Loading
Journal of Diabetes and Clinical Research
ISSN: 2689-2839


Lawrence Lavery
The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, USA
Featured Article
Ephrin B1 Regulates Inflammatory Pathways in Retinal Müller Cells
Featured Article
Sex Differences in Diabetic Ocular Surface Complications and Dysregulation of the OGF-OGFr Pathway
Featured Article
Prevalence of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Osteoarthritis Patients Derived from Primary Care Records: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies
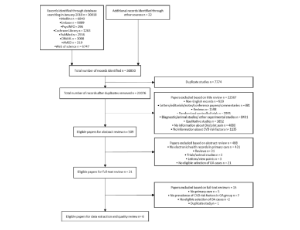
About this Journal
Journal of Diabetes and Clinical Research is an international publication initiated with the motto of stimulating the research in diabetes disease management and treatment. The journal focuses on various aspects of diabetes and clinical research such as diabetes and trials, neuropathology of diabetes, diabetes and innovative therapies, merging technologies in disease management etc.
Articles
Discriminatory Ability of Adiposity Phenotypes in Identifying Cardiometabolic Disorders in Indigenous and Non-indigenous African Populations
A population-based cross-sectional study recruited 1921 participants from the settled Fulani, nomadic pastoral Fulani and the general population. Body weight (BW), height, waist circumference (WC), and hip circumference (HC) were measured and body mass index (BMI), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), waist-to-height ratio (WHtR), Conicity Index (Cindex), body adiposity index (BAI), body roundness index (BRI) and body shape index (ABSI) were determined. The associations of anthropometric indices with cardiometabolic disorders were assessed by multivariable adjusted logistic regression and the area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve compared the predictive abilities.
Enhancing Clinical Collaboration: Interface Linking between Laboratories and Clinics for Translational Healthcare
Clinical laboratories are pivotal in modern healthcare, providing essential diagnostic information that influences patient management and healthcare efficiency. Technological advancements and economic pressures have continuously shaped laboratory medicine, leading to significant transformations in diagnostic capabilities. This article explores the evolving role of clinical laboratories, emphasizing their impact on disease prevention, early diagnosis, and patient safety.
Decline in Physical Activity after Age 35 Increases the Risk of Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Diabetes: A Cross-sectional Analysis of the MIDUS Study
Data were analyzed from 1,395 participants in the Midlife in the United States (MIDUS) study, including biomarker subsamples. Participants reported their physical activity levels during young adulthood and currently (≥ 20 min, three times per week). Participants were categorized as persistently active, increased, decreased, or persistently inactive. Obesity was defined as body mass index (BMI) ≥ 30 kg/m², insulin resistance by HOMA-IR ≥ 2.8, and diabetes by self-reported diagnosis. Multivariable logistic regression was used to assess associations.
Inhibition of Sortilin Improves Retinal Function in Diabetic Mice Through Decreased Inflammatory Mediators
Inflammation is a key factor in retinal damage in response to diabetes. Sortilin represents a new regulator of retinal inflammation. Sortilin is involved in over 50 different signaling cascades. To investigate sortilin in the diabetic retina, we first measured protein levels in retinal lysates from diabetic humans and diabetic mice. We then inhibited sortilin using a small molecule inhibitor, AF38469, and evaluated retinal function using electroretinogram (ERG) and fluorescein angiography.
BCG Immunotherapy: Promising Protection from COVID-19 and Other Infectious Diseases in Type 1 Diabetics
Individuals with type 1 diabetes are more vulnerable than the general population to morbidity and mortality from infectious disease, including COVID-19. Over the last 20 years, the >100-year-old tuberculosis vaccine, known as Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG), has been observed in global populations to protect from viral, bacterial and parasitic infections, among others.
From Seed to Solution: Expert Insights on Sesame’s Role in Diabetes and Beyond
Sesame (Sesamum indicum L) has garnered attention for its potential in diabetes management due to its rich bioactive compounds, including sesamin, sesamolin, and unsaturated fatty acids. This commentary explores recent advances in sesame research, emphasizing its role in improving glycemic control, lipid profiles, inflammation, and oxidative stress, as evidenced by a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mechanistic insights reveal sesame’s effects on PPARα activation, Nrf2 signaling, and NF-κB suppression, which underpin its metabolic benefits.
Management of Metabolic Diseases: From Reactive Care to Preventive Strategies
Metabolic diseases such as hypertension, obesity, diabetes, and vascular disorders have reached epidemic proportions worldwide [1–6]. Despite major advances in medicine, cardiovascular disease has remained the leading cause of death for more than a century. Among these disorders, diabetes mellitus stands out as a major contributor to morbidity and mortality, placing a heavy burden on patients, healthcare systems, and economies.
Plasma Non-Esterified Fatty Acids (NEFA) in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Evidence on Pathophysiology
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a metabolic dysfunction characterized by elevated levels of blood glucose as well as impaired lipid and protein metabolism. The mobilization of fatty acids is augmented in insulin resistance due to the failure of lipolysis inhibition by the hormone that further augments the increase in plasma NEFA levels.
Vitamin D and Insulin Resistance in Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia-a Commentary and Natural Expansion
In our previous focused review, the journal emphasized Type 2 diabetes (T2DM), excluding intimately associated disorders that should be considered integral components of the insulin resistance (IR) syndrome e.g., polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH), and gout.
Validation of a New Test for Assessing the Quality of Life Perceived in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
The World Health Organization defines quality of life (QoL) as “the perception that an individual has of his life, in the context of the culture in which he lives, integrating personal goals, expectations and concerns, well-being and discomfort”.
Improved Wound Closure Rates and Mechanical Properties Resembling Native Skin in Murine Diabetic Wounds Treated with a Tropoelastin and Collagen Wound Healing Device
Chronic, non-healing, or slow to heal wounds present a significant and growing health problem in the United States, with an estimated 6.5 million people affected, at an annual cost of US $20 billion, with the highest risk groups represented by the elderly and the increasing prevalence of lifestyle diseases such as diabetes and obesity.
Risks and Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy in Children and Young People with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is associated with microvascular and macrovascular complications.Duration of diabetes, poor glycaemic control, high blood pressure and proteinuria are reported risk factors contributing to the development of diabetes related complications.
Can Vitamin D Supplementation Reduce Insulin Resistance and Hence the Risks of Type 2 Diabetes?
The question of whether or not correction of vitamin D deficiency might reduce the risks of later type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has been under debate for many decades. The necessity of vitamin D for normal insulin secretion was first identified experimentally in the 1980s.
A Customized Artificial Pancreas System with Neural Network based Model Predictive Control for Type 1 Diabetic Rats
Advances in sensor and computing technology have enabled researchers to develop artificial pancreas systems (APS) that can mimic the glucose regulation function of a healthy pancreas to treat type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). APS use a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) sensor to read the latest blood glucose level (BGL).
Dysregulation of the OGF-OGFr Pathway and Associated Diabetic Complications
Diabetes is a major healthcare concern worldwide. In addition to the financial burden estimated at $760 billion, the human suffering related to complications of diabetes as well as the disease itself are immense. Complications associated with diabetes affect both men and women, but there is a higher incidence reported in the aging population, women, and people of color.
CERT-Dependent Ceramide Transport, A Crucial Process in Cells
In mammalian cells, ceramides are central lipids in sphingolipid metabolism and serve both as signaling lipids and as precursors for other bioactive sphingolipids, ranging from complex glycosphingolipids to “simpler” lipids such as ceramide-1-phosphate, sphingomyelin (SM), sphingosine and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P).
Adapting the Escape Room to Engage Learners Two Ways During COVID-19
When creating the project, “An Escape Room Simulation Focused on Renal-Impairment for Prelicensure Nursing Students” [1] the author’s goal was to increase positive health outcomes for patients with acute kidney injury (AKI). AKI is complicated, but nurses who can help identify those at risk for the disorder and help initiate early treatment can improve patients’ results.
Can Monoclonal Antibodies against CGRP Offer New Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes?
The neuropeptide Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) is a 37-amino acid peptide, with a wide-range of biological activities including vasodilation, neurogenic inflammation, immune function and hypertension. In addition to these various roles, it has also been heavily implicated in metabolic disease, with roles in feeding, energy dissipation processes and pancreatic β-cell insulin secretion.
Improved Wound Closure Rates and Mechanical Properties Resembling Native Skin in Murine Diabetic Wounds Treated with a Tropoelastin and Collagen Wound Healing Device
Chronic, non-healing, or slow to heal wounds present a significant and growing health problem in the United States, with an estimated 6.5 million people affected, at an annual cost of US $20 billion, with the highest risk groups represented by the elderly and the increasing prevalence of lifestyle diseases such as diabetes and obesity.
Epac1 Regulates Ephb1/Ephrin B1 in Retinal Müller Cells
Eph B1/Ephrin B1 signaling has been shown to play a role in inflammation and pain in some targets; however, its upstream regulation is less clear. To investigate whether exchange protein for cAMP1 (Epac1) can regulate EphB1/ephrin B1 in retinal Müller cells, we generated Epac1-Müller cell specific knockout mice. We used protein analyses to show that Epac1 regulates both EphB1/ephrin B1, as well as high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) and NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3).
A Clinical Case Report: Utility of Amniotic Membrane in Treating a Geriatric Diabetic Patient with a Chronic Pressure Ulcer
Chronic wound closure is the inability for a wound to progress through the standard wound healing stages and timeframe, often stalling during the inflammatory stage. This paper presents a two-year open wound endured by a Native American patient of geriatric age and uncontrolled type II diabetes based on elevated A1c levels. Multiple therapeutic modalities had been attempted to close the wound, without improvement.
Ephrin B1 Regulates Inflammatory Pathways in Retinal Müller Cells
The role of inflammation has been accepted as a factor in the complications of diabetic retinopathy. Discovery of the upstream regulation of these inflammatory factors has remained a challenge. In this study, we explored the actions of ephrin B1 in retinal Müller cells and their actions on inflammatory proteins. We used diabetic human and mouse samples, as well as Müller cells in culture to measure ephrin B1 in Müller cells.
Validation of a New Test for Assessing the Quality of Life Perceived in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
The World Health Organization defines quality of life (QoL) as “the perception that an individual has of his life, in the context of the culture in which he lives, integrating personal goals, expectations and concerns, well-being and discomfort”.
Adapting the Escape Room to Engage Learners Two Ways During COVID-19
When creating the project, “An Escape Room Simulation Focused on Renal-Impairment for Prelicensure Nursing Students” [1] the author’s goal was to increase positive health outcomes for patients with acute kidney injury (AKI). AKI is complicated, but nurses who can help identify those at risk for the disorder and help initiate early treatment can improve patients’ results.
Can Monoclonal Antibodies against CGRP Offer New Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes?
The neuropeptide Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) is a 37-amino acid peptide, with a wide-range of biological activities including vasodilation, neurogenic inflammation, immune function and hypertension. In addition to these various roles, it has also been heavily implicated in metabolic disease, with roles in feeding, energy dissipation processes and pancreatic β-cell insulin secretion.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
