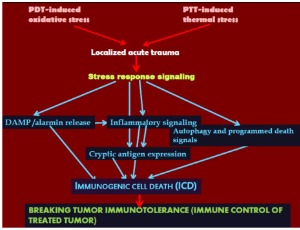
Interrelation among TLR4, EGFR and Rab Proteins Induced by LPS
Jinling Zhuang, Xiaolei Liu, Guixi Mo, Jie Fan, Jing Tang
TLR4, as an on-membrane receptor of LPS, plays a crucial part in the process of sepsis, and EGFR phosphorylation promotes cell inflammation in response to LPS, which plays an indispensable role in modulating LPS/TLR4 signaling pathway. However, the mechanism of interaction between TLR4 and EGFR signaling is still unclear.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p1-8 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.031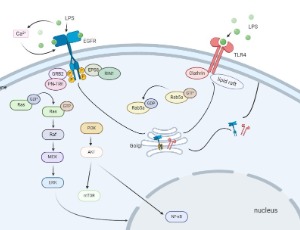
Signaling of Mitogenic and Metabolic Activities by Fibroblast Growth Factors
Patience Salvalina Okoto, Zeina Alraawi, Thallapuranam Krishnaswamy Suresh Kumar
Fibroblast growth factors are signaling molecules that play crucial roles in fundamental processes such as cell migration, proliferation, differentiation, angiogenesis, and cell survival. FGFs signal by forming a complex with tyrosine kinase FGF receptors and cofactors. It is well known that FGFs play diverse roles in different tissues and at different developmental stages due to factors such as receptors, specific FGFs, and environmental conditions such as temperature and pH.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p1-8 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.127
Specific Subcellular Localization of Phosphoinositide-Specific Phospholipase C enzymes in Different Human Osteosarcoma Cell Lines
Matteo Corradini, Marta Checchi, Marta Benincasa, Marzia Ferretti, Francesco Cavani, Carla Palumbo, Vincenza Rita Lo Vasco
The role of signal transduction in cancer progression is well established and actively studied, including in osteosarcoma. The signal transduction pathways involved in the regulation of calcium metabolism are being intensively studied, with particular regard to phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PLC) signaling. This family of enzymes helps to modulate calcium metabolism and is interconnected with additional signaling molecules belonging to different pathways.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p1-9 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.107
Augmenting Venetoclax Activity Through Signal Transduction in AML
Ian Michael Bouligny, Keri Renee Maher, Steven Grant
Venetoclax, a small-molecule B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) inhibitor, selectively eradicates leukemic stem cells (LSCs). While venetoclax has revolutionized the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), treatment failure and disease relapse are common. Mechanisms underlying venetoclax resistance are surprisingly heterogeneous.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p1-12 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.085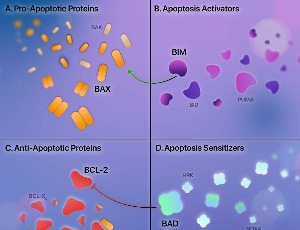
Emerging Role of TRPML1 Mucolipin Endolysosomal Channel in Cancer
Giorgio Santoni, Matteo Santoni, Massimo Nabissi, Oliviero Marinelli, Consuelo Amantini, Maria Beatrice Morelli
The transient receptor potential mucolipin 1 (TRPML1) is an endolysosomal channel belonging to the TRP family. Clinically, mutations of TRPML1 have been responsible for a severe lysosomal storage disorder called mucolipidosis type IV.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p4-7 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.002
TRPM8 Channels and SOCE: Modulatory Crosstalk between Na+ and Ca2+ Signaling
Guilherme Henrique Souza Bomfim
The electrochemical driving forces across the plasma membrane both in excitable and non-excitable mammalian cells are finely regulated by different ion channels, pumps, and exchangers that are essential for a wide range of biological processes. The modulation between sodium (Na+), calcium (Ca2+), and intracellular downstream pathways is tightly linked through several mechanisms that generate spatiotemporal ion waves.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p5-13 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.063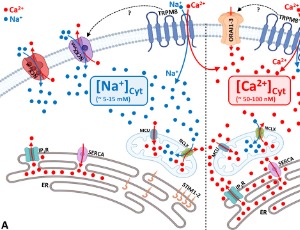
Manipulating Oxidative Stress Following Ionizing Radiation
Adriana Haimovitz-Friedman, Aviram Mizrachi, Edgar A. Jaimes
It is now well accepted that the ionizing radiation-generated reactive oxygen species (ROS), that constitute ~2/3 of the effects of external beam radiation, do not only produce direct tumor cell death, but also affect the surrounding microenvironment. Moreover, this indirect effect of radiation may result in systemic effects, specifically the initiation of an inflammatory response.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p8-13 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.003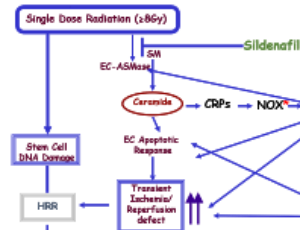
Calcitriol Implications on Human Rhabdomyosarcoma: An Unexplored Field
Claudia Buitrago, Ana P. Irazoqui
Calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D3, is also acknowledged as 1α, 25-dihydroxy vitamin D3. This steroid hormone is known for its role in calcium homeostasis and bone metabolism. Recent studies suggest that calcitriol also exerts anti-cancer effects in various malignancies. We previously reported (in 2022) that treatment with this steroid hormone triggers apoptosis in RD cells, a known rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) cell line.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p9-12 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.128
FOXP1 Interacts with MyoD to Repress its Transcription and Myoblast Conversion
Woodring E. Wright, Chuan Li, Chang-xue Zheng, Haley O. Tucker
Forkhead transcription factors (TFs) often dimerize outside their extensive family, whereas bHLH transcription factors typically dimerize with E12/E47. Based on structural similarities, we predicted that a member of the former, Forkhead Box P1 (FOXP1), might heterodimerize with a member of the latter, MYOD1 (MyoD).
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p9-26 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.032
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
MKP-2 Deficiency Leads to Lipolytic and Inflammatory Response to Fasting in Mice
Sadie Junkins, Gabrielle Westenberger, Jacob Sellers, Isabel Martinez, Nabin Ghimire, Cassandra Secunda, Morgan Welch, Urja Patel, Kisuk Min, Ahmed Lawan
The liver plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis for lipid and glucose. Hepatic lipid synthesis is regulated by nutritional signals in response to fasting and refeeding. It is known that overnutrition regulates MAPK-dependent pathways that control lipid metabolism in the liver by activating MAPK phosphatase-2 (MKP-2). Uncertainty still exists regarding the regulatory mechanisms and effects of MKP-2 on hepatic response to fasting.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p10-23 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.108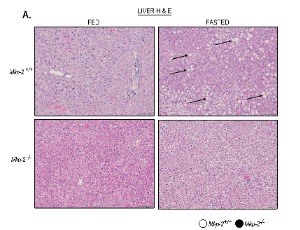
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Extracellular Long Non-coding Punisher as Biomarker and Effector In-patient with Coronary Artery Disease via Regulating Endothelial Cell Function
Zhexi Li, Yunjing Sheng, Annisa Mardianing Utami, Mohammed Rabiul Hosen
Coronary artery disease (CAD) stands as one of the foremost contributors to cardiovascular events and death on a global scale. The primary underlying mechanism for CAD is atherosclerosis, which can precipitate severe cardiovascular events, including myocardial infarction and stroke. Despite significant advancements in clinical diagnosis and treatment modalities, the incidence and mortality rates associated with CAD remain alarmingly high, necessitating continuous research into novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p13-17 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.129
Radiation-induced Bystander Effect and Its Possible Countermeasures
Goutam Ghosh
Ionizing radiation has been indispensable to medical diagnosis. In cancer, radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT) offers patients a better chance of survival. It destroys cancer by depositing high-energy radiation on the cancer tissues, though it may directly damage a few normal cells.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p13-20 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.086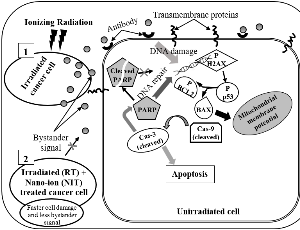
Activation of NLRP3 Inflammosome by N4-Acetyl Cytidine and Its Consequences
Hua Bai
N4-acetylcytidine (N4A) is an organic compound and a metabolite of transferrable ribonucleic acid. Its molecular formula is C11H15N3O6. Earlier studies suggest that N4A was mainly found on tRNA and 18S rRNA, while recent studies have shown that there is also a large amount of N4A on mRNA, whose abundance is not even lower than the m7G cap modification carried by mRNA.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p14-17 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.004
Differentiation and Subtype Specification of Enteric Neurons: Current Knowledge of Transcription Factors, Signaling Molecules and Signaling Pathways Involved
Nastasia Popowycz, Leen Uyttebroek, Guy Hubens, Luc van Nassauw
The enteric nervous system is the largest component of the autonomic nervous system. It contains a broad network of interconnected plexuses and enteric neuronal subtypes which are in charge of the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Vagal and sacral neural crest cells are at the basis of the enteric nervous system development. These cells undergo multiple processes such as migration, proliferation and differentiation to finally form a functional enteric nervous system.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p14-27 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.064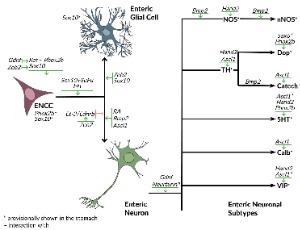
Cyclic Nucleotide Signaling Pathways in Apicomplexan Parasites Provide a Valuable Source for Novel Drug Targets
Annette Kaiser
Malaria is one of the most important disabling human, tropical disease caused by different Plasmodium species, which are protozoan parasites belonging to the Apicomplexa. The Apicomplexan parasites have a plastid like structure the “apicoplast” and comprise the genera Plasmodium, Toxoplasma and Cryptosporidium causing malaria, toxoplasmosis, and cryptosporidiosis.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p18-22 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.005
Nicotiana glauca Induces Apoptosis in Human Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells: Molecular Targets
Natalia Frattini, Nicolás Blanco, Lucía Pronsato, Lorena Milanesi, Andrea Vasconsuelo
Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma is a soft tissue sarcoma whose resistance to chemotherapies is associated with defective apoptosis or/and cell cycle. Given that we have reported that the liposoluble extract from the leaves of Nicotiana glauca induces apoptosis in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma cells, this research aims to know the molecular mechanism involved, to elucidate the pharmacological potential of the Nicotiana glauca.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p18-28 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.130
Purinergic P2X7 Receptor as a Potential Targeted Therapy for COVID-19-associated Lung Cancer Progression
Hamidreza Zalpoor, Abdullatif Akbari, Mohsen Nabi-Afjadi, Ali Norouzi, Farhad Seif, Majid Pornour
Severe acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection is a serious threat to lung cancer patients. Hereby, we hypothesize that Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) may contribute to lung cancer progression by increasing extracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels and hyperactivating the purinergic P2X purinoceptor 7 receptor (P2X7R).
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p21-25 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.087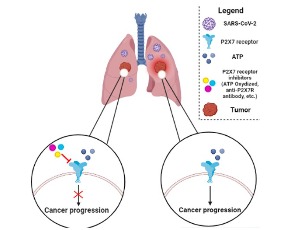
COVID-19 Clinical Research
Jeffrey Chi, David Chitty, Meeyoung Lee, Nausheen Hakim, Shamsah Lakhani, Lakshmi Rajdev, Xinhua Zhu, Muhammad Wasif Saif
While the global COVID-19 pandemic has challenged the entire humanity and health systems, it also triggered researchers to urgently perform clinical trials to assess the safety and efficacy of many agents and modalities to combat COVID-19. As of April 22, over 650 clinical studies have been registered both in USA and internationally. Results from these studies are also coming at a brisk pace in this unprecedented emergency.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p23-30 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.006
Monitoring Transcription of miR-15a and miR-124 in Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Adipose Tissue Origin Differentiated into Pancreatic Beta-cells
Hadi Rajabi
MicroRNAs are small, noncoding pieces of nucleic acid with the potential to control mRNA translation. These sequences participate in the regulation of cell dynamic growth and differentiation. In this study, the expression of miR-15a and miR-124 was monitored in adipose-derived tissue stem cells committed to pancreatic β cells in vitro over 28 days. In the current experiment, adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells were incubated in an induction medium to accelerate differentiation toward the endocrine pancreatic lineage for 28 days with a three-stage protocol.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p24-29 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.109
Targeting SCUBE3 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Teng Liu, Xia Yang, Ke Wang, Qiang Luo
HCC is one of the most common malignant tumors. The life and health of humans are gravely threatened by HCC because of its hidden onset, high recurrence rate, poor therapeutic effect, and high mortality. It is essential to explore the particular pathological mechanisms of HCC in order to increase the rate of early diagnosis and enhance patient therapy outcomes.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p26-29 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.088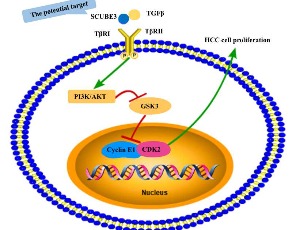
The Role of Membrane-embedded DUOX2 on Ectodomain Shedding via G protein-coupled Receptor Signaling
Rui Yamaguchi, Reona Yamaguchi, Arisa Sakamoto, Shinji Narahara, Hiroyuki Sugiuchi, Yasuo Yamaguchi
Protease-activated receptors (PARs) and the neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R) belong to the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family. In this review, we focus on the regulatory mechanism of ectodomain shedding by ADAM10/17 metalloprotease via GPCR signaling. PAR2 and NK1R induce membrane blebbing, resulting in phosphatidylserine externalization in the cellular membrane, which is required for ADAM10/17 metalloprotease activation. Membrane-embedded dual oxidase 2 (DUOX2) has NADPH oxidase and peroxidas
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p27-46 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.033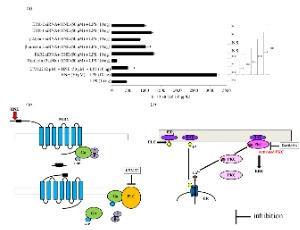
Interferon Gamma, MHC Class I Regulation and Immunotherapy
Maria Gómez-Herranz, Magdalena Pilch, Ted Hupp, Sachin Kote
The activation of endogenous IFNγ signaling pathway or the administration of recombinant IFNγ increases the expression of MHC-I. MHC-I molecules are core elements for antigen recognition in tumor cells. A better understanding of the regulation of their expression would contribute to counteracting tumor immune escape and enduring permanent tumor rejection. Efficient and functional expression of HLAs dramatically impacts the number of tumor-associated antigens presented to CTL for cell recognition.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p28-39 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.065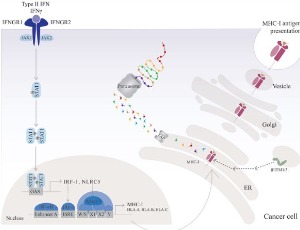
Microcystin: From Blooms to Brain Toxicity
Ethan Hedrick, Aryaman Tiwari, Suryakant Niture, Qing Cheng, Deepak Kumar, Somnath Mukhopadhyay
An increase in the temperature of lakes and ponds facilitates the over-growth of photosynthetic cyanobacteria that produce a class of toxins called cyanotoxins. The abundance of cyanobacteria poses a significant threat to drinking and irrigation water supplies, and therefore, cyanotoxins have become a major class of environmental pollutants. Microcystins, the most common cyanotoxins, are cyclic peptides produced by cyanobacteria through non-ribosomal peptide synthases, and currently, approximately 279 microcystins have been identified to date.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p29-38 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.131
Phorbol-12-Myristate-13-Acetate (PMA) Reactivates Replication from HIV-1 Latency and Induces Jurkat Cell Death
Xue Wang, Jiangqin Zhao, Indira Hewlett
HIV-1 has the capability to establish latency during early infection in CD4+ cells, posing a significant challenge to the efforts aimed at curing HIV-1/AIDS. One extensively explored strategy to address this viral latency is the "shock-and-kill" approach. This involves reactivating viral replication using latency reversal agents (LRAs) to induce the death of infected cells. Regrettably, no LRAs with proven effectiveness have been identified thus far.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p30-40 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.110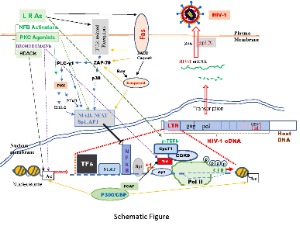
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
A Computational Investigation on Rho-related GTP-binding Protein RhoB through Molecular Modeling and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study
Shamrat Kumar Paul, Chowdhury Lutfun Nahar Metu, Sunita Kumari Sutihar, Md. Saddam, Bristi Paul, Md. Lutful Kabir, Md. Mostofa Uddin Helal
An indispensable member of the Rho family, RhoB is an isoprenylated small GTPases that modulate the cellular cytoskeletal organization. While DNA gets damaged, it takes part in the neoplastic apoptotic mechanism. In this study, we evaluated the structure of Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoB due to the unavailability of 3D structure in the protein data bank database.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p30-48 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.089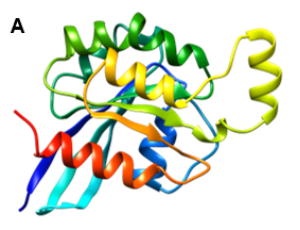
Ubiquitin Proteasome System Regulates Biological Particles Interaction in Particle Disease (PD) via NF-κB Signaling
Xiaolei Hu, Xiaomian Wu
Considering their outstanding mechanical character, it is inevitable to utilize titanium and titanium composite for biomedical engineering application [1-6]. However, the particles releasing from these bulks or composites of biomaterials after long term implanting in human body will cause cell apoptosis or cell death, inflammation, bone
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p31-34 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.007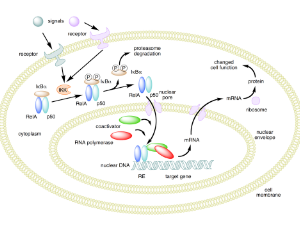
DNA Nanotechnology Engineered Vesicle for Mimicking Biomolecular Signaling
Ruizi Peng, Yingzi Ma, Yan Zhou, Yongbo Peng, Xiaofang Zheng, Qiang Zhang
Bio-inspired strategy is kind of interesting to fabricate devices and perform dynamic operations [1]. Various devices have been made, such as airplane, radar and submarine. In life science, as the fundamental entity, million years’ evolution enables cell becomes the most successful functionality.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p35-37 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.009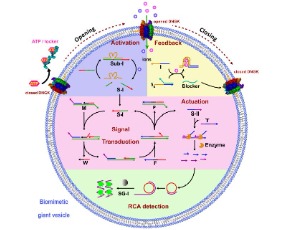
Prospective Evaluation of Effect of Metformin on Activation of AMP-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) and Disease Control in a Sub-group Analysis of Patients with GI Malignancies
Amandeep Godara, Nauman S. Siddiqui, Hilal Hachem, Philip N. Tsichlis, Robert E. Martell, Muhammad Wasif Saif
Observational studies have demonstrated association of metformin with reduced cancer incidence and mortality in multiple cancer types, including gastrointestinal (GI) malignancies. Anti-neoplastic effects of metformin are believed through many mechanisms including activation of AMP-activated protein kinase, which controls mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) growth regulatory pathway.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p35-41 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.008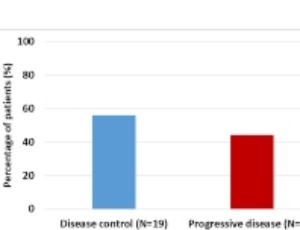
Novel Hippocampal Interaction between Spexin and Corticotropin Releasing Factor
Jin Bai, Chengyuan Lin
Nowadays, people pay more and more attention to homeostatic regulation, which is the detrimental effect of stress on physiological and psychological well-being and cannot be ignored. The public perception of anxiety has been associated with the hypothalamic hormones, because of the pivotal role of the hypothalamic-pituitaryadrenal axis to promote the pituitary-adrenal functions and endocrine responses.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p38-41 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.010
Tumor Lipid Signaling Involved in Hyperoxidative Stress Response: Insights for Therapeutic Advances
Mladen Korbelik, Albert W. Girotti
Most malignantly transformed cells are metabolically rewired to promote their survival and progression, even under conditions that would be unfavorable for normal counterparts. Arguably the most impactful metabolic transformation and recognized cancer hallmark is the reprogrammed lipid metabolism. Lipids are not only primary constituents of cell membranes but essential participants in fundamental cellular functions including cell signaling, protein regulation, energy provision, inflammation, and cell-cell interaction. Engagement of lipids in critical physiological functions in cells is additionally accentuated upon malignant transformation. Pivotal roles of lipids as influential inter- and intracellular signaling molecules, particularly under conditions of hyper oxidative stress, are delineated.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 2, p39-47 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.132
AID and APOBEC3 Involvements in Non-Conventional IgD Class Switch Recombination in Mice
Melissa Ferrad, Nour Ghazzaui, Hussein Issaoui, Jeanne Cook-Moreau, Yves Denizot
In mature B-cells, class switch recombination (CSR) substitutes the constant (C) μ gene with other C genes (such as γ, ε and α) thereby generating IgG, IgE and IgA antibodies with new effector functions but same the antigenic specificity compared to IgM. CSR is a complex process with I-promoter transcription, targeting of the DNA-editing enzyme activation-induced deaminase (AID) to specific DNA switch (S) regions preceding C regions (except Cδ), generation of double strand breaks and recruitment of DNA repair factors for the end-joining process.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p40-43 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.066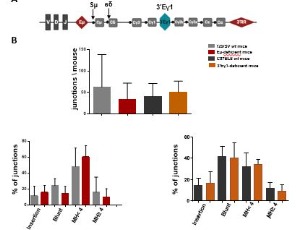
Role of Exosomal MicroRNAs in Modulating the Response of Cancer Cells to Paclitaxel Treatment
Lanqing Zhao, Cheng Lv, Hui Xie, Xiaoxu Ding
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles in gene regulation and have been implicated in various human diseases, including cancer. MiRNAs can be packaged in exosomes and transferred between cells. These exosomal miRNAs regulate intercellular communication and influence almost all aspects of cancer biology, including proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p41-50 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.111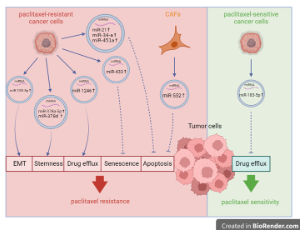
The Effect of Glucocorticoids on Angiogenesis in the Treatment of Solid Tumors
Bing Liu, Julie E. Goodwin
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are defined by their role in maintaining glucose homeostasis and natural GCs are a class of corticosteroids secreted by the adrenal cortex. Cortisol is the most important natural GC in humans. Cellular cortisol levels are regulated by the tissue-specific metabolic enzymes 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 and 2 (11β-HSD 1 and 2); 11β-HSD 1 converts inactive cortisone to active cortisol, while 11β-HSD 2 has the opposite function.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p42-49 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.011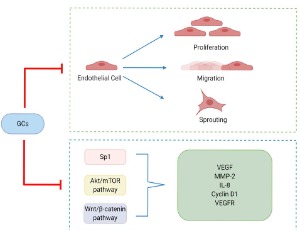
Expression and Localization of Phosphoinositide-Specific Phospholipases C in Cultured, Differentiating and Stimulated Human Osteoblasts
Sara Daisy Casoni, Alessia Romanelli, Marta Checchi, Serena Truocchio, Marzia Ferretti, Carla Palumbo, Vincenza Rita Lo Vasco
The osteoblasts contribute to bone homeostasis maintaining the bone mass, and intervene in bone injuries repair. Insights in the events leading to the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts might allow uncover potential molecular targets to control the complex mechanisms underlying bone remodeling. Signal transduction pathways contribute to the differentiation and metabolic activities of osteoblasts, with special regard to calcium-related signaling, including the Phosphoinositide (PI) pathway.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p44-61 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.067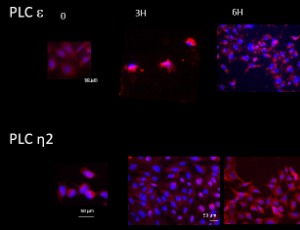
S1P Generation by Sphingosine Kinase-2 in Recruited Macrophages Resolves Lung Inflammation by Blocking STING Signaling in Alveolar Macrophages
Jagdish C Joshi, Bhagwati Joshi, Ian Rochford, Dolly Mehta
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is the major cause of mortality among hospitalized acute lung injury (ALI) patients. Lung macrophages play an important role in maintaining the tissue-fluid homeostasis following injury. We recently showed that circulating monocytes recruited into the alveolar space suppressed the stimulator of type 1 interferon genes (STING) signaling in alveolar macrophages through sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P).
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p47-51 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.034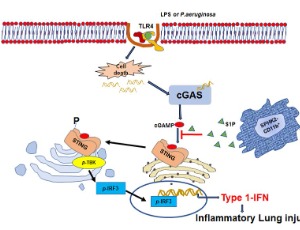
Toward a Deeper Understanding of Clonal Evolution in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Translational and Clinical Impacts
Keri Renee Maher, Graeme F. Murray, Thuy Ho, Steven Grant
To understand disease biology of Acute Myeloid Leukemia requires an appreciation of initial clonal heterogeneity of the disease, as well as the selective pressures on these clones and the resulting change in cytomolecular profiles over time. Elucidating these underpinnings of leukemogenesis is critical for attempts to enhance therapeutic efficacy. Here, we review key findings derived from a retrospective analysis of a diverse acute myeloid leukemia cohort of 207 patients and discuss biological mechanisms underlying these trends.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 2, p48-52 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.133
Potential Mechanism of CDC42 Promoting HCC Metastasis
Miaoling Tang, Rongni Feng, Jun Li
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an aggressive malignancy with increasing morbidity and mortality worldwide. The migration and motility of HCC tumor cells are enhanced by the formation of invadopodia, which comprise membrane protrusions at the leading edge. Previous studies have showed that cell division cycle 42 (CDC42) plays an essential role in remodeling the cytoskeleton, which is associated with invadopodia formation and thus mediates cellular movement.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 2, p49-55 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.091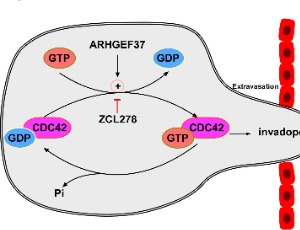
Distinct Phosphorylation of STAT1 Confers Distinct DNA Binding and Gene-regulatory Properties
Hozaifa Metwally, Tadamitsu Kishimoto
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) protein plays a pivotal role in various biological processes especially the regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses. Phosphorylation represents a key step in the activation of STAT1 and its transcriptional outcome. Binding of various extracellular ligands to their specific cell-surface receptors activates different phosphorylation of STAT1 followed by a distinct change of gene expression patterns.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p50-55 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.012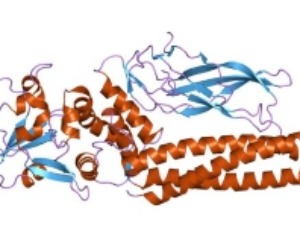
Teaching an Old Drug a New Trick: Targeting Treatment Resistance in Genitourinary Cancers
Karina Aguilar, Anuj K. Sharma, Tianyu Yang, Dipen Mehta, Chandramukhi S. Panda, Vinata B. Lokeshwar
In the quest for improving the clinical outcome of patients with metastatic genitourinary cancers, including metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC), the emphasis often is on finding new targeted therapies. However, two studies by Jordan et al. (Oncogenesis 2020) and Wang et al. (Cancer Cell Int 2022) demonstrate the feasibility of improving the efficacy of a modestly effective drug Sorafenib against mRCC by attacking a mechanism hijacked by RCC cells for inactivating Sorafenib.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 2, p51-56 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.112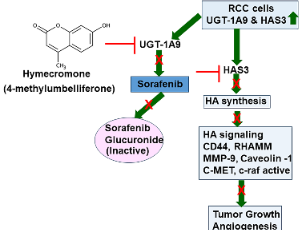
Wnt Signaling Cascades and Their Role in Coronary Artery Health and Disease
Nadisha Weerackoon, Kushan L. Gunawardhana, Arya Mani
The Wnt signaling is classified as two distinct pathways of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling, and the non-canonical pathways of planar cell polarity and Wnt/Ca2+ pathways. However, the scientific discoveries in recent years have shown that canonical and noncanonical Wnts pathways are intertwined and have complex interaction with other major signaling pathways such as hedgehog, Hippo and TOR signaling.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p52-62 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.035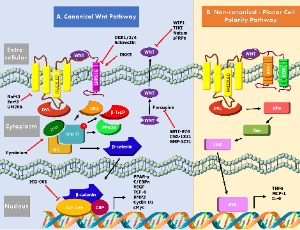
Monoamine Oxidase B in Astrocytic GABA Synthesis: A Central Mechanism in Neurodegeneration and Neuroinflammation
Moawiah M Naffaa
Monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) is a mitochondrial enzyme predominantly expressed in astrocytes, where it plays a crucial role in neurotransmitter metabolism, oxidative stress regulation, and neuroinflammation. In addition to its well-characterized function in the oxidative deamination of monoamines such as dopamine, noradrenaline, and serotonin, MAO-B is increasingly recognized for its involvement in astrocytic GABA synthesis.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 2, p53-70 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.134
Role of Sphingolipid Signaling in Glomerular Diseases: Focus on DKD and FSGS
Alla Mitrofanova, Yelena Drexler, Sandra Merscher, Alessia Fornoni
Being a sophisticated and highly organized living system, mammals harbor a large number of biomolecular machineries which represent a dynamic and complex network of interconnections responsible for the effective operation, development and survivability of their body cells. Sphingolipids are a special class of lipids in eukaryotic cells, which have recently gained the attention of researchers because of their involvement in several fundamental processes of living cells, including proliferation
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p56-69 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.013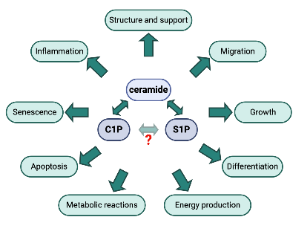
Novel Drug Development for Treatment of COVID-19 by In Silico Analysis: Identification of SARS-Cov-2 Inhibiting Streptomyces Compounds
Jayant Kumar, Prachiti Gholap, Thulasi G Pillai
In accordance with the present epidemiological paradigm, viral mutations of the virus are on the rise, and their natural effects are being selected for at a higher rate than normal. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the global COVID-19 pandemic induced by the Delta and Omicron strain of the SARS-CoV-2 virus could propagate and disseminate more rapidly than other viruses thanks to its many mutations, and these also caused some very significant health problems.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 2, p56-72 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.092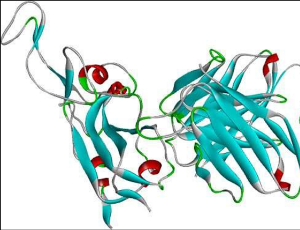
Signaling Modifications Associated with Obesity and Dysbiosis and Their Impact on Metabolic Disorders
Ferah Armutcu, Eugene McCloskey
The gut microbiota plays a crucial role in various physiological functions such as the production of essential compounds like short-chain fatty acids and vitamins, as well as in controlling inflammation, immune response, and maintaining intestinal barrier integrity. The imbalance in microbial composition, termed dysbiosis, is closely associated with both the pathogenesis of obesity and the development of obesity-related metabolic disorders such as metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes (T2D).
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 2, p57-64 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.113
c-JUN n-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Signaling in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
Abigail O. Smith, Julie A. Jonassen, Kenley M. Preval, Roger J. Davis, Gregory J. Pazour
Polycystic kidney disease is an inherited degenerative disease in which the uriniferous tubules are replaced by expanding fluid-filled cysts that ultimately destroy organ function. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is the most common form, afflicting approximately 1 in 1,000 people and is caused by mutations in the transmembrane proteins polycystin-1 (Pkd1) and polycystin-2 (Pkd2).
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p62-78 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.068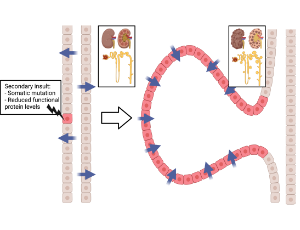
Possible Therapeutic Use of Natural Compounds Against COVID-19
Nabab Khan, Xuesong Chen, Jonathan D. Geiger
The outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) has led to coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19); a pandemic disease that has resulted in devastating social, economic, morbidity and mortality burdens. SARS-CoV-2 infects cells following receptor-mediated endocytosis and priming by cellular proteases.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p63-79 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.036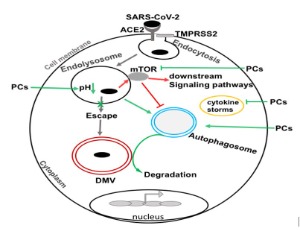
Navigating the Adipocyte Precursor Niche: Cell-Cell Interactions, Regulatory Mechanisms and Implications for Adipose Tissue Homeostasis
Devesh Kesharwani, Aaron Clifford Brown
Support for stem cell self-renewal and differentiation hinges upon the intricate microenvironment termed the stem cell 'niche'. Within the adipose tissue stem cell niche, diverse cell types, such as endothelial cells, immune cells, mural cells, and adipocytes, intricately regulate the function of adipocyte precursors. These interactions, whether direct or indirect, play a pivotal role in governing the balance between self-renewal and differentiation of adipocyte precursors into adipocytes.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 2, p65-86 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.114
Metabolic Syndrome is an Important Cornerstone in the Health-disease Line and Pathological Organ Interaction
Ferah Armutcu, Suheyla Akyol, Huseyin Vural
Today, metabolic syndrome (MS) has been regarded as a very important disease due to its complex multifactorial etiology and damage to different organs. In general, obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, hyperglycemia, and insulin resistance are the main metabolic abnormalities of the MS. Compared with the others; in particular, insulin resistance and central obesity are considered the main causes in the pathogenesis
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p70-75 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.014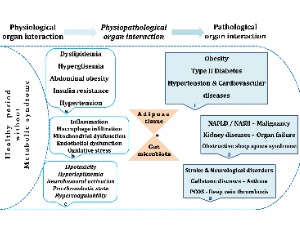
The Intersection of Lipid Signaling and Metabolism in Cancer and Tuberculosis
Vikash Kumar, Sidra Khan
Lipids are an essential class of complex biomolecules involved in maintaining cellular energy homeostasis, structural organization and signal transduction. Dysregulated lipid signaling and metabolism have increasingly been reported in various pathological settings like diabetes, cardiomyopathy, neurological pathologies, malignancies and infectious diseases. Recent technological advances in metabolomics and lipidomics have shown enormous complexities and functionalities of lipids.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 2, p71-82 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.135
A Study on the Usage of Probiotics as a Safer Antipyretic
Shantanu Shrivastava, Nimisha Bhatu
Most medicines and supplements which include probiotics have both expected clinical outcomes and unwanted side effects, which plays a major role when considering them as a mode of treatment. This review is an update about the advantages and disadvantages associated with the use of probiotics as part of a safe therapeutic armamentarium in health and other diseases. The advantages of probiotics run across multiple tissue systems in the body and a has a wide age spectrum.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 2, p73-77 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.093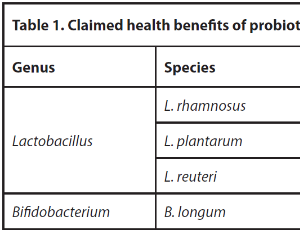
Machine Learning for Healthcare: Emerging Challenges and Opportunities in Disease Diagnosis
Sachin Kumar Deshmukh
Diagnosis is a process that identifies, explains, or establishes the individual’s disease from its symptoms and signs. Early and precise diagnosis is crucial since it influences the efficacy of treatment and avoids longterm complications for the infected person. Further, in the case of infectious diseases, undiagnosed patients can transmit the disease to a healthy population unknowingly. Besides, most of the diseases evolve with the time that significantly affects the clinical outcomes.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p76-78 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.015
Understanding Chromosome Replication and Segregation Unit of Mycobacterium and Its Comparative Analysis with Model Organisms: From Drug Targets to Drug Identification
Preeti Jain
Bacterium maintains its pathogenicity in the host by continuing replication and adopting temporal and spatial coordination of cell division steps such as cell wall synthesis, DNA replication, chromosome segregation, Z ring assembly, septum formation and finally cytokinesis. This multistep process requires spatiotemporal assembly of macromolecular complexes and is probably regulated by redundant and multifunctional activities of cell replication and division proteins.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 2, p78-85 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.094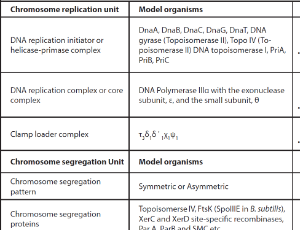
Kv1.3 Potassium Channels: Promising Therapeutic Targets in Hematological Malignancies
Theresa Lowinus, Tanima Bose, Luca Simeoni, Burkhart Schraven, Ursula Bommhardt
Voltage-gated Kv1.3 potassium channels control the membrane potential, cellular activation and cell death. Kv1.3 channels have been extensively studied in autoimmune disorders and are promising drug targets for the treatment of solid cancer.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p79-86 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.016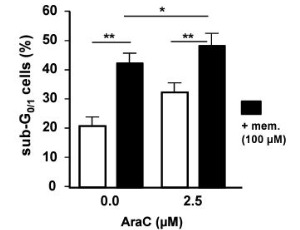
C-di-GMP and Its Role in Regulation of Natural Products Production
Olaf Latta, Andreas Bechthold
Among clinical and industrial important microorganisms Streptomyces are the largest source of natural products. But only a fraction of all Biosynthetic Gene Clusters in their genome is active under laboratory conditions. During the last years research has clarified the role of cyclic dimeric 3`-5` guanosine monophosphate, c-di-GMP, as an ubiquitous secondary messenger.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p79-90 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.069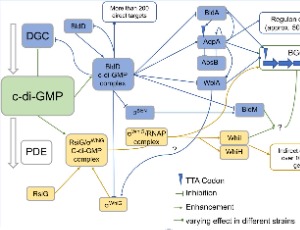
Neoadjuvant Therapy (NAT) in Localized Pancreatic Cancer: Should We Do It and What Should We Do?
Shreya Prasad Goyal, Morana Vojnic, Jung-in Yang, Jyothi Jose, Elliot Newman, Muhammad Wasif Saif
In 2019, approximately 56,770 new cases of pancreatic cancer were diagnosed in the United States, resulting in an estimated 45,750 deaths. Pancreatic cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related death, with a fiveyear survival rate of 9%. Based on the eighth edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging system for pancreatic adenocarcinoma, multi-center analyses have validated that poorer prognosis is associated with node-positive disease (N1 and N2).
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p80-84 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.037
Astrocyte and Microglial Disparities in PI3K/AKT Signaling: Implications for Parkinson's Disease Inflammation
Atiyeh Poursadoughian Yaran, Reihaneh Balali, Shahriar Gharibzadeh
Parkinson's Disease (PD), following Alzheimer's Disease, is the second most prevalent neurological condition globally. This progressive disorder is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, leading to motor dysfunction. Neuroinflammation, a complex process involving astrocytes and microglia, significantly contributes to PD pathogenesis. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, a pivotal regulator of cell survival and function, is dysregulated in PD.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 2, p83-91 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.136
Effects of a CB2 Subtype Selective Agonist ABK5-1 on Cytokine Production in Microglia
Yaliang Tang, Barbara Wolk, Debra A. Kendall
Neuroinflammation is closely associated with various diseases including neuropathic pain. Microglia are immune cells in the central nervous system which are the main players of immunity and inflammation. Since microglia are activated by nerve injury, and they produce proinflammatory mediators to cause neuropathic pain, targeting activated microglia is considered to be a strategy for treating neuropathic pain.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p85-93 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.038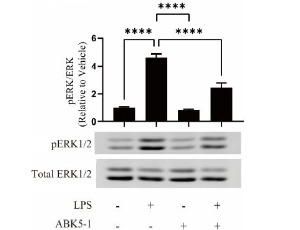
Improving Cancer Epigenetic Therapy; A Glimpse of NRF2
Tahereh Kashkoulinejad-Kouhi
One of the mechanisms used by epigenetic therapy is the elevation of host cell-derived double stranded RNA (dsRNA) baseline levels through overexpression of genomic repetitive elements especially Alu retroelements. The dsRNAs trigger immunogenic responses since immune system cannot distinguish between endogenous and exogenous dsRNAs derived from viral infections; hence called “Viral mimicry response”. These dsRNAs are recognized by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) such as MDA-5
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 2, p86-92 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.095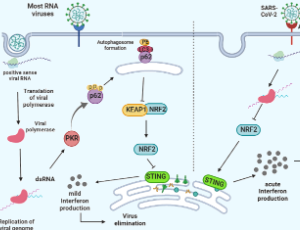
Can Yerba Maté (Ilex paraguariensis A.-St.-Hil) and Its Constituents Affect Health and Obesity?
Alexander V. Sirotkin
The present commentary is a short narrative review of the available data concerning the influence of Yerba Maté, its relatives and constituents on health with special attention to its anti-obesity effects and their physiological mechanisms. The possible adverse side-effects of Yerba Maté, form and doses of its consumption are discussed.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 2, p87-90 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.115
Is Citrate A Critical Signal in Immunity and Inflammation?
Alessia Zotta, Zbigniew Zaslona, Luke A. O’Neill
When immune cells are activated, they undergo metabolic change in order to have sufficient energy to function effectively. The Krebs cycle is one of the most important pathways involved in this response and citrate, a critical component of this pathway, regulates carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p87-96 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.017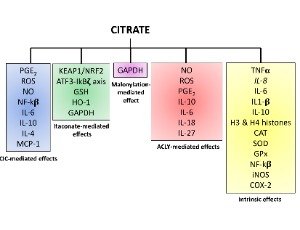
The Role of FCH Domain Only 1 (FCHO1) as an Oncogene in Lung Cancer
Myung-Haing Cho, Seung Jin Park, Soon-Kyung Hwang
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death in men and women with a 5-year survival rate of 18%. The PI3K/Akt pathway plays a role in non-small cell lung cancer tumorigenesis and progression. FCH domain only 1(FCHO1) is overexpressed in lung cancer and promotes entry into mitosis and G1/S phase transition, leading to cancer cell growth. Our group has investigated the relationship between FCHO1 and the Akt signaling pathway, which plays an important role in lung cancer growth.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p91-95 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.070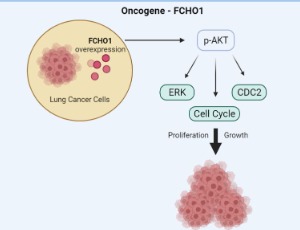
Targeting Lipid Metabolism for Better Management of Coronavirus SARS-COV-2 Infections: Intervention, Antiviral Drug Development, and Challenges
Yuting Wang, Peiran Chen, Ming-Liang He
The global pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), although has faded from public view, the virus itself remains highly active and continues to mutate, continuously causing infections. The population faces the risk of severe outcomes caused by virus infection (e.g., multi-organ tissue injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)). Furthermore, patients with chronic diseases (cardiovascular diseases, diabetes) are at risk of developing severe sequelae or even elevated mortality.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 2, p91-95 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.116
The Contribution of Signaling to Unraveling the Natural History of Cancer. The Lesson of the Phosphoinositide-specific Phospholipase C Pathway
Vincenza Rita Lo Vasco
Signal transduction pathways represent the bases of physiological cell activities, and the disruption of one or more pathways is involved in several human diseases.
Phospholipases are well conserved enzymes identified in different organisms, including bacteria, yeast, plants, animals, and viruses. Phosphoinositide-specific Phospholipases C (PI-PLC) belongs to the inositide signaling pathways.

F-ATP Synthase Inhibitory Factor 1 in Regulation of Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore and Metabolic Reprogramming
Lishu Guo
Mitochondrial permeability transition pore (PTP) plays an important role in mitochondrial physiology and cell fate. Emerging studies highlight PTP forms from F-ATP synthase, but whether F-ATP synthase inhibitory factor 1 (IF1) regulates the activity of PTP is basically unknown. We have recently demonstrated that IF1 interacts with p53-CyPD complex and promotes opening of the PTP, and IF1 is necessary for the formation of p53-CyPD complex.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 3, p93-98 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.096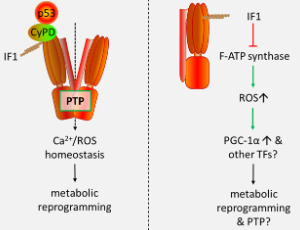
Cancer-associated Molecular Abnormalities in Human NK cells
Gulnur K. Zakiryanova, Michael R. Shurin
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. The immune system plays an important role in all steps of cancer development, growth and spreading as was repeatedly proven in a variety of experimental and clinical studies. Among the immune cells, Natural Killer cells, or NK cells, are critical to the innate immunity as one of the key effector cells of cancer immunosurveillance.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p94-99 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.039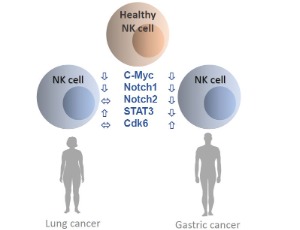
Low-level Laser Therapy in the Oral Cavity: A Retrospection in the Future
Eirini Papamanoli, Kyriaki Kyriakidou, Ioannis K Karoussis
Lasers have gained rather broad application in the field of medicine, as well as in dentistry. Different wave lengths are appropriate for a variety of uses, such as hemostasis, antimicrobial effect, tissue section and excision. Low level laser therapy (LLLT) is particularly interesting, since it stands out for its biostimulatory effect on tissues.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p96-104 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.071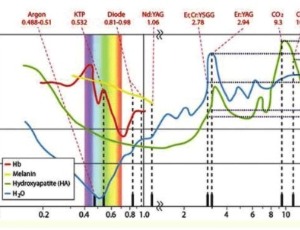
Evaluation of Plasmodium berghei Models in Malaria Research
Sarah Oluwatobi Otun, Richard Graca, Olalekan Onisuru, Ikechukwu Achilonu
As a key model organism for studying malaria, Plasmodium berghei provides essential information on pathophysiology, host immunological responses, and possible targets for treating this debilitating illness. This narrative review compares other Plasmodium species models, including P. falciparum and P. vivax, to assess the evolution, traits, and applicability of P. berghei models. We discuss the development of P. berghei research and its historical background, emphasizing its advantages in genetic modification and experimental accessibility.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 3, p96-113 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.117
Using Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein Deficiency to Understand Maternal Health
Jason W. Miklas, Hannele Ruohola-Baker
Fatty acid oxidation disorders unfortunately can result in the sudden unexplained death of infants. Mitochondrial trifunctional protein (MTP) deficiency is one such disease where long-chain fatty acids cannot be fully oxidized through beta-oxidation which, can lead to cardiac arrythmias in an infant.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p97-101 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.018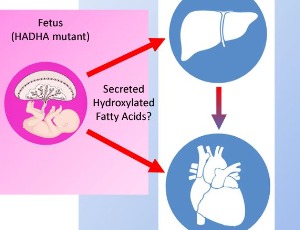
The Finer Points of Podocyte Sphingolipid Metabolism in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Alla Mitrofanova, Rachel Njeim, Alessia Fornoni
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a common complication of diabetes, characterized by kidney damage. Podocytes are specialized, terminally differentiated cells in the kidney’s filtration barrier that are key responders to the metabolic and environmental changes that occur in diabetes. Change in the function and in the number of podocytes is the main signature of the development and progression of DKD.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 3, p99-103 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.097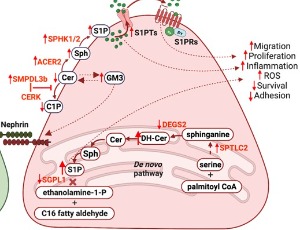
The Effects of Emtricitabine Pre-treatment on Inhibition of HIV-1 Infection in Jurkat Cells
Xue Wang, Jiangqin Zhao, Indira Hewlett
Emtricitabine (FTC) is an antiviral medication designed to diminish the presence of HIV in the body, thereby impeding or preventing harm to the immune system and the onset of AIDS-related illnesses. The precise mechanisms underlying emtricitabine's inhibition of HIV-1 replication in pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) are not fully comprehended. This investigation delves into the impact of emtricitabine treatments in vitro, utilizing the susceptible Jurkat cell line.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 3, p99-108 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.138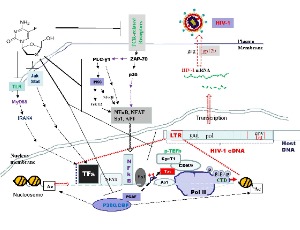
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Ectodomain Shedding May Play a Pivotal Role in Disease Severity in COVID-19
Rui Yamaguchi, Yasuo Yamaguchi
Ectodomain shedding mediated by a disintegrin and metalloprotease 10/17 (ADAM10/17) modulates the function of immune effector cells and may be involved in the novel coronavirus disease COVID-19. Toll-like receptor 7/8 (TLR7/8) recognizes single-strand RNA from viruses such as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19) during the innate immune response
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p100-102 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.040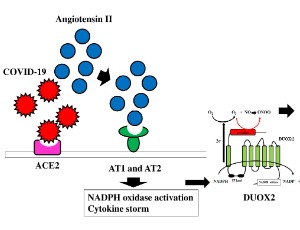
Dendorbium Nobile Lindl. Alkaloids Suppress NF-κB and NLRP3 Signaling Pathways to Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-induced Neuroinflammation
Jiaojiao Liu, Bo Liu, Xi He, Wu Qin, Jingshan Shi
The important immune cells in the brain are called microglia acting as the central junction between neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. In patients of cognitive disorders and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) animal models, amoebic morphology and inflammatory pathways are activated to release numerous cells in the inflammatory factors by active microglia.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 4, p102-114 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.019
Phosphorylation of RIAM Activates Its Adaptor Function in Mediating Integrin Signaling
Baihao Su, Jinhua Wu
Extracellular matrix (ECM) surrounding cells in solid tissue provides mechanical support and communicates with cells through cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) at the cell surface. Integrin is a major group of CAMs represented by a family of αβ heterodimeric single transmembrane receptors.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p103-110 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.041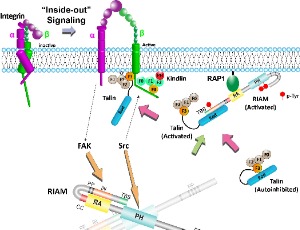
Structural Insights into Protein-Ligand Interactions of Small Leucine Rich Repeat Proteoglycans with a Large Number of Binding Partners: An Overview
Norio Matsushima, Hiroki Miyashita, Dashdavaa Batkhishig, Robert H. Kretsinger
Small leucine rich repeat proteoglycans (SLRPs) exist in the extracellular matrix. SLRPs contain tandem arrays of LRRs flanked by cysteine clusters at the both N- and C-termini. The extreme N- and/or C-termini contain low complexity sequences, glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain and/or sulfated tyrosine residues in some members of SLRPs.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 3, p104-124 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.098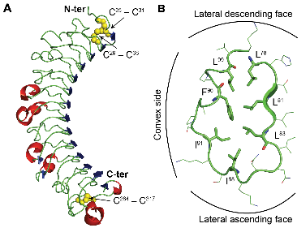
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Novel Therapeutic Strategies for Exosome-Related Diseases
Hiroshi Ageta, Kunihiro Tsuchida
Exosomes, a type of extracellular vesicles (EVs), are secreted from cells and taken up again by other cell types. They have attracted attention as new intercellular communication factors involved in various biological processes. Multivesicular bodies (MVBs) are intracellular organelles that are sources of exosomes. Recently, molecular regulatory mechanisms of EVs and MVBs mediated by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins (UBLs) have been elucidated.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p105-109 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.072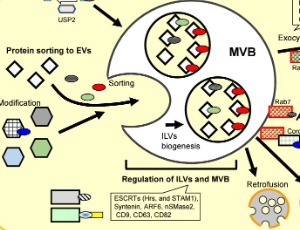
Metabolic Killing of Mitosis Addicted Cancer Cells by Targeting Aerobic Glycolysis: A New Achilles Heel of Cancer
Hilmar Warenius
The term “Achilles Heel” has often been used in relation to potentially vulnerable target molecules for anticancer drugs within cancer cells. Its generalized application to an increasing range of diverse possibilities, however, detracts from the uniquely valuable way it describes the wild-type aerobic glycolysis target which persists within the immortal cancer cell phenotype.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 3, p109-118 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.139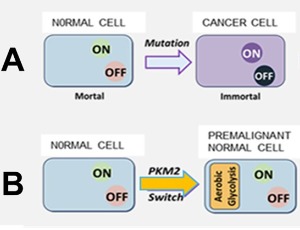
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Insights from Natural Product PHGDH Inhibitor Studies
Zhaodan Wang, Xueqin Chen, Qingxiang Sun
Cancer cells often exhibit a reprogrammed metabolism to accommodate their higher proliferation rates. Serine is a building block for de novo nucleic acids synthesis, and cancer cells typically require more of it. PHGDH is the rate limiting enzyme in human serine synthesis steps and is often highly expressed in cancer.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p110-114 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.073
Macrophages in Oral Tissues
Vitor CM Neves, Jing Zhao, Ana J Caetano, Paul T Sharpe
The balance between cell removal following tissue damage and new cell formation to facilitate repair has long been linked to the behaviour of inflammatory macrophages and their interactions with tissue-resident non-immune cells. The main aim of the inflammatory response is to modulate the tissue environment by removing unwanted cells and recruiting cells and soluble factors from the bloodstream to help protect the damaged tissue against infective foreign bodies.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p111-114 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.042
Linking Phosphoinositides to Proteins: A Novel Signaling Pipeline
Noah D. Carrillo, Poorwa Awasthi, Jeong Hyo Lee, Tianmu Wen, Mo Chen, Colin Sterling, Trevor J. Wolfe, Vincent L. Cryns, Richard A. Anderson
Phosphoinositide (PIPn) signaling plays pivotal roles in myriad biological processes and is altered in many diseases including cancer. Canonical PIPn signaling involves membrane-associated PIPn lipid second messengers that modulate protein recruitment and activity at membrane focal points. In the nucleus, PIPn signaling operates separately from membranous compartments defining the paradigm of non-canonical PIPn signaling.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 3, p114-121 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.118
Galectin 3 and Glial Cells of the CNS: A Fruitful Crosstalk with Remyelinating Potential
Laura A. Pasquini
Galectin-3 (Gal-3), the only chimera-like galectin, has three structural domains: (a) the NH2 terminal domain containing serine phosphorylation, important for nuclear localization, secretion and oligomerization; (b) a sequence susceptible to metalloprotease (MMP) cleavage; and (c) a C-terminal domain containing the carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD) and an anti-death motif.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 4, p115-126 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.020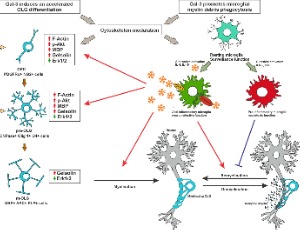
The Effect of Diet Induced Obesity on Serotonin in Zebrafish
Leen Uyttebroek, Samuel Van Remoortel, Laura Buyssens, Nastasia Popowycz, Guy Hubens, Jean-Pierre Timmermans, Luc van Nassauw
Obesity is a worldwide epidemic and a major risk factor for numerous diseases. The regulation of feeding behavior and body weight depends on a wide range of neuronal pathways influencing satiety and hunger. Serotonin (5-HT) is one of those players identified to have a profound effect on energy homeostasis. The effect of obesity on 5-HT metabolism in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and its underlying mechanisms still needs to be further elaborated.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p115-128 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.074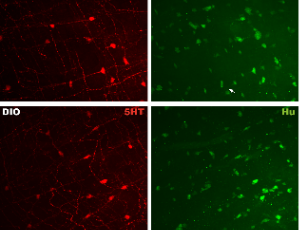
HGF/MET Signalling and DNA Damage Response: Strategies to Conquer Radiotherapy Resistance in Head and Neck Cancer
Aaran Vijayakumaran, Mahvash Tavassoli
Head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCCs) are a group of aggressive and genetically complex cancers, derived from the mucosal epithelium in the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx. Radiotherapy, often combined with chemotherapy remains the mainstay treatment options for patients.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p115-132 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.043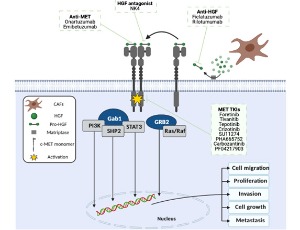
A Renewed Interest in Bioelectric Signaling: Unveiling an Epigenetic Layer of Neural Stem Cell Self-renewal and Differentiation
Chun-Chih Tseng
Neural stem cells (NSCs) are the foundation of brain development, giving rise to the vast diversity of neurons and glial cells that form the central nervous system. In the embryonic cerebral cortex, radial glia arise from primitive neuroepithelium and act as the main source of NSCs and progenitors of other glial cells that balance self-renewal with differentiation in a spatially and temporally regulated manner. Neural stem and progenitor cells can also be found in the neural crest during development, the subgranular zone (SGZ) of the dentate gyrus in the hippocampus, and subventricular zone (SVZ) of the lateral ventricles in the adult brain.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 3, p119-121 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.140
CRABP1 Signalosomes in Cellular Stress Response and Health Maintenance
Jennifer Nhieu, Fatimah Najjar, Li-Na Wei
CRABP1 is an evolutionarily conserved retinoic acid (RA) binding protein that was originally characterized to bind and sequester cytosolic RA. Classical RA signaling involves RA binding to nuclear retinoic acid receptors (RARs) to regulate gene transcription. However, recent studies have established that CRABP1 in fact forms protein complexes, with or without RA, in the cytoplasm to modulate (mostly suppress) specific signaling pathways in a cell context-dependent manner.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 3, p122-125 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.141
ALK1 Signaling in Human Cardiac Progenitor Cells Promotes a Pro-angiogenic Secretome
Michayla Moore, Sergey Ryzhov, Douglas B. Sawyer, Carlos Gartner, Calvin P.H. Vary
Pro-angiogenic paracrine/autocrine signaling impacts myocardial repair in cell-based therapies. Activin A receptor-like type 1 (ACVRL1, ALK1) signaling plays a pivotal role in cardiovascular development and maintenance, but its importance in human-derived therapeutic cardiac cells is not well understood. Here, we isolated a subpopulation of human highly proliferative cells (hHiPCs) from adult epicardial tissue and found that they express ALK1, a high affinity receptor for bone morphogenetic protein-9 (BMP9), which signals via SMAD1/5 to regulate paracrine/autocrine signaling and angiogenesis.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 3, p122-142 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.119
Activation of the 5-hydroxytryptamine Degradation System in Cells and Organ Injury
Jihua Fu
This paper summarizes the research results of Fu et al. on the pathological mechanism of organ injury. A hypothesis was proposed that "organ injury is a consequence of the activation of the 5-hydroxytryptamine degradation system (5DS) axis in cells". The basic composition of the 5DS axis in cells and the principle of its activation leading to cell lesions were determined.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 3, p125-127 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.099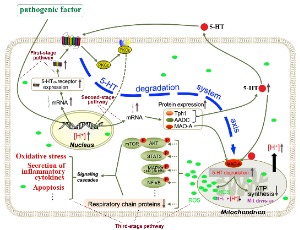
PAX-Interacting Protein 1 (PTIP) Promotes Apoptosis
Ching-Jung Huang, Hyein Cho, Chuan Li, Kangsan Kim, Danyang Yu, Daechan Park, Y. Jessie Zhang, Haley O. Tucker
PAX-interacting protein 1 (PTIP/PAXIP1) was discovered and initially characterized over three decades ago as a 1,056 amino acid-containing protein with six tandem BReast cancer C-Terminal (BRCT) repeats. PTIP functions broadly to catalyze histone methylation in DNA damage repair and within the hematopoietic lineage, to promote immunoglobulin variable region (variable, diversity, joining [VDJ]) and class switch recombination (CSR).
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 4, p126-141 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.142
NOXA the BCL-2 Family Member behind the Scenes in Cancer Treatment
Alison Dumont, Steven Lohard, Laurent Maillet, Philippe P Juin, Sophie Barillé-Nion
NOXA is a critical mediator of stress responses to anticancer drugs. This BH3-only protein sets the apoptotic threshold in cancer cells in response to chemotherapies by counteracting the prosurvival BCL-2 family protein MCL-1. A complex and dynamic network relying on both highly controlled gene transcription activity and protein degradation by proteasome, regulates cellular NOXA levels from low in steady state to rapidly enhanced upon stressful condition.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 4, p127-143 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.021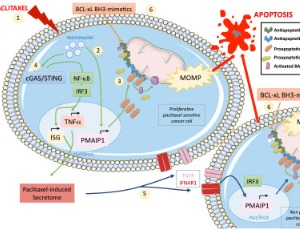
The Human Gut Phageome: Identification and Roles in the Diseases
Mohsen Nabi-Afjadi, Samane Teymouri, Fatemeh Nafe Monfared, Seyed Mostafa Noorbakhsh Varnosfaderani, Hossein Halimi
The human gut is a complex environment that contains a diversity of microorganisms commonly known as the microbiome. Numerous factors influence the composition of human gut bacterial communities, either contributing to homeostasis or the instability associated with a variety of diseases.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 3, p128-141 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.100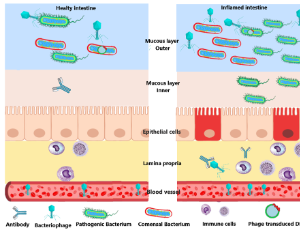
Phosphoinositide-Specific Phospholipases C in Psychiatric Diseases and Suicide
Vincenza Rita Lo Vasco
Mood disorders represent a major medical need requiring chronic treatment. About one million people die by suicide worldwide each year, both as a consequence of major depression or not. Multiple deficits, including cell atrophy and loss, were described in the brains of mood disorders affected patients and in experimental animal models. Numerous changes in gene expression and activity were described in limbic and cortical brain regions.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p129-140 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.075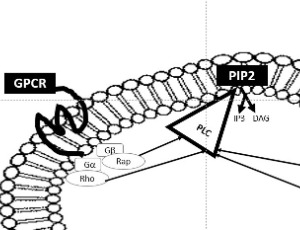
APE1/Ref-1 as a Novel Target for Retinal Diseases
Curtis Heisel, Jonah Yousif, Mahmut Mijiti, Kostas Charizanis, Mitchel Brigell, Timothy W. Corson, Mark R. Kelley
APE1/Ref-1 (also called Ref-1) has been extensively studied for its role in DNA repair and reduction-oxidation (redox) signaling. The review titled: “The multifunctional APE1 DNA repair-redox signaling protein as a drug target in human disease” by Caston et. al. summarizes the molecular functions of Ref-1 and the role it plays in a number of diseases, with a specific focus on various types of cancer.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p133-138 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.044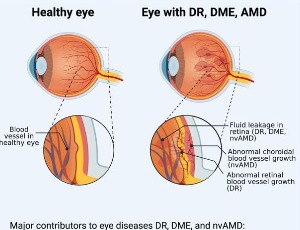
Altering CAR Construct Design to Ameliorate CAR-T Cell Therapy Associated Cytokine Release Syndrome
Zhicheng Du, Shijun Zha, Yu Yang Ng, Shu Wang
Cytokine release syndrome represents a significant barrier to the widespread application of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapies. We performed a broad analysis of preclinical and clinical studies that tested different designs of the CAR construct to tune CAR signaling, with an emphasis on effects of CAR designs on cytokine release from activated CAR-T cells.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p139-146 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.045
MAGIs: Junctional Scaffolds Linking Inter-Cellular Junction Architecture, Actin Cytoskeleton Dynamics, and Signaling Pathways
Lisa Heron-Milhavet, Alexandre Djiane
MAGIs (membrane-associated guanylate-kinases (MAGUK) inverted) are apical scaffolds conserved across evolution, which regulate cellular junctions. Low expression of MAGIs has been associated with tumorigenesis in a wide variety of cancers. This “tumor-suppressive” function of MAGIs has stimulated many studies to better understand the processes they control, and how their misregulation could contribute to cancer progression.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p141-147 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.076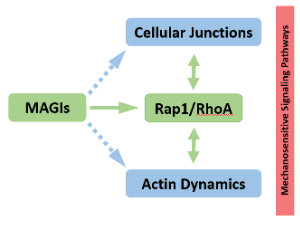
Understanding Elongasome Unit of Mycobacterium and its Comparative Analysis with Other Model Organisms
Preeti Jain
The reported incidences of 10.6 million tuberculosis cases worldwide with 1.6 million deaths in 2021 indicate that this disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis pathogen is difficult to treat and requires exploring newer possible therapeutic interventions. To identify novel drug targets, it is important to understand the basic physiological processes of each pathogen in detail. Cell division is the fundamental physiological process which maintains the replicative state of bacteria.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 3, p142-150 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.101
A Newly Characterized, Two BRCT Domain-Containing Isoform of PAX-Interacting Protein (PTIP) Generated via Frame Shift and Alternative Pre-mRNA Splicing
Ching-Jung Huang, Chuan Li, Danyang Yu, Hyein Cho, Kangsan Kim, Y. Jessie Zhang, Daechan Park, Haley O. Tucker
In an effort to clone polyglutamine-rich factors from activated B lymphocytes of mice, we discovered and describe here a previously uncharacterized isoform of PTIP/PAXIP1. By virtue of a two-nucleotide frameshift followed by alternative pre-mRNA splicing, this shorter isoform of 576 amino acids (termed PTIP576) retained only the two central BRCT domains of previously characterized PTIP and encodes a unique and structurally disordered 50 residue C-terminus.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 4, p142-155 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.143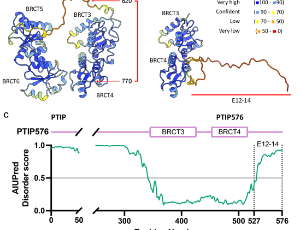
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
LncRNAs, Critical Regulators of Cellular Stress in Cancer: A New Player in the Old Game
Vikash Kumar, Eitan Shaulian
Due to deregulated control of the cell cycle, proliferation and metabolism, cancer cells are constantly exposed to a wide range of stresses, including DNA damage, nutrient deprivation, heat shock, hypoxia, and oxidative stresses, often, in a non-exclusive manner. Maintaining homeostasis, survival, and proliferation under these adverse conditions is a hallmark of cancer cells. Understanding the factors that enable cancer cells to endure such harsh environments is an important topic in cancer pathology.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 3, p143-148 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.120
Refining the Class IIa HDAC/MEF2 Paradigm in Muscle Biology: More than Meets the Eye
F. Dequiedt, Thomas Cherrier
For several decades, the transcription factor MEF2 (myocyte enhancer factor-2) has been known as a master regulator of myogenesis that orchestrates the first step in muscle formation: the differentiation of myoblasts into myocytes. Because of its importance during myoblast differentiation, the potential roles of MEF2 during later steps of myogenesis, in particular myocyte fusion, could not be properly investigated.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 4, p144-150 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.022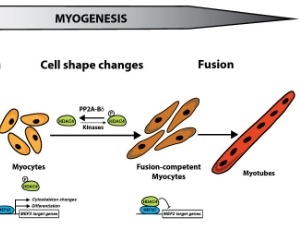
SPOCK1: New Mechanistic Insight into Liver Fibrosis
Zhipeng Du, Yuhui Fan, Dean Tian
Chronic liver diseases with different etiologies can provoke a fibrotic wound-healing response, which leads to liver fibrosis. Liver fibrosis is characterized by abnormal deposition and distribution of extracellular matrix (ECM), which restricts the regeneration of normal liver, and finally results in liver cirrhosis, liver failure or even hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p147-150 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.046
Repurposed Anti-IL-6 Therapeutics, Another Way to Quell the Cytokine Storm in Tuberculosis
Funmilayo Grâce Boni, Insaf Hamdi, Liadrine Moukendza Koundi, Lamine Baba-Moussa
Study on ‘‘cytokine storms’’ has been braced up in infectious diseases. The pertinence of this research begins to be evident in tuberculosis as it was observed that increased levels of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) were connected with disease severity. The IL-6 blockers therapeutics approaches for tuberculosis are currently a key line of research, with many in progress clinical trials, as IL-6 has become an important factor of the immune response to tuberculosis.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p148-152 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.077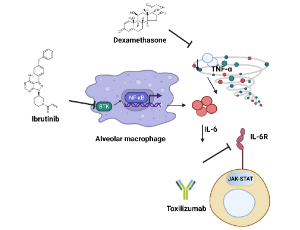
ACE 2/Ang (1-7)/Mas, Non-conventional RAS Axis: Endogenous Contributor of Cardio, and Reno-protective Responses
Supriya Sarkar, K. Jayachandra, Bannikuppe Sannanaik Vishwanath
The Renin angiotensin system (RAS) is an intricate pathway that regulates homeostasis. The proliferative arm of RAS that includes angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), angiotensin II (Ang II), and angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) contributes to pathophysiological responses such as vasoconstriction, hypertension, and cardiovascular, cerebral, and renal complications. The discovery of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE 2), the analog of ACE, synthesizes angiotensin (1-7) [Ang (1-7)] from Ang II or even from angiotensin I (Ang I) or angiotensin (1-9) [Ang (1-9)] less efficiently.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 3, p149-161 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.121
A Novel Regulatory Mechanism to Regulate the Deubiquitinating Activity of USP25 by Oligomerization
Ying Li, Bing Liu, David Reverter
Protein ubiquitination is a major post-translational mechanism that regulates fate and function of many proteins in the cell, either by regulating their abundance by the 26S-proteasome-ubiquitin system or by modulating protein activity by the attachment of the ubiquitin modifier
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 4, p151-154 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.023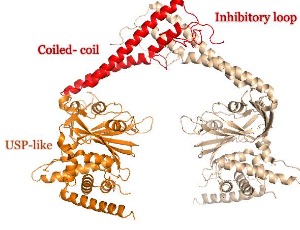
APE1/Ref-1 – One Target with Multiple Indications: Emerging Aspects and New Directions
Mahmut Mijiti, Rachel Caston, Silpa Gampala, Melissa L. Fishel, Jill C. Fehrenbacher, Mark R. Kelley
In the realm of DNA repair, base excision repair (BER) protein, APE1/Ref-1 (Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1/Redox Effector - 1, also called APE1) has been studied for decades. However, over the past decade, APE1 has been established as a key player in reduction-oxidation (redox) signaling. In the review by Caston et al. (The multifunctional APE1 DNA repair-redox signaling protein as a drug target in human disease), multiple roles of APE1 in cancer and other diseases are summarized.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p151-161 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.047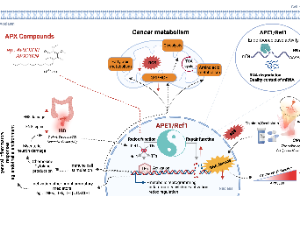
Depleting Cellular Retinoic Acid Binding Protein 1 Impairs UPRmt
Chin-Wen Wei, Thomas Lerdall, Fatimah Najjar, Li-Na Wei
Mitochondrial dysfunction underlines neurodegenerative diseases which are mostly characterized by progressive degeneration of neurons. We previously reported that Cellular retinoic acid Binding protein 1 (Crabp1) knockout (CKO) mice spontaneously developed age-dependent motor degeneration, with defects accumulated in spinal motor neurons (MNs), the only cell type in spinal cord that expresses CRABP1.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 4, p151-162 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.102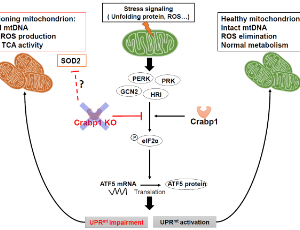
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
New Aspects in the Mechanism of Action of ALDH1A1 and 1A3 Isoforms in Carcinogenesis
Martina Poturnajova, Miroslava Matuskova
The ALDH gene superfamily encodes a group of evolutionarily-related proteins catalyzing the irreversible oxidation of aldehyde substrates to their corresponding carboxylic acids. Aldehyde dehydrogenases (ALDH) isoforms 1A1 and 1A3 belong to intracellular enzymes with a broad spectrum of functions linked with an advanced stage of solid tumors and the stemness potential of the neoplastic cells.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p153-159 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.078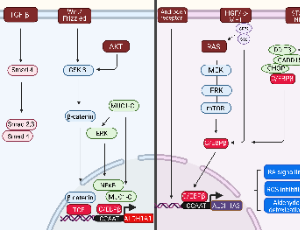
Role of PI3K/Akt/GSK-3 Pathway in Emesis and Potential New Antiemetics
Weixia Zhong, Darmani NA
Nausea and vomiting are protective defense mechanisms by which vomit competent species avoid ingestion of potentially toxic substances. More specifically, vomiting is the act of forceful expulsion of gastrointestinal contents through the mouth, whereas nausea is an unpleasant painless subjective feeling that one will imminently vomit.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 4, p155-159 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.024
Pathogenic Pathways and Therapeutic Strategies in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)
Kenley M. Preval, Abigail O. Smith, Gregory J. Pazour
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is the most common inherited kidney disorder and a major cause of end-stage renal disease. The disorder is primarily caused by pathogenic variants in PKD1 or PKD2, which encode the ciliary proteins polycystin-1 and polycystin-2. Loss of polycystin function disrupts calcium and cAMP signaling within the primary cilium, altering epithelial proliferation and fluid secretion that drive cyst formation and progressive kidney enlargement.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 4, p156-169 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.144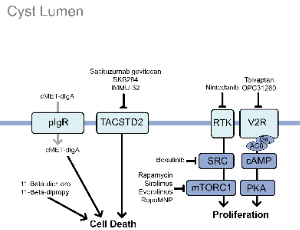
Oxidative DNA Damage: A Role in Altering Neuronal Function
Adib Behrouzi, Mark R. Kelley, Jill C. Fehrenbacher
A role for oxidative stress in the etiology of myriad neuropathologies is well accepted. However, the specific effects of oxidative DNA damage in the onset or promotion of neuronal dysfunction have been less studied. In our recent publication by Behrouzi et al. (Oxidative DNA Damage and Cisplatin Neurotoxicity Is Exacerbated by Inhibition of OGG1 Glycosylase Activity and APE1 Endonuclease Activity in Sensory Neurons), inhibition of enzymes that play a role in repairing oxidative DNA damage exacerbated neurotoxic effects of the chemotherapeutic agent, cisplatin.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p160-166 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.079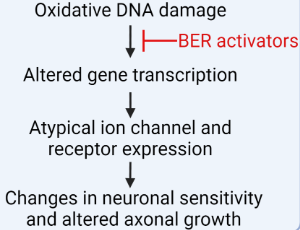
Improving Obesity and Insulin Resistance by Targeting Skeletal Muscle MKP-1
Anton M. Bennett, Ahmed Lawan
Obesity has reached a global epidemic and it predisposes to the development of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and related metabolic diseases. Current interventions against obesity and/or type 2 diabetes such as calorie restriction, exercise, genetic manipulations or established pharmacological treatments have not been successful for many patients with obesity and/or type 2 diabetes.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 4, p160-168 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.025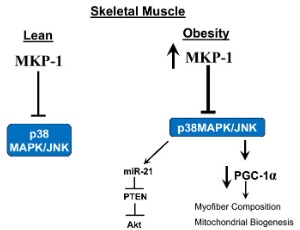
NH2-Terminal Cleavage of Cardiac Troponin I Signals Adaptive Response to Cardiac Stressors
Chad M. Warren, Monika Halas, Han-Zhong Feng, Beata M. Wolska, Jian-Ping Jin, R. John Solaro
Cardiac sarcomeres express a variant of troponin I (cTnI) that contains a unique N-terminal extension of ~30 amino acids with regulatory phosphorylation sites. The extension is important in the control of myofilament response to Ca2+, which contributes to the neuro-humoral regulation of the dynamics of cardiac contraction and relaxation.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p162-171 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.048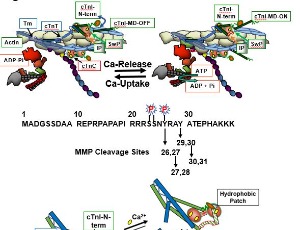
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
One-to-one Benefit Provided by Antioxidants to Cultured Skin Fibroblasts from Friedreich Ataxia Patients
Paule Bénit, Malgorzata Rak, Pierre Rustin
As to better understand and characterize the dramatic differences in antioxidant response of human cells harboring mutations in the frataxin gene responsible for Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA), we studied primary cultures of skin fibroblasts derived from five FRDA patients with different major frataxin gene expansion sizes. Since oxidative stress has been previously established to play a critical role in FRDA, among the many enzymes that may modulate oxidative stress sensitivity, we selected some that have previously been shown to be critical in oxidative stress.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 4, p162-175 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.122
Presence of Elevated Interleukin – 6 (IL-6) in the Blood of COVID-19 Convalescent Patients (40 – 93 Days) Post Onset of Symptoms Could be an Indicator of Ongoing Activation of the Immune System
John Bolodeoku, C Anyaeche, M Bass, TK Kim
IL-6 concentrations rise with the onset of COVID-19 infection and is detected in 68% of patients on admission but is expected to reduce after the acute phase. IL-6 concentrations at time points: (2-7 days), (6-11 days), (11-15 days) and (13-20 days) after intensive care unit (ICU) admission showed the highest level of IL-6 concentrations at time point 2-7 days, we decided to characterize IL-6 concentrations in serum samples collected in the sera of COVID-19 convalescent patients (40 – 93 days) post onset of symptoms.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 4, p163-168 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.103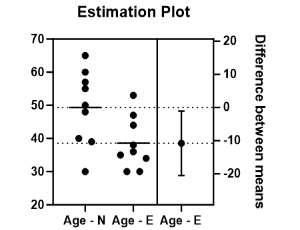
Can Mono- or Combination Therapy of Metformin with Cimetidine and Ibuprofen be a Promising Potential Therapy for Breast Cancer?
Samaneh Mostafavi, Hamidreza Zalpoor, Zuhair Mohammad Hassan
Metformin (MET), either alone or in combination with other drugs, has been considered a promising drug in cancer therapy. MET via activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathway and inhibiting the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) mediates tumor proliferation. Moreover, as an antagonist of the histamine H2-receptor (H2R), cimetidine (CIM) is also attributed to several immune-stimulatory responses in non-immunogenic cancers.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p167-170 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.080
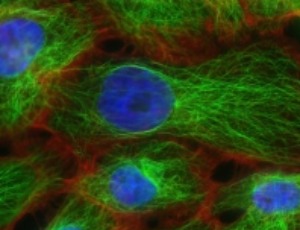
DIS3L2: Unveiling a New Player in Tumorigenesis, with a Key Role in Colorectal Cancer
Juan F. García-Moreno, Paulo Matos, Luísa Romão
DIS3L2 is a 3’-5’ exoribonuclease that recognizes and degrades uridylated transcripts in an exosome-independent manner and participates in several RNA degradation pathways, such as the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, or the surveillance of aberrant structured non-coding RNAs. Although some studies have linked DIS3L2 to tumorigenesis and cancer-related processes, its exact role in the development and progression of cancer
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 4, p169-177 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.104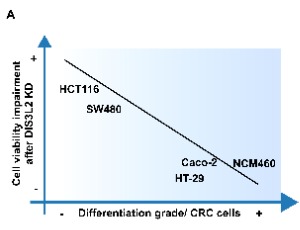
A Novel Regulatory Pathway of Desmoglein-3 in Keratinocyte Stress Response
Ambreen Rehman, Hong Wan
The desmosomal cadherin Desmoglein-3 (Dsg3) is a core adhesion component in desmosome junctions that occur with high frequency in the stratified squamous epithelial membrane lining the skin and mucous membrane. Dsg3 is identified as a major target of the circulating autoantibodies in Pemphigus Vulgaris (PV), an autoimmune blistering skin disease, and many signaling pathways have been demonstrated to be activated by PV-IgG targeting Dsg3, highlighting its role as a surface regulator in cell signa
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 4, p169-179 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.026
Ubiquitination of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors and Associated Synaptic Proteins In Vitro and In Vivo
Li-Min Mao, John Q. Wang
Metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors are a family of G protein-coupled receptors. These receptors are widely distributed in the brain and are critical for the modulation of synaptic transmission and plasticity. Emerging evidence shows that mGlu receptors themselves are subject to a dynamic posttranslational modification involving protein ubiquitination.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 4, p170-177 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.145
New Insights into the Proteolytic Regulation of the Structural Protein Junctophilin-2 by Calpain
Gunnar Weninger, Stephan E. Lehnart
Junctophilin-2 (JP2) is a key structural protein of junctional membrane complexes (JMCs) that stabilize contacts between the sarcoplasmic reticulum and transverse tubules required for excitation-contraction (EC) coupling in cardiomyocytes. Under pathophysiological conditions, the intracellular cysteine protease Calpain activated by disturbed intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis cleaves JP2 and, hence, disturbs EC coupling.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p171-178 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.081
Function of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases in Hepatic Inflammation
Gabrielle Westenberger, Jacob Sellers, Savanie Fernando, Sadie Junkins, Sung Min Han, Kisuk Min, Ahmed Lawan
The western diet and overuse of anti-inflammatory medication have caused a great deal of stress on the liver. Obesity and the associated inflammatory state in insulin-responsive tissues result in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokine that activates the stress-responsive MAPKs, p38 MAPK, and JNK. These MAPKs have figured prominently as critical effectors in physiological and pathophysiological hepatic inflammation.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p172-180 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.049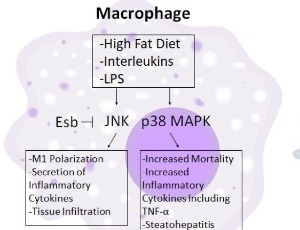
Elevated Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Levels with Ig (G & M) Antibodies in the Recovery Phase of Patients with COVID-19: Indication of Cytokine Storm and Re-infection
John Bolodeoku, Terry Gbaa
The innate immune response to coronavirus disease (COVID-19) by inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin 6 (IL-6), has been described as an early response, followed by an adaptive immune response with the production of antibodies. IL-6 is produced in response to viral infections and is crucial for the activation of T cells and the differentiation of B cells, which produce antibodies. Immunoglobulin M (IgM) and immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies are produced during the initial acute period of infection and the recovery period from the period of onset of symptoms.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 4, p176-182 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.123
When Cells Speak in Many Languages: The Evolving Story of Cellular Signaling
Vivek K Pandey
The current issue of the Journal of Cellular Signaling brings together a diverse set of studies that collectively broaden our understanding of cellular communication, from canonical biochemical pathways to emergent bioelectric and metabolic signaling systems. This editorial review synthesizes the major findings and conceptual advances presented in Volume 6 Issue 3, highlighting the converging trends that redefine how we view signaling as an integrative, dynamic, and multi-dimensional process.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 4, p178-180 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.146
Optogenetics Sheds Light on Brown and Beige Adipocytes
Aaron Clifford Brown
Excessive food intake leads to lipid accumulation in white adipose tissue, triggering inflammation, cellular stress, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. In contrast, the dynamic energy expenditure and heat generation of brown and beige adipose tissue, driven by specialized mitochondria, render it an appealing candidate for therapeutic strategies aimed at addressing metabolic disorders.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 4, p178-186 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.105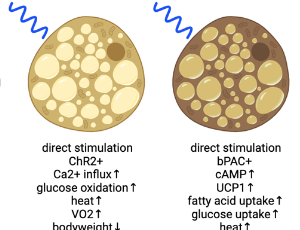
Targeting the Complex Protein Network of MYCN-amplified Anaplastic Ependymoma: A Case Report
Michael P. Castro
The MYCN oncoprotein has been notoriously undruggable and is infamous for causing aggressive cancer with poor outcomes in children and adults. Following surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, patients who develop progressive disease have few treatment options. An analysis of the dysregulated protein network caused by MYCN amplification suggested co-targeting PLK1, AURKA, CKS1, AKT, MTOR, and USP7 would be useful to take advantage of synthetic lethal vulnerabilities
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p179-192 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.082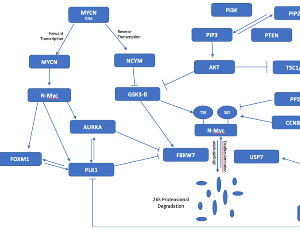
The Possible Role of Molecular Vibration in Intracellular Signalling
Werner Jaross
The exchange of information within the cell is extremely complex. Besides the well-studied chemical signalling, physical signalling is required to fulfil spatial and temporal aspects. The Golgi apparatus and the microtubule skeleton system are the decisive structures for numerous intracellular transport tasks.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 4, p180-186 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.027
A Brief Update on STAT3 Signaling: Current Challenges and Future Directions in Cancer Treatment
Keisuke Taniguchi, Momomi Tsugane, Akira Asai
Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3 plays a key role not only in regulating a variety of biological properties, including survival, proliferation, and metastasis of cancer cells, but also in modifying the tumor microenvironment to promote angiogenesis and immunosuppression, rendering STAT3 a valuable target in cancer.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p181-194 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.050
Obesity Significantly Modifies Signaling Pathways Associated with Bone Remodeling and Metabolism
Ferah Armutcu, Eugene McCloskey, Mehmet Ince
It is obvious that obesity-related diseases are increasing in parallel with the prevalence of obesity, which has reached epidemic proportions worldwide. Cardiovascular disease, multiple cancers, stroke, type 2 diabetes and many other non-communicable diseases are more likely to develop in people living with obesity compared to those living at a healthy weight. In recent years, deeper investigation of the role of multi-organ interaction mechanisms in obesity and related chronic diseases has contributed to the development of new treatment and prevention strategies for obesity and its related-diseases.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 4, p183-194 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.124
The Role of TIGAR-mediated Metabolic Processes in Autophagy and Cell Survival
Dingmei Zhang, Mei Li, Zheng-Hong Qin
Autophagy is the one of the essential pathways for maintaining homeostasis of cells and plays an important regulatory role in cell survival and death. Tp53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR) is a Tp53 target protein and is not only involved in the regulation of metabolism, cell cycle progression and radiation response, but also plays a role in autophagy.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 4, p187-194 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.028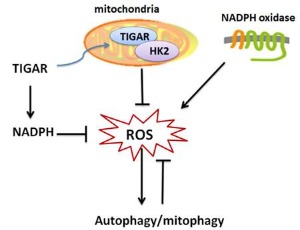
Retinoic Acid Induced Cell Signaling as a Counter Against Disease
Justin H. Franco, Zhixing K. Pan
Many disease processes result from disruption of physiologic cell signaling pathways. Cancer often develops from the loss of cell cycle regulation, while inflammatory disease results from dysregulated immune activity. Likewise, many microbial infections avoid immune clearance by interfering with cellular antimicrobial pathways. Retinoic Acid (RA) is a dynamic compound, derived from vitamin A, that can regulate various signaling pathways.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 4, p187-198 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.106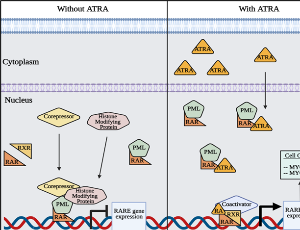
Redox Homeostasis in Well-differentiated Primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells
Ayaho Yamamoto, Peter D. Sly, Anna Henningham, Nelufa Begum, Abrey J. Yeo, Emmanuelle Fantino
Oxidative stress (OS) in the airway epithelium is associated with inflammation, cell damage, and mitochondrial dysfunction that may initiate or worsen respiratory disease. Redox regulation maintains the equilibrium of pro-oxidant/antioxidant reactions but can be disturbed by environmental exposures. The mechanism(s) underlying the induction and impact of OS on airway epithelium and how these influences on respiratory disease is poorly understood.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p193-206 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.083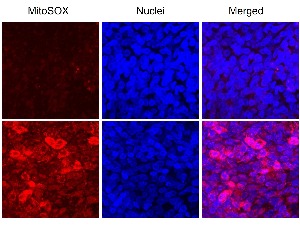
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Kinetin/N6-furfuryladenine: A New Neurodegenerative Disease Lead from an Old Plant Cytokine
Tamara Maiuri, Ray Truant
N6-fufuryladenine (N6FFA), or kinetin, has a long history as a plant cytokine with practical applications in agriculture. This adenosine analog is now commonplace in natural product small molecule chemical screening libraries, and as such has been discovered as active in mammalian disease pathways that include Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease (HD) and Familial Dysautonomia.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 4, p195-199 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.029
Targeting Cullin-RING E3 Ubiquitin Ligase 4 by Small Molecule Modulators
Kenneth Wu, Benjamin D. Hopkins, Roberto Sanchez, Robert J. DeVita, Zhen-Qiang Pan
Cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase 4 (CRL4) plays an essential role in cell cycle progression. Recent efforts using high throughput screening and follow up hit-to-lead studies have led to identification of small molecules 33-11 and KH-4-43 that inhibit E3 CRL4’s core ligase complex and exhibit anticancer potential.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p195-205 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.051
Indole Family and Neomycin Sulfate: Inductors of Differentiation in C2C12 and RD cell Lines
Lorena Milanesi, Andrea Vasconsuelo, Lucía Pronsato, Natalia Frattini, Nicolás Blanco
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a highly aggressive tumor primarily affecting the pediatric population, that generally originates from a failure in the embryonic differentiation of myogenic precursor cells. Standard treatment involves surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy, with a poor prognosis, especially when it spreads to other parts of the body, highlighting the need for new treatment approaches.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 4, p195-207 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.125
PRMT1-catalyzed SMAD7 Arginine Methylation Bridges EMT and Stemness
Jian Qin, Jian Xu
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a lineage transition from epithelium to mesenchyme, is induced by a convergence of signaling pathways and often driven by TGFß/SMAD signaling. Except for its critical roles on cell shape and motility during cancer invasion and metastasis, TGFß/SMAD activation-induced EMT has also been reported to be involved in cancer stem cell (CSC) generation.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 4, p200-205 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.030
Hydrogen Peroxide-induced Cell Death in Mammalian Cells
Tamutenda Chidawanyika, Surachai Supattapone
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is an important intra- and extra-cellular signaling molecule that can determine cell fate. At low concentrations, H2O2 plays roles in proliferation, immunity, and metabolism. Cellular exposure to higher non-physiologic concentrations of H2O2 can result in oxidative stress.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p206-211 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.052
Resveratrol and Astaxanthin Protect Primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells Cultured at an Air-liquid Interface from an Acute Oxidant Exposure
Ayaho Yamamoto, Peter D. Sly, Nelufa Begum, Abrey J. Yeo, Emmanuelle Fantino
Oxidative stress (OS) in the airway epithelium is associated with cell damage, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction that may initiate or worsen respiratory disease. However, it is unclear whether exogenous antioxidants can provide protection to the airway epithelium from OS. Resveratrol and astaxanthin are nutritional compounds that have shown diverse benefits including protection against OS and inflammation in various situations.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p207-217 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.084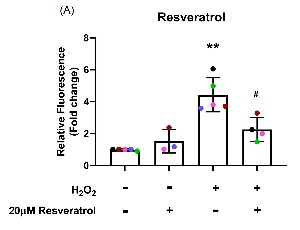
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Combating PDAC Drug Resistance: The Role of Ref-1 Inhibitors in Accelerating Progress in Pancreatic Cancer Research
Eyram K. Kpenu, Mark R. Kelley
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains one of the most lethal solid tumor diagnoses given its limited treatment options and dismal prognosis. Its complex tumor microenvironment (TME), heterogeneity, and high propensity for drug resistance are major obstacles in developing effective therapies. Here, we highlight the critical role of Redox effector 1 (Ref-1) in PDAC progression and drug resistance, focusing on its redox regulation of key transcription factors (TFs) such as STAT3, HIF1α, and NF-κB, which are pivotal for tumor survival, proliferation, and immune evasion.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 4, p208-216 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.126
TTK: A Promising Target in Malignant Tumors
Weiping Yao, Mingyun Jiang, Minjun Zhang, Haibo Zhang, Xiaodong Liang
TTK is a dual-specific protein kinase that phosphorylates serine and threonine. The spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) acts as a molecular monitoring mechanism that regulates mitosis and ensures accurate separation of chromosomes. TTK is a key regulator of the SAC. Activated TTK localizes to kinetochores and activates SAC function. Simultaneously, TTK promotes error correction by phosphorylating several substrates.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p212-220 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.053
Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 and Oncogenesis in the Liver Disease
Da-eun Nam, Hae Chang Seong, Young S. Hahn
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a significant cause of cancer mortality worldwide. Chronic hepatic inflammation and fibrosis play a critical role in the development of HCC. Liver fibrosis develops as a result of response to injury such that a persistent and excessive wound healing response induces extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition leading to HCC.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p221-227 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.054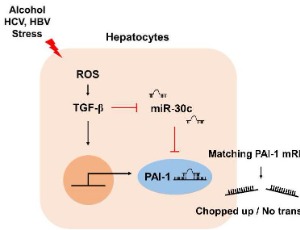
Novel Treatments Targeting the Dysregulated Cell Signaling Pathway during Sepsis
Justin H. Franco, Xiaohuan Chen, Zhixing K. Pan
Previously characterized as a purely immune mediated disease, sepsis is now recognized as a dysregulated multisystem response against a pathogen. Recognition of the infectious agent by pathogen recognition receptors (PRRs) can initiate activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway and promote the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines. During sepsis, the activation of NF-κB is dysregulated and results in cytokine storm, or the pathologic release of cytokines.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p228-234 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.055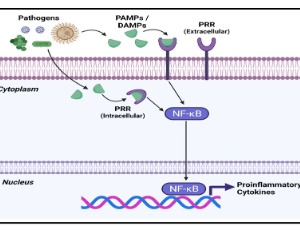
Ethanol Consumption and Sepsis: Mechanisms of Organ Damage
Alessandra Oliveira Silva, Clare C. Prohaska, Carla Speroni Ceron
Sepsis is highly prevalent, and is one of the main causes of mortality among hospitalized patients. Ethanol consumption in large quantities compromises the normal functioning of the body, leading to dysfunction of multiple different organ systems. The association between sepsis and ethanol is not fully understood, but it is well accepted that ethanol
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p235-241 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.056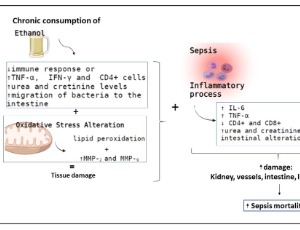
ZBP1, a dsRNA Sensor for Cell Death and Inflammation
Wei Mo, Jiahuai Han
ZBP1 has aroused a wide interest since it was identified as the first cytosolic dsDNA sensor ahead of the finding of cGAS in 2013. However, the investigations on ZBP1 declined when researchers found the binding of ZBP1 with dsDNA is not absolutely required for the activation of innate response.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p242-247 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.057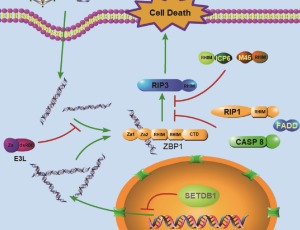
Chronic IL-1 Exposed AR+ PCa Cell Lines Show Conserved Loss of IL-1 Sensitivity and Evolve Both Conserved and Unique Differential Gene Expression Profiles
Shayna E. Thomas-Jardin, Mohammed S. Kanchwala, Haley Dahl, Vivian Liu, Rohan Ahuja, Reshma Soundharrajan, Nicole Roos, Sydney Diep, Amrit Sandhu, Chao Xing, Nikki A. Delk
Inflammation drives prostate cancer (PCa) progression. While inflammation is a cancer hallmark, the underlying mechanisms mediating inflammation-induced PCa are still under investigation. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) is an inflammatory cytokine that promotes cancer progression, including PCa metastasis and castration resistance. We previously found that acute IL-1 exposure represses PCa androgen receptor (AR) expression concomitant with the upregulation of pro-survival proteins, causing de novo accumulation of castration-resistant PCa cells.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p248-260 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.058
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Guanylin Peptides Signaling: Insights into Guanylate Cyclase C Dependent and Independent Signaling Pathways
Ivan Strinic, Nikola Habek, Aleksandra Dugandžic
Guanylin peptides (GPs) and their receptor, guanylate cyclase C (GC-C), have recently become a topic of great interest in metabolic research. Guanylin and uroguanylin are the most investigated GPs and they belong to a larger family of natriuretic peptides. GPs play a physiological role in regulation of electrolyte balance via the intestine and the kidney by regulating the energy balance via their action in the brain.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p261-268 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.059
Anti-tumor Mechanisms of Short-chain Fatty Acids, and the Relationship between the Gut Microbiome, Carcinogenesis, Tumor Growth, and Proliferation in Colorectal Carcinoma
Tadashi Ohara, Yasuyuki Taki
We reviewed the anti-tumor mechanisms of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) as well as the relationship between the gut microbiome and the pathology of colorectal carcinoma (CRC). According to our in silico analysis of human CRC cell lines, it was shown that SCFAs suppress various genes and transcription factors that participate in tumor growth/proliferation and cell turnover, and butyric acid displayed the strongest inhibitory effects among SCFAs.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p269-280 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.060
Aberrant Signaling Pathways in Cancer Cells: Application of Nanomaterials
Indrajit Roy, Goutam Ghosh
Cell signaling pathways involve several proteins, called kinases, to pass on vital messages from the transmembrane-proteins, e.g., receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) to the nucleus of a cell through a cascade of processes for various activities such as controlled cell division, proliferation, apoptosis, metabolism, DNA replication and repair. Alterations in these signaling proteins combined with genetic and/or epigenetic mutations spawn various types of cancer that empowers the cells to ignore or maneuver the immune signals and carry on felonious activities such as uncontrolled cell division and growth, genetic instability, angiogenesis around the tumor in hypoxia, eluding the body’s immune system, cell migration, and invasion of surrounding healthy cells.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p281-299 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.061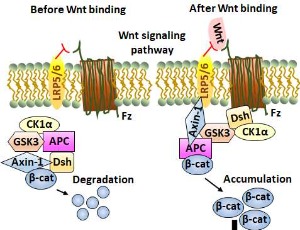
Trending Special Issues
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.