Loading
Journal of Diabetes and Clinical Research
ISSN: 2689-2839
All Articles
Integrated Community Diabetes Model: Future of Diabetes Services and Way Forward?
Parijat De
Prevalence of diabetes is increasing. Diabetes is more prevalent in the socially deprived, ethnic minority population (based on continuing rise in elderly population, growing obesity and BME groups). Compliance is a major stumbling block in the management of most long-term conditions including diabetes.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p1-1 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.001
Atypical Diabetes Mellitus Presentation, an Early Warning of Pancreatic Carcinoma
Holtrop R, Creyghton WM, Holtrop J
In 2020 we published a case-series detailing patients who died from pancreatic cancer (Appendix). These three patients were diagnosed with new-onset type 2 mellitus or deterioration of pre-existing type 2 diabetes shortly before their pancreatic malignancy was detected.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p1-5 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.030
Ephrin B1 Regulates Inflammatory Pathways in Retinal Müller Cells
Li Liu, Youde Jiang, Mohamed Al-Shabrawey, Jena J. Steinle
The role of inflammation has been accepted as a factor in the complications of diabetic retinopathy. Discovery of the upstream regulation of these inflammatory factors has remained a challenge. In this study, we explored the actions of ephrin B1 in retinal Müller cells and their actions on inflammatory proteins. We used diabetic human and mouse samples, as well as Müller cells in culture to measure ephrin B1 in Müller cells.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p1-7 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.056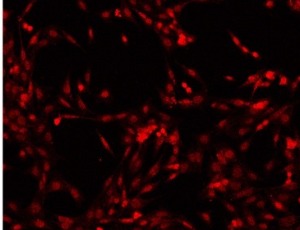
Can Vitamin D Supplementation Reduce Insulin Resistance and Hence the Risks of Type 2 Diabetes?
Barbara J Boucher
The question of whether or not correction of vitamin D deficiency might reduce the risks of later type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has been under debate for many decades. The necessity of vitamin D for normal insulin secretion was first identified experimentally in the 1980s.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p1-8 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.011
A Customized Artificial Pancreas System with Neural Network based Model Predictive Control for Type 1 Diabetic Rats
Omer Batuhan Kirilmaz, Masoud Mahdavi, Hoo Sang Ko, H. Felix Lee, Sarah Park, Guim Kwon
Advances in sensor and computing technology have enabled researchers to develop artificial pancreas systems (APS) that can mimic the glucose regulation function of a healthy pancreas to treat type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). APS use a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) sensor to read the latest blood glucose level (BGL).
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p1-9 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.4.049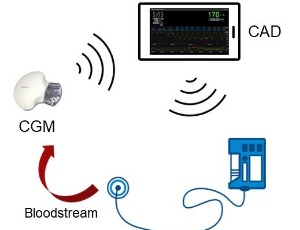
Elevated Opioid Growth Factor Alters the Limbus in Type 1 Diabetic Rats
Patricia J. McLaughlin, Joseph W. Sassani, David Diaz, Ian S. Zagon
Ocular surface complications occur in more than 50% of individuals diagnosed with diabetes. The financial and health-related burden of diabetes is increasing annually. Several major ocular complications associated with diabetes involve the limbus. The vascular limbus, adjacent to the avascular cornea, is the source of circulating growth factors, elevated glucose, and cytokines for the cornea.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p1-10 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.4.054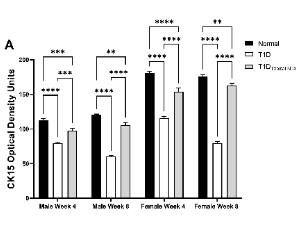
Discriminatory Ability of Adiposity Phenotypes in Identifying Cardiometabolic Disorders in Indigenous and Non-indigenous African Populations
Clement Nyuyki Kufe, Jean Claude Mbanya
A population-based cross-sectional study recruited 1921 participants from the settled Fulani, nomadic pastoral Fulani and the general population. Body weight (BW), height, waist circumference (WC), and hip circumference (HC) were measured and body mass index (BMI), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), waist-to-height ratio (WHtR), Conicity Index (Cindex), body adiposity index (BAI), body roundness index (BRI) and body shape index (ABSI) were determined. The associations of anthropometric indices with cardiometabolic disorders were assessed by multivariable adjusted logistic regression and the area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve compared the predictive abilities.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p1-18 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.065
Global Syndemic of Metabolic Diseases: Editorial Comments
Gundu H. R. Rao
Editorial is usually a brief article, written by the editor that expresses publishers or journals collective views on a current issue. As an Emeritus Professor, I have taken the liberty of writing these editorial comments, at the invitation of the Editorial Board of the Journal of Diabetes and Clinical Research.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p2-4 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.002
The Profiling and Role of miRNAs in Diabetes Mellitus
Michael Kim, Xiaokan Zhang
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is an age-related metabolic disorder affecting 347 million people in modern society. Expanding its prevalence beyond developed countries, DM has emerged as a global public health issue associated with a high morbidity and mortality.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p5-23 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.003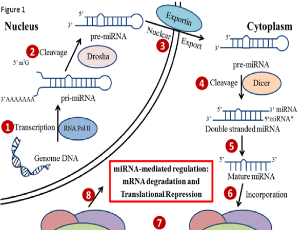
Adapting the Escape Room to Engage Learners Two Ways During COVID-19
Laura Wynn
When creating the project, “An Escape Room Simulation Focused on Renal-Impairment for Prelicensure Nursing Students” [1] the author’s goal was to increase positive health outcomes for patients with acute kidney injury (AKI). AKI is complicated, but nurses who can help identify those at risk for the disorder and help initiate early treatment can improve patients’ results.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p6-8 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.031
A Clinical Case Report: Utility of Amniotic Membrane in Treating a Geriatric Diabetic Patient with a Chronic Pressure Ulcer
Alison L. Ingraldi, Kristina Galbreath, Denise Jones, Darlene Lee, Aaron J. Tabor
Chronic wound closure is the inability for a wound to progress through the standard wound healing stages and timeframe, often stalling during the inflammatory stage. This paper presents a two-year open wound endured by a Native American patient of geriatric age and uncontrolled type II diabetes based on elevated A1c levels. Multiple therapeutic modalities had been attempted to close the wound, without improvement.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p8-14 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.057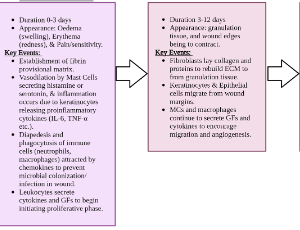
Investigation of Regimen Adjustment for T2DM Patients Inadequately Controlled on Basal Insulin – Interpretation of the 4200 Study
Wenying Yang
Epidemiological survey indicated that majority of Chinese T2DM patients were with postprandial hyperglycemia, which may be related to more significant decline of ? cell function and more carbohydrates in dietary structure.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p9-11 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.012
Validation of a New Test for Assessing the Quality of Life Perceived in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
Pala L, Cosentino C, Acciaioli S, Dicembrini I, Lazzeretti L, Rotella F, Mannucci E
The World Health Organization defines quality of life (QoL) as “the perception that an individual has of his life, in the context of the culture in which he lives, integrating personal goals, expectations and concerns, well-being and discomfort”.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p9-16 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.032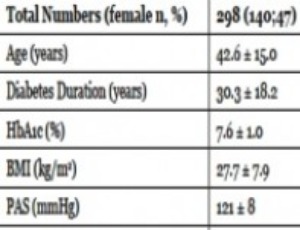
A Machine Learning Study of 534,023 Medicare Beneficiaries with COVID-19: Implications for Personalized Risk Prediction for People Over 65
Chen Dun, Christi M. Walsh, Sunjae Bae, Amesh Adalja, Eric Toner, Timothy A. Lash, Farah Hashim, Joseph Paturzo, Dorry L. Segev, Martin A. Makary
The global outbreak of COVID-19 has resulted in over 378 million infections and worldwide deaths have surpassed 5.6 million. In the United States, there have been over 75 million confirmed cases and over 886,000 deaths as of February 1, 2022.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p10-16 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.4.050
Long-term Effects of Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Six-year Follow-up Retrospective Analysis
Soo-Bong Choi
The aim of this study was to evaluate the long-term effects of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) therapy on the improvement of metabolic control and beta-cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. A single-center retrospective observational study was carried out in patients with T2DM who required CSII therapy due to suboptimal glycemic control. T2DM patients treated with the DANA-R Diabe care insulin pump (SOOIL Development Co., Ltd.) was followed for 6 years.
J Diabetes Clin Res, Volume 8, Issue 1, p10-18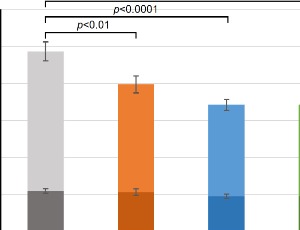
A Commentary on “Better TIR, HbA1c, and Less Hypoglycemia in Closed-loop Insulin System in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Meta-analysis”
Xiaojuan Jiao, Yunfeng Shen
Our team’s previous meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of closed-loop insulin system (CLS) in non-pregnant individuals with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). In this study, we aim to discuss the broader application of CLS in a more diverse population and address the current challenges and future development directions.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p11-14 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.4.055
Insulin Signal Transduction is Impaired in the Type 2 Diabetic Retina
Youde Jiang, Li Liu, Hainan Li, Jie-Mei Wang, Jena J. Steinle
With increasing rates of obesity, rates of type 2 diabetes and diabetic complications are expected to rise exponentially over the next few decades (American Diabetic Association). A key feature of type 2 diabetes is a resistance to insulin. Insulin signaling is key to a number of physiological processes, including glucose metabolism, cell growth, general gene expression, and apoptosis.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p12-15 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.013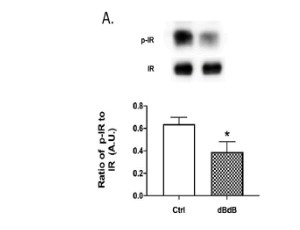
Use of Sodium-Glucose Co-transporter-2 Inhibitors after Acute Myocardial Infarction
Nasser Mikhail
Whether sodium-glucose co-transporters-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have beneficial effects on cardiovascular (CV) events and mortality if given within few days from acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is unknown. The DAPA-MI trial (n= 4,107) is the only available study designed to evaluate the impact of administration of dapagliflozin on CV outcomes and mortality if started within 10 days from occurrence of an AMI.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p15-17 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.058
Commentary on – ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines: Fasting during Ramadan by Young People with Diabetes
Asma Deeb
This is a commentary on the recent work by our group on fasting during Ramadan by young people with diabetes which was published as ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines. In this commentary, themes of selected studies published following the guidelines release are highlighted.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p16-19 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.014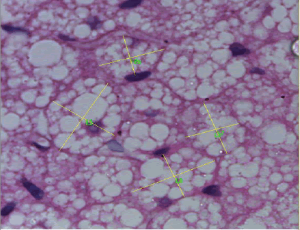
Introducing m-Health and Digital Diabetes Apps in Clinical Pharmacy Education in Germany
Emina Obarcanin, Bushra Ali-Sherazi, Armin Dabidian, Sabina Schlottau, Maira Anna Deters, Stephanie Läer
Germany was the first country worldwide to implement German Digital Healthcare Act in 2019 to allow prescription and reimbursement of digital health applications (Digitale Gesundheitsanwendungen, DiGA). The German Federal Government has prioritized increased usage of mobile-Health (m-Health: use of mobile devices and digital technology in health care), recommending that physicians, other healthcare professionals, and patients work together to utilize the potential benefits of such technology.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p17-19 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.4.051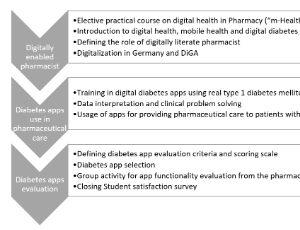
Vitamin D and Insulin Resistance in Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia-a Commentary and Natural Expansion
Alan Sacerdote
In our previous focused review, the journal emphasized Type 2 diabetes (T2DM), excluding intimately associated disorders that should be considered integral components of the insulin resistance (IR) syndrome e.g., polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH), and gout.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p17-27 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.033
Semaglutide for Treatment of Obesity-Related Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction in Patients with and without Diabetes
Nasser Mikhail, Soma Wali
The glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonist semaglutide is effective for the treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The purpose of this article is to define the therapeutic role of semaglutide for obesity-related heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HF-pEF). Methods: Critical review of 2 recent randomized trials, the Subjects with Obesity-related Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (STEP-HFpEF) and STEP-HFpEF DM.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p18-23 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.059
Enhancing Clinical Collaboration: Interface Linking between Laboratories and Clinics for Translational Healthcare
Pradeep Kumar Dabla, Harleen Kaur Sethi
Clinical laboratories are pivotal in modern healthcare, providing essential diagnostic information that influences patient management and healthcare efficiency. Technological advancements and economic pressures have continuously shaped laboratory medicine, leading to significant transformations in diagnostic capabilities. This article explores the evolving role of clinical laboratories, emphasizing their impact on disease prevention, early diagnosis, and patient safety.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p19-21 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.066
Sex Differences in Diabetic Ocular Surface Complications and Dysregulation of the OGF-OGFr Pathway
Ian S. Zagon, Joseph W. Sassani, Patricia J. McLaughlin
Diabetes is a chronic disorder that affects more than 500 million individuals worldwide. It is a life-long disease with complications that attack nearly all other systems within the body. Although there is a slight increase in the prevalence of diabetes in males, ocular surface complications are equally present in males and females.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p20-24 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.4.052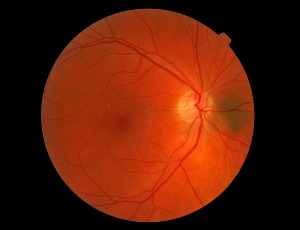
Perivascular Adipose Tissue: Quantitative Analysis by Morphometry and Stereology in Rodents
Felipe Demani Carneiro, Stephanie Christinne Sinder Mello, Emiliana Barbosa Marques, Rogerio Barbosa Magalhaes Barros, Christianne Bretas Vieira Scaramello, Caroline Fernandes-Santos
Virtually all arteries, except brain arteries, are surrounded by a significant amount of perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT). It was thought that the PVAT was only responsible for the mechanical protection of vessels against neighboring tissues during contraction.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p20-29 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.015
Diabetes Mellitus and Dengue
Viroj Wiwanitkit
Diabetes mellitus is a common metabolic disorder that present with abnormal glucose metabolism. This metabolic disease is prevalent in many countries, worldwide. It is no doubt there might be a chance that diabetes mellitus might co-occur with other medical problems.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p24-25 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.004
Lifestyle Modification Practice and Associated Factors among Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Oromia: A Multicenter Study
Dursa Hussein, Tinsae Abeya Geleta, Amanuel Girma, Tadesse Bekele, Derara Girma, Seifu Mohammed Ibrahim, Meron Seyoum Lakew, Bedo Megersa Kumbe, Befekadu Tesfaye Oyato
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood glucose levels due to insulin irregularities. It is frequently accompanied by difficulties in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Despite the significant loss of life and resources associated with DM, management remains insufficient. This management typically involves pharmacologic interventions and lifestyle modifications (LSM). However, a majority of patients and caregivers tend to disregard LSM in the management of type 2 diabetic patients.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p24-34 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.060
The Clinical Utility of Outpatient Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Establishing Insulinoma Diagnosis in a Patient with Impaired Nocturnal Hypoglycemia Awareness
Aundrea E. Loftley, Christopher Woody, Colin Russell
Insulinomas are insulin secreting tumors arising from spontaneous mutations of the ductal, acinar, or islet cells of the pancreas. They are rare, having an incidence of only four cases per million people per year. Patients typically present with fasting hypoglycemia, experiencing neurologic symptoms like confusion, changes in vision, or abnormal behavior and autonomic symptoms like palpitations, diaphoresis, or tremulousness.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p26-36 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.005
Decline in Physical Activity after Age 35 Increases the Risk of Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Diabetes: A Cross-sectional Analysis of the MIDUS Study
Tomoya Sato
Data were analyzed from 1,395 participants in the Midlife in the United States (MIDUS) study, including biomarker subsamples. Participants reported their physical activity levels during young adulthood and currently (≥ 20 min, three times per week). Participants were categorized as persistently active, increased, decreased, or persistently inactive. Obesity was defined as body mass index (BMI) ≥ 30 kg/m², insulin resistance by HOMA-IR ≥ 2.8, and diabetes by self-reported diagnosis. Multivariable logistic regression was used to assess associations.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p27-37 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.068
Identification of Risk Markers for Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study with Focus on Quality Assurance Based on Real World Data
C. Laustsen, J. Rungby, E. Christensen, L. Christrup, N. J. Jensen
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a metabolic disease defined by hyperglycemia. If not treated, chronic and even short periods (i.e. weeks) of undesirable hyperglycemia increases the risk for developing diabetic microvascular complications such as retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy, foot ulcers and amputations, and macrovascular complications such as cardiovascular disease including stroke
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p30-36 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.016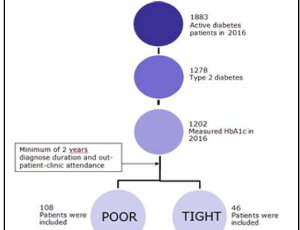
To Quell Childhood Obesity: The Pacific Ending Childhood Obesity Network’s Response
Amerita Ravuvu, Si Thu Win Tin, Solene Bertrand, Elisiva Na’ati, Ilisapeci Kubuabola
The need to accelerate collective and concerted action to combat Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) and childhood obesity is particularly relevant in the Pacific context.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p33-36 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.034
Epac1 Regulates Ephb1/Ephrin B1 in Retinal Müller Cells
Li Liu, Youde Jiang, Jena J. Steinle
Eph B1/Ephrin B1 signaling has been shown to play a role in inflammation and pain in some targets; however, its upstream regulation is less clear. To investigate whether exchange protein for cAMP1 (Epac1) can regulate EphB1/ephrin B1 in retinal Müller cells, we generated Epac1-Müller cell specific knockout mice. We used protein analyses to show that Epac1 regulates both EphB1/ephrin B1, as well as high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) and NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3).
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p35-39 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.061
Commentary: A Herbal Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes – The Dangers of Adulterated and Falsified Products
David W Holt, Atholl Johnston
In 2018, our group published a letter in The Lancet detailing a case in which a patient had taken a herbal preparation to treat her diabetes [1]. In essence, our laboratory was approached by the treating physician after the patient, a 58 year old lady of south Asian origin with a 30 year history of type 2 diabetes said that, during the previous two years, she had replaced some of her prescribed anti-diabetic medication with a herbal remedy purchased in India.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p37-39 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.006
Implementation of Technology in the Follow-up of Patients with Diabetes: Is it Possible in a South American Country?
Diana Henao
Despite better treatments and technology available in usual clinical practice, achieving a good glycemic control in patients with diabetes is challenging. In times of SARSCoV- 2/COVID-19 infection, chronic diseases like diabetes have been associated with adverse outcomes.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p37-39 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.035
Clinician's Review of Thyroid and Parathyroid Disease
Aundrea E. Loftley
The presentation of thyroid disease is on a spectrum with clinical presentations and disease severity ranging from subclinical to critical. The principal function of the thyroid gland is to produce T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine). The hypothalamus and pituitary glands release thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) respectively, and this stimulates the release of T3 and T4 directly from the thyroid gland.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p37-44 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.017
BCG Immunotherapy: Promising Protection from COVID-19 and Other Infectious Diseases in Type 1 Diabetics
Denise L Faustman, Miriam Davis, Willem M Kuhtreiber
Individuals with type 1 diabetes are more vulnerable than the general population to morbidity and mortality from infectious disease, including COVID-19. Over the last 20 years, the >100-year-old tuberculosis vaccine, known as Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG), has been observed in global populations to protect from viral, bacterial and parasitic infections, among others.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p38-43 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.069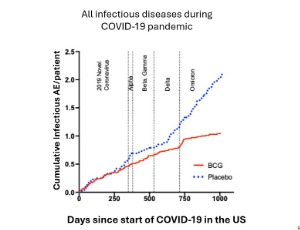
Obesity, Family History of Diabetes, and Consanguineous Marriages are Risk Factors among Urban Population in South Indian City of Bengaluru
Aravinda Jagadeesha
In 2017, approximately 424.9 million adults (age 20- 79 yrs) were affected by diabetes, with 4 million deaths. Global diabetes burden is estimated to increase up to 628.9 million people. Moreover, diabetes care costed approximately $727 billion in 2017.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p40-42 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.007
CERT-Dependent Ceramide Transport, A Crucial Process in Cells
Cécile L. Bandet, Eric Hajduch
In mammalian cells, ceramides are central lipids in sphingolipid metabolism and serve both as signaling lipids and as precursors for other bioactive sphingolipids, ranging from complex glycosphingolipids to “simpler” lipids such as ceramide-1-phosphate, sphingomyelin (SM), sphingosine and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P).
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p40-45 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.036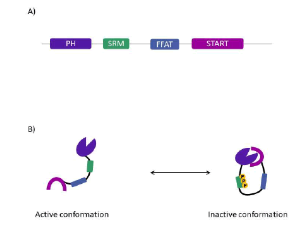
Comorbidity of Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia among Factory Workers: A Study on the Interrelationship of Metabolic Disorders in Occupational Settings
Benjamin Tetteh Mensah, Dorinda Naa Okailey Armah, Jemima Okyere, Lawrence Annison, Samuel Antwi-Baffour
Hyperglycemia, characterized by elevated blood glucose levels, often leads to diabetes mellitus and severe complications if unmanaged. Globally, hyperglycemia is a pressing public health issue, exacerbated by increasing diabetes prevalence. In sub-Saharan Africa, including Ghana, the rise in diabetes cases is alarming, necessitating urgent health interventions. Concurrently, dyslipidemia, marked by abnormal lipid levels, contributes significantly to cardiovascular diseases. This study aims to investigate the comorbidity of hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia among factory workers in an urban center in Ghana, providing insights into this high-risk group's health status.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p40-47 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.062
Altered Peak C-peptide and Fasting Blood Glucose in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Mengxiang Zhang, Rui Ding, Zuqun Wang, Juan Zhang, Jing Liu, Juan Wang
ASD refers to a group of complex neurodevelopmental disorders, characterized by deficits in social communication, interaction and demonstrating restricted, repetitive, and stereotyped patterns of behavior. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention forecasted that the prevalence of ASD would be 1 in 45 in USA.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p43-52 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.008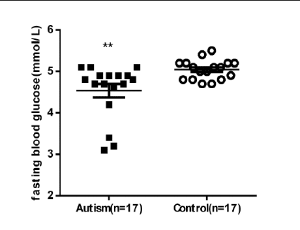
Inhibition of Sortilin Improves Retinal Function in Diabetic Mice Through Decreased Inflammatory Mediators
Li Liu, Youde Jiang, Robert Wright, Mohamed Al-Shabrawey, Jena J. Steinle
Inflammation is a key factor in retinal damage in response to diabetes. Sortilin represents a new regulator of retinal inflammation. Sortilin is involved in over 50 different signaling cascades. To investigate sortilin in the diabetic retina, we first measured protein levels in retinal lysates from diabetic humans and diabetic mice. We then inhibited sortilin using a small molecule inhibitor, AF38469, and evaluated retinal function using electroretinogram (ERG) and fluorescein angiography.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p44-51 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.070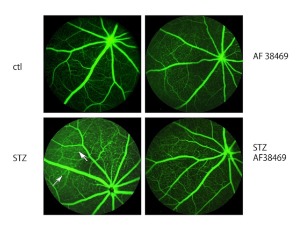
Neuromotor Impairment, Hearing Loss and Blindness in a Preclinical Mouse Model of Charcot Marie-Tooth Disorder
Sergio Gonzalez-Gonzalez, Chantal Cazevieille
In the peripheral nervous system (PNS), Schwann cells (SCs) are responsible for myelin production, which contributes to axonal protection and allows for efficient action potential transmission. Unfortunately, acquired and hereditary demyelinating diseases of the PNS are numerous and affect an increasing number of people.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p45-53 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.018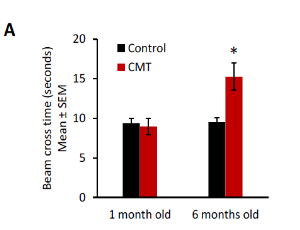
Plasma Non-Esterified Fatty Acids (NEFA) in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Evidence on Pathophysiology
Kailash Chandra, Vineet Jain, Swatantra Kumar Jain
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a metabolic dysfunction characterized by elevated levels of blood glucose as well as impaired lipid and protein metabolism. The mobilization of fatty acids is augmented in insulin resistance due to the failure of lipolysis inhibition by the hormone that further augments the increase in plasma NEFA levels.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p46-50 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.037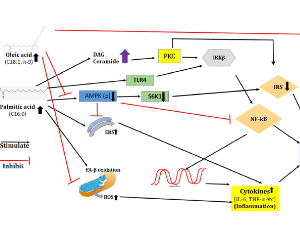
Incidence of Diabetic Mellitus among HIV Patients Receiving Antiretroviral Therapy in Ethiopia: Ten Years Retrospective Follow-up Study
Lidiya Tekle Gebreyohannes, Addisu Dabi Wake
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is an important chronic comorbid condition that occurs in people living with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). It is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Many cases of comorbidities with diabetes mellitus have been reported, particularly in areas of the world where the prevalence of HIV is high. The rate of diabetes hospitalizations among HIV-infected individuals increased from 3.9 to 8.4 per 100 hospitalizations. Although the cost of HIV care has increased, the burden of DM among people living with HIV has economic consequences.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p48-55 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.063
Short Commentary on African Cuisine-Centered Insulin Therapy: Expert Opinion on the Management of Hyperglycaemia in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Andrew E. Uloko, Roberta Lamptey, Jean Claude Mbanya
The traditional African diet is considered a very rich source of nutrition being largely whole with minimal processing [1]. There are unique challenges when managing Diabetes in Africa especially when making nutritional recommendations. An appropriate diet protects organ (heart, liver, pancreas etc.) health and vice versa.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p51-54 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.038
From Seed to Solution: Expert Insights on Sesame’s Role in Diabetes and Beyond
Ali Jafari
Sesame (Sesamum indicum L) has garnered attention for its potential in diabetes management due to its rich bioactive compounds, including sesamin, sesamolin, and unsaturated fatty acids. This commentary explores recent advances in sesame research, emphasizing its role in improving glycemic control, lipid profiles, inflammation, and oxidative stress, as evidenced by a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mechanistic insights reveal sesame’s effects on PPARα activation, Nrf2 signaling, and NF-κB suppression, which underpin its metabolic benefits.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p52-59 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.071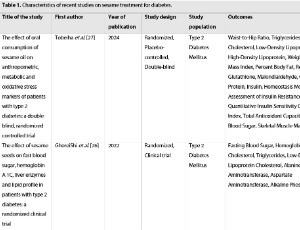
Cut-off Value of Random Blood Glucose among Asian Indians for Preliminary Screening of Persons with Prediabetes and Undetected Type 2 Diabetes Defined by the Glycosylated Haemoglobin Criteria
Priscilla Susairaj, Chamukuttan Snehalatha, Arun Raghavan, Arun Nanditha, Ramachandran Vinitha, Krishnamoorthy Satheesh, Desmond G Johnston, Nicholas J Wareham, Ambady Ramachandran
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) remains undiagnosed for many years in large number of persons living in developing countries. The cost of diagnostic tests and the invasive procedures involved in conventional screening methods remain a major setback to timely testing
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p53-58 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.009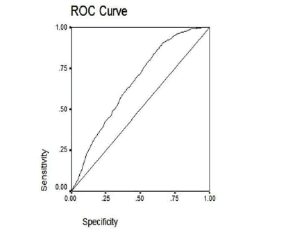
Hyperglycemia and diabetes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19
Nasser Mikhail, Soma Wali
The prevalence of diabetes in COVID-19 patients ranges from 5.3% to 58% representing the second comorbidity after hypertension. However, when adjusted for age, diabetes prevalence among COVID-19 patients is similar to its prevalence in the general population.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p54-58 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.019
Lessons from My Grandmother’s Garden: Intergenerational Learning and Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Jasmin Tahmaseb McConatha, Melina McConatha, Nikki DiGregorio
Researchers suggest that grandmothers are often the invisible support helping to maintain the health and well-being of the family and community. Studies have explored the important role that grandmothers play in the well-being of families over time.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p55-58 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.039
Effect of UV Photo Functionalization on the Antimicrobial Properties of Implants in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hakob Khachatryan, Lazar Yessayan, Gagik Hakobyan
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of ultraviolet UV photo functionalization on the antimicrobial properties in implants installed in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The study included 74 patients with diabetes with unilateral/bilateral missing teeth (aged 36 to 63 years). The participants were randomly divided into 2 groups; Group-A included 38 patients with UV photo functionalized 204 implants and Group-B included 36 patients with non UV photo functionalized 183 implants.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p56-64 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.064
Screening of Peripheral Arterial Disease in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus – A Commentary Article
Nahid Hashemi-Madani, Mohammad.E. Khamseh
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a prevalent form of atherosclerotic vascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Diagnosis and treatment of PAD is more challenging in these patients. Presence of concomitant neuropathy masks typical pain symptoms, and typical criteria for intermittent claudication are not clearly met.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p59-63 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.040
Resveratrol Treatment Reduces Neuromotor Impairment and Hearing Loss in a Mouse Model of Diabetic Neuropathy and Nerve Injury
Sergio Gonzalez-Gonzalez, Chantal Cazevieille, Bastien Caumes
In the peripheral nervous system (PNS), Schwann cells (SCs) are responsible for myelin production, which contributes to axonal protection and allows for efficient action potential transmission. Unfortunately, acquired and hereditary demyelinating diseases of the PNS are numerous and affect an increasing number of people.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p59-67 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.020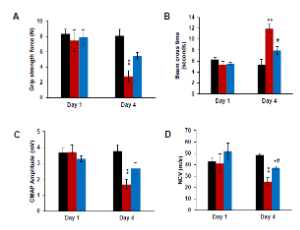
The Diabetic Shoulder – A Literature Review
Sana’a A. Alsubheen, Joy C. MacDermid, Tom J. Overend, Kenneth J. Faber
The shoulder complex is composed of three bony structures: the clavicle, scapula, and humerus, which are connected to form three synovial (glenohumeral, acromioclavicular, and sternoclavicular) and two functional (scapulothoracic and subacromial) joints.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p59-70 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.010
Management of Metabolic Diseases: From Reactive Care to Preventive Strategies
Gundu H. R. Rao
Metabolic diseases such as hypertension, obesity, diabetes, and vascular disorders have reached epidemic proportions worldwide [1–6]. Despite major advances in medicine, cardiovascular disease has remained the leading cause of death for more than a century. Among these disorders, diabetes mellitus stands out as a major contributor to morbidity and mortality, placing a heavy burden on patients, healthcare systems, and economies.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p60-62 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.072
Dysregulation of the OGF-OGFr Pathway and Associated Diabetic Complications
Patricia J. McLaughlin, Joseph W. Sassani, Ian S. Zagon
Diabetes is a major healthcare concern worldwide. In addition to the financial burden estimated at $760 billion, the human suffering related to complications of diabetes as well as the disease itself are immense. Complications associated with diabetes affect both men and women, but there is a higher incidence reported in the aging population, women, and people of color.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p64-67 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.041
Risks and Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy in Children and Young People with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Rebecca Louise Thomas, Sze May Ng
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is associated with microvascular and macrovascular complications.Duration of diabetes, poor glycaemic control, high blood pressure and proteinuria are reported risk factors contributing to the development of diabetes related complications.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p68-74 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.021
Prevalence of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Osteoarthritis Patients Derived from Primary Care Records: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies
Xiaoyang Huang, Ross Wilkie, Mamas A Mamas, Dahai Yu
Health intelligence on the frequency of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and its risk factors identifies targets and populations for preventative strategies and allows evaluation of health outcomes, behaviors and interventions in populations and health care settings.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p68-77 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.042
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown Measures on Diabetic Retinopathy Services in the East Kent Area of the United Kingdom - A Special Focus on the Pregnant Diabetic
Alamin Alkundi, Rabiu Momoh
The COVID-19 pandemic has shaped activities across almost all human endeavours. Changes are still ongoing to accommodate all the challenges it poses. The healthcare sector, working closely with governments of nations and regulatory agencies, has helped to control the impact of this highly contagious virus.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p75-77 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.022
Epidemiological Characteristics of Diabetic Foot and Affecting Factors for Amputation in China
Weibo Zhao, Zhangrong Xu, Aihong Wang
With the increased prevalence of diabetes from 0.67% in 1980 to 11.2% in 2017, the prevalence of diabetic foot has been growing in China in recent years. Diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) was one of the most serious complications of diabetes. Complicated general condition, severe infection and poor outcomes were feature characteristics of Chinese DFU patients.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p78-80 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.043
Anti-diabetic Potential of Aqueous Extract of Moringa oleifera, Ocimum gratissimum and Vernonia amygdalina in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats
Ayobami AL, Kade EA, Oladimeji KA, Kehinde S, Gurpreet K
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is characterized by absolute or relative deficiencies in insulin secretion and insulin action associated with chronic hyperglycemia and disturbances of carbohydrate, lipid and protein metabolism. It results from either defect in insulin secretion by the pancreas or inability of the cells to utilize the insulin produced.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p78-85 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.023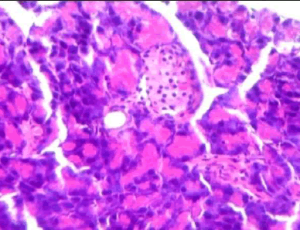
Commentary on Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity
Erica M. Garner, Kevin D. Niswender, Gitanjali Srivastava
Obesity is an undertreated global epidemic that increases morbidity and mortality by causing widespread harm to multiple organ systems. Severe obesity or obesity with associated comorbidities warrants a comprehensive treatment approach including lifestyle modifications plus either bariatric surgery or prescription medications.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p81-84 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.044
New Recommendations for T2D Management: Beneficial Impact of Exerkines on Pancreatic β-Cells Function and Glucose Homeostasis in Skeletal Muscle
Allan LANGLOIS, Julie VION, Aurore DUMOND, Michel PINGET, Karim BOUZAKRI
Nowadays, physical activity is strongly considered as an effective strategy in both preventing and treating type 2 diabetes (T2D). Indeed, it is well established that exercises improve β-cell insulin signaling, insulin secretion, prevent pancreatic β-cell failure and impacts glucose homeostasis regulation in T2D patients.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 3, p85-93 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.045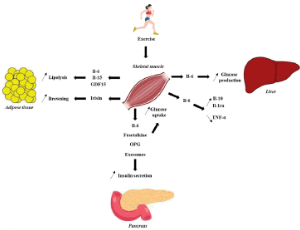
Improved Wound Closure Rates and Mechanical Properties Resembling Native Skin in Murine Diabetic Wounds Treated with a Tropoelastin and Collagen Wound Healing Device
Robert S. Kellar, Robert B. Diller, Aaron J. Tabor, Dominic D. Dominguez, Robert G. Audet, Tatum A. Bardsley, Alyssa J. Talbert, Nathan D. Cruz, Alison L. Ingraldi, Burt D. Ensley
Chronic, non-healing, or slow to heal wounds present a significant and growing health problem in the United States, with an estimated 6.5 million people affected, at an annual cost of US $20 billion, with the highest risk groups represented by the elderly and the increasing prevalence of lifestyle diseases such as diabetes and obesity.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p86-99 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.024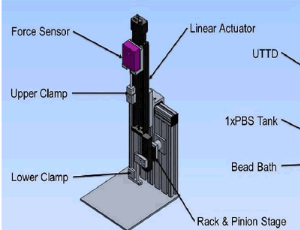
Colchicine in COVID-19 —The Colcorona Trial
Protásio Lemos da Luz
Colcorona was a multicenter, international study promoted by the Montreal Heart Institute, Canada, whose main objective was to test the effects of colchicine in non-hospitalized patients with COVID-19. So far, the majority of studies addressed hospitalized patients which is understandable since mortality occurs mainly among those individuals.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p94-95 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.046
Lessons from Laron Syndrome on the Role of IGF-I on Carbohydrate Metabolism
Zvi Laron
Laron Syndrome (LS) (OHIM #262500:ICD-10: primary growth hormone insensitivity) is a rare fully penetrant autosomal recessive type of dwarfism caused by exon deletion or mutations of the growth hormone receptor (GH-R) gene. The majority of the mutations are in the extracellular domain of the receptor and few are in the trans membranal or intracellular domain.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p96-98 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.047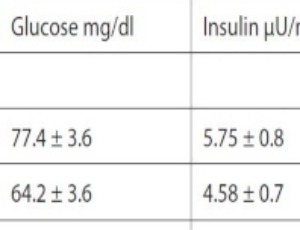
The Emerging Target Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management
Sónia Rocha, M. Luísa Corvo, Eduarda Fernandes, Marisa Freitas
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic multifactorial disorder affecting an increasing number of patients worldwide [1]. DM can be classified into four general categories, based on the classification reported in 2021 by the American Diabetes Association
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 4, p99-105 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.048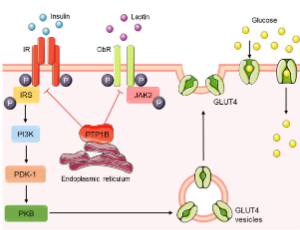
Metformin in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure
Henrik Wiggers, Anders Hostrup Larsen, Lars Køber, Gunnar Gislason, Morten Schou, Mikael Kjær Poulsen, Søren Vraa, Olav Wendelbo Nielsen, Niels Eske Bruun, Morten Bøttcher, Kirsten Vilain Mikkelsen, Jens Lomholdt, Søren Lund Kristensen, Christian Torp-Petersen, Hans Eiskjær, Jacob Møller, Bo Martin Bibby, Christian Hassager, Flemming Hald Steffensen, Jens Refsgaard, Dan Eik Høfsten, Søren Mellemkjær, Finn Gustafsson, Helene Nørrelund
Heart failure affects 1-2% of the adult population in developed countries and the lifetime risk of a heart failure diagnosis is 20%. Patients with heart failure have markedly reduced life expectancy, physical capacity and quality of life. One-year all-cause mortality rates for heart failure patients range between 7 and 17% and the yearly hospitalization rate can be as high as 44%.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 3, p100-105 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.025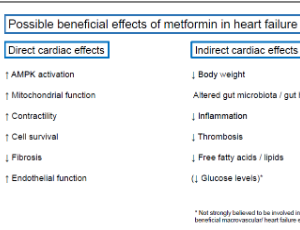
The Impact of COVID-19 on Diabetic Foot Care
Stella Papachristou, Nikolaos Papanas
Among all late complications of diabetes, those involving the foot have traditionally required more face-to-face patient visits to clinics [1]. The COVID-19 (corona virus infectious disease) pandemic has resulted in the closing of most outpatient clinics for face-to-face consultations.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p106-108 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.026
Continuing Medical Education Rarely Addresses Leading Public Health Problems Including Diabetes and Obesity
Nicholas A. Berry, Nicole E. Fumo, Bruce B. Berry
Medical schools sponsor continuing medical education (CME) to help fulfill their mission of improving the health of the community. CME programs can help physicians stay up-to-date with the best practices associated with disease prevention and treatment.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p109-113 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.027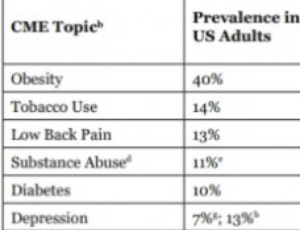
Can Monoclonal Antibodies against CGRP Offer New Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes?
Celine E Riera
The neuropeptide Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) is a 37-amino acid peptide, with a wide-range of biological activities including vasodilation, neurogenic inflammation, immune function and hypertension. In addition to these various roles, it has also been heavily implicated in metabolic disease, with roles in feeding, energy dissipation processes and pancreatic β-cell insulin secretion.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p114-118 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.028
Short Update on Bisphenol A Exposure and Type 2 Diabetes: Focus on Workers
Lidia Caporossi, Mariangela De Rosa, Bruno Papaleo
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is one of the most prevalent metabolic disorders, characterized by impaired metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. The prevalence of diabetes worldwide has grown from about 108 million adults (4.7% of population) in 1980 to 463 million (9.3%) in 2019 and it is estimated that it will rise to 700 million by 2045
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 4, p119-126 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.029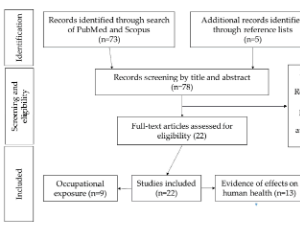
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
