Loading
Journal of Cellular Signaling
ISSN: 2692-0638
Featured Articles
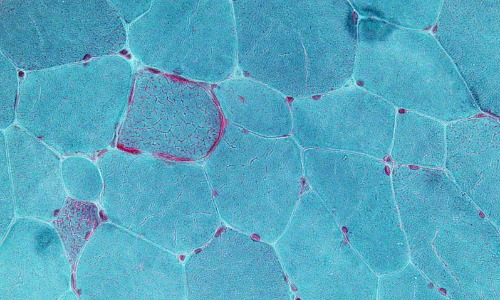
Augmenting Venetoclax Activity Through Signal Transduction in AML
Ian Michael Bouligny, Keri Renee Maher, Steven Grant
Venetoclax, a small-molecule B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) inhibitor, selectively eradicates leukemic stem cells (LSCs). While venetoclax has revolutionized the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), treatment failure and disease relapse are common. Mechanisms underlying venetoclax resistance are surprisingly heterogeneous.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 1, p1-12 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.085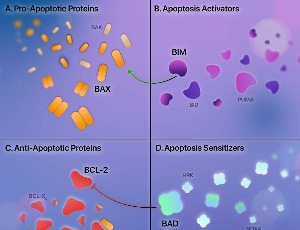
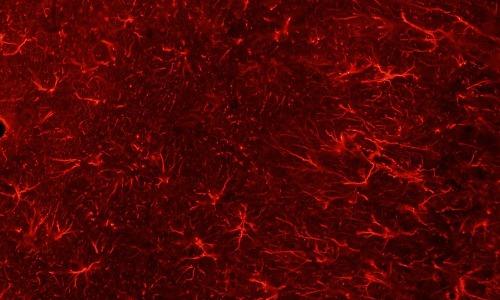
Signaling of Mitogenic and Metabolic Activities by Fibroblast Growth Factors
Patience Salvalina Okoto, Zeina Alraawi, Thallapuranam Krishnaswamy Suresh Kumar
Fibroblast growth factors are signaling molecules that play crucial roles in fundamental processes such as cell migration, proliferation, differentiation, angiogenesis, and cell survival. FGFs signal by forming a complex with tyrosine kinase FGF receptors and cofactors. It is well known that FGFs play diverse roles in different tissues and at different developmental stages due to factors such as receptors, specific FGFs, and environmental conditions such as temperature and pH.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p1-8 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.127
Manipulating Oxidative Stress Following Ionizing Radiation
Adriana Haimovitz-Friedman, Aviram Mizrachi, Edgar A. Jaimes
It is now well accepted that the ionizing radiation-generated reactive oxygen species (ROS), that constitute ~2/3 of the effects of external beam radiation, do not only produce direct tumor cell death, but also affect the surrounding microenvironment. Moreover, this indirect effect of radiation may result in systemic effects, specifically the initiation of an inflammatory response.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p8-13 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.003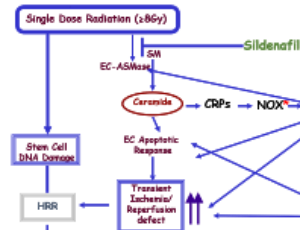
FOXP1 Interacts with MyoD to Repress its Transcription and Myoblast Conversion
Woodring E. Wright, Chuan Li, Chang-xue Zheng, Haley O. Tucker
Forkhead transcription factors (TFs) often dimerize outside their extensive family, whereas bHLH transcription factors typically dimerize with E12/E47. Based on structural similarities, we predicted that a member of the former, Forkhead Box P1 (FOXP1), might heterodimerize with a member of the latter, MYOD1 (MyoD).
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p9-26 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.032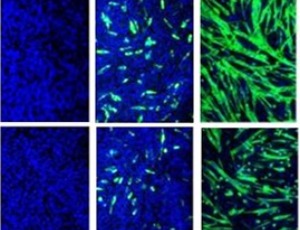
COVID-19 Clinical Research
Jeffrey Chi, David Chitty, Meeyoung Lee, Nausheen Hakim, Shamsah Lakhani, Lakshmi Rajdev, Xinhua Zhu, Muhammad Wasif Saif
While the global COVID-19 pandemic has challenged the entire humanity and health systems, it also triggered researchers to urgently perform clinical trials to assess the safety and efficacy of many agents and modalities to combat COVID-19. As of April 22, over 650 clinical studies have been registered both in USA and internationally. Results from these studies are also coming at a brisk pace in this unprecedented emergency.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 2, p23-30 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.006
Microcystin: From Blooms to Brain Toxicity
Ethan Hedrick, Aryaman Tiwari, Suryakant Niture, Qing Cheng, Deepak Kumar, Somnath Mukhopadhyay
An increase in the temperature of lakes and ponds facilitates the over-growth of photosynthetic cyanobacteria that produce a class of toxins called cyanotoxins. The abundance of cyanobacteria poses a significant threat to drinking and irrigation water supplies, and therefore, cyanotoxins have become a major class of environmental pollutants. Microcystins, the most common cyanotoxins, are cyclic peptides produced by cyanobacteria through non-ribosomal peptide synthases, and currently, approximately 279 microcystins have been identified to date.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p29-38 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.131
Prospective Evaluation of Effect of Metformin on Activation of AMP-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) and Disease Control in a Sub-group Analysis of Patients with GI Malignancies
Amandeep Godara, Nauman S. Siddiqui, Hilal Hachem, Philip N. Tsichlis, Robert E. Martell, Muhammad Wasif Saif
Observational studies have demonstrated association of metformin with reduced cancer incidence and mortality in multiple cancer types, including gastrointestinal (GI) malignancies. Anti-neoplastic effects of metformin are believed through many mechanisms including activation of AMP-activated protein kinase, which controls mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) growth regulatory pathway.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 2, p35-41 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.008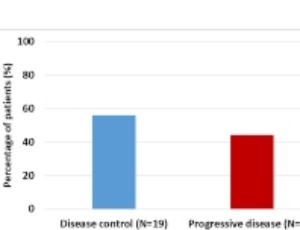
Tumor Lipid Signaling Involved in Hyperoxidative Stress Response: Insights for Therapeutic Advances
Mladen Korbelik, Albert W. Girotti
Most malignantly transformed cells are metabolically rewired to promote their survival and progression, even under conditions that would be unfavorable for normal counterparts. Arguably the most impactful metabolic transformation and recognized cancer hallmark is the reprogrammed lipid metabolism. Lipids are not only primary constituents of cell membranes but essential participants in fundamental cellular functions including cell signaling, protein regulation, energy provision, inflammation, and cell-cell interaction. Engagement of lipids in critical physiological functions in cells is additionally accentuated upon malignant transformation. Pivotal roles of lipids as influential inter- and intracellular signaling molecules, particularly under conditions of hyper oxidative stress, are delineated.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 2, p39-47 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.132
The Effect of Glucocorticoids on Angiogenesis in the Treatment of Solid Tumors
Bing Liu, Julie E. Goodwin
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are defined by their role in maintaining glucose homeostasis and natural GCs are a class of corticosteroids secreted by the adrenal cortex. Cortisol is the most important natural GC in humans. Cellular cortisol levels are regulated by the tissue-specific metabolic enzymes 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 and 2 (11β-HSD 1 and 2); 11β-HSD 1 converts inactive cortisone to active cortisol, while 11β-HSD 2 has the opposite function.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p42-49 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.011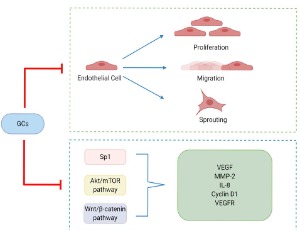
S1P Generation by Sphingosine Kinase-2 in Recruited Macrophages Resolves Lung Inflammation by Blocking STING Signaling in Alveolar Macrophages
Jagdish C Joshi, Bhagwati Joshi, Ian Rochford, Dolly Mehta
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is the major cause of mortality among hospitalized acute lung injury (ALI) patients. Lung macrophages play an important role in maintaining the tissue-fluid homeostasis following injury. We recently showed that circulating monocytes recruited into the alveolar space suppressed the stimulator of type 1 interferon genes (STING) signaling in alveolar macrophages through sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P).
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p47-51 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.034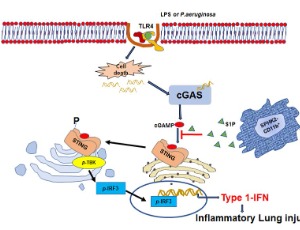
Teaching an Old Drug a New Trick: Targeting Treatment Resistance in Genitourinary Cancers
Karina Aguilar, Anuj K. Sharma, Tianyu Yang, Dipen Mehta, Chandramukhi S. Panda, Vinata B. Lokeshwar
In the quest for improving the clinical outcome of patients with metastatic genitourinary cancers, including metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC), the emphasis often is on finding new targeted therapies. However, two studies by Jordan et al. (Oncogenesis 2020) and Wang et al. (Cancer Cell Int 2022) demonstrate the feasibility of improving the efficacy of a modestly effective drug Sorafenib against mRCC by attacking a mechanism hijacked by RCC cells for inactivating Sorafenib.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 2, p51-56 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.112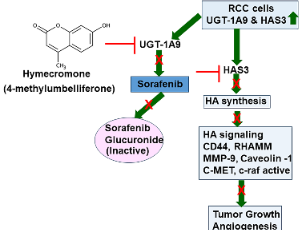
Wnt Signaling Cascades and Their Role in Coronary Artery Health and Disease
Nadisha Weerackoon, Kushan L. Gunawardhana, Arya Mani
The Wnt signaling is classified as two distinct pathways of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling, and the non-canonical pathways of planar cell polarity and Wnt/Ca2+ pathways. However, the scientific discoveries in recent years have shown that canonical and noncanonical Wnts pathways are intertwined and have complex interaction with other major signaling pathways such as hedgehog, Hippo and TOR signaling.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p52-62 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.035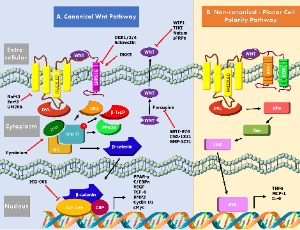
Role of Sphingolipid Signaling in Glomerular Diseases: Focus on DKD and FSGS
Alla Mitrofanova, Yelena Drexler, Sandra Merscher, Alessia Fornoni
Being a sophisticated and highly organized living system, mammals harbor a large number of biomolecular machineries which represent a dynamic and complex network of interconnections responsible for the effective operation, development and survivability of their body cells. Sphingolipids are a special class of lipids in eukaryotic cells, which have recently gained the attention of researchers because of their involvement in several fundamental processes of living cells, including proliferation
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p56-69 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.013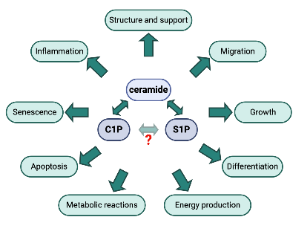
c-JUN n-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Signaling in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
Abigail O. Smith, Julie A. Jonassen, Kenley M. Preval, Roger J. Davis, Gregory J. Pazour
Polycystic kidney disease is an inherited degenerative disease in which the uriniferous tubules are replaced by expanding fluid-filled cysts that ultimately destroy organ function. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is the most common form, afflicting approximately 1 in 1,000 people and is caused by mutations in the transmembrane proteins polycystin-1 (Pkd1) and polycystin-2 (Pkd2).
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 1, p62-78 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.068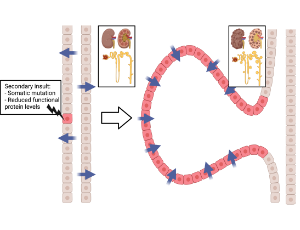
Possible Therapeutic Use of Natural Compounds Against COVID-19
Nabab Khan, Xuesong Chen, Jonathan D. Geiger
The outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) has led to coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19); a pandemic disease that has resulted in devastating social, economic, morbidity and mortality burdens. SARS-CoV-2 infects cells following receptor-mediated endocytosis and priming by cellular proteases.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p63-79 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.036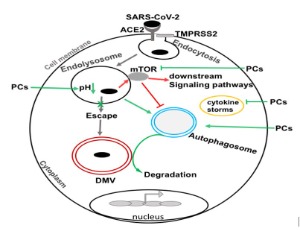
Navigating the Adipocyte Precursor Niche: Cell-Cell Interactions, Regulatory Mechanisms and Implications for Adipose Tissue Homeostasis
Devesh Kesharwani, Aaron Clifford Brown
Support for stem cell self-renewal and differentiation hinges upon the intricate microenvironment termed the stem cell 'niche'. Within the adipose tissue stem cell niche, diverse cell types, such as endothelial cells, immune cells, mural cells, and adipocytes, intricately regulate the function of adipocyte precursors. These interactions, whether direct or indirect, play a pivotal role in governing the balance between self-renewal and differentiation of adipocyte precursors into adipocytes.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 2, p65-86 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.114
Neoadjuvant Therapy (NAT) in Localized Pancreatic Cancer: Should We Do It and What Should We Do?
Shreya Prasad Goyal, Morana Vojnic, Jung-in Yang, Jyothi Jose, Elliot Newman, Muhammad Wasif Saif
In 2019, approximately 56,770 new cases of pancreatic cancer were diagnosed in the United States, resulting in an estimated 45,750 deaths. Pancreatic cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related death, with a fiveyear survival rate of 9%. Based on the eighth edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging system for pancreatic adenocarcinoma, multi-center analyses have validated that poorer prognosis is associated with node-positive disease (N1 and N2).
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p80-84 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.037
Effects of a CB2 Subtype Selective Agonist ABK5-1 on Cytokine Production in Microglia
Yaliang Tang, Barbara Wolk, Debra A. Kendall
Neuroinflammation is closely associated with various diseases including neuropathic pain. Microglia are immune cells in the central nervous system which are the main players of immunity and inflammation. Since microglia are activated by nerve injury, and they produce proinflammatory mediators to cause neuropathic pain, targeting activated microglia is considered to be a strategy for treating neuropathic pain.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p85-93 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.038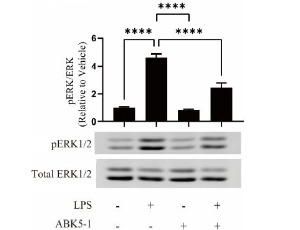
Using Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein Deficiency to Understand Maternal Health
Jason W. Miklas, Hannele Ruohola-Baker
Fatty acid oxidation disorders unfortunately can result in the sudden unexplained death of infants. Mitochondrial trifunctional protein (MTP) deficiency is one such disease where long-chain fatty acids cannot be fully oxidized through beta-oxidation which, can lead to cardiac arrythmias in an infant.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p97-101 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.018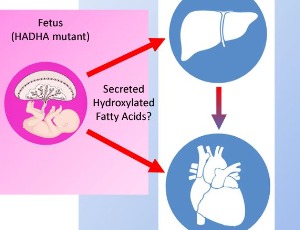
Phosphorylation of RIAM Activates Its Adaptor Function in Mediating Integrin Signaling
Baihao Su, Jinhua Wu
Extracellular matrix (ECM) surrounding cells in solid tissue provides mechanical support and communicates with cells through cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) at the cell surface. Integrin is a major group of CAMs represented by a family of αβ heterodimeric single transmembrane receptors.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p103-110 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.041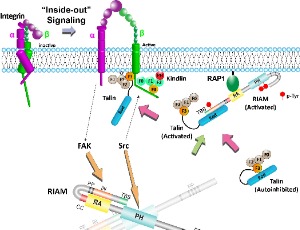
Linking Phosphoinositides to Proteins: A Novel Signaling Pipeline
Noah D. Carrillo, Poorwa Awasthi, Jeong Hyo Lee, Tianmu Wen, Mo Chen, Colin Sterling, Trevor J. Wolfe, Vincent L. Cryns, Richard A. Anderson
Phosphoinositide (PIPn) signaling plays pivotal roles in myriad biological processes and is altered in many diseases including cancer. Canonical PIPn signaling involves membrane-associated PIPn lipid second messengers that modulate protein recruitment and activity at membrane focal points. In the nucleus, PIPn signaling operates separately from membranous compartments defining the paradigm of non-canonical PIPn signaling.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 3, p114-121 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.118
ALK1 Signaling in Human Cardiac Progenitor Cells Promotes a Pro-angiogenic Secretome
Michayla Moore, Sergey Ryzhov, Douglas B. Sawyer, Carlos Gartner, Calvin P.H. Vary
Pro-angiogenic paracrine/autocrine signaling impacts myocardial repair in cell-based therapies. Activin A receptor-like type 1 (ACVRL1, ALK1) signaling plays a pivotal role in cardiovascular development and maintenance, but its importance in human-derived therapeutic cardiac cells is not well understood. Here, we isolated a subpopulation of human highly proliferative cells (hHiPCs) from adult epicardial tissue and found that they express ALK1, a high affinity receptor for bone morphogenetic protein-9 (BMP9), which signals via SMAD1/5 to regulate paracrine/autocrine signaling and angiogenesis.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 3, p122-142 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.119
CRABP1 Signalosomes in Cellular Stress Response and Health Maintenance
Jennifer Nhieu, Fatimah Najjar, Li-Na Wei
CRABP1 is an evolutionarily conserved retinoic acid (RA) binding protein that was originally characterized to bind and sequester cytosolic RA. Classical RA signaling involves RA binding to nuclear retinoic acid receptors (RARs) to regulate gene transcription. However, recent studies have established that CRABP1 in fact forms protein complexes, with or without RA, in the cytoplasm to modulate (mostly suppress) specific signaling pathways in a cell context-dependent manner.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 3, p122-125 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.141
PAX-Interacting Protein 1 (PTIP) Promotes Apoptosis
Ching-Jung Huang, Hyein Cho, Chuan Li, Kangsan Kim, Danyang Yu, Daechan Park, Y. Jessie Zhang, Haley O. Tucker
PAX-interacting protein 1 (PTIP/PAXIP1) was discovered and initially characterized over three decades ago as a 1,056 amino acid-containing protein with six tandem BReast cancer C-Terminal (BRCT) repeats. PTIP functions broadly to catalyze histone methylation in DNA damage repair and within the hematopoietic lineage, to promote immunoglobulin variable region (variable, diversity, joining [VDJ]) and class switch recombination (CSR).
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 4, p126-141 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.142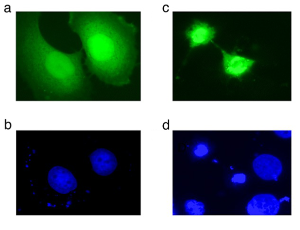
APE1/Ref-1 as a Novel Target for Retinal Diseases
Curtis Heisel, Jonah Yousif, Mahmut Mijiti, Kostas Charizanis, Mitchel Brigell, Timothy W. Corson, Mark R. Kelley
APE1/Ref-1 (also called Ref-1) has been extensively studied for its role in DNA repair and reduction-oxidation (redox) signaling. The review titled: “The multifunctional APE1 DNA repair-redox signaling protein as a drug target in human disease” by Caston et. al. summarizes the molecular functions of Ref-1 and the role it plays in a number of diseases, with a specific focus on various types of cancer.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p133-138 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.044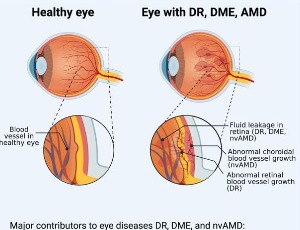
APE1/Ref-1 – One Target with Multiple Indications: Emerging Aspects and New Directions
Mahmut Mijiti, Rachel Caston, Silpa Gampala, Melissa L. Fishel, Jill C. Fehrenbacher, Mark R. Kelley
In the realm of DNA repair, base excision repair (BER) protein, APE1/Ref-1 (Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1/Redox Effector - 1, also called APE1) has been studied for decades. However, over the past decade, APE1 has been established as a key player in reduction-oxidation (redox) signaling. In the review by Caston et al. (The multifunctional APE1 DNA repair-redox signaling protein as a drug target in human disease), multiple roles of APE1 in cancer and other diseases are summarized.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p151-161 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.047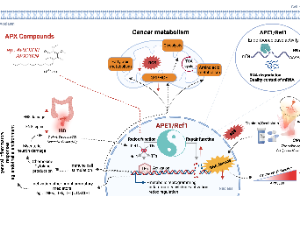
Depleting Cellular Retinoic Acid Binding Protein 1 Impairs UPRmt
Chin-Wen Wei, Thomas Lerdall, Fatimah Najjar, Li-Na Wei
Mitochondrial dysfunction underlines neurodegenerative diseases which are mostly characterized by progressive degeneration of neurons. We previously reported that Cellular retinoic acid Binding protein 1 (Crabp1) knockout (CKO) mice spontaneously developed age-dependent motor degeneration, with defects accumulated in spinal motor neurons (MNs), the only cell type in spinal cord that expresses CRABP1.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 4, p151-162 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.102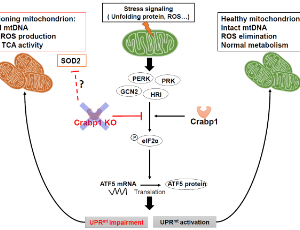
Role of PI3K/Akt/GSK-3 Pathway in Emesis and Potential New Antiemetics
Weixia Zhong, Darmani NA
Nausea and vomiting are protective defense mechanisms by which vomit competent species avoid ingestion of potentially toxic substances. More specifically, vomiting is the act of forceful expulsion of gastrointestinal contents through the mouth, whereas nausea is an unpleasant painless subjective feeling that one will imminently vomit.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p155-159 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.024
Pathogenic Pathways and Therapeutic Strategies in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)
Kenley M. Preval, Abigail O. Smith, Gregory J. Pazour
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is the most common inherited kidney disorder and a major cause of end-stage renal disease. The disorder is primarily caused by pathogenic variants in PKD1 or PKD2, which encode the ciliary proteins polycystin-1 and polycystin-2. Loss of polycystin function disrupts calcium and cAMP signaling within the primary cilium, altering epithelial proliferation and fluid secretion that drive cyst formation and progressive kidney enlargement.
J Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 4, p156-169 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.144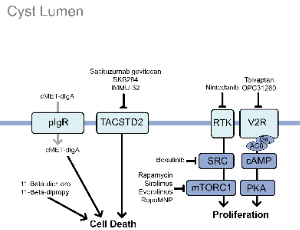
Improving Obesity and Insulin Resistance by Targeting Skeletal Muscle MKP-1
Anton M. Bennett, Ahmed Lawan
Obesity has reached a global epidemic and it predisposes to the development of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and related metabolic diseases. Current interventions against obesity and/or type 2 diabetes such as calorie restriction, exercise, genetic manipulations or established pharmacological treatments have not been successful for many patients with obesity and/or type 2 diabetes.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p160-168 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.025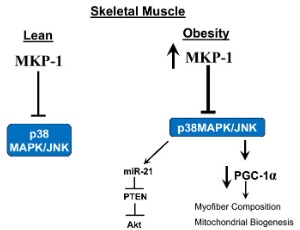
Oxidative DNA Damage: A Role in Altering Neuronal Function
Adib Behrouzi, Mark R. Kelley, Jill C. Fehrenbacher
A role for oxidative stress in the etiology of myriad neuropathologies is well accepted. However, the specific effects of oxidative DNA damage in the onset or promotion of neuronal dysfunction have been less studied. In our recent publication by Behrouzi et al. (Oxidative DNA Damage and Cisplatin Neurotoxicity Is Exacerbated by Inhibition of OGG1 Glycosylase Activity and APE1 Endonuclease Activity in Sensory Neurons), inhibition of enzymes that play a role in repairing oxidative DNA damage exacerbated neurotoxic effects of the chemotherapeutic agent, cisplatin.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 3, p160-166 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.079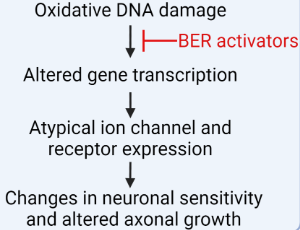
NH2-Terminal Cleavage of Cardiac Troponin I Signals Adaptive Response to Cardiac Stressors
Chad M. Warren, Monika Halas, Han-Zhong Feng, Beata M. Wolska, Jian-Ping Jin, R. John Solaro
Cardiac sarcomeres express a variant of troponin I (cTnI) that contains a unique N-terminal extension of ~30 amino acids with regulatory phosphorylation sites. The extension is important in the control of myofilament response to Ca2+, which contributes to the neuro-humoral regulation of the dynamics of cardiac contraction and relaxation.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p162-171 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.048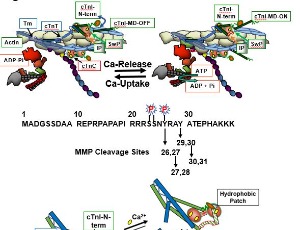
Function of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases in Hepatic Inflammation
Gabrielle Westenberger, Jacob Sellers, Savanie Fernando, Sadie Junkins, Sung Min Han, Kisuk Min, Ahmed Lawan
The western diet and overuse of anti-inflammatory medication have caused a great deal of stress on the liver. Obesity and the associated inflammatory state in insulin-responsive tissues result in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokine that activates the stress-responsive MAPKs, p38 MAPK, and JNK. These MAPKs have figured prominently as critical effectors in physiological and pathophysiological hepatic inflammation.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p172-180 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.049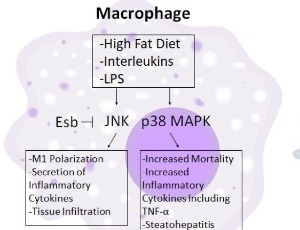
Optogenetics Sheds Light on Brown and Beige Adipocytes
Aaron Clifford Brown
Excessive food intake leads to lipid accumulation in white adipose tissue, triggering inflammation, cellular stress, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. In contrast, the dynamic energy expenditure and heat generation of brown and beige adipose tissue, driven by specialized mitochondria, render it an appealing candidate for therapeutic strategies aimed at addressing metabolic disorders.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 4, p178-186 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.105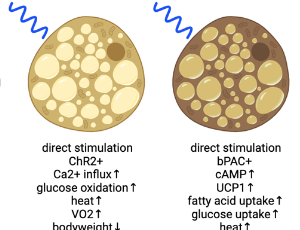
Redox Homeostasis in Well-differentiated Primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells
Ayaho Yamamoto, Peter D. Sly, Anna Henningham, Nelufa Begum, Abrey J. Yeo, Emmanuelle Fantino
Oxidative stress (OS) in the airway epithelium is associated with inflammation, cell damage, and mitochondrial dysfunction that may initiate or worsen respiratory disease. Redox regulation maintains the equilibrium of pro-oxidant/antioxidant reactions but can be disturbed by environmental exposures. The mechanism(s) underlying the induction and impact of OS on airway epithelium and how these influences on respiratory disease is poorly understood.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 4, p193-206 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.083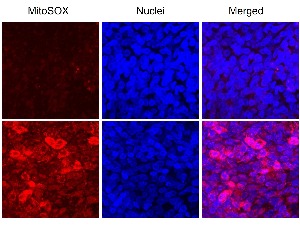
Targeting Cullin-RING E3 Ubiquitin Ligase 4 by Small Molecule Modulators
Kenneth Wu, Benjamin D. Hopkins, Roberto Sanchez, Robert J. DeVita, Zhen-Qiang Pan
Cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase 4 (CRL4) plays an essential role in cell cycle progression. Recent efforts using high throughput screening and follow up hit-to-lead studies have led to identification of small molecules 33-11 and KH-4-43 that inhibit E3 CRL4’s core ligase complex and exhibit anticancer potential.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p195-205 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.051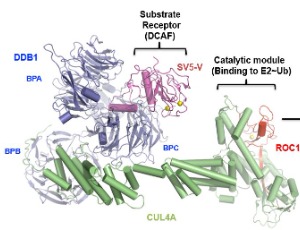
Hydrogen Peroxide-induced Cell Death in Mammalian Cells
Tamutenda Chidawanyika, Surachai Supattapone
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is an important intra- and extra-cellular signaling molecule that can determine cell fate. At low concentrations, H2O2 plays roles in proliferation, immunity, and metabolism. Cellular exposure to higher non-physiologic concentrations of H2O2 can result in oxidative stress.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p206-211 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.052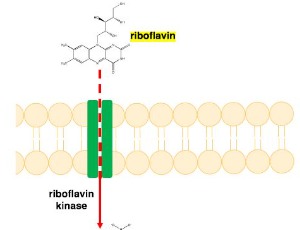
Resveratrol and Astaxanthin Protect Primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells Cultured at an Air-liquid Interface from an Acute Oxidant Exposure
Ayaho Yamamoto, Peter D. Sly, Nelufa Begum, Abrey J. Yeo, Emmanuelle Fantino
Oxidative stress (OS) in the airway epithelium is associated with cell damage, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction that may initiate or worsen respiratory disease. However, it is unclear whether exogenous antioxidants can provide protection to the airway epithelium from OS. Resveratrol and astaxanthin are nutritional compounds that have shown diverse benefits including protection against OS and inflammation in various situations.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 4, p207-217 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.084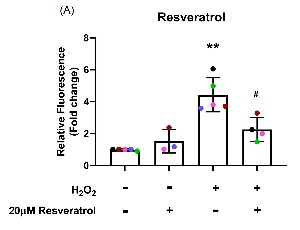
Combating PDAC Drug Resistance: The Role of Ref-1 Inhibitors in Accelerating Progress in Pancreatic Cancer Research
Eyram K. Kpenu, Mark R. Kelley
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains one of the most lethal solid tumor diagnoses given its limited treatment options and dismal prognosis. Its complex tumor microenvironment (TME), heterogeneity, and high propensity for drug resistance are major obstacles in developing effective therapies. Here, we highlight the critical role of Redox effector 1 (Ref-1) in PDAC progression and drug resistance, focusing on its redox regulation of key transcription factors (TFs) such as STAT3, HIF1α, and NF-κB, which are pivotal for tumor survival, proliferation, and immune evasion.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 4, p208-216 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.126
Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 and Oncogenesis in the Liver Disease
Da-eun Nam, Hae Chang Seong, Young S. Hahn
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a significant cause of cancer mortality worldwide. Chronic hepatic inflammation and fibrosis play a critical role in the development of HCC. Liver fibrosis develops as a result of response to injury such that a persistent and excessive wound healing response induces extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition leading to HCC.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p221-227 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.054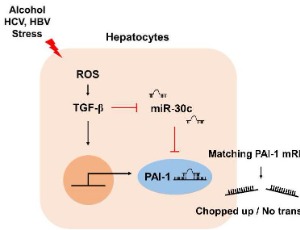
Novel Treatments Targeting the Dysregulated Cell Signaling Pathway during Sepsis
Justin H. Franco, Xiaohuan Chen, Zhixing K. Pan
Previously characterized as a purely immune mediated disease, sepsis is now recognized as a dysregulated multisystem response against a pathogen. Recognition of the infectious agent by pathogen recognition receptors (PRRs) can initiate activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway and promote the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines. During sepsis, the activation of NF-κB is dysregulated and results in cytokine storm, or the pathologic release of cytokines.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 4, p228-234 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.055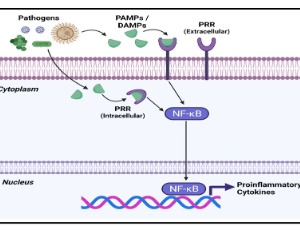
Chronic IL-1 Exposed AR PCa Cell Lines Show Conserved Loss of IL-1 Sensitivity and Evolve Both Conserved and Unique Differential Gene Expression Profiles
Shayna E. Thomas-Jardin, Mohammed S. Kanchwala, Haley Dahl, Vivian Liu, Rohan Ahuja, Reshma Soundharrajan, Nicole Roos, Sydney Diep, Amrit Sandhu, Chao Xing, Nikki A. Delk
Inflammation drives prostate cancer (PCa) progression. While inflammation is a cancer hallmark, the underlying mechanisms mediating inflammation-induced PCa are still under investigation. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) is an inflammatory cytokine that promotes cancer progression, including PCa metastasis and castration resistance. We previously found that acute IL-1 exposure represses PCa androgen receptor (AR) expression concomitant with the upregulation of pro-survival proteins, causing de novo accumulation of castration-resistant PCa cells.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 4, p248-260 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.058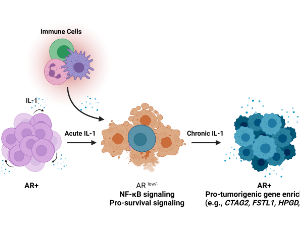
Trending Special Issues
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.