Loading
Archives of Pharmacology and Therapeutics
ISSN: 2688-9609
All Articles
The Use of Hydroxychloroquine and Interferons for the Prophylaxis of COVID-19
Catherine Teng, Moses Shrestha, Bing Yang
At the beginning of Covid-19 pandemic, we proposed to use hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) and intranasal interferon (IFN) a-2b spray to prevent SARS-CoV-2. Since then, clinical trials testing these two drugs separately for the treatment and prophylaxis have been reported. A consensus is forming that HCQ and IFNs are not effective in treating severe Covid-19. However, the pathogenesis of Covid-19 suggests that early intervention could reduce the infection and prevent the progression from mild to severe Covid-19.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p1-4 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.3.019
Off Label Use as an Indicator of Therapeutic Need in Pediatrics
Silvia Miriam Cammarata
Unapproved use of an approved drug is called “off-label” use. In line with European Medicine Agency’s pharmacovigilance directive, off-label use “relates to situations where a medicinal product is intentionally used for a medical purpose not in accordance with the authorised product information (SmPC).
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p1-4 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.036
Dexamethasone: The First Drug to be Shown to Decrease Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19
Nasser Mikhail, Soma Wali
Background: The precise role of corticosteroids for treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is unclear due to lack of randomized trials. Objective: To review the therapeutic value of corticosteroids for treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 with more emphasis on randomized trials. Methods: English literature search of electronic databases supplemented by manual search up to June 29, 2020. Search terms included corticosteroids, COVID-19, dexamethasone, methylprednisolone, hydrocortisone, mortality, safety. Randomized trials were the main focus of research, but observational studies were also reviewed.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p1-5 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.2.011
Why Do Patients Not Meet the Pharmacological Treatment?
Jose Luis Turabian
Therapeutic compliance has been defined as the degree to which the behaviour of a person corresponds with the recommendations of the health professional [1].
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p1-7 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.1.001
Why Can Modulation of α6-Containing GABAA Receptors Reduce the Symptoms of Multiple Neuropsychiatric Disorders?
Werner Sieghart
α6-containing GABAA receptors (α6GABAARs) are strongly expressed in cerebellar granule cells, where they mediate a correctly timed and precise coordination of all muscle groups that execute behavior and protect the brain from information overflow. Recently, it was demonstrated that positive modulators with a high selectivity for α6GABAARs (α6-modulators) can reduce the symptoms of multiple neuropsychiatric disorders in respective animal models to an extent comparable with established clinical therapeutics.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p1-7 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.6.047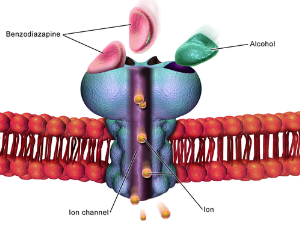
Recurrent MPNST in Mosaic Localized Neurofibromatosis: A Rare Scenario – Review
Betty Abraham, YM Fazil Marickar
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is a rare spindle cell neoplasm accounting for approximately 3-5% of soft tissue sarcomas. It often arises from a peripheral nerve, from a pre-existing benign nerve sheath tumor, or in a patient with neurofibromatosis type 1(NF1). In the absence of these settings, particularly in sporadic or radiation associated tumors, the diagnosis can be more challenging and is based on the histological and immunohistochemical features suggesting Schwannian differentiation.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p1-12 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.029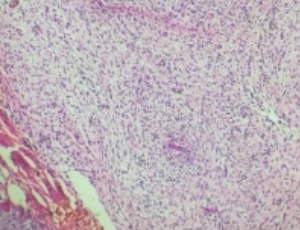
Integrating Mathematical Models in Clinical Oncology: Enhancing Therapeutic Strategies
Gobinda Debnath, B. Vasu, Rama Subba Reddy Gorla, O. Anwar Bég, Tasveer A. Bég
Cancer remains a formidable challenge in the field of medical research, necessitating novel approaches to better comprehend its complex dynamics and develop effective treatment strategies. This article presents a comprehensive review of the latest mathematical models employed in the study of tumor growth dynamics and its treatment. The heterogeneous nature of cancer poses unique complexities, requiring interdisciplinary efforts involving mathematics and other relevant domains.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p1-27 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.7.060
The Role of the General Practitioner in Vaccination against COVID-19
Jose Luis Turabian
The SARS-CoV-2 virus, responsible for covid-19, had an animal origin and jumped to humans in 2019. In 2020 alone, COVID-19 infected almost 100 million people around the planet and ended with the lives of 2 million people. The development in a very short space of time, of vaccines against COVID-19, in response to the urgency of the pandemic, is a transcendental milestone in the history of medicine.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p5-7 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.037
COVID-19 Disease and SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Patients with Cancer
Daniel A. King, Jeffrey Chi, Shreya Prasad Goyal, Muhammad Wasif Saif
Since the declaration of COVID-19 as a pandemic in March 2020, there have been more than 100 million reported cases of COVID-19 worldwide and more than 2.1 million deaths. The purpose of this editorial is to review recent updates regarding COVID-19 disease and SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in cancer patients.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p5-9 | DOI: https://doi.org/10.33696/Pharmacol.3.020
Pharmacogenetic Variants in the DPYD and TYMS Genes are Clinically Significant Predictors of Fluoropyrimidine Toxicity: Are We Ready for Use in our Clinical Practice
Muhammad Wasif Saif, Hilal Hachem, Sneha Purvey, Ruchi Hamal, Lulu Zhang, Nauman Saleem Siddiqui, Amandeep Godara, Robert B. Diasio
Fluoropyrimidines have been extensively used for almost 6 decades to treat a variety of solid cancers, especially colon, gastric, anal, rectal, head & neck and breast. However, 31–34% of patients encountered grade 3–4 adverse events (AEs) with 0.5% mortality oftennecessitating dose reduction or discontinuation. A significant proportion of these AEs are likely to be the result of inter-individual genetic variation, in particularly such as dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPYD). DPYD gene encodes DPD, the rate-limiting enzyme responsible for catabolism of 5-FU and is responsible for >85% of 5-FU elimination.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p6-8 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.2.012
POSTCOVID-19WAR Era, Interaction between Cancer-Hematologic Disorders- Diabetes Significantly Increased by COVID-19 Variants, Aggressively
Bahram Alamdary Badlou
Understanding the mechanism of bidirectional interaction between different angles of the death triangle is a lifesaving novel idea that I invented in 2018. Platelet hyperactivity and dysfunction in diabetes and cancer patients were already known facts [1] but whether different COVID-19 variants could activate and/or accelerate death triangle machinery?
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p8-10 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.038
Aldosterone Synthase Inhibitors for Treatment of Hypertension and Chronic Kidney Disease
Nasser Mikhail
Aldosterone excess is known to worsen hypertension and kidney function. Three selective aldosterone synthase inhibitors (ASIs) were evaluated in 3 phase 2 trials. In the first study, the ASI baxdrostat 2 mg orally once daily decreased systolic blood pressure (SBP) by 11.0 mmHg compared with placebo after 12 weeks in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension. In the second study including patients with uncontrolled hypertension, placebo-corrected reduction in SBP with lorundrostat 50 mg once daily was 9.6 mmHg after 8 weeks.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p8-12 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.6.048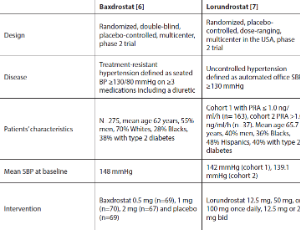
Domination of Nephrotic Problems among Diabetic Patients of Bangladesh
Mohiuddin AK
Nearly 80% of people with diabetes live in low and middle-income countries. It increases healthcare use and expenditure and imposes a huge economic burden on the healthcare systems. The International Diabetes Federation estimated 7.1 million people with diabetes in Bangladesh and almost an equal number with undetected diabetes. This number is estimated to double by 2025.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p8-13 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.1.002
Classical Drug and its New Role in COVID-19 Management
Viroj Wiwanitkit
COVID-19 is the new emerging viral infection that already cause global public health problem. More than 220 countries/territories are already attacked and there are more than 17 million patients around the world. This disease was firstly reported in China then in Indochina and extended worldwide. The patient can have febrile respiratory illness and there are many asymptomatic and mild symptomatic cases. The new viral respiratory infection causes several medical and non-medical problems and it is a big challenge to be managed.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p9-11 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.2.013
COVID-19 and the Health of Illicit Substance Users: Preliminary Analysis from Illicit Drug Transaction Data
Andréanne Bergeron, David Décary-Hétu
While much attention has been given to how COVID-19 patients are treated (or fail to be treated), the impact of the pandemic on illicit drug users remains largely undiscussed. The consequences of COVID-19 on substance users and on the health care system are exposed.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p10-13 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.3.021
Keeping Ready against Omicron and Future Variants: Can Ivermectin Prophylactic Effects Improve the Vaccination Effects against COVID-19?
Hamidreza Zalpoor, Mohsen Nabi-Afjadi, Fatemeh Aziziyan, Chanour Tavakol
The standard treatment options for Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) remain challenging despite community vaccinations and reduced mortality. As the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus continues to evolve and new strains emerge, diversity in the use of existing antiviral drugs has become a crucial therapeutic tool in combating the COVID-19 epidemic.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p11-17 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.039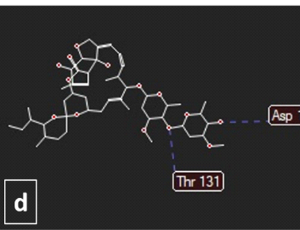
Beta-Sitosterol: As Immunostimulant, Antioxidant and Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein
Sharuk L. Khan, Falak A. Siddiqui
This article is an extension to our recently published article in Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, entitled “Β-Sitosterol: Isolation from Muntingia Calabura Linn. Bark Extract, Structural Elucidation, and Molecular Docking Studies as Potential Inhibitor of SARSCoV-2 Mpro (COVID-19)”[1].
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p12-16 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.2.014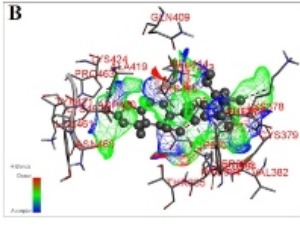
Comprehensive Network and Structural Analysis of Bovine Papillomavirus, Squamous Cell Carcinoma Markers, and Elucidation of Efficacy Mechanisms of Phytochemicals from Thuja Occidentalis
Shafiqur Rahman, Arun HS Kumar
Papillomaviruses infect cutaneous tissue in various species including bovines and from benign warts to malignant squamous cell carcinoma causing severe economic losses to the farmers. The mechanisms by which bovine papillomaviruses interact with host tissue are unclear. Hence in this study using classical network analysis tools, we evaluated interactions of Bovine papilloma (BPV) variants, with markers and receptors implicated in squamous cell carcinoma.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p13-20 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.6.049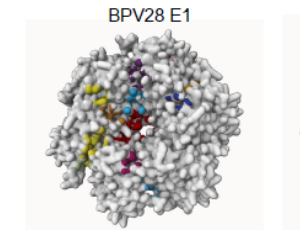
Pharmacologic Therapies for Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: Current and Future Treatments
Ilana P. Goldberg, Benjamin Lichtbroun, Eric A. Singer, Saum Ghodoussipour
Bladder cancer is the sixth most common malignancy in the United States and 70% of cases are non-muscle invasive at the time of diagnosis. Effective treatment is crucial to prevent progression, which occurs in about 30% of patients. The American Urological Association (AUA) guidelines recommend treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) with intravesical Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) and chemotherapy.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p13-22 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.030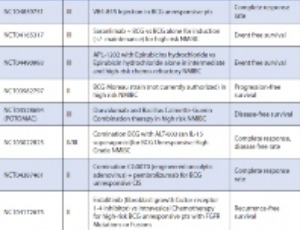
Diverse Therapeutic Applications of Onion
Preetismita Borah, Bimal Krishna Banik
Onion has been a very useful vegetable for human. The organic molecules present in onion are extremely diverse and exert numerous pharmacological pathways to prevent diseases. Although, mechanism of action of the compounds present in onion has been investigated, clearly there remains enough scope to study this subject further. In general, many scientists believe that the medicinal values of onion are because of a series of oxidation processes of the molecules present in it.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p14-16 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.1.003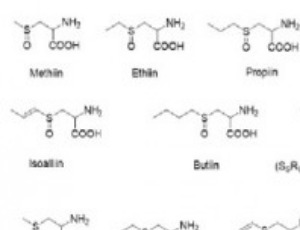
COVID-19 Rapid Diagnostic Test Results and their Associations with Certain Factors Among the Residents of Balochistan
Ehsan Larik, Muhammad Arif, Abid Saeed, Zirza Amir Baig, Zakir Hussain, Ambreen Chaudhary, Mirza Zeeshan Iqbal Baig, Zubair Bugti, Jan Inayat, Khair Muhammad, Muhammad Abdullah, Zubair Ahmed Khoso, Qurat-ul- ain, Aftab Kakar, Nasir Sheikh
Background: This paper analyses any possible association of various factors like gender, last COVID-19 PCR test results, BCG Vaccination, Seasonal Flu vaccination, occupation and confirmed case contact history with COVID-19 RDT results of the participants. COVID-19 will soon become endemic in Pakistan, the government should adopt COVID-19 RDT kits for trace, test and quarantine activities.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p14-20 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.3.022
Current Issues of Novel Drug Versus Thrombosis as Main Cause of Death
Bahram Alamdary Badlou
Appropriate medicinal drugs can save life of any patientat risk with high mortality and morbidity. All ongoingcosts and benefits are covered mainly by the health insurance, the pharmaceutical, and alternative medicine industry.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p17-18 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.1.004
Drugs and Family Medicine: Form and Content
Jose Luis Turabian
Choosing an individual medication for a particular patient is one of the most important clinical decisions in family medicine (FM). Prescription of drugs is currently the main tool of FM and that’s the main source of prescription of drugs. The drugs are used by general practitioners (GPs) to manage a wide range of health problems that are addressed at this level of medical care have tangible results. But should the drug be the GP’s main therapeutic resource? Drugs arrive to serve the purposes of the GP, but finally, the GP redefines its own goals according to the drugs.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p17-20 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.2.015
Proto-oncogenes Crosstalk, Feedback and Expression, and Anticancer Drugs Resistance
Mahmoud M. Elalfy, Mona G. Elhadidy, Eman Mohamed El Nashar
Proto-oncogenes like C-MYC, EGFR and others have physiological function in regeneration, wound and any stressfully injury to maintain tissue echotexture and healing. Notably, these growth factors work together and had life span to retain to basal level after tissue remodeling and retain its function like what happen in partial hepatectomy.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p18-21 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.040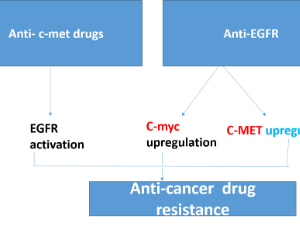
Molecular Detection of Plasmid - Mediated Quinolone Resistant Genes in Uropathogenic E. coli from Tertiary Referral Hospital in Tehran , Iran
Ali Badamchi, Shima Javadinia, Reza Farahani, Hamid Solgi, Azardokht Tabatabaei
Fluoroquinolone antibiotics are usually used for the treatment of urinary tract infections. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence and molecular characterization of Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance (PMQR) genes among ESBL-producing Escherichia coli isolates obtained from tertiary referral hospital in Tehran, Iran.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p19-24 | DOI: doi.org/10.33696/Pharmacol.1.005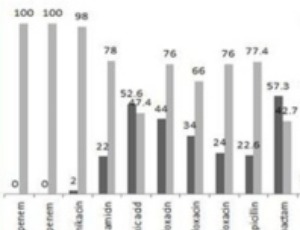
Biological Activity of Miscanthus capensis Root Extract
Idowu Jonas Sagbo, Wilfred Otang-Mbeng
Miscanthus capensis is a hardy, evergreen, medium-high, clump-forming grass that belongs to the Poaceae family. It is used in South Africa for the treatment of pimples, wounds, eczema, and acne. The present study was investigated to examine the biological activity of Miscanthus capensis roots extract. The effect of the plant extract on protein glycation and collagen production was investigated using in vitro assays.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p21-23 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.2.016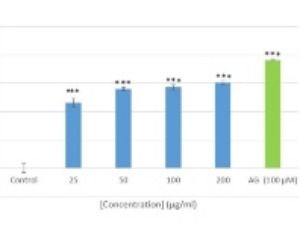
The Domino Effect of Polypharmacy. A Dangerous Catalyst That Starts Numerous Bio-Psycho-Social Chain Reactions
Jose Luis Turabian
Increasing medicalization causes some disconcerting trends in medical decision making. Polypharmacy is one of its most important consequences. The tendency to equate the concepts of risk factor and disease, the changes in the biomedical assessment of the severity of many health problems, and the increase in the number of pharmacological treatments create a growing set of multimorbidity and polypharmacy, and this produces a dramatic domino effect
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p21-23 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.6.050
Clerodendrum Chinensis Extracts; AeC and EeC Exerts Rapid Antihypertensive Effects in L-NAME Hypertensive Experimental Models
Joy I. Odimegwu, Tolulope F. Okanlawon, Noel Obumneme, Ismail Ishola
The rise in the occurrence of hypertension, a non-communicable disease and a major factor for chronic renal failure, cardiovascular disease, and stroke, which most times lead to sudden death is worrisome. Resistant hypertension is more common and may have no symptoms at all for months or years, but then can cause heart attack, stroke, and vision and kidney damage. Prevention and quick management of hypertension is therefore essential in reducing the risk of these debilitating ailments. Aqueous and ethanolic extracts of the leaves of Clerodendrum chinensis (AeC and EeC) are used by local communities of West Africa as medicine for rapid anti-hypertensive actions. We aim to discover the scientific basis for the use of the herb as medicine.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p21-28 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.3.023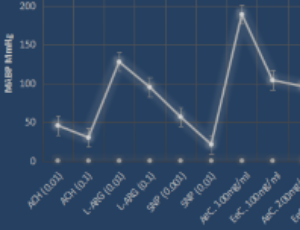
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Reflections on COVID-19 Pharmacological Treatment and Beyond: Beware of “Salads” with Many Ingredients but Low Scientific Content
Jose Luis Turabian
The pandemic triggered by SARS-CoV-2 has changed since that first case in Wuhan in 2019. We currently have efficient vaccines that have allowed us to return to our daily activities. But, SARS-CoV-2 remains a public health emergency of international concern.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p22-24 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.041
Relative COVID-19 Vaccine Booster Effectiveness and ClinicalEpidemiological Characteristics Before and After 29 Days of Shot
Jose Luis Turabian
Background: When the highest vaccine COVID-19 booster effectiveness (VBE) is obtained is not clearly known. Objective: To compare the cases of COVID-19 in booster vaccinated people with a time of <29 days vs. ≥ 29 days from booster to infection diagnosis and assess their relative VBE. Methodology: An observational, longitudinal and prospective case series study of adult patients with COVID-19 breakthrough infections in booster vaccinated people, in general medicine and for the period December 2021 to February 2022, during the omicron variant contagion wave.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p23-34 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.031
POSTCOVID-19 WAR Era, Abnormally Some Patients being Affected by Exceptional Disease Progression, and Accelerated Excessive Mortality Rate
Bahram Alamdary Badlou
From 2019, POSTCOVID-19 pandemic attacks, human beings were under pandemic-attacked condition that caused by different industrial modern diseases, and being confronted with unusual disease progression, which increased abnormal excess mortality and morbidity rates. The exact mechanism of action is not completely elucidated yet. What is (un)known?
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p24-26 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.6.051
Artificial Intelligence in Pharma: Positive Trends but More Investment Needed to Drive a Transformation
Peter Henstock
Pharmaceutical companies have been actively adopting artificial intelligence (AI) approaches for drug discovery and are starting to focus this technology on clinical trials. The shift from large-scale collaborations to smaller strategic partnerships and recently to internal teams has led to increased headcounts that are being organized to deliver AI across the enterprise. Although the urgency of the COVID-19 could have been a perfect test case for leveraging AI, it drew awareness to the obstacles of data access.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p24-28 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.2.017
Platelet Hyperactivity and Dysfunction in Diabetes and Cancer
Bahram Alamdary Badlou
However, the entire coagulation cascade is dysfunctional, in progressed chronic diabetes and cancer patients. Platelets (PLTs) in type 2 diabetic (DT2) involved in Thrombosis and Haemostasis (T&H) of individuals adhere to vascular endothelium and aggregate more voluntarily than those in healthy individuals, as are abnormalities in the microvascular and macrovascular circulations. However it is already known that the circulating PLTs are essential for T&H, inflammation growth factors delivery, regeneration; and knowledge of their function is fundamental to understanding the pathophysiology of vascular disease in diabetes and cancer-related diseases.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p25-26 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.1.006
Application of Halides Complexes of Ruthenium (II) in Metallopharmaceuticals and in Material Science: Part-I
Vishnu Kumar Sahu, Anil Kumar Soni, Kavindra Kumar Mishra, Rajesh Kumar Singh
Ruthenium readily forms coordinate-complexes and these complexes have their applications in diverse fields. A survey of literature shows that designing of new ligands that can be complexed with Ruthenium (Ru) in various oxidation states can lead to development of new materials with diverse applications.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p25-35 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.042
Schisandra chinensis in Liver Disease: Exploring the Mechanisms and Therapeutic Promise of an Ancient Chinese Botanical
Tamer A. Addissouky, Ibrahim El Tantawy El Sayed, Majeed M. A. Ali, Mahmood Hasen Shuhata Alubiady, Yuliang Wang
Background: Schisandra chinensis is a traditional Chinese herbal medicine that has been used for centuries for liver health. The active lignans in Schisandra, including schisandrin and gomisins, have exhibited anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and hepatoprotective properties in preliminary studies. With rising rates of chronic liver diseases globally, there is interest in the potential therapeutic role of Schisandra.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p27-33 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.6.052
Psychosocial Aspects of Drug Prescription: Recognizing These Phenomena to Improve the Quality of Clinical Practice
Jose Luis Turabian
The psychosocial aspects of pharmacological prescription are the factors that intervene in ways of reacting of the doctor and the patient to the prescription of a drug, as well as the role of social structures that determine it. The role of psychosocial factors in pharmacologic treatment of patients remains unclear and is notably absent in the literature of the discipline of general medicine. Biological (specific) and psychosocial (nonspecific) effects of drugs are not simply additive, but interact with each other.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p27-34 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.1.007
Effective Cognitive Responses to Treatment Failure
H. Paul Putman III
Half of current treatment plans in psychiatry disappoint, and 3/4 of our medical errors are cognitive in nature. We can positively influence clinical outcomes by reconceptualizing our suboptimal results as single treatment failures (TF) and temporary impasses, rather than misapplying the term “treatment resistance.” Reflective consideration of TF as feedback on our diagnostic and therapeutic hypotheses triggers alterations in our conceptual structure apparatus that can lead to new, creative insights and result in more effective clinical solutions.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p28-34 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.7.061
Remdesivir in COVID-19 Patients with End Stage Renal Disease on Hemodialysis
Vijairam Selvaraj, Karl Herman, Arkadiy Finn, Atin Jindal, Kwame Dapaah-Afriyie
To date, only glucocorticoids have been shown to reduce mortality in COVID-19. Use of remdesivir was associated with reduced length of stay in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. A deadly second wave in Asian countries has caused increased demand and usage of remdesivir in these countries. However, there is limited data about its efficacy in patients with severe renal dysfunction or end-stage renal disease on dialysis.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p29-31 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.3.024

Is There a Simple and Easy Way to Detect Singlet Oxygen? Comparison of Methods for Detecting Singlet Oxygen and Application to Measure Scavenging Activity of Various Compounds
Tokuko Takajo, Kazunori Anzai
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are known to exert both beneficial and harmful effects in the human body. Singlet oxygen (1O2), is highly reactive and considered as one of the ROS, although it is not a radical molecule. 1O2 reacts with many kinds of biological components such as lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. 1O2 is short lived because it reacts with biomolecules and collisions with water molecules rapidly causing the return of 1O2 to the ground state, and is therefore not easy to quantify. Antioxidants, such as β-carotene, lycopene and astaxanthin, are quenchers of 1O2.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2020, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 2, p29-33 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.2.018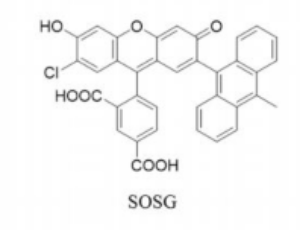
Statins and the Diabetic Kidney
Emad A. El-Bassiouni, Eman Elabd
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common chronic diseases that affect people of all ages and races worldwide.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p32-36 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.3.025
How Traditional Healers Diagnose and Treat Diabetes Mellitus in the Pretoria Mamelodi Area and How Do These Purported Medications Comply with Complementary and Alternative Medicine Regulations
Ondo Z.G
In South Africa, new amended regulations required a review of complementary and alternative medicine (CAMs) call-up for registration from November 2013. This impacted traditional healers (THs)’ compliance with the regulatory authorities’ on the good manufacturing practice which in return affected the public’s access to CAMs. This investigation embraces methods, THs use to diagnose and treat diabetes (DM) in Mamelodi. Furthermore, it assesses what their purported medications comprise of.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p33-45 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.1.008
Validating the Use of Rational Modification of Compounds to Reduce P-gp Efflux
Jay Conrad, Roy J Vaz
In both the Central nervous system (CNS) as well as Oncology small molecule drug discovery programs, efflux due to P-glycoprotein (P-gp) could be a deterrent during the discovery phase to obtain in vitro or in vivo pharmacological readouts. Several different strategies have been utilized in the past in order to overcome efflux by P-gp, many of which have been described in a recent article [5] from our labs.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p34-39 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.6.054
Co-intervention of an Immune Modulator - SIVA Herbal Drops versus Treatment Outcome
Gayathri Rajagopal, Amruthavalli GV
S.I.V.A herbal drops are a poly herbal preparation in drops formulation. It is indicated in the immune modulating benefit. The in vitro studies have established its activity of boosting phagocyted based immunity. In the present study the immune boosting efficacy of S.I.V.A herbal
drops in infectious disease conditions was evaluated in the human subjects in Apollo Wellness Plus Centre and Apollo Children’s Hospital between 2009-2010.
Dual-Rheological Model and Finite Element Simulation of Hemodynamics Through a Multiple Stenotic Artery with Nanodrug-Eluting Stent
B. Vasu, Ankita Dubey, Rama Subba Reddy Gorla, Mustaque H. Borbora, Shabih-ul-Hasan
A two-dimensional rheological study of hemodynamics through a diseased artery with multiple stenosis and drug-eluting stent is simulated computationally. The homogeneous suspension of metallic gold nanoparticles in the blood is considered motivated by pharmacology applications. The Casson (viscoplastic) and Sisko (viscoelastic) fluid models are employed, to mimic non-Newtonian characteristics of the blood flow in the core and in the peripheral arterial region respectively.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p35-51 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.7.062
From Data to Knowledge: A Mini-Review on Molecular Network Modeling and Analysis for Therapeutic Target Discovery
Mustafa Ozen, Effat S. Emamian, Ali Abdi
Successful drug development is a risky and lengthy process that can take over ten years and consume billions of dollars. Target discovery is a critical stage of drug development for the identification of key molecules and pathways that can be targeted by novel therapeutics to find more effective treatments. Due to the rapid development in artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques over the past decade
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p36-43 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.043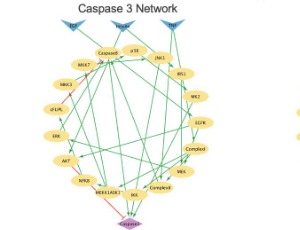
Study of the Tableting Properties of MCR, a Newly Coprocessed Cellulose-based Direct Compression Excipient
SAS Aly
The current need for strategies to accelerate and optimize the efforts to develop new in-expensive multifunctional direct compression tableting excipients with minimum risk to the products has urged the workers in pharmaceutical industry field to search for a simple and low cost-effective technique to tailor and engineer multi-functional excipients.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p37-38 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.3.026
Use of second Anti-Tumour Necrosis Factor Agent in Inflammatory Bowel Disease When First Agent Failed: A South African Retrospective Study
Ernst Fredericks, Abigail Titis, Suereta Fortuin, Shiraaz Gabriel, Mashiko Setshedi
Inflammatory bowel disease is a chronic relapsing and remitting inflammation of the bowel. Tumour necrosis factor α - antagonists are safe and effective in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Indications and outcomes with consecutive anti-tumour necrosis factor agents, although often used, are not clear. Since data for this treatment choice is scarce, we set out to evaluate the use of consecutive anti-tumour necrosis factor agents in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2022, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p39-50 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.033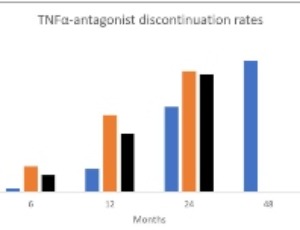
Ecological Impact of Drug Prescription
Jose Luis Turabian
Ecological thinking goes beyond humans and animals, this approach considers the inextricable links between ecosystems and health. Thus, ecology ranges from molecules to the ecological and sociocultural context, including the relationship between the economy and ecological and social processes. While pharmaceuticals are essential for human and animal well-being, their release into the environment is of growing concern.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p40-42 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.6.055
Targeted Therapy in Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer-Clinical Updates
Rachel Passarelli, John Pfail, David Golombos, Thomas L. Jang, Vignesh T. Packiam, Saum Ghodoussipour
Non muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) comprises almost 75% of all bladder cancer (BC) diagnoses. Longstanding intravesical treatment options include chemotherapy or Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG). However, despite these treatment options, there is a high rate of relapse for NMIBC patients, reaching up to 40-50% for patients with high risk disease. Radical cystectomy is recommended by guideline committees for patients with high risk NMIBC and for patients who fail intravesical treatment options
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p43-49 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.6.056
Dose-dependent Oxidative Damage of Molnupiravir (Antiviral Drug for Treatment of COVID-19) in Lung, Liver, Heart, and Kidney Tissues in Rats
Kevser TANBEK, Suleyman SANDAL
Molnupiravir (MOL) is an orally absorbed prodrug of the ribonucleoside analogue N-hydroxycytidine, which has in vitro activity against several coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-1 and 2. It remains to be seen whether long term MOL has serious side effects. The side effects of MOL, which was the first to be allowed for oral use during the pandemic process, are not yet fully known. In this study, it was aimed to investigate the the mechanisms of possible dose-dependent damage on liver, lung, heart, and kidney tissues.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p44-52 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.044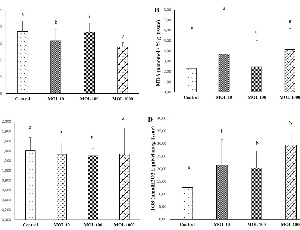
Nematocidal Effect of Japanese Traditional Intestinal Medicine ‘Seirogan’ on Larval Anisakid and Raphidascaridid Nematodes
Tatsuomi Matsuoka
‘Seirogan’ is a well-known Japanese traditional herbal medicine for stomachache or diarrhea due to digestive disorders. Recently, it was reported that the administration of Seirogan alleviated gastric anisakiasis symptoms, and that Seirogan quickly suppressed the motility of Anisakis larvae in vitro.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p48-51 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.3.027
The Pathogenesis of Continuous Spike and Waves during Slow Sleep Syndrome: Short Communication
Miriam Kessi, Jing Peng, Lifen Yang, Yulin Tang, Chen Chen, Fei Yin, MD, Ph.D
Continuous spikes during slow wave sleep (CSWS) syndrome is an age-related and self-limited severe epileptic encephalopathy characterized by electrical status epilepticus in sleep (ESES) on electroencephalogram, seizures, and developmental regression. The mechanisms that lead to the development of CSWS syndrome are complex and not clear. Surprisingly, steroids and benzodiazepines offer a good treatment outcome compared to conventional anti-epileptic drugs. Of concern, this condition has a long-term poor prognosis due to the persistence of neuropsychological impairment. Many questions are yet to be answered in this syndrome.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p48-56 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.1.009
Post COVID-19 War Era, Overall Updates and Upgrades Needed to Protect Patients Against Unpredictable Disease’s Progression
Bahram Alamdary Badlou
In these post-COVID-19 periods, overall updates and upgrades are needed to protect patients against unpredictable disease progression, radically. (Re)Consideration of guidelines, standard operating procedures (SOPs), all kinds of old-fashioned model systems, and mechanisms between different angles of the death triangle could play a pivotal role as a lifesaving novel idea, sooner or later.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p50-52 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.6.057
Preclinical Protective Activity of Lutein on Diclofenac-induced Hepatotoxicity
Elias Adikwu, Bonsome Bokolo, Tobechi Brendan Nnanna, Favour Yaakor
Diclofenac (DF), a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, may cause hepatotoxicity. Lutein (LT), a naturally occurring compound, has potential therapeutic activities. The protective activity of LT against DF-induced hepatotoxicity in adult Wistar rats was evaluated in this study.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p52-58 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.7.063
ProLung™-budesonide Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Replication and Reduces Lung Inflammation
Kameswari S. Konduri, Ram Pattisapu, Jogi Pattisapu, Girija G. Konduri, John Zwetchkenbaum, Bidhan Roy, Monalisa Barman, Adria Frazier, Brett L. Hurst, Nejat Duzgunes
Inhaled budesonide benefits patients with COVID-19. ProLung™-budesonide enables the sustained, low dose administration of budesonide within a delivery vehicle similar to lung surfactant. ProLung™-budesonide may offer anti-inflammatory and protective effects to the lung in COVID-19, yet it’s effect on SARS-CoV-2 replication is unknown.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2021, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 2, p52-65 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.3.028
Could the Norms for International Radiation Protection Be a Model for Pharmaceuticals?
Daniel Serwer
There is no international norm-setting mechanism for pharmaceutical registration. By contrast, the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) has been recommending widely respected norms for X-rays and radioactive isotopes in medical and other uses for almost a century. It does so with no legal authority on the basis of collaborative deliberations by a self-selected group that includes experts concerned about both health effects and the benefits of ionizing radiation.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p53-57 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.6.058
Recent Advances in Diagnosing and Treating Helicobacter pylori through Botanical Extracts and Advanced Technologies
Tamer A. Addissouky, Majeed M. A. Ali, Ibrahim El Tantawy El Sayed, Yuliang Wang
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is a major global health concern, with an estimated 50% of the world's population infected. The bacterium colonizes the stomach and is associated with a range of gastrointestinal diseases, including chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and gastric cancer. The current standard of care for H. pylori infection involves a combination of antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), but the widespread use of antibiotics has led to the development of antibiotic-resistant strains of H. pylori, making treatment more difficult. Recent advances in diagnostic strategies include the use of non-invasive tests and serological biomarkers.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p53-66 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.045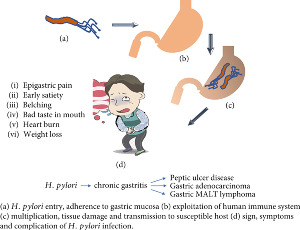
Admitting UnKnown Biosimilar- Drugs Affects Thrombosis and Haemostasis Processes
Bahram Alamdary Badlou
Accidental admitting and using (un-) known drugs might manipulate health and/or disease(s) of a subject in a positive (healing) and/or negative way (increased mortality and morbidity rate). Now a days, different kinds of drug development technologies are available, which might help affect global health. Though, the psychiatric comorbid disorders were important risk factors for premature drug-related deaths despite so many developed tools and technologies.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p57-58 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.1.010
Could Ayahuasca Communities Play a Role in the Compassionate Communities Movement?: A Commentary
Débora González, Jordi Cantillo, José Carlos Bouso
Globally, approximately 58 million deaths occur annually. Each death is estimated to directly affect about nine close relatives, underscoring that grief is not only a universal experience but also a potential recurrent process throughout life. Bereavement could trigger profound psychological and physiological reactions, including an elevated risk of cardiovascular complications. The risk of mortality is higher than in the general population, particularly among older adults following the death of a spouse.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2024, Volume Volume 6, Issue Issue 1, p58-62 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.6.059
Post-COVID-19 War Era, Remarkable Highlights 2025 Concerning Both Preventive and Curative Medicines
Bahram Alamdary Badlou
Series of updates and upgrades can help scientific communities stay current with new research and developments in modern diseases’ prevention/treatment planning, especially during these post-COVID-19 war periods with more than 65 million long COVID patients (2025). For over two millennia, medical consultative services and (co)related preventive & curative medicine have supported human survival against various pathological causes, with certain (un)known factors capable of inducing effects in a bidirectional manner, which I have called the “death triangle machinery”, since 2018 (Cancer- Platelets- Microorganisms, so-called CPM).
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p59-60 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.7.064
Antibiotics: Between the Tortoise and the Crab
Jose Luis Turabian
Antibiotics play an important role in both the prophylaxis and treatment of infectious diseases and are a cornerstone of modern healthcare. Antibiotics are lifesaving medicines and have enabled many advances in modern medicine. However, the more they are used, the less effective they become. Thus, the issues of their availability, selection, and appropriate use are of critical importance to the global community.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2025, Volume Volume 7, Issue Issue 1, p61-64 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.7.065
Evaluation of the Effect of Acute Catha edulis (Vahl) Forssk. ex Endl. Crude Extract and Tramadol Oral Administration on Spatial Learning and Memory in Rodent Experimental Model
Alfoalem Araba Abiye, Iman Yakutelarsh, Ermias Alemayehu Beriso, Wondmagegn Tamiru Tadesse
The concurrent use of tramadol and khat has been increasing in Ethiopia, raising concerns about their potential neurocognitive consequences. Despite growing trend, the effects of combined tramadol and khat exposure on learning and memory (LM) have not been previously investigated. Accordingly, the present study was designed to evaluate the impact of co-administration of khat and tramadol on spatial learning and memory in a mouse model.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, Volume 7, Issue 1, p65-74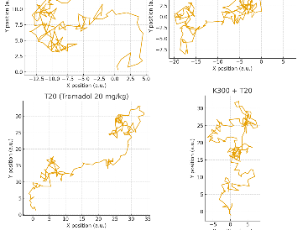
Pharmacology of Berberine and Its Metabolites, Is It the Natures Ozempic or Imatinib?
Naresh Kumar Singh, Muralikrishnan Dhanasekaran, Arun HS Kumar
Berberine, a naturally occurring alkaloid, is widely explored for several health benefits, including weight management and metabolic disorders. The major pharmacological action of berberine is reported to be by activation of AMP-activated protein kinase, while its other clinical outcomes are devoid of clear mechanism of action/s. Hence in this study a detailed pharmacology of berberine and its two major metabolites (berberrubine, and jatrorrhizine) in humans was evaluated using well established Insilco tools.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume Volume 5, Issue Issue 1, p67-81 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.046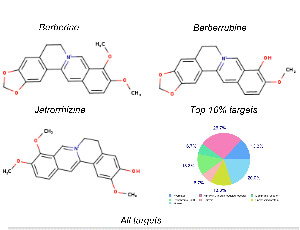
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
