Loading
Archives of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
ISSN: 2692-787X
All Articles
A Review of the Applications of Intraoperative Ultrasound Guidance in Cervical Cerclage and Selected Gynecological Procedures
Noa Leybovitz-Haleluya, Reli Hershkovitz
The role of ultrasound (US) in gynecological procedures is increasing. Transabdominal ultrasound image–guided intrauterine procedures are not new. In this article, we reviewed the use of ultrasound some of the main gynecological procedures, focusing on the cerclage procedures.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.034
Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology
Elliot M. Levine
Advanced ultrasound offers an important diagnostic clinical tool for the specialty of Obstetrics (OB) and Gynecology (GYN). The advanced ultrasound technologies, such as power Doppler angiography, with its assessment of vascular flow, adds to the described clinical benefits. The imaging technology that this represents, offers diagnostic abilities for a variety of obstetric and gynecologic conditions
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p1-4 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.1.001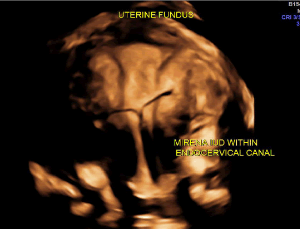
Intrauterine Device Embedment Resulting in Its Fracture: A Case Series
Carlos M. Fernandez, Elliot M. Levine, Marie Cabiya, Imaan Ansari, Leah Delfinado
Purpose: As long-acting reversible contraceptive choices are becoming more popular among young women, proper informed consent over potential complications should be addressed when such decisions are made. A local case series was analyzed to consider the risk of intrauterine device (IUD) fracture. Materials and Methods: A retrospective review of provider experience with the intrauterine device over a seven-year period was undertaken, to specifically analyze the incidence of IUD embedment and fracture in the studied population.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p1-4 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.2.009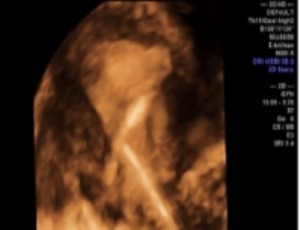
Sexual Abuse of Minors: 63 Cases at Mouila Regional Hospital in Gabon in 2022
Ulysse Pascal Minkobame Zaga Minko, Opheelia Makoyo Komba, Pamphile Assoumou Obiang, Jean Pierre Malanda, Ernest Junior Minto’o, Elsy Ntsame Mezui, Robert Eya’ama, Nyingone S, Anouchka Mewie Lendzinga, Jacques Albert Bang Ntamack, Jean François Meye
Sexual abuse of a minor is defined as any sexual violation or act of a sexual nature committed against a human being under the age of eighteen, by violence, coercion, threat, surprise, or deception [1]. Similarly, rape of a minor is any act of sexual penetration of any kind committed against a human being under the age of eighteen using violence, coercion, threats, or deception [1].
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p1-5 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.056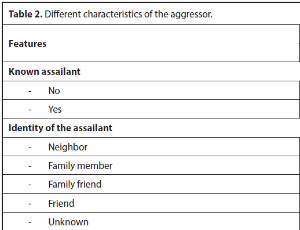
Vasa Praevia: Diagnosis and Management in a Sub-Saharan Maternity Unit
Jacques Albert Bang Ntamack, Elsy Ntsame, Robert Eya’ama, Chiesa Moutandou, Opheelia Makoyo Komba, Pamphile Assoumou Obiang, Ulysse Pascal Minkobame Zaga Minko, Jean François Meye
The presence of vasa previa is a rare but serious complication for the fetus due to the occurrence of Benckiser’s hemorrhage. This report presents a clinical case of vasa previa diagnosed antenatally in a spontaneous pregnancy. Performing a transvaginal ultrasound combined with pulsed Doppler in pregnant women with risk factors for placenta previa or low-lying placenta allows diagnosis in nearly 98% of cases.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, Volume 7, Issue 1, p1-5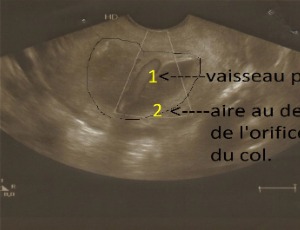
Racial Disparities in Surgical Outcomes for Uterine Fibroids: A Systematic Review
Devaun Reid, Britannia Noel, Janetta Lam, Julyssa Renteria, Sarah McCrackin, Gwendolyn Quinn
Objective: To systematically review disparities in surgical outcomes for uterine fibroids among Black women compared to non-Black women and identify contributing factors. Data sources: Systematic searches of PubMed, Embase, and Scopus from January 2010 to May 2024 were conducted. Study eligibility criteria: Included studies focused on surgical interventions for uterine fibroids in diverse populations, evaluating outcomes such as efficacy, safety, and complications. Excluded studies lacked racial stratification or reported non-surgical treatments.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p1-10 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.6.078
A New Isolated Local Varicella Virus: Isolation, Identification, Comparative Growth Characteristics and Immunological Evaluation in an Animal Model
Fatemeh Esna-Ashari, Abbas Shafyi, Mehrdad Ravanshad, Zohreh Azita Sadigh, Reza Shahbazi, Abbas Noori, Maryam Pourabdollahy, Ashraf Mohammadi
A panel of 4 different cell lines was optimized for isolation, identification, and authentication of a varicella zoster virus from a swab sample of an 8-year-old boy suspected to varicella zoster infection. The system enabled highly efficient and rapid isolation of viruses in 33°C by serial sub culturing to more than 25 passages. The technique relies on isolation of viral genes by increasing the number of particles that are statistically represented in cell culture and verified by cell culture infectious dose 50% assay
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p1-18 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.3.024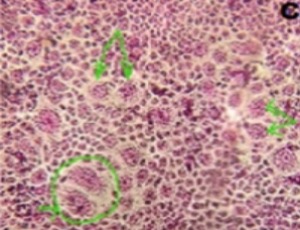
Racial/Ethnic Bias and Its Role in Severe Maternal Morbidity
Elliot M. Levine, Leah Delfinado, Carlos M. Fernandez
Racial and ethnic health disparities have been identified by many information sources in recent years, and a specific example of this is severe maternal morbidity and mortality, which includes mortality from postpartum hemorrhage. It is this racial/ethnic health disparity that has been highlighted in news reports that should be of concern to all physicians and healthcare providers, recognizing that women of color have more than three times the risk of dying in childbirth than white women.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p4-6 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.035
Recommendation of Tetanus Toxoid Vaccination for Pregnant Females in a Country that Achieved Elimination of Maternal and Neonatal Tetanus. A commentary on the Study: Knowledge and Health Beliefs of Reproductive-age Women in Alexandria about Tetanus Toxoid Immunization
Azza A. Mehanna
The study “knowledge and health beliefs of reproductive-age women in Alexandria about tetanus toxoid immunization” has shed a new light on the attitude of obstetricians in Alexandria (Egypt) towards recommending tetanus toxoid vaccination to pregnant females. According to the study, the use of tetanus toxoid vaccine among females in child-bearing age in Alexandria was low.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p5-8 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.2.010
Early Onset Fetal Growth Restriction: Does Path to Diagnosis Impact Outcomes and Pathology?
Brian Burnett, Linda Street, Kristen H. Quinn, Jeffrey M. Denney
Objective: To evaluate demographics and outcomes of maternal-fetal pairs in early onset fetal growth restriction (FGR) requiring delivery prior to 34 weeks’ gestation based on ultrasound indication leading to diagnosis. Study Design: This is a descriptive study of maternal-fetal pairs with early FGR diagnosed prior to 30 weeks’ gestation and delivering between 22w0d and 34w0d under the care of Wake Forest University Perinatology 01/2012-12/2016.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p5-12 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.1.002
Novel Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis Pilot Study
Timothy J. Hardy
Use of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is well established in treatment of orthopedic patients. This pilot study aims to determine the efficacy of using instillation of PRP paired with hydrodistention of the bladder to treat patients with interstitial cystitis (IC).
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p7-11 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.036
Evaluation and Management of chronic Hypertension in Pregnancy
Sangeeta Yadav, Neeta Singh, Mandakini Pradhan
Chronic hypertension is present in 1-2% of pregnant women. Women with chronic hypertension are at an increased risk of maternal and perinatal complications when compared with normotensive women. It is not uncommon for the women with chronic hypertension to present first time during pregnancy and obstetricians are the first one to encounter them during antenatal checkup. Secondary hypertension is often unrecognised and misdiagnosed thus leading to improper treatment with significant risk to the mother and fetus.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p9-15 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.2.011
Treatment of Iatrogenic Thermal Bladder Injury
Dimitrios Megaritis, Annette Kuhn, Anna-Sophie Villiger
Injuries to the urinary tract are a frequent occurrence during gynecological procedures, particularly laparoscopic hysterectomy, with acute and chronic complications being reported. Urinary tract injuries occur in about 0.73% of laparoscopic hysterectomies, similar to abdominal hysterectomy rates. These injuries can lead to significant complications, including the formation of vesicovaginal (3.4%) and ureterovaginal (2.4%) fistulas, often requiring additional surgery.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p11-16 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.6.079
Evaluation of Sexual Dysfunction in Brazilian Women with Infertility Undergoing Assisted Reproduction Treatment
Ana Carolina Sater, Renato Nisihara, Danielle Medeiros Teixeira Miyague, Alessandro Schuffner, André Hadyme Miyague
The increase in infertility around the world has a negative impact on sexual desire and function. The objective of this study was to evaluate the presence of sexual dysfunction in women diagnosed with infertility, comparing them with healthy controls.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p12-17 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.037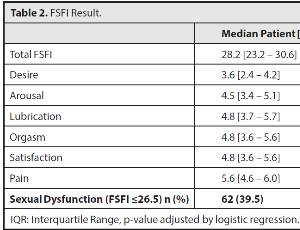
Family Planning Laboratory Review of Factors Affecting the Choice of Contraceptive Methods in Three Teenagers' Populations in Thrace, Greece
Panagiotis Tsikouras, Georgios Galazios, Xanthoula Anthoulaki, Anna Chalkidou, Anastasia Bothou, Theodora Deuteraiou, Michael Koutsogiannis, Irini Babageorgaka, Fotini Gaitatzi, Konstantinos Nikolettos, Stefanos Zervoudis, Nikolaos Nikolettos
Contraception encompasses the concept of avoiding a pregnancy, and is aimed at women of reproductive age who, although are sexually active, do not want to achieve any pregnancy at their option fertility preservation and family planning. It should be underlined that no method of contraception is 100% guaranteed because its success depends on many factors such as patient’s compliance to gynecologists instructions, woman’s age, the advantages and disadvantages of each method, the frequency of sexual intercourse and of course the type of contraception.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p13-22 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.1.003
Use of Algorithms to Predict Disease in Obstetrics: A Clinical Perspective
Elliot M. Levine
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been the subject of many contributions to the lay and professional literature in the past few years. While it may seem that the medical benefits of its use are immense, there may be reasons to consider a degree of caution in this regard. In particular, the clinical value of using algorithms to predict disease should be measured against the cases in which such algorithms are not used. Then, the resultant costs can be measured to show possible clinical benefit of AI.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p16-17 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.058
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Followed by Fertility Sparing Surgery in Stage 1B2 Cervical Cancer
JWM Aarts, PLM Zusterzeel
In 2020 we published a series of 18 patients who underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) and vaginal radical trachelectomy (VRT) as a fertility sparing alternative in stage 1B2 cervical cancer.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p16-19 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.2.012
COVID-19 Vaccine Acceptance during Pregnancy: Lessons Learned and How to Design the Best Strategy to Increase Vaccination Acceptance in the Future
Ioanna S. Tsiaousi, Marianna K. Theodora, Panagiotis G. Antsaklis, Alexandros V. Psarris, Michalis I. Sindos, Pelopidas A. Koutroumanis, Dimitrios N. Zaharakis, George I. Daskalakis
The present study aimed to study the vaccination acceptance of COVID-19 vaccine in the Hellenic pregnant population and make a high relative analysis of the factors that contribute to decision-making concerning the acceptance of the vaccine during pregnancy. Findings could be leveraged for improving the vaccination communication strategy to pregnant women to increase the vaccination acceptance rate.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p18-27 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.038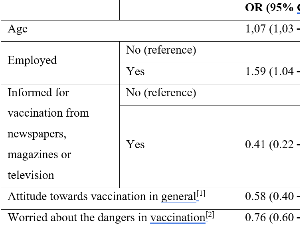
Bacterial Diversity in Placentas from Complicated Pregnancies Using 16s rRNA Gene Sequencing
Kaitlin Elizabeth Sprong, Colleen Anne Wright, Sureshnee Pillay, James Emmanuel San, Eduan Wilkinson, Sharlene Govender
Introduction: The ‘sterile womb paradigm’ is currently under debate and the advent of next generation 16S rRNA gene sequencing is driving the characterization of microbes associated with the amniotic cavity during pregnancy. Objective: To characterize the bacterial diversity in placentas from preterm and term births using next generation 16S rRNA gene sequencing in association with adverse pregnancy outcomes and histopathology studies.
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Peritoneal Fluid Leptin Levels in Endometriosis: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Cloé Vaineau, Konstantinos Nirgianakis, Thomas Andrieu, Brett McKinnon, Sara Imboden, Michael D.Mueller
Background: Leptin has been proposed as a biomarker for endometriosis. Previous studies have shown mixed results. The aim of this study was to compare peritoneal fluid (PF) leptin concentrations between patients with and without endometriosis in a cohort of sufficient size to detect a significant difference. Methods: Patients of reproductive age undergoing laparoscopic surgery for endometriosis or other benign indications in the Department of Gynecology, University of Bern between 2007 and 2018 were recruited.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p19-28 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.3.025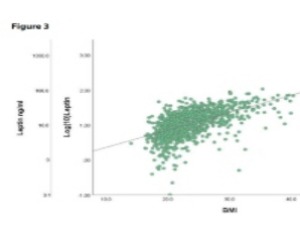
Gene Therapy for Sickle Cell Disease: Start of a New Era
Norman Ginsberg, Lee P Schulman
This manuscript reviews treatment of Sickle Cell disease over time. The application of allogeneic stem cells proved the sickle cell disease could be permanently corrected and cured but limited to those with a compatible donor.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p20-23 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.2.013
Low-level Progesterone on the Day of hCG Injection Has No Detrimental Effect on the Pregnancy Outcome after IVF with GnRH-a Protocol: A Retrospective Study
Jie Hao, Bin Xu, Yonggang Wang, Yanping Li, Jing Zhao
Objective: To investigate the effect of low progesterone (P) level on the day of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) injection on the outcome of in vitro fertilization (IVF) with GnRH- agonist (GnRH-a) long protocol. Methods: A retrospective study was conducted in a reproductive medicine center of University-affiliated teaching hospital. 1115 women included were divided into two groups according to the P level: Group 1 (233 women with P level ≤ 0.5 ng/ml, and Group 2 (882 women with P level >0.5, ≤ 1.5 ng/ml).
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p23-29 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.1.004
Challenges Regarding the Management of Gynecological and Obstetric Complications in Women with Inherited Factor XIII Deficiency
Lucia Rugeri, Stéphanie Désage, Sandrine Meunier
Women with rare bleeding disorders (RBDs) can be exposed throughout their life to several complications such as menorrhagia or hemorrhagic complications during pregnancies and deliveries. Among RBDs, factor XIII deficiency leads to life-threatening hemorrhages such as intracranial hemorrhage, and women during their reproductive period may experience gynecological and obstetric complications, and more specifically recurrent miscarriages due to the role of FXIII in placenta attachment.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p24-28 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.2.014
Primary Dysmenorrhea: A Questionable Diagnosis in the Modern Era
Elliot M. Levine, Carlos M. Fernandez, Teresa Tam
The term “Primary Dysmenorrhea” may no longer adequately describe a patient’s diagnosis, given the capabilities of modern imaging technology to detect possible deep infiltrating endometriosis. Laparoscopy alone may not be sufficient for diagnosing endometriosis. Considering the availability of specific therapeutic interventions tailored for endometriosis, there is a compelling case for pursuing a more targeted diagnostic approach.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p27-29 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.6.081
Can the Systemic Immune Inflammation Index Predict the Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy?
Sevcan Sarikaya, Emre Uysal, Oğuzhan Günenç
Objective: The aim of this study was to predict the selection of treatment for ectopic pregnancy (EP) using the values of platelet/lymphocyte ratio (PLR), neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR), monocyte/lymphocyte ratio (MLR) and systemic immune inflammation index (SII) obtained from hematological parameters routinely used in clinical practice.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 2, p28-33 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.039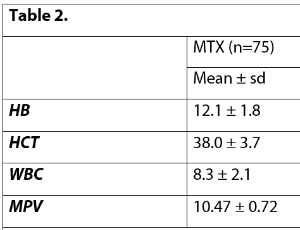
Practical Considerations Regarding Recommendations for an Educational Program in Robot Assisted Gynaecological Surgery
Karlijn De Vocht, Jasper Verguts, Guy Orye, Tom Tuytten
Robot assisted gynaecological surgery is exponentially expanding its field and gynaecologists need to be prepared to implement this new approach in clinical practice. Training on this new device is thus mandatory but the method by which the training is best organized remains open for debate. In 2019, 12 experts invited by the Society of European Robotic Gynaecological Surgery (SERGS), agreed on 39 recommendations about education in robot-assisted surgery (RAS) in gynaecology.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p29-31 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.2.015
Maternal Psoriasis – Pregnancy Outcomes and Long-term Infectious Morbidity of the Offspring: A Population-based Study
Moran Shahar, Gil Gutvirtz, Gali Pariente, Tamar Wainstock, Eyal Sheiner
Background: Limited data exists regarding long-term morbidity of the offspring in women with psoriasis. The objective of this study was to assess long-term infectious morbidity of the offspring born to women with psoriasis. Study Design: We conducted a population-based cohort study comparing the long-term infectious-related morbidity of offspring (up to the age of 18) born to mothers with and without psoriasis, between the years 1991-2021 in a regional tertiary medical center.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p30-35 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.6.083
Impact of Estradiol Supplementation during Luteal Phase Support on the In vitro Fertilization Clinical Outcome: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jie Hao, Bin Xu, Yonggang Wang, Yanping Li, Jing Zhao
Background: At present, progesterone administration is widely used. There is no agreement on whether estradiol (E2) addition should be supplement to progesterone (P) as luteal phase support (LPS). The present meta-analysis was conducted to clarify whether E2 supplementation as LPS has beneficial effect on the clinical outcome after in vitro fertilization (IVF)/intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p30-36 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.1.005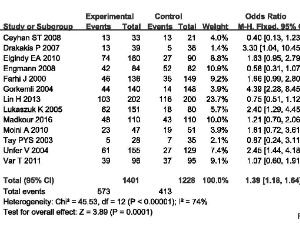
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Critical Appraisal OF Cervical Pregnancy Management
Ibrahim A Albahlol
For a long time, it was rare to see a case of cervical pregnancy (CP) throughout the journey in the field of obstetrics. Recently, the circumstances showed dramatic changes and I think not uncommonly every one elsewhere in the field may face this problem to some extent and the CP term strikes his/her ears. This may be attributed to an actual increase in CP rate that go parallel to widespread application of Assisted Reproduction Techniques (ART) procedures all over the world on one hand and earlier diagnosis owing to liberal utilization and more familiarity with Transvaginal Sonography (TVS) on the other hand.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p32-33 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.2.016
Comparison and Analysis of Cerebroplacental Ratio and Umbilicocerebral Ratio in the Prenatal Diagnosis and Severity Assessment of Fetal Growth Restriction: A Retrospective Study and Systematic Review
Jing-jie Zheng, Hui-rong Zhao, Min-hong Mao, Li-yuan Guo, Han-xue Zou, Zhi-hui Liu, Jing Liu, Chen Chen
Purpose: Doppler flow parameters of fetal umbilical artery (UA) and middle cerebral artery (MCA) have been widely used for fetal growth restriction (FGR), but their diagnostic efficacy remains contentious. The purpose of this study is to clarify the superiority of cerebroplacental ratio (CPR) and umbilicocerebral ratio (UCR) in terms of their correlation and predictive accuracy in diagnosing FGR.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p33-39 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.060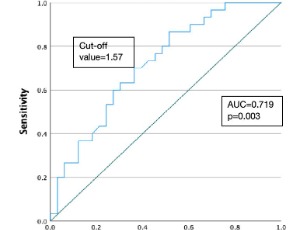
After Surgical Menopause, Should Menopausal Hormonal Therapy Started Only Before the Age of 45 Years?
Kitirat Techatraisak
The published study Compliance and health consequences of menopausal hormonal therapy after surgical menopause: A retrospective study in Thailand showed that menopausal hormonal therapy soon after bilateral oophorectomy before the age of natural menopause in Thailand possibly prevented subsequent osteopenia compared with menopausal hormonal therapy non-users, also without significant adverse breast outcomes comparing between hormonal therapy users and non-users.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p34-38 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.2.017
Association between Maternal Serum Leptin Level and Preterm Birth among Parturients in Lagos, Nigeria
Olubunmi Olufunke Ogein, Adeyemi Adebola Okunowo, Gbenga Olorunfemi, Benedetto Osunwusi, Omololu Adegbola
Preterm birth is one of the major causes of neonatal morbidity and mortality worldwide. The association between occurrence of preterm birth and biomarkers measured in the maternal serum maybe helpful in predicting preterm birth especially in low resource settings.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 2, p34-40 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.040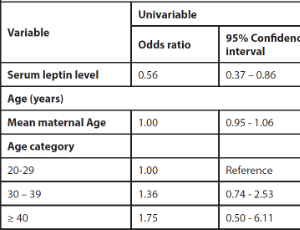
Origins of the Obstetric and Gynaecological Syndromes
MJ Quinn
For many decades (1945–2011) narrowed, uterine arterioles were thought to be the histological hallmark of preeclampsia after their original description by AT Hertig, Harvard, MA, in 1945. More recently Professors Brosens & Romero, described narrowed, uterine arterioles in many of the “great” obstetric syndromes
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p36-45 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.6.084
Circulating Cell-Free RNA: A New Perspective for Endometrial Cancer
Francesca Malentacchi, Flavia Sorbi, Natasha Cipriani, Chiara Sgromo, Lorenzo Antonuzzo, Serena Pillozzi
In order to implement the knowledge of cancer to monitor its evolution and setting, in the last decade, new minimally invasive and repeatable samples collection have been developed such as liquid biopsy. Cancer biomarkers originating from tumors can represent the molecular status of the tumor or its metastases which release them directly into body fluids or indirectly due to disruption of tumor/metastatic tissue. These biomarkers are detectable in liquid biopsy.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p37-42 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.1.006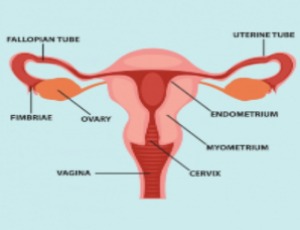
Looking Ahead: Interesting Developments in Menopause Management
Kristi Tough DeSapri
There are many exciting developments in the field of midlife women’s health which explain how menopause symptoms, particularly hot flashes, may be an important vital sign and predictor of future health status. Additionally, in the therapeutic realm, there is a new class of medications that affect the thermoregulatory channels in the brain that control vasomotor symptoms (VMS). This development may unlock treatment options for women who cannot tolerate or cannot safely take hormone therapy.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p37-42 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.1.007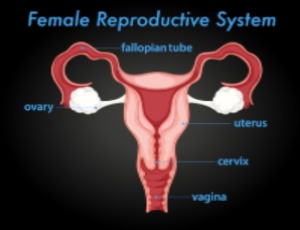
The Role of Anemia in Term and Preterm Pregnancies: Evidence from the Brazilian Multicenter Study on Preterm Birth (EMIP)
Camilla O. Figueira, Helena M Gomide, José P. Guida, Tabata Z. Dias, Giuliane J. Lajos, Ricardo P. Tedesco, Marcelo L. Nomura, Patrícia M. Rehder, José G. Cecatti, Renato Passini Jr, Fernanda G. Surita, Maria Laura Costa, Brazilian Multicenter Study on Preterm Birth study group
Objective: Evaluate the prevalence of anemia in term and preterm pregnancies and compare maternal and perinatal outcomes among groups. Methods: Secondary analysis of Brazilian Multicenter Study on Preterm Birth (EMIP). Cross sectional study on preterm births, with sample of term births to evaluate risk factors and comparisons. Current analysis compared prevalence of anemia in term and preterm births and among their types (spontaneous preterm birth (sPTB)
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p39-50 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.2.018
Harnessing Technology to Revolutionize Personalized Therapies for Metrorrhagia
Tamer A. Addissouky
Background: Metrorrhagia is defined as irregular uterine bleeding occurring between normal menstrual cycles. Unlike normal menstruation, metrorrhagia is irregular in frequency, duration, and volume. Understanding the etiology of metrorrhagia requires reviewing the hormonal regulation of the normal menstrual cycle.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p40-47 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.061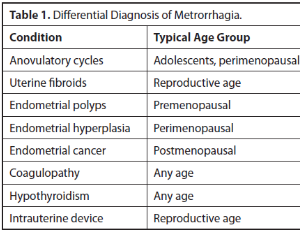
Utero-Vesical Fistula Closure after 3 Weeks Treatment with Intravenous Mesenchymal Stem Cells Infusion: Case Report
Di Silvio Mauricio, Luján-Irastorza Jesús Estuardo, Durand-Montaño Carlos, Henández-Ramos Roberto, Barrón-Vallejo Jesús, Ávila-Rebollar Daniela, Myslabodski Julio, Pariente-Fernández Maruxa, Tagle-Rodríguez Jorge Mario, Ramírez-Amezcua Miguel Ángel, Paredes-Núñez María Angélica, Vargas-Hernández Víctor Manuel
Objective: To describe the evolution of Utero-Vesical Fistula (UVF) of one patient who received conservative treatment using intravenous (IV) infusion of 120x106 Adipose tissue Mesenchymal Stem Cells (ADMSCs). Clinical case report: A 36-year-old female presented with postcesarean hematuria 3 hours after an emergency c-section was performed consequently to placental abruption during labor.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 2, p41-45 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.041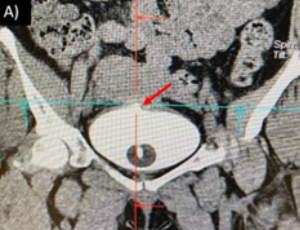
Preliminary Study Assessing the Efficiency of a New Singleuse Obstetrical Vacuum Device: Icup2®
D’Antona A, Mottet N, Lenoir P, Toubin C, Bourtembourg A, Ramanah R, Riethmuller D
A national perinatal survey in France in 2016 showed that 12.2% of women have instrumentally assisted vaginal births with vacuum extraction used in 49.8% of cases, making it the most frequently used form of obstetrical assistance. The 2006 initial concept of the Icup® vacuum extractor was based on the development of a single-use device with a partially deformable cup to avoid any fetal scalp injury.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p45-51 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.1.008
Hemostatic Pelvic Irradiation: A Rarely Reported Approach to Benign Gynecological Bleeding
Bouguerra F, Boudhina E, Chahdoura H, Souissi M, Tbessi S, Bouzid N, Belajouza S, Tebra S
Background: Ovarian cysts are usually treated using medical or surgical interventions. However, in some cases, these treatments may not be feasible or effective, and alternative options need to be considered. Case presentation: We report a case of a 43-year-old woman with a history of recurrent hemorrhagic ovarian cysts, who was on anticoagulant therapy due to tight mitral stenosis and had multiple autoimmune disorders.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 2, p46-49 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.042
Uterine Electrical Signals and Cervical Dilation During the First Stage of Labor
Pin Li, Qian Huang, Lele Wang, Robert E. Garfield, Huishu Liu
Objective: The purpose of this study was to explore the changes in uterine electrical signals recorded by electromyography in relationship with the progression of cervical dilation during the first stage of labor. Methods: Uterine electromyography was recorded from the abdominal surface for 30 min in 200 nulliparous women presenting at ≥ 370/7 weeks of gestation. Eight groups were defined as follows: Group 1 (n=10), non-laboring patients with no cervical effacement; Group 2 (n=15), patients with cervical effacement;
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p47-52 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.3.028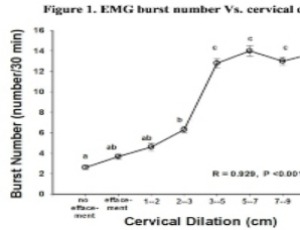
Early Cumulus Cell Removal Increases Cumulative Live Birth Rate while Having No Negative Effect on the Malformation Rate in In vitro Fertilization: A Propensity Score-Matched Cohort Study
Li Juan Sun, Shan Shan Liang, Min Hao Liu, Jia Ping Pan, Mei Yuan Huang, Xiao Ming Teng, Hai Xia Wu
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy and safety of early cumulus cell removal (ECCR) during human in vitro fertilization (IVF). Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed between January 2011 and December 2019. The study enrolled 1,131 couples who underwent IVF treatment with ECCR. After propensity score matching at a 1:1 ratio, 1,131 couples who underwent overnight coincubation of gametes were selected.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 2, p50-55 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.043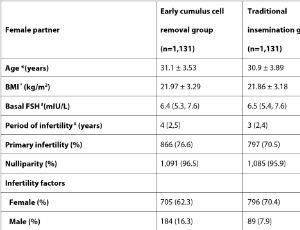
Strong Association Between Placental Pathology and Second-trimester Miscarriage
H J Odendaal
The survival probability of early human conceptions is very low. At least 73% of natural single conceptions have no real chance of surviving six weeks of gestation. After six weeks, survival rates improve rapidly as 90% of the remainder will survive to term. This low fetal loss rate is close to the low rates of 1% - 2.9% for different methods of artificial reproduction. From 16 weeks the rate of loss reduces further, to around 1%.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p51-56 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.2.019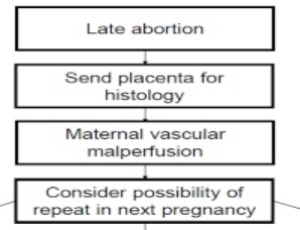
Diagnosis and Management of Chorioamnionitis: A Case Report and Short Review of Literature
Gunjan Bahuguna, Pratyasha Swain, Ashok Anand, Naheeda Shaikh, Rajashree Thatikonda, Nidhi Kurkal, Nisha Jha
Chorioamnionitis is an unprecedented complication arising during labor and the intrapartum period which can lead to adverse outcomes in the mother such as sepsis and postpartum infections and the neonate such as stillbirth, neonatal sepsis, cerebral palsy, and delayed milestones with an increased NICU stay. Several studies have been done over the past years to study the pathophysiology and outcomes of chorioamnionitis.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p53-58 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.3.029
Acute Urinary Retention Due to Non-Peuperal Uterine Inversion - A Case Report
Eustace Ehikioya, Chibuzor Andrew Okoronkwo, Obietonbara Emodi, Okelue Edwards Okobi, Olukunle Samuel Omolayo, Sanu Jarjusey
Non-puerperal uterine inversion (NPUI) is an extremely rare cause of acute urinary retention in women of reproductive age. The delay in diagnosing this rare clinical entity presenting with acute urinary retention further complicates the management. The condition's rarity makes it difficult to carry out a study on its prevalence. Hence, most of the evidence comes from case reports or case series.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 2, p55-61 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.063
The Effectiveness of Methotrexate in Hemodynamically Stable Women with Tubal Ectopic Pregnancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Hossam Abdelfatah Mansour, Ruqayyah Ali Ahmed, Ahmed Mohamed, Ekramy A. Mohamed
Background: Ectopic pregnancy (EP) is a leading cause of acute abdominal pain in gynecology. Most women with tubal EP present hemodynamically stable, making non-surgical therapy a viable option. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of methotrexate (MTX) regimens in this population. Methods: We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs). A comprehensive search of PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, LILACS, SciELO, and CINAHL was conducted from database inception to April 2025.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 2, p55-65 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.6.087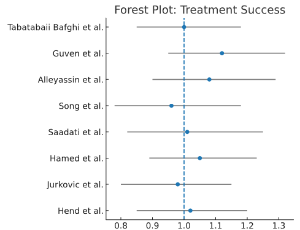
Enterocele with Risk of Intestinal Incarceration: A Case Report
María Cuaresma González, Sonia De Miguel Manso, Paula Suárez Mansilla, Marta Ibáñez Nieto, Esther Ruiz Pérez, Álvaro Sanz Díaz-Heredero
Purpose: To describe the diagnosis and management of enterocele with high risk of bowel ischemia in patients with pelvic organ prolapse. Methods: We describe the clinical case of an 81-year-old patient, hypertensive, obese, anticoagulated because of an atrial fibrillation and pelvic organ prolapse. Initially, conservative treatment was offered due to the high surgical risk, but sometime later the patient came to the emergency department with enterocele and risk of intestinal ischemia.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 3, p56-61 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.044
Postmenopausal Hyperhidrosis and Vasomotor Symptoms in Menopause Should be Treated Differently – A Narrative Review
Carl Swartling, Hans Naver, Philip Cabreus
Postmenopausal hyperhidrosis (PMH) is an important differential diagnosis to vasomotor symptoms (VMS) in menopause. The objective is to describe the differences in clinical presentation and treatment of the two conditions. Patients suffering from PMH represent a unique cohort of patients with primary hyperhidrosis and should therefore not be treated in the same way as those displaying VMS during menopause.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p57-63 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.2.020
The Effects of Vaginal Probiotic Administration on Perinatal Outcomes in Patients with Premature Preterm Rupture of Membrane
Fereshteh Kahvazi, Kaveh Rahimi, Nasrin Soufizadeh, Shamsi Zare, Fariba Seyedoshohadaei, Khaled Rahmani
Preterm premature rupture of membrane is the rupture of the chorionic-amniotic membrane and leakage of amniotic fluid before the onset of labor pains and prior to the 37th week of pregnancy. Preterm premature rupture of membrane (PPROM) occurs in 3% of pregnancies and is the cause of about 25 to 30% of all preterm births. PPROM is an important contributor to perinatal morbidity.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p59-63 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.3.030
Addressing Racial/Ethnic Healthcare Disparities and the Rising Incidence of Syphilis
Elliot M. Levine, Carlos M. Fernandez
Some sexually transmitted infections have posed a particular epidemiologic problem for some communities, in that racial/ethnic disparities have been demonstrated. Syphilis represents a specific example of such an infection, compounding the medical problem further by adding to the serious consequences of its vertical perinatal transmissibility to the neonate, in addition to its sexual, or horizontal, transmission.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 3, p62-64 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.045
Role of Laparoscopy in Treatment of Uterine Arteriovenous Malformation after Failure of Uterine Arteries Embolization
Tamagnini M, Saccardi C, Litta P, Stella A, Bonora M, Vassallo L
Uterine arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an uncommon, potentially life-threatening condition, and the primary therapeutic method is embolization. We describe a case of a 33-year-old woman with acquired uterine AVM accompanied by abnormal vaginal bleeding. The diagnosis was established by Doppler flow ultrasonography and angiography. Because this uterine AVM was extensive, uterine arterial embolization was not conclusive.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 2, p62-69 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.064
Our State Just Passed a Near-Total Abortion Ban
Lucy Brown, Alexandra McKinzie
On Friday, August 5th, the Indiana legislature passed Senate Bill 1 (SB1), a near-total abortion ban, which was signed into law by Governor Holcomb. Exceptions for rape and incest only exist up to 10 weeks. Both medical and surgical abortions must be performed in a hospital. And, if a physician performs the procedure on someone who does not meet these exceptions, it is categorized as a level 5 felony for an “unlawful abortion”.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p64-65 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.3.031
Cerclage Related Complications after Trachelectomy: A Retrospective Case Series
Nicole B. Burger, Nour Abdulrahman, Marjon A. DE Boer, Guus Fons, Judith A.F. Huirne
Purpose: Cerclage related complications in patients after trachelectomy are rare, but can have an immense effect on fertility and obstetric outcomes. We aim to report on cerclage related complications after trachelectomy and to increase awareness and develop preventive strategies. Methods: Retrospective case series from 2006-2021 in a single tertiary referral center, including patients who experienced cerclage related complications after vaginal or abdominal trachelectomy because of early-stage cervical cancer.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p64-75 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.2.021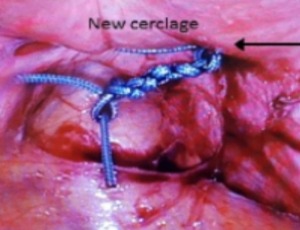
Strawberry Cervix- A Clinical Image of Trichomonas vaginalis: A Case Report
Mequanint Melesse Bicha, Ayalew Lingerih Arefeayinie
Trichomonas vaginalis is a common cause of symptomatic vaginitis in women. Trichomoniasis occurs more frequently in people with multiple sexual partners. Women often present with vaginal discharge, painful intercourse, urinary tract infection symptoms, vaginal itching, or pelvic pain. The strawberry cervix is a finding upon physical examination where the cervix has an erythematous, punctate, and papilliform appearance.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 3, p65-68 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.046
The Safety of High Dose Labetalol in the Pregnant Population
Katherine M. RIDDLE, Pooja M. GREEN, Jennifer A. WILLIAMS, Jason P. HECHT
Medical management of hypertension in pregnancy is indicated for severe range blood pressures. This is diagnosed with either systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥ 160 mm Hg and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥110 mm Hg on two occasions at least 4 hours apart. When this diagnosis is established, fast-acting anti-hypertensive medications can be utilized for acutely severe range blood pressures.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p66-70 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.3.032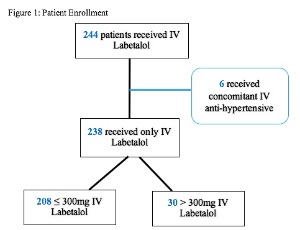
Bacterial Profile and Drug Resistance Patterns among Pregnant Women with Bacteriuria in East Africa: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis
Molla Getie Mehari, Mekdes Molla
Due mostly to the growth of multidrug resistant infections, antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has limited the arsenal of medical professionals against infectious diseases on a global scale. Thus, the purpose of this systematic review and meta-analysis is to present the pooled prevalence, bacterial profile, and current trend of antibiotic resistance in pregnant women who have significant bacteriuria in East Africa.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 2, p66-81 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.6.089
A Comparison of Pregnancy and Neonatal Outcomes in Women with the Hyperandrogenic Disorders Polycystic Ovary syndrome and Cushing’s Syndrome
Mary Roper, Ahmad Badeghiesh, Haitham Baghlaf, Michael H Dahan
How does the risk for adverse obstetric outcomes differ among women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and women with Cushing’s syndrome (CUS)? A retrospective population-based study utilizing data from the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project—Nationwide Inpatient Sample (HCUP-NIS), 2004-2014. 14, 881 deliveries to women with PCOS and 134 deliveries to women with CUS were identified.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 3, p69-77 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.048
Assessing Vitamin D's Impact on Pregnancy Success: A Predictive
Songwei Jiang, Zushun Chen, Xianyan Tang, Shiyang Wei
Infertility, defined as the inability to conceive after at least 12 months of unprotected intercourse, affects up to 15.5% of couples of childbearing age. Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) offers hope for successful pregnancy, though clinical pregnancy rates remain around 40%, with delivery success rates at 20%-30%. Despite numerous influencing factors, age, Antral Follicle Count (AFC), and Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH) serve as the current predictors of ART outcomes.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 2, p70-77 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.065
Ectopic Pregnancy: Vascularity Index as a Novel Diagnostic Criterion
Carlos M. Fernandez, Elliot M. Levine, Irma Sodini, Mai Britt Campbell, Stephen Locher
Since the medical management of ectopic pregnancy (EP) was introduced by Dr. Steven Ory, and published in 1986 in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, diagnostic criteria have been established to predict its successful medical treatment with methotrexate (MTX), including its maximum diameter (MaxDia), its associated human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) level, and whether there was identified cardiac motion (CM).
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p71-78 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.3.033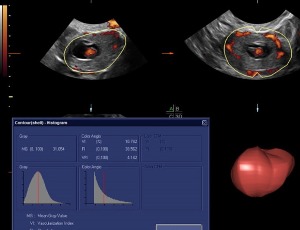
Adnexal Torsion During the Second Trimester of Pregnancy: Mc Burney Incision and Management Strategy
Matthieu Chamagne, Iptissem Naoura, Grégoire Le Conte, Jean Marc Ayoubi
A 33-year-old pregnant woman at 26 weeks gestation presented with abdominal pain in the right iliac fossa. She had a history of a left ovarian cyst. The current pregnancy was normal. The patient was apyretic. Laboratory testing revealed no inflammatory syndrome (leukocyte count of 10G/L and pro c reactive levels were 8 mg/L). In the absence of a diagnosis and given a non-contributory abdominal ultrasound, MRI was requested and revealed a right ovarian teratoma measuring 55 × 73 mm.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p76-78 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.2.022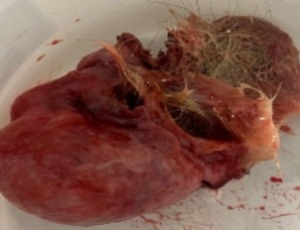
The Effects of COVID-19 on Pregnancy Outcomes, as well as the Impact on Fetuses and Newborns: Cross-Sectional Study
Nasrin Soufizadeh, Farzaneh Hajizadeh, Fariba Seyedoshohadaei, Siroos Hemmatpour, Shamsi Zare, Ashkan Kamalzadeh
Background: Pregnant women, fetuses, and newborns are at a higher risk of exposure to infectious diseases during outbreaks compared to other populations. Objectives: The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of COVID-19 on pregnancy outcomes, as well as the impact on fetuses and newborns in Kurdistan, Iran. The study will cover the period from February 2020 to January 2021.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 3, p78-83 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.049
Umbilical Vein Varix Ultrasound Characteristics and Perinatal Outcomes: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Kristen H. Quinn, Tara Streich-Tilles, Jessica Wade, Julia Cartledge, Jeffrey M. Denney
A. Why was this study conducted? Current recommendations for delivery of all pregnancies affected by umbilical vein varix (UVV), isolated or not, at 37 weeks are not well-supported by published data and needs to be evaluated further. B. What are the key findings? Stratification by isolated UVV versus non-isolated UVV is helpful in determining fetuses at risk for poor outcomes. UVV size or presence of filling defect does not affect perinatal outcomes.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 2, p78-86 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.066
Reproductive Issues in Neurofibromatosis Type 1: An Update
Franco Pepe, Paolo Santoro, Morena Maria Monteleone, Giulio Insalaco
Neurofibromatosistype 1 (NF1) is a complex, multisystem, autosomal dominant disease that has widespread effects on ectodermal and mesodermal tissues. The progress in genetic studies and in cosmetics and aesthetic and reconstructive surgery have ameliorated the quality of life in women with NF1. In this review we update the most relevant data on gynecological life and reproductive issues in women with NF1.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p79-86 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.2.023
Comprehensive Management of Endometriosis: Implementation from Research to Clinical Practice
Elliot M. Levine, Carlos M. Fernandez, Teresa Tam
Appendiceal endometriosis (AE) represents a clinically significant yet frequently overlooked manifestation of endometriosis that may contribute to persistent symptoms and suboptimal treatment outcomes. Multiple comprehensive reviews demonstrate that appendiceal involvement occurs in a notable percentage of women with endometriosis and can present with distinctive symptom patterns.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 2, p82-84 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.6.090
Pneumoperitoneum in a Patient with Endometriosis and Bilateral Salpingectomy after Sexual Activity
Rachid Kaddoura, Karim Abdalbari, Mohammad Ayach, Abdul Kader Weiss
Pneumoperitoneum commonly occurs due to perforated viscus, yet a minority of cases can occur due to gynaecological causes, particularly following sexual activities. While not yet established, various hypotheses have been posited to explain the development of a spontaneous pneumoperitoneum after sexual intercourse. We herein present a unique case of a woman with a history of endometriosis and bilateral salpingectomy who presented with sudden abdominal pain that started after sexual activity.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 4, p84-90 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.050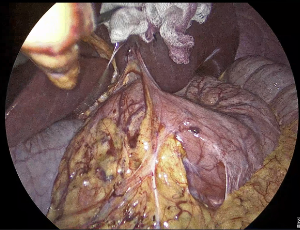
Research Progress of Molecular Classification Guiding Targeted Therapy Combined with Fertility-Preserving Treatment for Endometrial Cancer
Xiyao Ma, Yuanjing Hu
In recent years, the incidence of endometrial cancer has continued to increase and tends to be younger. An increasing number of young patients wish to preserve reproductive function during treatment. Although progestin therapy has a high remission rate, some patients experience hormone resistance, recurrence, or even disease progression, making this traditional treatment unsuitable for everyone.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 2, p85-90 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.6.091
The Evaluation of Autonomic Dysfunction in Adolescent Patients with Premenstrual Syndrome
Ozlem Akbulut, Ilker Ertugrul, Melis Pehlivantürk-Kızılkan, Musa Oztürk, Orhan Derman, Sinem Akgül
Introduction: The relationship between premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and autonomic nervous system (ANS) is complex, with limited data on PMS-related stress further inducing disturbances in the ANS balance. We aimed to investigate the ANS functions through heart rate changes in adolescents with and without PMS.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 2, p87-94 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.067
Shared Experiences and Reflections on Sexual and Reproductive Health Rights
Maheshor Kaphle, Nirmala Regmi
Male involvement in sexual and reproductive health (SRH) is increasingly recognized as a crucial factor for improving maternal, neonatal, and family well-being. This paper shares personal, peer, and community experiences from Nepal, highlighting both the benefits and barriers to men’s engagement in SRH.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2025, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 2, p91-94 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.6.092
Methotrexate Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy
Elliot M. Levine
In their detailed review of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of intact tubal ectopic pregnancies (EPs) treated with methotrexate (MTX), the benefit of single dose MTX treatment was made clear,recognizing the easily administered low-cost treatment as having an 81% success rate.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, Volume 6, Issue 3, p95-95
The Surgical Treatment of Advanced Urinary Incontinence
Wolfram Jäger, André Päffgen, Anna Hagemeier, Peter Mallmann
Purpose: Current treatments of urgency urinary incontinence (UUI) are aimed to reduce the neurological influence on bladder detrusor muscle function. A previous observation after posterior exenteration led to the hypothesis that UUI is caused by a laxity of the uterosacral ligaments (USL). In a previous Clinical Phase I trial in patients with UUI continence was achieved in 40% of patients by replacement of the USL.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 3, p95-106 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.068
Time to Put Women-Controlled Multipurpose Prevention Technologies for Their Protection in Full Gear
Rabeea F. Omar, Mathieu Leboeuf, Michel G. Bergeron
In this concise communication, we shed some light on the urgent need to support and fund women’s sexual and reproductive health research in the area of STIs/HIV/unintended pregnancy prevention that is largely underserved. We stress the need for developing affordable safe and effective innovative vaginal products under the control of women to protect themselves against unintended pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 4, p99-101 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.052
Community Based Study of Rural Tribal Women’s Prepregnancy Health
Chhabra S, Anand N, Bhise K
In addition to health during pregnancy, labour, post-birth, an optimal state of physical and mental health at the onset of pregnancy is essential for health of women and their babies during pregnancy, birth, and post birth over decades. The concept of preconception health has been old; however it has received little attention until recently. There has now been momentum because of persisting sufferings of women during pregnancy, birth and beyond in spite of best of care during pregnancy.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 4, p102-108 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.053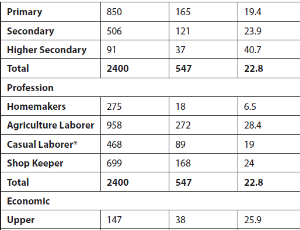
Evidence-based Management of Multiple Gestation
Sophia Nicole Brancazio, Lexi Rose Frankel, Kristen H. Quinn, Jeffrey M. Denney
Objective: The goal of this review is to provide a succinct, yet comprehensive, guide to the antepartum management of multiple gestations. Methods: This narrative review on twins and multiple gestation provides a concise guide for providers with this ever-growing patient population. PubMED was utilized for literature search. Each reference was evaluated and graded for quality of evidence by US Preventative Services Task Force and Cochrane Review guidelines.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 3, p107-123 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.069
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Social and Cultural Issues of Menstruation and Abnormal Uterine Bleeding in Nepal
Maheshor Kaphle, Rajesh Karki, Nirmala Regmi, Pragati Poudyel
Practice difficulties during menstruation and abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) are major global concerns. So, this review will explore the issues of cultural and social for menstruation and AUB in Nepal. Nearly one-third of menstruating girls and women were facing abnormal menstruation and uterine bleeding worldwide. All religions have negative views and enforce prohibitions on menstruation and abnormal uterine bleeding except Sikhism.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 4, p109-113 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.054
Predatory versus Non-Predatory Journals: An Important Distinction to be Made
Elliot M. Levine
The term, “predatory”, is defined in Webster’s dictionary as “inclined or intended to injure or exploit others for personal gain”. This term was first applied to some journals by Professor Beall in 2012, describing those journals as being without scholarly merit and being exploitative for a journal’s gain.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 4, p114-115 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.055
Navigating a Rare Presentation: Case Report of a Large Gartner’s Duct Cyst
Rajesh Kumari, Ashita Aggarwal, Nisha, Manasi Deoghare, Muntaha Khan, Smita Manchanda, Jai Bhagwan Sharma
Background: Mullerian ducts form the female genital tract and wolffian ducts form the male genital tract. In females, sometimes the wolffian duct persists and form the Gartner duct and its total or partial occlusion results in the formation of Gartner’s cyst. It is typically small and asymptomatic and occurs along the antero-lateral wall of vagina. Methods and Results: We report a case of 40-year-old woman who presented with a big mass coming out per vaginum.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 3, p124-126 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.070
Exploration of Real-World Obstetric Data Regarding Cesarean Delivery Rate Since the ARRIVE Trial
Elliot M. Levine, Teresa Tam, Carlos M. Fernandez
The cesarean delivery rate reported for the USA is an important element which impacts parturients in many ways, and which is a measurable factor. It is essential to determine if this rate compares with what had been predicted according to a previously published randomized controlled trial recommending an early term induction of labor. Such a comparison is possible, and should be reviewed, and which follows.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 3, p127-128 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.071
Determinants of Syphilis among Pregnant Women Attending Antenatal Care Clinic at Public Hospital in South West Shoa, Ethiopia, Unmatched Case-control Study, 2023
Bacha Merga Chuko, Fikru Assefa Kibrat, Zufela Sime Gari, Ararso Tafese, Teka Girma, Shambal Negese Marami, Gada Edea
Background: Syphilis is an infectious, sexually transmitted disease caused by the Spirochete Treponema palladium. Untreated maternal syphilis causes adverse pregnancy outcomes such as spontaneous miscarriage, low birth weight, neonatal death, and congenital syphilis. This is a limited case control study to identify determinants of syphilis infections at the study area. Objectives: The aim of this study is to identify determinants of syphilis infections among pregnant women attending ANC clinic at Public hospital in South West Shoa, Ethiopia, 2023.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 3, p129-139 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.072
Influence of Endometriosis on Women's Sexual Health
Tomás Gómez Rodríguez, M.C. Cortés Azuaga, Raquel Cocera, Alfonso Javier Ibañez Vera, Miguel Ángel Infantes Rosales, Esther Díaz Mohedo
Endometriosis is a gynecologic disease caused by endometrial tissue growing outside the uterus resulting in an inflammatory state in the affected area related to estrogenic stimulus [1,2]. An estimated 10% of women in their childbearing age suffer from the disease [3-4] and, most of them with symptoms that reduce their quality of life (QoL). Pelvic pain, usually associated with menstruation (dysmenorrhea), is the main symptom.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 4, p140-144 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.073
Uterocervical and Posterior Cervical Angle Compared with Cervical Length and Bishop’s Score as Predictors of Labor Induction in Singleton Pregnancies: A Prospective Study
Ayse Gizem Yildiz, Mujde Can Ibanoglu, Serap Topkara Sucu, Ali Turhan Çaglar
Labor induction is the stimulation of uterine contractions before the spontaneous onset of labor. The goal is to achieve vaginal delivery within 24 hours. Nowadays, labor induction has become one of the most frequently performed procedures due to maternal and fetal conditions.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 4, p145-153 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.074
Effect of Video-based Multimedia Information on Anxiety Levels and Pain Perception in Patients Undergoing Endometrial Sampling Procedure: A Prospective Randomized Case-control Study
Jule Eriç Horasanlı, Hasan Energin
The endometrial sampling procedure (ESP) with Pipelle is frequently used for diagnostic purposes in cases where endometrial pathologies are suspected in abnormal uterine bleeding [1,2]. Endometrial sampling in the office setting has replaced the diagnostic dilatation and curettage (D&C) procedure often performed in the hospital.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 4, p154-159 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.075
Tumor Size Impact on Endometrial Cancer Prognosis
Ahmad Ameri, Ainaz Sourati, Mansour Lesan, Nazanin Rahnama, Fereshteh Talebi, Zeinab Abiar, Sima Davoudi, Sanaz Poshtmahi, Simin Badiei Moghadam, Pooya Ameri, Azam sadat Mousavi, Nadereh Behtash
Endometrial cancer (EC) is a prevalent gynecological malignancy, with an increasing incidence of 2.5% every year. Although it is highly curable when found early, still we are expected to some locoregional or distant recurrence of this tumor in some cases with different survival rates [1-3].
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 4, p160-169 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.076
Puerperal uterine inversion
Asaf Romano, Gil Zeevi
A 30-year-old woman, in her fourth pregnancy ,at 39+1 weeks gestational age ,experienced a precipitous vaginal delivery. Following delivery, the placenta remained attached and did not spontaneously separate after 20 minutes.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2024, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 4, p170-171 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.5.077
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
