Loading
Archives of Orthopaedics
ISSN: 2692-8299
All Articles
EMG Signal Processing for Hand Motion Pattern Recognition Using Machine Learning Algorithms
Yang Zhou, Chaoyang Chen, Juan Ni, Guoxin Ni, Min Li, Guanghua Xu, John Cavanaugh, Mark Cheng, Stephen Lemos
Stroke is a major cause of death and disability in the world. There were approximately 25.7 million stroke survivors and 6.5 million deaths from stroke [1]. Stroke can result in arm disability and reduce daily life activity via weak arm muscle activity [2]. Studies have been performed to discover therapeutic and assistive approaches to compensate for disabilities and restore functions.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.005
Ultrasound-Guided Bone Surgery: A New Perspective
Alvaro Martínez-Ayora, Manuel Cuervas-Mons, Javier Vaquero
Metatarsalgia is a frequent cause of forefoot pain. Surgical treatment is based on the performance of osteotomies at the level of the minor radii to restore a normal distribution of pressure within the forefoot and improve the biomechanics during gait.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p1-4 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.001
Atypical Presentation of Tibia and Fibula Fracture in an Old Woman - Case Report
Esam Lawand, Michael Krasheninnikoff, Jacob Fyhring Mortensen
This case report presents the clinical details, diagnostic findings, and management of a 64-year-old female patient who suffered a tibia and fibula fracture, presented in an atypical manner, after twisting her ankle during daily activities. The medical background, physical examination, radiological results, and course of treatment of the patient are detailed.
Arch Orthop, 2024, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p1-4 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.4.030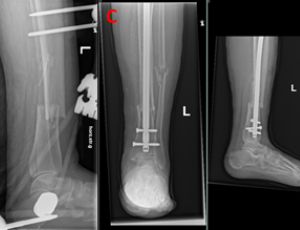
Academic Productivity and Demographic Analysis of Adult Reconstruction Fellowship Program Directors
Maximillian P. Ganz, Giles R. Scuderi
Introduction: Variation between academic quality of American College of Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) and non-ACGME accredited adult reconstruction fellowship programs has not been previously examined. The purpose of this study is to compare ACGME and non-ACGME-accredited adult reconstruction fellowship programs’ degree of diversity and academic contribution by evaluating program directors’ diversity, academic impact, and contribution to the field of arthroplasty.
Arch Orthop, Volume 5, Issue 1, p1-6
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Study of the Element Concentrations in Synovial Fluids of Patients with Arthritis and Rheumatic Diseases
Pawel Konieczynski, Grzegorz Szreder, Marek Wesolowski
Rheumatic diseases are one of the most common problems in modern societies. The majority of rheumatic diseases occur when the human immune system attacks its own tissues, including the joints. There is no single cause of rheumatic diseases. Sometimes it may be a genetic factor, but in other cases cigarette smoking is responsible for the disease, or pollution, or other factors such as an infection. Seidman and Limaiem claim that “synovial fluid aspiration and analysis is a necessary therapeutic and diagnostic procedure useful in alleviating pain from a joint effusion and in the diagnosis of potentially serious joint pathologies.”
Arch Orthop, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p1-9 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.3.024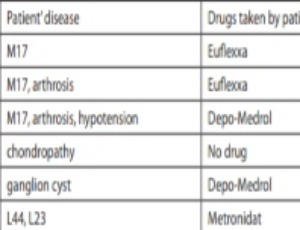
Efficacy of a Virtual Fracture Clinic Model Created During Covid-19 Pandemic
Anne-Marie Hutchison, Paul Williams, Andrew Bebbington, Mark Mullins, Andrew Lewis, David Beard
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused delivery of orthopaedic services to require extra consideration and substantial revision. Alternative ways to manage patients with urgent injuries have been instigated to minimize patient’s exposure to the disease, spread within the hospital system and reduce the overall impact on stretched resources.
Arch Orthop, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p1-11 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.2.020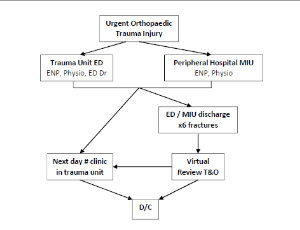
Rearfoot and Ankle Reconstruction for Charcot Joint Disease: A Review
Gabriel Santamarina
Charcot joint disease refers to the structural breakdown of the joints in the presence of neuropathy [1]. It has multiple pseudonyms but one of the most descriptive names of this condition is “Diabetic Neuroarthropathy.” The first cases studied by Jean-Marie Charcot however were not due to diabetic peripheral neuropathy but syphilis-related peripheral neuropathy.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p5-10 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.002
Doctor, Can We Reuse this Brace; Patient Attitudes towards Reuse of Orthopedic Braces
Raja Jambulingam, Yusuf Mirza, Mark Kemp
Introduction: Climate change presents an important threat to human health and wellbeing. Paradoxically, many facets of healthcare provision contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. An important example of this is the use of single use, disposable orthopedic orthotics, widely dispensed in emergency departments and fracture clinics. This study aimed to understand patients’ attitudes towards climate change, single use plastics, and recycling of orthotics.
Arch Orthop, 2024, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p5-12 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.4.031
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Application of Ultrasonic Bone Scalpel System for Laminectomy and Osteotomy of PLL Ossification Blocks Combined with Kyphosis Deformity Correction in Multilevel Thoracic OPLL Treatment
Yuwei Li, Xiu-Zhi Li, Zimin Wang, Haijiao Wang, Shifeng Gu, Wei Cui, Yan He
Objective: To explore the safety and clinical efficacy of using the ultrasonic bone scalpel (UBS) system for laminectomy, osteotomy of posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL) ossification, combined with correction of kyphosis deformity in the treatment of multilevel thoracic ossification of the PLL. Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on patients with multilevel thoracic ossification of the PLL who underwent laminectomy, osteotomy of PLL ossification, combined with correction of kyphosis deformity using the UBS system from January 2020 to April 2023.
Arch Orthop, Volume 5, Issue 1, p7-16
Evaluation of Specific Cementation Criteria on Total Elbow Arthroplasty – A Mono-Center Analysis of 31 Cases, with Minimum Follow-up of 4 Years
Arnaldo Sousa, Joao Rosa, Diogo Sousa, Alexandre Pereira, Cesar Silva
Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) has gained popularity in recent years and the indications for performing this surgery have been expanding. Initially this arthroplasty was used predominantly in patients with severe rheumatoid arthritis of the elbow, however, nowadays, TEA has been performed also in other situations like osteoarthritis, comminuted intraarticular fractures or tumors.
Arch Orthop, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p10-16 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.3.025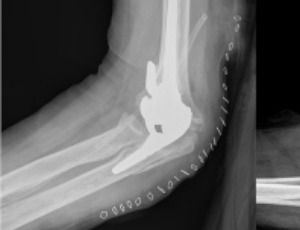
Viscosupplementation in Horses: What do We Really Know?
Anderson Fernando de Souza, André Luis do Valle De Zoppa
The importance of osteoarthritis (OA) is undeniable in equine medicine, with a high occurrence in the routine, several studies have been carried out to understand the pathophysiology of the disease and to seek more efficient methods of prevention and treatment.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p11-13 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.003
Improve the Efficiency of the Yaskawa Motoman MH5 Robot for Utilization in Robot-Assisted Orthopedic Surgery
Arshia Eskandari, Arash Sherafati, Samir Zein
Using robots in surgeries dates back to the mid-1980s. The robotic was applied in a wide range of biological and medical sciences such as clinical medicine, neuroscience, cardiovascular, dentofacial, and cellular and molecular life sciences. Orthopedic robots are much more widely used and complex in medical engineering sciences.
Arch Orthop, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p12-19 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.2.021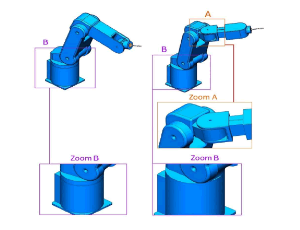
The Incidence and Risk Factors of Pelvic Stress Fracture, Delayed-healing and Non-union Following Periacetabular Osteotomy in Adolescents
Daniel Lazar, Daniel Bomark, Ole Ovesen, Morten Bøgehøj, Søren Overgaard
Background: Periacetabular Osteotomy (PAO) is a well-established procedure, however more prospective cohort studies are required to assess all clinical factors related to this invasive intervention. The aims of this study are as follows 1) quantifying stress fractures, delayed-healing and non-union post PAO and 2) to correlate possible risk factors for developing symptomatic stress fracture, delayed-healing or non-union.
Arch Orthop, 2024, Volume Volume 4, Issue Issue 1, p13-19 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.4.032
Editorial Commentary for In Throwers with Posterior Instability, Rotator Cuff Tears are Common but Do Not Affect Surgical Outcomes
Andrew J. Sheean, James P. Bradley
Superior labral pathology is an exceedingly common entity among throwers, and in recent years, a number of reports have elucidated the prevalence of posterior glenohumeral instability among overhead athletes (baseball, softball, volleyball.) However, within this unique patient population, these conditions should not be viewed as separate clinical entities, but, rather as findings that exist on a single pathomechanic spectrum.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 1, p14-16 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.004
Surgical Management of Patella Fractures: A Review
Andrew D. Posner, Joseph P. Zimmerman
Patella fractures account for 1% of fractures in adults and are seen in all age groups. The treatment options for fractures requiring surgery have evolved over time in response to postoperative complications and with the advent of new technologies which optimize fixation.
Arch Orthop, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p17-21 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.3.026
Performance Validation of An Upper Limb Exoskeleton Using Joint ROM Signal
Yousef Alshahrani, Yang Zhou, Chaoyang Chen, Hannah Joines, Tangfei Tao, Guanghua Xu, Stephen Lemos
Upper extremity (UE) exoskeletons were developed for industrial applications where assistive force enhancement was needed, but there have also been developments for use in telemanipulation and virtual reality, clinical applications such as assistance in orthopedic surgery, and orthopedic rehabilitation.
Arch Orthop, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p20-29 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.2.022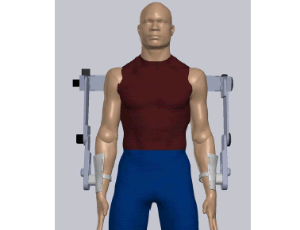
L-shaped Corrective Osteotomy for Distal Radius Malunion
Nicolás Gabriel Cuestas, Ana Laura Douglas Price, María Candelaria Torre, Hernán Esteban Blanchetiere
For many years it was widely believed that the functional outcome of distal radius fractures (RDF) was usually satisfactory, even in the absence of treatment or when treatment had failed to achieve acceptable anatomic reduction.
Arch Orthop, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p22-26 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.3.027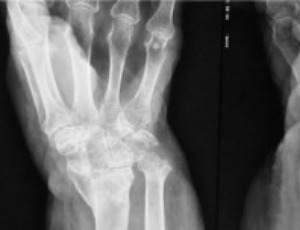
The Natural History of Developmental Patellar Dislocation in Dogs
Michael Farrell
Developmental dislocation of the patella (DDP) is rare in humans but common in dogs. The canine syndrome, termed patellar luxation (PL), is an inherited condition related to genetic selection of dogs with conformational defects. Breeds with short, bowed legs, including chihuahuas, toy poodles, and bull terriers are predisposed to medial patellar luxation (MPL).
Arch Orthop, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p27-32 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.3.028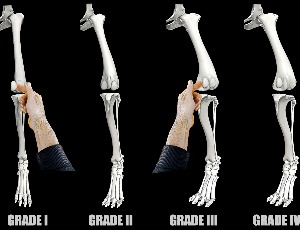
Physiotherapy Exercise Program for Managing Adhesive Capsulitis in Patients with and without Diabetes: A Pilot Randomized Trial
Sana’a A. Alsubheen, Joy C. MacDermid, Tom J. Overend, Kenneth J. Faber, Rochelle Furtado
Adhesive capsulitis (AC), also known as ‘frozen shoulder’, is characterized by the development of dense adhesions and capsular thickening leading to a progressive and painful restriction of shoulder range of motion (ROM) and functional disability [1]. The onset is gradual, usually occurs between the ages of 40 and 60 years and is more common in females and diabetics.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p27-39 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.006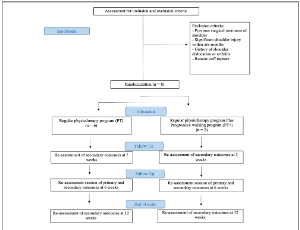
Evaluation of Patellofemoral Complications by Comparing the Medial Parapatellar and Subvastus Approaches
Mehmet Menken, Raif Özden, Mehmet Karadag, Ibrahim Gökhan Duman, Aydiner Kalaci, Yunus Dogramaci
Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is considered to be the best method for treating advanced knee osteoarthritis in terms of reducing pain, improving joint functions, and increasing the patient’s quality of life. The most commonly used approach in TKA is the standard medial parapatellar (MPP) approach described by Insall. The MPP approach provides a good view of the operating field.
Arch Orthop, 2021, Volume Volume 2, Issue Issue 1, p31-36 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.2.023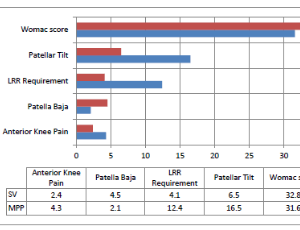
Surgical Fixation of Severe Rib Fractures: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis
Adam M. Shiroff, Simone Wolf, Alex Wu, Mollie Vanderkarr, Raymark Salonga, Thibaut Galvain, Chantal E Holy
Rib fractures are a commonly encountered traumatic injury and are associated with significant morbidity and mortality. They are a marker of severe injury and can lead to defects in the chest wall and severe pain which may hinder breathing.
Arch Orthop, 2022, Volume Volume 3, Issue Issue 1, p33-45 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.3.029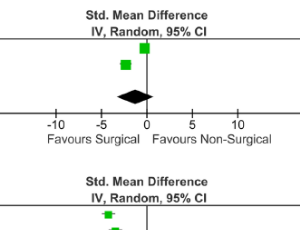
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Relationship between Plate Length and Fracture Height as a Predictor of Non-Union in Distal Femur Fractures. A Restrospective Study
Alvaro Martínez-Ayora, Marina Diaz-Jumain, Eudaldo José Gallo-del Valle, Manuel Cuervas-Mons Cantón, Juan Arnal-Burró, Javier Vaquero
The distal femur constitutes the region between the metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction and the femoral condyles. Fractures of this segment, which includes supracondylar and intercondylar fractures, represent between 4 and 7% of all the femur fractures, with an incidence of 37 cases per 100,000 habitants/year. These fractures present a bimodal distribution depending on the injury mechanism.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p40-48 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.007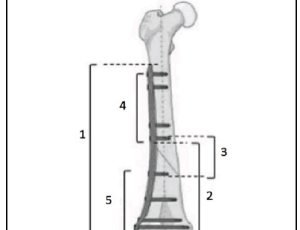
The Role of the MPFL and MPTL in Patellar Stability – A Biomechanical Study
James P. Halloran, Amanda O. Esquivel, Allison M. Cracchiolo, Chaoyang Chen, Stephen E. Lemos
The medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) is a thickened band of tissue that originates from the adductor tubercle and inserts on the proximal medial patella. It is expected that the MPFL, under patellar lateral subluxation, will fail at approximately 12-18 mm of displacement due to the failing of collagen based structures at 20% to 30% elongation.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p49-54 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.008
The Role of the Sciatic Nerve Ultrasound Elastography in the Clinical Pathway: A Meta-analysis
Stajic Sava, Misic Miroslav
Ultrasound elastography is a diagnostic method, to measure elasticity and strain in tissues and organs. The aim of this review was to highlight the usefulness of sciatic nerve ultrasound elastography in clinical practice. Different changes affect the sciatic nerves through various diseases and conditions.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p55-60 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.009
Clinical and Histological Proof that Surgical Incisions along Skin Folding Lines Result in Optimal Scars
Gottfried Lemperle
In an early publication, we could show that striae distensae always develop perpendicular to the skin tension lines. In another article, we demonstrated that virtual skin tension lines are identical to the obvious Main Folding Lines; we recommended their use as optimal directions for orthopedic incisions, when inconspicuous scar formation is a prerequisite, as in children, younger adults, and women.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 2, p61-67 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.010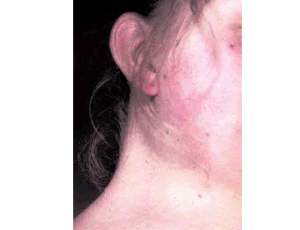
Epidemiology of Displaced Supracondylar Fractures
Nicholas I. Pilla, John M. Rinaldi, Mark D. Hatch, William L. Hennrikus
Supracondylar fractures of the humerus are the most common elbow fracture in the pediatric population and comprise nearly 60% of all elbow fractures. Supracondylar fractures most commonly occur in children aged five to seven. Historically, males had a higher incidence of supracondylar humeral fractures. More recent studies support a more equal distribution amongst males and females.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p68-73 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.011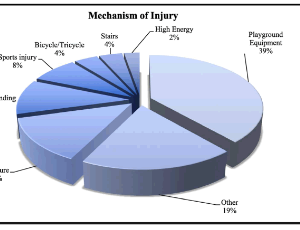
Pain in Patients undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty
Ramlall Y, Cameron HU, Sawhney M
Pain continues to be reported by patients waiting for total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and after undergoing this surgery despite advances in the delivery of pain management. The motivation for carrying out this initial work was due to the concerns of the surgeons based on patients reports of pain, at their 6-week return to clinic appointments. Concerns of addiction, overdosing, multi-modal analgesia and lack of pain education were the factors.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p73-74 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.012
Incidental Spinal Durotomies Noted During Spinal Surgery: Incidence and Management
Ishvinder Singh Grewal, Urpinder Singh Grewal, Tom Eadsforth, Robin Pillay
An incidental durotomy or dural tear is defined by ICD- 10 as an accidental puncture or laceration of dura during a procedure. These procedures include spinal surgery and interventional procedures such as epidural injection. The published incidence of incidental durotomy varies in the literature and is dependent on the procedure being performed, the experience of the surgeon, and patient factors but can range from 1% to 17%.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p76-82 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.013
The use of Percutaneous Achilles’ Tendon Lengthening as an Adjunct Procedure in Foot and Ankle Surgery: A Review
Gabriel Santamarina, George Zislis
The goal of reconstructive foot and surgery for diabetic foot pathologies is to create a plantigrade foot that is braceable and has low risk of ulcer formation or recurrence. Experienced surgeons are cognizant that foot pathologies are defined in three planes: frontal, transverse and sagittal. The Achilles’ tendon is the chief deforming force in the foot along the sagittal plane.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p83-88 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.014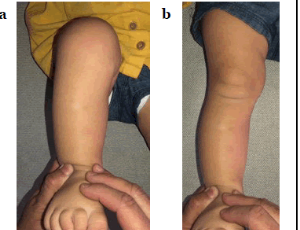
Hamstrings Injuries with MRI Findings in a Major League Soccer Team
Gabriella Bucci, Nicolas Galante, Ryan P. McGovern, Skylar Richards, John J.Christoforetti, Steven B. Singleton
Hamstring injuries are the most common pathology reported in professional soccer players and represent about 10-30% of all injuries. The hamstring complex is comprised of three muscles located in the posterior compartment of the thigh including the semimembranosus (SM), semitendinosus (ST), and biceps femoris (BF), which is comprised of the long head (BFLH) and short head (BFSH).
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 3, p89-97 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.015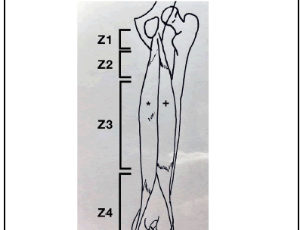
Bacterial Biofilms and Implant Infections: A Perspective
T. Subba Rao
Human body implants are rapidly covered by a conditioning film (which contains the biochemical moieties) when they interact with human body fluids and its components. This surface-bound biochemical blend elicits a chemotactic response to attract bacteria that are transmitted through infection or by contamination.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 4, p98-105 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.016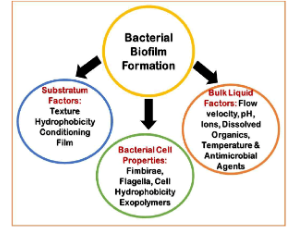
Submuscular Anterior Transposition for Treatment of Ulnar Nerve Syndrome: Outcomes and Final Satisfaction
Alvaro Martínez-Ayora, Julio Morán, Antonio Benjumea-Carrasco, Eudaldo José Gallodel Valle, Javier Vaquero
Ulnar neuropathy is the second most common peripheral neuropathy in the upper limb after carpal tunnel syndrome, with an incidence of 30 cases per 100,000 persons/year. It is characterized by the appearance of sensory symptoms such as pain, dysesthesia, and paresthesia, initially intermittent and then continuous, in the ulnar territory of the forearm and hand.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 4, p106-114 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.017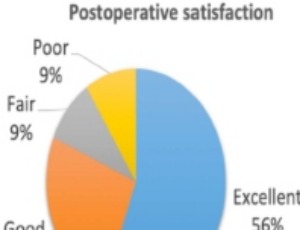
The Use of a New Type of Heart Rate-controlled Training System HeartGo® for Patients with Chronic Heart Failure on the Pedelec
Erik B. Friedrich, Herbert Löllgen, Helmut Röder, Wolfgang Baltes, Oliver Adam, Martin Schlickel, Günter Hennersdorf
Secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease such as heart failure includes regular physical activity with endurance and strength training, which is used for this purpose with high prevalence. Early rehabilitation should begin in hospital (phase I), be continued in a rehabilitation clinic or as an outpatient close to home (phase II), and then (phase III) preferably in outpatient heart groups (AHG).
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 4, p115-125 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.018
A Pilot Study for Assessing a Novel Method of Measuring Shoulder Activation in Healthy Volunteers Using Surface Electromyography
Sreten Franovic, Yang Zhou, Emily Lau, Alexander D Pietroski, Noah A Kuhlmann, Vishwajeet Singh, Chaoyang Chen, Stephanie J Muh
Over the years, healthcare providers have used a host of physical examinations and clinical tools to assess a patient’s physical functioning and health, but many of these assessment tools lack generalizability among physicians or the specificity and sensitivity to accurately diagnose a patient. Range of motion measures are one-way physicians assess many physical deficiencies in the upper and lower extremity.
Arch Orthop, 2020, Volume Volume 1, Issue Issue 4, p126-134 | DOI: 10.33696/Orthopaedics.1.019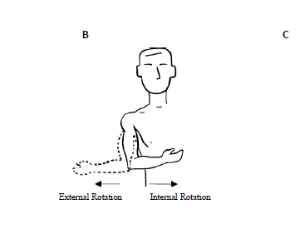
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
