Loading
2025
Volume 6, Issue 1, p1-94
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Functionalized Carbon Nano-onions for Polymer Composites
Ahmad Adlie Shamsuri
Functionalized CNOs can be tailored through chemical modifications to enhance their compatibility with various polymer matrices, a practice that has seen increasing utilization across diverse fields. This editorial article examines the role of these functionalized nanoparticles in revolutionizing polymer composites, specifying briefly the techniques for their functionalization, the general types of polymer matrices used, their effects on composite properties, and their broadening range of applications.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.057
Cardiac Stents from Research to Clinical Applications
Shabnam Hashemzadeh, Saber Hashemzadeh, Fateme Bina
Early diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis are of vital importance in cardiology. Because of high risk and complexity of open-heart surgery, nowadays balloon angioplasty and stent implantation are common techniques to extend arterial vessels narrowed by atherosclerosis. Serious drawbacks of previous stents, such as complications induced by delayed healing and local hypersensitivity reactions and so re-narrowing and vascular reocclusion, have led to the development of stent designs, stent delivery systems, ultrasonic guidance of stent situation, and high-pressure dilatation post-stenting modifications [2-5].
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p4-11 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.058
Recent Advances in Different Nanoprecipitation Methods for Efficient Drug Loading and Controlled Release
A. W. Zaibudeen
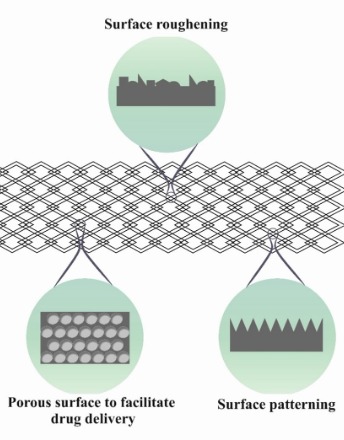
Nanoprecipitation has emerged as a versatile and efficient technique for formulating nanoparticles, providing significant advantages in drug delivery applications. Nanomaterials, particularly polymer nanoparticles (PNPs), play a crucial role in encapsulating and controlling the release of drug molecules, serving as an alternative to traditional drug delivery methods. Various types and morphologies of PNPs have been synthesized using different nanoprecipitation methods that are being used as drug carriers, demonstrating superior performance in targeted drug delivery with controlled release compared to conventional methods.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p12-25 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.059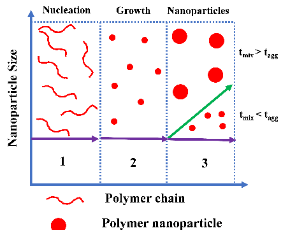
Comment on “Cholesterol Induced Asymmetry in DOPC Bilayers Probed by AFM Force Spectroscopy”
Dhruva Bhat, Appala Venkata Ramana Murthy
In the recent article, Adhyapak et al., used Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) and Force Spectroscopy to investigate the influence of cholesterol on the phase state behaviour of fluid phase DOPC membranes and found that the excess cholesterol conditions (above 20%) can induce an asymmetry in the lipid bilayer leading to changes both topography and more significantly in the nanomechanical properties of the lipid bilayer.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p26-27 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.060
Nanoscale Diagnosis and Therapy: Nanotheranostics as an Advance in Nanotechnology
Bianca Pizzorno Backx
The term "nanotechnology," introduced in 1986, refers to the emergence of a novel technology poised to transform existing protocols at the nanoscale. For many years, publications regarding nanotechnology have generated significant expectations related to discoveries and solutions. In 1990, with the inception of green chemistry, the scientific community began to reassess its approach, inspired by adaptations of protocols established by various eco-friendly institutions.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p28-42 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.061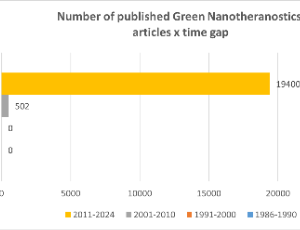
Cutting-Edge Nanoparticle Innovations in Biomedical Science: Synthesis, Applications, Challenges, and Future Prospects
Joicy John
Nanoparticles (NPs), identified as particles measuring between 1 and 100 nanometers, exhibit distinct physical and chemical properties that set them apart from larger materials. These attributes, which encompass a substantial surface area relative to volume and quantum phenomena, render them highly across various sectors.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p43-66 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.062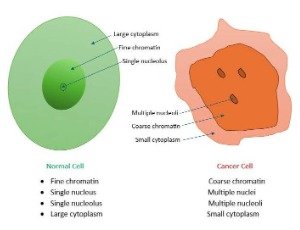
Development of Functional Nano-, Micro-Biostructures with Generation of New Enhanced Light Pathways for Life Science Applications
Daniela Alejandra Quinteros, M. Valeria Amé, A. Guillermo Bracamonte
Life sciences involve a broad overview of fundamental research of high interest, accompanied by the development of applications based on emerging needs. The generation of non-classical light is a high-impact area of research that could lay the foundation for functional materials, particularly in applications requiring tracking and switchable (on/off) properties. In this regard, the present communication is intended to present and discuss how natural and synthetic bio-structures, along with Nanotechnology, could provide versatile platforms for developing functional and multi-functional structures accompanied by the generation of novel non-classical light pathways.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p67-75 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.063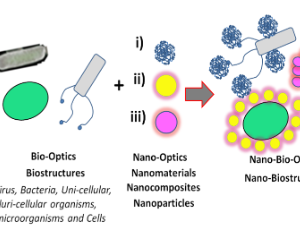
Enhancing p-type DSSC Performance through Nio-carbon Allotrope Hybrids: A Study of Functionalized MWCNT Integration
Nidhi Prajapati, Chivukula Narayana Murthy
In this study, we systematically investigated the influence of various carbon allotropes on the photovoltaic performance of p-type dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) using nickel oxide (NiO) nanotubes as the base semiconductor. The selected carbon nanostructures multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), reduced graphene oxide (RGO), graphene quantum dots (GQDs), and fullerenes (C60) were integrated with NiO and evaluated based on their structural and electrochemical characteristics.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p76-88 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.064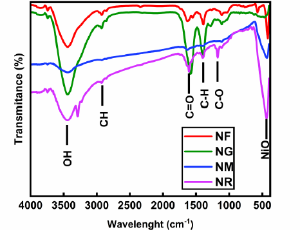
Weak Interactions in Catalysis
Xinyu Guo, Ziyang Feng, Bingyuan Zeng, TingTing Xia, Yuetong Zhao, Wenliang Zhang, Zumin Wang, Kun Zhao
Traditional catalytic theory has predominantly centered on static chemical bond processes, specifically the weakening, breaking, strengthening, and formation of chemical bonds – representing relatively fixed patterns of transformation. Whereas the dynamic regulatory mechanisms of weak interactions have been relatively understudied. This paradigm shift emerges from recognizing how precisely engineered 3D spatial arrangements govern catalytic efficiency: directional hydrogen bonds, size-matched hydrophobic cavities, and π-π stacking at optimal distances collectively create confined microreactors that steer reaction pathways.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p89-94 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.6.065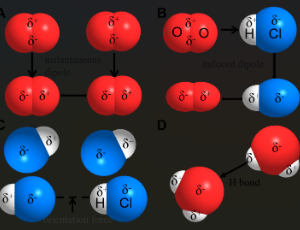
Recommended Articles
CO-Releasing Materials: Therapeutic Implications and Challenges towards Drug Discovery
Since last century, carbon monoxide (CO) generally regarded as “silent killer” and life-threatening for living organisms because of its colourless, odourless and poisonous nature. Haldane explored the poisonous nature of CO can be exerted as car-boxy hemoglobin (COHb) through hemoglobin dissociation parameters
Development of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Semiconductors
The variety of methods employed during the fabrication of MONPs can alter the characteristics and control the properties of the obtained nano-oxides. The reaction mechanisms and, therefore, the functionality of nanostructured MOx depend on their composition
Exploiting Nanotechnology to Target Viruses
Infectious diseases caused by microorganisms of the most varied natures and by viral entities cause millions of deaths every year. Around the world, viral infections have impacted civilizations’ circumstances since the earliest times, including the current panorama of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic known as coronavirus disease in 2019 (COVID-19). In this sense, in the last century,
Bioconjugation of AuNPs with HPV 16/18 E6 Antibody through Physical Adsorption Technique
HPV 16/18 E6 oncoprotein has been evaluated as a useful biomarker with prognostic abilities as it can detect pre-cancer and cancerous states of cervical cancer progression. A positive E6 assay indicates a high correlation to the cervical cancerous phenotype, not the potential for cervical cancer, thus high specificity in triaging patients during screening. E6 levels of expression associate directly with the severity of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) lesions and the risk of
Structural Characterization of Commercial Graphite and Graphene Materials
The most important elemental-carbon-based materials include zero-, one-, two-, and three-dimensionalstructured fullerenes, carbon nanotubes, graphene, and graphite, respectively. These non-metallic carbon materials have properties that are similar to semiconducting metals.
Development of HPV 16/18 E6 Oncoprotein Paperbased Nanokit for Enhanced Detection of HPV 16/18 E6 Oncoprotein in Cervical Cancer Screening
According to global cancer statistics GLOBOCAN, carcinoma of cervix is ranked as the fourth most common malignancy among women worldwide with an estimation of 570,000 cases and 311,000 deaths in 2018. It is the second most common female malignancy in Lowand- Middle Income Countries (LMICs). In Kenya, the prevalence is 25 cases per 100,000 women. Approximately 75% cases of cervical cancer are caused by persistent infections of the cervical mucosal epithelium with carcinogenic types of human papillomaviruses (HPVs) mainly 16 and 18.
Engineered Rh Nano-networks on DNA for SERS Applications
The study of surface and interfacial science via analytical techniques is a growing interest in the easy mode of diagnosing probe molecules adsorbed on the surface. In that line, Raman spectroscopy is an analytical method that is inefficient to carry the surface analysis employing their weak cross-sectional scattering until the discovery of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) in late 1970s
Multidirectional Benefits of Nanotechnology in the Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Tuberculosis
Despite the curious advancement in medical science and therapeutics, tuberculosis (TB) persist the primary factor of mortality than any other infectious disease and socioeconomic disaster for millions of people around the world. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), World’s One-third of the population is infected with this disease and of these, 8 to 10 million people develop active disease and 2 million people die each year and the rest of the infected people remain asymptomatic.
Ligand-free Few Atoms Ag Nanoclusters Synthesis and Their Potential Application as Photocatalytic Agents
Reducing the size of a metal from macroscopic to the nanoscale generates a scaling behavior in physical and chemical properties due to the large surface-to-volume fraction. While a further size reduction to small clusters under 2 nm (<~100 atoms) yield geometric and electronic structurwhich are still different from their nanoparticle (NP) counterpart.
Developing Neo-bioplastics for the Realization of Carbon Sustainable Society
Plastic is a composite material made from organic polymers and can be freely molded into a film, fiber, or plate by heat or pressure processing. In 1839, Goodyear proposed the vulcanization of natural rubbers, while E. Simon discovered polystyrene
Cancer Nanomedicine: Strategies to Enhance Tumor Delivery and Immunotherapy
Cancer nanomedicine was originally developed for more efficient delivery of chemotherapeutic agents into tumor, and has been extensively employed as a therapeutic for cancer treatment owing to its unique features in drug delivery, diagnosis and imaging, as well as the therapeutic nature of some nanomaterials themselves.
Current Progress in Vanadium Oxide Nanostructures and Its Composites as Supercapacitor Electrodes
In recent time, supercapacitors (SCs) are one of the emerging technologies used for clean energy prospect. The higher power density, low specific energy, longer cycle life, and environmental affability made the SCs superior compared to conventional batteries. However, the scientific community is working towards increasing the specific energy of SCs by finding a suitable electrode material. Carbon materials, conducting polymers, and metal oxide or hydroxides are
Green Nanotechnology: The Influence of Intermolecular and Supramolecular Interactions
In the last decade, the study of nanometer-scale particles has grown exponentially worldwide. This growth is due to the broad field of nanostructures applications, which, due to their dimensions in nanometric sizes, have new properties not found in micro and macro scale. These properties result from the increase in the ratio between the surface area and volume, and the nanostructures’ size directly influences these. Tolerance to temperature, variety of colors, changes in chemical reactivity,
Rapid Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 by Coupling Tungsten Trioxide (WO3) Photocatalyst with Copper Nanoclusters
At the end of 2019, a novel severe respiratory disease (coronavirus disease 2019, COVID-19) spread to Wuhan, China, it became pandemic in few months, with more than 41 million people infected worldwide as of October 2020. COVID-19 is caused by a novel virus called severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) CoV-2 to distinguish it from SARS-CoV that emerged in Guangdong province in China in 2003 and caused the severe clinical condition known as SARS. Like SARS-CoV, SARS- CoV-2 causes a severe inter
Quantifying Respiratory Airborne Particle Dispersion Control Through Improvised Reusable Masks: The Physics of Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions for Reducing SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Airborne Transmission
In light of the current pandemic from rapid transmission of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2 or COVID-19) and significant morbidity, there has been inconsistent medical guidance given to the public regarding the wearing of non-medical improvised fabric masks or face coverings to reduce the transmission of COVID-19.
In Silico Proteome Analysis of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARSCoV- 2) is a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA with genome size 26.2, and 31.7 kb coronavirus, covered by an enveloped structure, which is a major source of disaster in the 21st century. A typical CoV contains at least six ORFs in its genome. SARS-CoV-2 is the seventh coronavirus that is known to cause human disease.
Emerging Nanogenerators for Rehabilitation Monitoring and Information Interaction
Patients with limb motor dysfunction caused by trauma and stroke have poor mobility to take care of themselves, which seriously affects the quality of life of them. Through reasonable rehabilitation training, the damaged motor function can be relieved to a certain extent. In the rehabilitation training, the monitoring of limb movement can reflect the recovery state of patients’ physiological function and make a systematic evaluation on the rehabilitation training effect of patients,
Nanofibers Based on Concentrated Collagen Hydrolysate Loaded with Essential Oils
The manufacture of scaffolds for wound healing has become important, especially the formation of tissuespecific scaffolding. In order to create scaffolds, it is essential to mimic the chemical composition, physical morphology and biological functions of the human body. Scaffolds can be created by using synthetic polymers (e.g. polycaprolactone) or natural polymers (e.g. chitosan) or a combination of both. The addition of natural polymers can be very advantageous as they can avoid
Functionalized Folic Acid with Chitosan and PAMAM Dendrimers for Delivery of DNA and RNA
The conjugation of polymers with multiple targeting ligands has become a popular approach for targeted gene and drug delivery. Functionalized polymer–drug conjugates are increasingly used to obtain biodegradable, targeted tools to further enhance localized gene and drug delivery systems. Folic acid (FA)-conjugated biodegradable polymers were tested as effective gene and drug delivery tools. Folate receptors are cellular markers highly expressed in various cancer cells and on
Nanotechnology in Water Treatment: An Optimistic Perspective for the Near Future
Unequal access to drinking water and basic sanitation are old issues in Brazil and worldwide. Besides, this situation foments the proliferation of infectious parasitic diseases. Moreover, mainly in underdeveloped countries, it victimizes socioeconomically vulnerable people. The degree of water contamination analysis, usually by fecal matter, is made by the number of microorganisms present in the sample, including Escherichia coli or thermotolerant coliforms. In addition, several
