Loading
Journal of Cellular Immunology
ISSN: 2689-2812
Most Cited Articles
Glucose Metabolism is a Better Marker for Predicting Clinical Alzheimer’s Disease than Amyloid or Tau
Tyler C. Hammond, Ai-Ling Lin
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) research has long been dominated with communications regarding the amyloid hypothesis and targeting amyloid clearance through pharmacological therapies from the brain. Unfortunately, this research strategy has yielded only one new FDA-accelerated approved therapeutic for early AD, and its clinical benefit still needs to be verified. It may be time to employ a new strategy in AD therapeutics research. Hammond et al. reported that diminished uptake of glucose in the brain is a better marker for classifying AD than beta-amyloid (Aβ) or phosphorylated tau deposition.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume 4, Issue 1, p15-18 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.128
Comparison of Gene Editing versus a Neutrophil Elastase Inhibitor as Potential Therapies for ELANE Neutropenia
Vahagn Makaryan, Merideth Kelley, Breanna Fletcher, Isabella Archibald, Tanoya Poulsen, David Dale
Heterozygous mutations in ELANE, the gene for neutrophil elastase, cause cyclic and congenital neutropenia through the programed cell death of neutrophil progenitors in the bone marrow. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor is an effective therapy for these diseases, but alternative therapies are needed, especially for patients who do not respond well or are at high risk of developing myeloid malignancies. We developed an HL60 cell model for ELANE neutropenia and previously demonstrated that transient and regulated expression of mutant ELANE causes cell death by accelerated apoptosis.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume 4, Issue 1, p19-28 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.129
Tenofovir at the Crossroad of the Therapy and Prophylaxis of HIV and HBV Infections
Erik De Clercq
Tenofovir, alias (R)-PMPA, was first divulged as an anti- HIV agent in 1993 [1]. That it would in 2012, become the first antiretroviral agent, approved by the US FDA (Food and Drug Administration) to prevent HIV infection, could have been predicted from the findings of Tsai et al.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 1, p23-30 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.015
TNFAIP8: Inflammation, Immunity and Human Diseases
Suryakant Niture, John Moore, Deepak Kumar
Inflammation can be caused by various environmental factors, including microbial infection and toxic chemical exposure. In response to inflammation, immune cells like macrophages, B and T lymphocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and various stromal cells secrete soluble polypeptide cytokine Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF?)
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p29-34 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.007
CAR-T cell Goes on a Mathematical Model
Luciana Rodrigues Carvalho Barros, Brendon de Jesus Rodrigues, Regina C Almeida
CAR-T cell immunotherapy is a great advance in hematological cancers treatment. New CARs and therapy schemes are being developed and a mathematical model could contribute to a rational design of treatment. Here we comment and show new results with previously published models of CAR-T cell therapy, emphasizing the contribution of initial tumor load, the proliferation of CAR-T cell and inhibition of CAR-T cell activity by the tumor resulting in different scenarios as tumor escape, equilibrium (stable disease) and tumor elimination.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 1, p31-37 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.016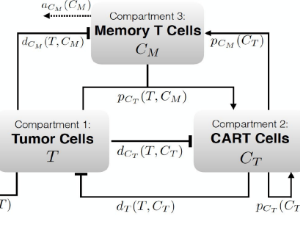
The Role of NETosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Ryan Salemme, Lauren N. Peralta, Sri Harika Meka, Nivetha Pushpanathan, Jessy J Alexander
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a devastating autoimmune disease that affects women to men at a ratio of 9:1 and is predominant in those of African ancestry. In SLE, the presence of autoantigens results in aberrant immune activation leading to systemic inflammation that predominantly affects the brain, kidneys, blood, and skin. Current guidelines recommend treatment with immunosuppressive drugs like prednisone, cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, and even some antimalarial drugs
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p35-44 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.008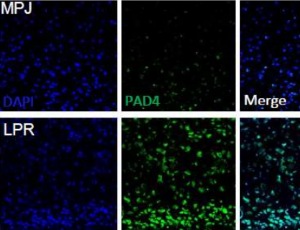
Naltrexone as a Novel Therapeutic for Diabetic Corneal Complications
Patricia J. McLaughlin, Joseph W. Sassani, Ian S. Zagon
Diabetes is a widespread autoimmune disorder that affects nearly 10% of the adult population in the United States. In addition to the primary disease, there are numerous complications associated with inflammation including abnormalities of the heart, visual system, and peripheral nervous system. More than half of the individuals with diabetes will have one or more ocular related complications such as dry eye disease (DED), keratopathy, or retinopathy.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 2, p42-46 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.018
Inulin Supplementation Mitigates Gut Dysbiosis and Brain Impairment Induced by Mild Traumatic Brain Injury during Chronic Phase
Lucille M. Yanckello, Brian Fanelli, Scott McCulloch, Xin Xing, McKenna Sun, Tyler C. Hammond, Rita Colwell, Zezong Gu, Aaron C. Ericsson, Ya-Hsuan Chang, Adam D. Bachstetter, Ai-Ling Lin
Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) has been shown to acutely alter the gut microbiome diversity and composition, known as dysbiosis, which can further exacerbate metabolic and vascular changes in the brain in both humans and rodents. However, it remains unknown how mTBI affects the gut microbiome in the chronic phase recovery (past one week post injury). It is also unknown if injury recovery can be improved by mitigating dysbiosis. The goal of the study is to fill the knowledge gap.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume 4, Issue 2, p50-64 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.132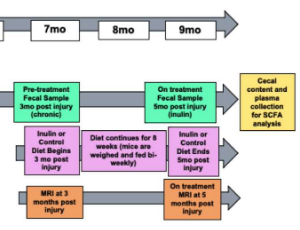
Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/NFkB Axis in Ovarian Cancer
Alia Ghoneum, Ammar Yasser Abdulfattah, Neveen Said
Ovarian cancer stands as the most lethal gynecologic malignancy and remains the fifth most common gynecologic cancer. Poor prognosis and low five-year survival rate are attributed to nonspecific symptoms at early phases along with a lack of effective treatment at advanced stages. It is thus paramount, that ovarian carcinoma be viewed through several lenses in order to gain a thorough comprehension of its molecular pathogenesis, epidemiology, histological subtypes, hereditary factors, diagnostic approaches, and methods of treatment.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 2, p68-73 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.022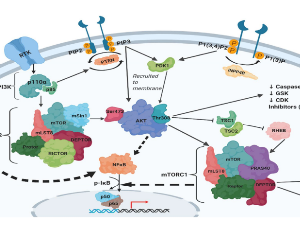
Review of the COVID-19 Risk in Multiple Sclerosis
Farhan Chaudhry, Cristina Jageka, Phillip D. Levy, Mirela Cerghet, Robert P Lisak
The ongoing pandemic of the novel coronavirus of 2019 (COVID-19) has resulted in over 1 million deaths, primarily affecting older patients with chronic ailments. Multiple sclerosis (MS) patients have been deemed particularly vulnerable given their high rates of disability and increased susceptibility to infections. There have also been concerns regarding disease-modifying therapy (DMT) during the pandemic as many DMTs may increase the risk of infection due to some of their immunosuppressive properties.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2, p68-77 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.080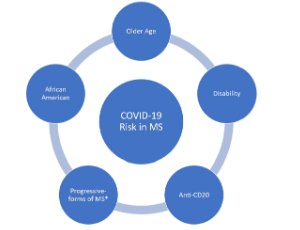
Breast Implant-associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: A Review with Emphasis on the Role of Brentuximab Vedotin
Anthony Stack, Nadia Ali, Nadia Khan
Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma is a recently recognized complication of textured breast implants. It typically presents as unilateral peri-implant swelling approximately 7-10 years after implantation. While the course is usually indolent, breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma may form a locally invasive mass and metastasize to regional lymph nodes or beyond to distant sites.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 3, p80-89 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.025
M1 Macrophages are More Susceptible to Necroptosis
Qin Hao, Steven Idell, Hua Tang
Macrophages play a crucial role in host innate immune defense against infection and tissue injury. Although macrophage activation and polarization has been well studied, we know less regarding the role of macrophage activation/polarization in inflammationassociated necrotic cell death. By using bone marrow-derived macrophages, we have recently demonstrated that M1 macrophages are much more susceptible than M0 and M2 subtypes of macrophages to necrotic cell death.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2, p97-102 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.084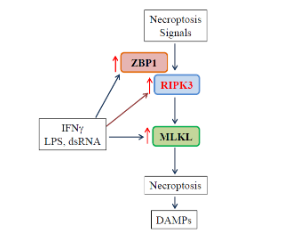
Structural Consequences of Variation in SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7
David A. Ostrov
New globally circulating SARS-CoV-2 strains are causing concern about evolution of virus transmissibility, fitness and immune evasion mechanisms. A variant emerging from the United Kingdom called SARS-CoV-2 VUI 202012/01, or B.1.1.7, is thought to exhibit increased transmissibility that results from replication 4-10 times faster than the original Wuhan virus (Wuhan-Hu-1).
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2, p103-108 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.085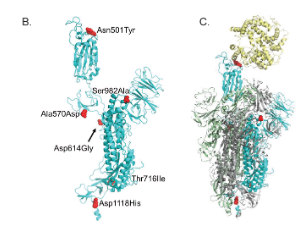
M1 and M2 Macrophages Polarization via mTORC1 Influences Innate Immunity and Outcome of Ehrlichia Infection
Ibrahim Ahmed, Nahed Ismail
Human monocytic ehrlichiosis (HME) is an emerging life-threatening tick-borne disease caused by the obligate intracellular bacterium Ehrlichia chaffeensis. HME is often presented as a nonspecific flu-like illness characterized by presence of fever, headache, malaise, and myalgia. However, in some cases the disease can evolve to a severe form, which is commonly marked by acute liver injury followed by multi-organ failure and toxic shock-like syndrome.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 3, p108-115 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.029
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinases in Leukemia Development
Changhao Cui, Chen Wang, Min Cao, Xunlei Kang
Ca2+/ calmodulin (CaM) signaling is important for a wide range of cellular functions. It is not surprised the role of this signaling has been recognized in tumor progressions, such as proliferation, invasion, and migration. However, its role in leukemia has not been well appreciated. The multifunctional Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinases (CaMKs) are critical intermediates of this signaling and play key roles in cancer development.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 3, p144-150 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.091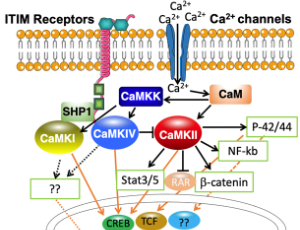
Lung-targeted SERCA2a Gene Therapy: From Discovery to Therapeutic Application in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis
Malik Bisserier, Lahouaria Hadri
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is an interstitial lung disease characterized by an accumulation of scar tissue within the lungs and the common presence of usual interstitial pneumonia. Unfortunately, only a few FDA-approved therapeutic options are currently available for the treatment of IPF and IPF remains associated with poor prognosis. Therefore, the identification of new pharmacological targets and strategies are critical for the treatment of IPF.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 4, p149-156 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.033
Allicin as an Adjunct Immunotherapy against Tuberculosis
Samreen Fatima, Ved Prakash Dwivedi
Allicin (diallylthiosulfinate) is a volatile, oxygenated, sulphur-containing compound, extracted from garlic (Allium sativum). It is responsible for the characteristic odor of garlic. Allicin is known to exert its effects as an antipathogenic agent mainly by targeting the thiol-containing proteins or enzymes in different microorganisms and also by regulating the key genes responsible for the virulence of the microorganism.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 4, p178-182 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.039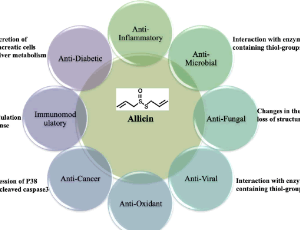
Current Advances in CAR T Cell Therapy for Malignant Mesothelioma
Astero Klampatsa, Steven M. Albelda
Malignant mesothelioma is a relatively rare malignancy arising in the body’s serosal surfaces, with malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) being the most common type. It is characterized by local spread within the thorax, poor prognosis and resistance to treatment. The development of various immunotherapeutic options has provided a new way- and hope- in treating cancer patients. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy has been proven very successful in treating hematological cancers, like leukemias and lymphomas, and its use is now being tested in solid tumors.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 4, p192-200 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.042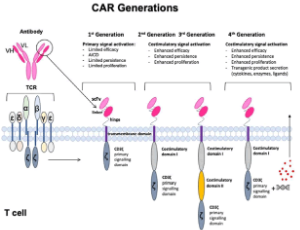
Is Cellular Senescence of Dopaminergic Neurons the Cause of Local Inflammation in the Midbrain Observed in Parkinson’s Disease?
Markus Riessland
Current research investigating the pathomechanisms of neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system (CNS), such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), or Parkinson’s disease (PD), led to the understanding that these diseases have to be seen in the context of immune responses. In other words, inflammation plays a central role in neurodegenerative disorders of the CNS.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 5, p201-204 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.043
The Importance of miRNA Identification During Respiratory Viral Infections
Ivan Martinez-Espinoza, Ma Del Rocio Banos-Lara, Antonieta Guerrero-Plata
The expression of small non-coding RNA MicroRNAs (miRNAs) during respiratory viral infections is of critical importance as they are implicated in the viral replication, immune responses and severity of disease pathogenesis. Respiratory viral infections have an extensive impact on human health across the globe. For that is essential to understand the factors that regulate the host response against infections.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 4, p207-214 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.101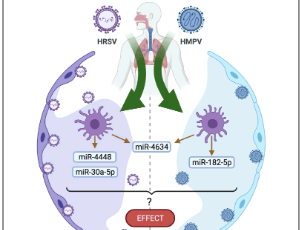
Updates of Recent Vinpocetine Research in Treating Cardiovascular Diseases
Chongyang Zhang, Chen Yan
Vinpocetine is a derivative of vincamine. It has been used to prevent and treat cerebrovascular disorders such as stoke and dementia, and remains widely available in dietary supplements that often marketed as nootropics. Due to its excellent safety profile at therapeutic dose regimen, vinpocetine has raised research interest in its new applications in various experimental disease models.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 5, p211-219 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.045
Immunotherapy for Dogs: Still Running Behind Humans
Hans Klingemann
Despite all good intentions, dogs are still running behind humans in effective cancer immunotherapies. The more effective treatments in humans, like infusions of CAR-T and NK-cells are not broadly pursued for canines due to significant costs, the rather complicated logistics and the lack of targetable surface antigens. Monoclonal antibodies are challenging to develop considering the limited knowledge about canine target antigens and about their mode of action.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 4, p226-233 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.103
Cyclosporine Broadens the Therapeutic Potential of Lenalidomide in Myeloid Malignancies
Aixia Dou, Jing Fang
The immunomodulatory drug lenalidomide is used for the treatment of certain hematologic malignancies, including myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Lenalidomide interacts with cereblon (CRBN), a component of the CRL4CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, leading to ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of substrates, such as transcription factor Ikaros (Ikaros family zinc finger 1, IKZF1).
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 5, p237-244 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.049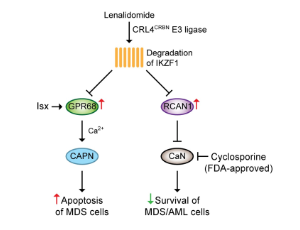
Emerging Functions of ICAM-1 in Macrophage Efferocytosis and Wound Healing
Prarthana J. Dalal, Ronen Sumagin
ICAM-1 is a transmembrane, cell surface glycoprotein expressed by a variety of cells, but has been best-studied in vascular endothelium. Structurally, ICAM-1 is composed of five extracellular IgG- like domains to help facilitate cell-cell interactions and has a short cytoplasmic tail anchored to the cytoskeleton to facilitate intracellular signal transduction.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 5, p250-253 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.051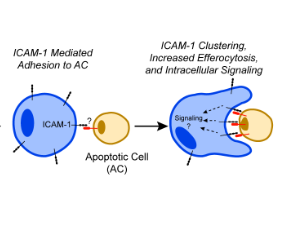
Short and Sweet: Viral 5`-UTR as a Canonical and Non-Canonical Translation Initiation Switch
Brandon M. Trainor, Natalia Shcherbik
The replication of viruses requires host cell functions, specifically for protein synthesis, as viruses lack their own translational machinery. Failure to translate viral mRNAs and generate viral proteins would affect the propagation and evolution of a virus. Thus, independently of their size, complexity, and genomes, viruses evolved sophisticated molecular mechanisms to hijack the translational apparatus of a host in order to recruit ribosomes for efficient protein production.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 5, p296-304 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.110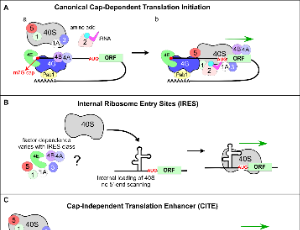
Maternal Diet Alters Trained Immunity in the Pathogenesis of Pediatric NAFLD
Karen R. Jonscher, Jesse Abrams, Jacob E. Friedman
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a spectrum of pathologies ranging from simple steatosis to fibrosis and cirrhosis, is the most common cause of chronic liver disease, affecting over 80% of adults with obesity, one third of obese children ages 3-18 in North America [2] and ~10% of the general pediatric population.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 6, p315-325 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.061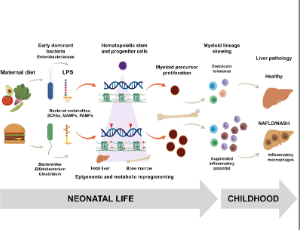
Potentials of Interferons and Hydroxychloroquine for the Prophylaxis and Early Treatment of COVID-19
Alexander Yang, Lakshmi S. Guduguntla, Bing Yang
The symptoms of the COVID-19 range from asymptomatic or mild disease to severe disease that results in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and eventually death. Understanding the molecular mechanisms responsible for the progression from mild to severe disease is the key to decreasing the mortality of COVID-19. Compared to mild cases, severe cases of the COVID-19 have decreased interferon (IFN) a, ß, λ production. Type I (IFN a/ß) and III IFNs (λ) work coordinately to induce inhibition of viral reproduction through the stimulation of interferon stimulated genes (ISGs).
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 6, p333-340 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.063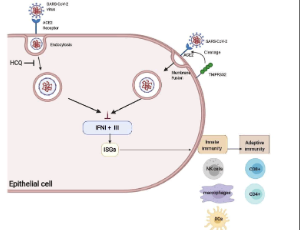
Newly Identified Function of Caspase-6 in ZBP1-mediated Innate Immune Responses, NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation, PANoptosis, and Host Defense
Min Zheng, Thirumala-Devi Kanneganti
Caspase-6 was discovered decades ago, but its roles in biological processes remain largely unknown. Recently, we have demonstrated that caspase-6 plays a critical role in influenza A virus (IAV)-induced cell death and innate immune responses. During IAV infection, Z-DNA binding protein 1 (ZBP1) initiates ZBP1-PANoptosome assembly to drive inflammasome activation and cell death, and we showed that caspase-6 interacts with RIPK3 to enhance the interaction between RIPK3 and ZBP1, thus promoting PANoptosome assembly.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 6, p341-347 | DOI: https://doi.org/10.33696/immunology.2.064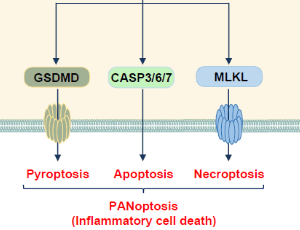
Megalin-Mediated Trafficking of Mitochondrial Intracrines: Relevance to Signaling and Metabolism
David Sheikh-Hamad, Michael Holliday, Qingtian Li
The multi-ligand binding protein megalin (LRP2) is ubiquitously expressed and facilitates cell uptake of hormones, nutrients and vitamins. We have recently shown megalin is present in the mitochondria of cultured epithelial and mesenchymal cells, as well as many organs and tissues. Mitochondrial megalin associates with stanniocalcin-1 and SIRT3; two proteins that promote anti-oxidant defenses.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 6, p364-369 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.118
Human Gray and White Matter Metabolomics to Differentiate APOE and Stage Dependent Changes in Alzheimer’s Disease
Tyler C. Hammond, Xin Xing, Lucy M. Yanckello, Arnold Stromberg, Ya-Hsuan Chang, Peter T. Nelson, Ai-Ling Lin
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia with hallmarks of ß-amyloid (Aß) plaques, tau tangles, and neurodegeneration. Studies have shown that neurodegeneration components, especially brain metabolic deficits, are more predictable for AD severity than Aß and tau. However, detailed knowledge of the biochemical composition of AD brain tissue vs. normal brain tissue remains unclear.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 6, p397-412 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.123
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
