Loading
Journal of Cellular Signaling
ISSN: 2692-0638
Editors Choice Articles
Flow Cytometric Characterization of Accidental Cell Death Highlights Connections to Regulated Cell Death
Gary Warnes
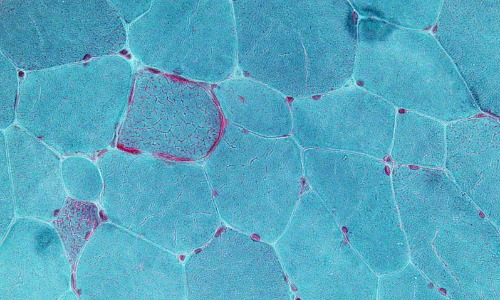
Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs) are known by their nature to cause inflammatory responses in numerous disease states from cancer, trauma to age related diseases (e.g. atherosclerosis, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases), these molecules are released by cells undergoing cell death.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.001
The Outcome of Tumor Ablation Therapies is Determined by Stress Signaling Networks
Mladen Korbelik
Increasingly prominent roles in interventional oncology are held by various tumor ablation therapies performed by direct applications of local acute trauma-inducing insult to the targeted lesion aiming for its rapid in situ destruction. These therapies include treatments based on various forms of thermal energy delivery (photothermal, cryoablation, microwave ablation, radiofrequency ablation), non-thermal illumination (photodynamic therapy), electric field exposure, or high hydrostatic pressure
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 1, p1-4 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.062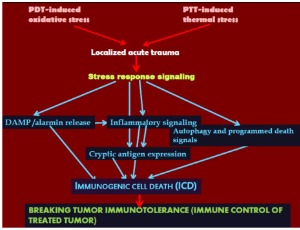
Emerging Role of TRPML1 Mucolipin Endolysosomal Channel in Cancer
Giorgio Santoni, Matteo Santoni, Massimo Nabissi, Oliviero Marinelli, Consuelo Amantini, Maria Beatrice Morelli
The transient receptor potential mucolipin 1 (TRPML1) is an endolysosomal channel belonging to the TRP family. Clinically, mutations of TRPML1 have been responsible for a severe lysosomal storage disorder called mucolipidosis type IV.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p4-7 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.002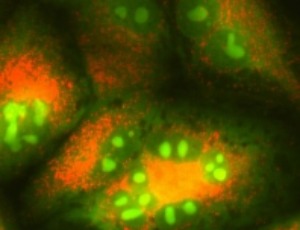
MKP-2 Deficiency Leads to Lipolytic and Inflammatory Response to Fasting in Mice
Sadie Junkins, Gabrielle Westenberger, Jacob Sellers, Isabel Martinez, Nabin Ghimire, Cassandra Secunda, Morgan Welch, Urja Patel, Kisuk Min, Ahmed Lawan
The liver plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis for lipid and glucose. Hepatic lipid synthesis is regulated by nutritional signals in response to fasting and refeeding. It is known that overnutrition regulates MAPK-dependent pathways that control lipid metabolism in the liver by activating MAPK phosphatase-2 (MKP-2). Uncertainty still exists regarding the regulatory mechanisms and effects of MKP-2 on hepatic response to fasting.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 1, p10-23 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.108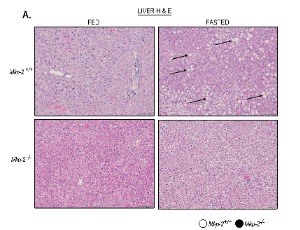
Differentiation and Subtype Specification of Enteric Neurons: Current Knowledge of Transcription Factors, Signaling Molecules and Signaling Pathways Involved
Nastasia Popowycz, Leen Uyttebroek, Guy Hubens, Luc van Nassauw
The enteric nervous system is the largest component of the autonomic nervous system. It contains a broad network of interconnected plexuses and enteric neuronal subtypes which are in charge of the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Vagal and sacral neural crest cells are at the basis of the enteric nervous system development. These cells undergo multiple processes such as migration, proliferation and differentiation to finally form a functional enteric nervous system.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 1, p14-27 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.064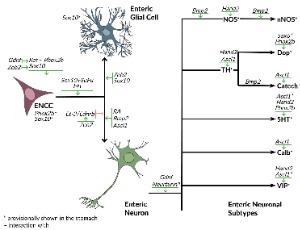
Phorbol-12-Myristate-13-Acetate (PMA) Reactivates Replication from HIV-1 Latency and Induces Jurkat Cell Death
Xue Wang, Jiangqin Zhao, Indira Hewlett
HIV-1 has the capability to establish latency during early infection in CD4+ cells, posing a significant challenge to the efforts aimed at curing HIV-1/AIDS. One extensively explored strategy to address this viral latency is the "shock-and-kill" approach. This involves reactivating viral replication using latency reversal agents (LRAs) to induce the death of infected cells. Regrettably, no LRAs with proven effectiveness have been identified thus far.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 1, p30-40 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.110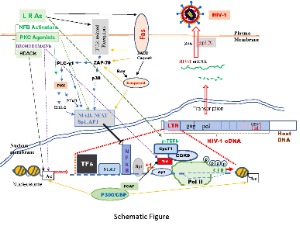
Expression and Localization of Phosphoinositide-Specific Phospholipases C in Cultured, Differentiating and Stimulated Human Osteoblasts
Sara Daisy Casoni, Alessia Romanelli, Marta Checchi, Serena Truocchio, Marzia Ferretti, Carla Palumbo, Vincenza Rita Lo Vasco
The osteoblasts contribute to bone homeostasis maintaining the bone mass, and intervene in bone injuries repair. Insights in the events leading to the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts might allow uncover potential molecular targets to control the complex mechanisms underlying bone remodeling. Signal transduction pathways contribute to the differentiation and metabolic activities of osteoblasts, with special regard to calcium-related signaling, including the Phosphoinositide (PI) pathway.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 1, p44-61 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.067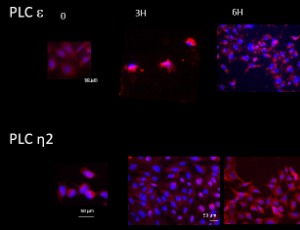
Teaching an Old Drug a New Trick: Targeting Treatment Resistance in Genitourinary Cancers
Karina Aguilar, Anuj K. Sharma, Tianyu Yang, Dipen Mehta, Chandramukhi S. Panda, Vinata B. Lokeshwar
In the quest for improving the clinical outcome of patients with metastatic genitourinary cancers, including metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC), the emphasis often is on finding new targeted therapies. However, two studies by Jordan et al. (Oncogenesis 2020) and Wang et al. (Cancer Cell Int 2022) demonstrate the feasibility of improving the efficacy of a modestly effective drug Sorafenib against mRCC by attacking a mechanism hijacked by RCC cells for inactivating Sorafenib.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 2, p51-56 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.112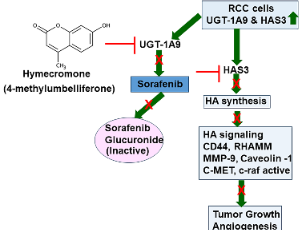
Navigating the Adipocyte Precursor Niche: Cell-Cell Interactions, Regulatory Mechanisms and Implications for Adipose Tissue Homeostasis
Devesh Kesharwani, Aaron Clifford Brown
Support for stem cell self-renewal and differentiation hinges upon the intricate microenvironment termed the stem cell 'niche'. Within the adipose tissue stem cell niche, diverse cell types, such as endothelial cells, immune cells, mural cells, and adipocytes, intricately regulate the function of adipocyte precursors. These interactions, whether direct or indirect, play a pivotal role in governing the balance between self-renewal and differentiation of adipocyte precursors into adipocytes.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 2, p65-86 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.114
Is Citrate A Critical Signal in Immunity and Inflammation?
Alessia Zotta, Zbigniew Zaslona, Luke A. O’Neill
When immune cells are activated, they undergo metabolic change in order to have sufficient energy to function effectively. The Krebs cycle is one of the most important pathways involved in this response and citrate, a critical component of this pathway, regulates carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p87-96 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.017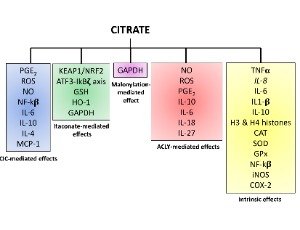
Targeting Lipid Metabolism for Better Management of Coronavirus SARS-COV-2 Infections: Intervention, Antiviral Drug Development, and Challenges
Yuting Wang, Peiran Chen, Ming-Liang He
The global pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), although has faded from public view, the virus itself remains highly active and continues to mutate, continuously causing infections. The population faces the risk of severe outcomes caused by virus infection (e.g., multi-organ tissue injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)). Furthermore, patients with chronic diseases (cardiovascular diseases, diabetes) are at risk of developing severe sequelae or even elevated mortality.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 2, p91-95 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.116
Dendorbium Nobile Lindl. Alkaloids Suppress NF-κB and NLRP3 Signaling Pathways to Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-induced Neuroinflammation
Jiaojiao Liu, Bo Liu, Xi He, Wu Qin, Jingshan Shi
The important immune cells in the brain are called microglia acting as the central junction between neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. In patients of cognitive disorders and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) animal models, amoebic morphology and inflammatory pathways are activated to release numerous cells in the inflammatory factors by active microglia.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p102-114 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.019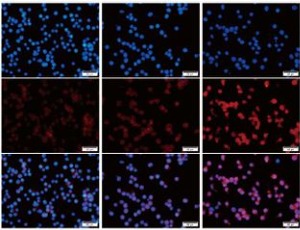
APE1/Ref-1 as a Novel Target for Retinal Diseases
Curtis Heisel, Jonah Yousif, Mahmut Mijiti, Kostas Charizanis, Mitchel Brigell, Timothy W. Corson, Mark R. Kelley
APE1/Ref-1 (also called Ref-1) has been extensively studied for its role in DNA repair and reduction-oxidation (redox) signaling. The review titled: “The multifunctional APE1 DNA repair-redox signaling protein as a drug target in human disease” by Caston et. al. summarizes the molecular functions of Ref-1 and the role it plays in a number of diseases, with a specific focus on various types of cancer.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p133-138 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.044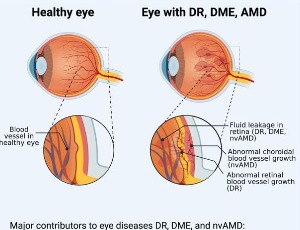
MAGIs: Junctional Scaffolds Linking Inter-Cellular Junction Architecture, Actin Cytoskeleton Dynamics, and Signaling Pathways
Lisa Heron-Milhavet, Alexandre Djiane
MAGIs (membrane-associated guanylate-kinases (MAGUK) inverted) are apical scaffolds conserved across evolution, which regulate cellular junctions. Low expression of MAGIs has been associated with tumorigenesis in a wide variety of cancers. This “tumor-suppressive” function of MAGIs has stimulated many studies to better understand the processes they control, and how their misregulation could contribute to cancer progression.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 3, p141-147 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.076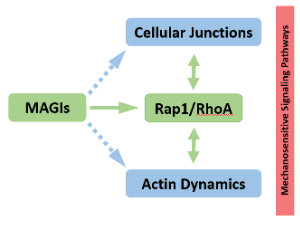
APE1/Ref-1 – One Target with Multiple Indications: Emerging Aspects and New Directions
Mahmut Mijiti, Rachel Caston, Silpa Gampala, Melissa L. Fishel, Jill C. Fehrenbacher, Mark R. Kelley
In the realm of DNA repair, base excision repair (BER) protein, APE1/Ref-1 (Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1/Redox Effector - 1, also called APE1) has been studied for decades. However, over the past decade, APE1 has been established as a key player in reduction-oxidation (redox) signaling. In the review by Caston et al. (The multifunctional APE1 DNA repair-redox signaling protein as a drug target in human disease), multiple roles of APE1 in cancer and other diseases are summarized.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p151-161 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.047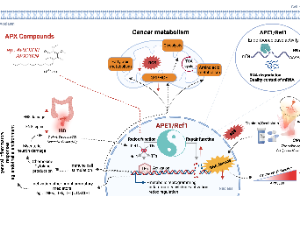
Depleting Cellular Retinoic Acid Binding Protein 1 Impairs UPRmt
Chin-Wen Wei, Thomas Lerdall, Fatimah Najjar, Li-Na Wei
Mitochondrial dysfunction underlines neurodegenerative diseases which are mostly characterized by progressive degeneration of neurons. We previously reported that Cellular retinoic acid Binding protein 1 (Crabp1) knockout (CKO) mice spontaneously developed age-dependent motor degeneration, with defects accumulated in spinal motor neurons (MNs), the only cell type in spinal cord that expresses CRABP1.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 4, p151-162 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.102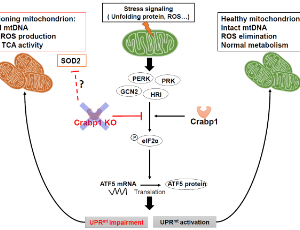
Improving Obesity and Insulin Resistance by Targeting Skeletal Muscle MKP-1
Anton M. Bennett, Ahmed Lawan
Obesity has reached a global epidemic and it predisposes to the development of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and related metabolic diseases. Current interventions against obesity and/or type 2 diabetes such as calorie restriction, exercise, genetic manipulations or established pharmacological treatments have not been successful for many patients with obesity and/or type 2 diabetes.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p160-168 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.025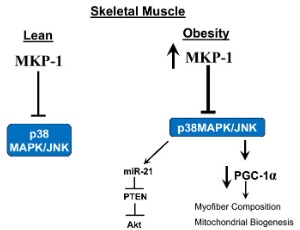
Oxidative DNA Damage: A Role in Altering Neuronal Function
Adib Behrouzi, Mark R. Kelley, Jill C. Fehrenbacher
A role for oxidative stress in the etiology of myriad neuropathologies is well accepted. However, the specific effects of oxidative DNA damage in the onset or promotion of neuronal dysfunction have been less studied. In our recent publication by Behrouzi et al. (Oxidative DNA Damage and Cisplatin Neurotoxicity Is Exacerbated by Inhibition of OGG1 Glycosylase Activity and APE1 Endonuclease Activity in Sensory Neurons), inhibition of enzymes that play a role in repairing oxidative DNA damage exacerbated neurotoxic effects of the chemotherapeutic agent, cisplatin.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 3, p160-166 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.079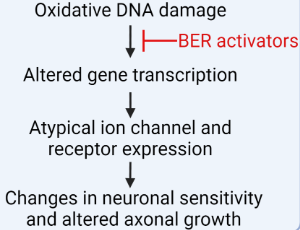
One-to-one Benefit Provided by Antioxidants to Cultured Skin Fibroblasts from Friedreich Ataxia Patients
Paule Bénit, Malgorzata Rak, Pierre Rustin
As to better understand and characterize the dramatic differences in antioxidant response of human cells harboring mutations in the frataxin gene responsible for Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA), we studied primary cultures of skin fibroblasts derived from five FRDA patients with different major frataxin gene expansion sizes. Since oxidative stress has been previously established to play a critical role in FRDA, among the many enzymes that may modulate oxidative stress sensitivity, we selected some that have previously been shown to be critical in oxidative stress.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 4, p162-175 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.122
Function of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases in Hepatic Inflammation
Gabrielle Westenberger, Jacob Sellers, Savanie Fernando, Sadie Junkins, Sung Min Han, Kisuk Min, Ahmed Lawan
The western diet and overuse of anti-inflammatory medication have caused a great deal of stress on the liver. Obesity and the associated inflammatory state in insulin-responsive tissues result in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokine that activates the stress-responsive MAPKs, p38 MAPK, and JNK. These MAPKs have figured prominently as critical effectors in physiological and pathophysiological hepatic inflammation.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p172-180 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.049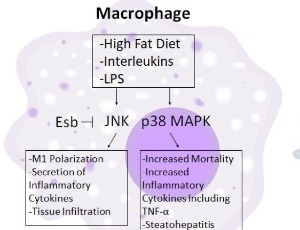
Elevated Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Levels with Ig (G & M) Antibodies in the Recovery Phase of Patients with COVID-19: Indication of Cytokine Storm and Re-infection
John Bolodeoku, Terry Gbaa
The innate immune response to coronavirus disease (COVID-19) by inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin 6 (IL-6), has been described as an early response, followed by an adaptive immune response with the production of antibodies. IL-6 is produced in response to viral infections and is crucial for the activation of T cells and the differentiation of B cells, which produce antibodies. Immunoglobulin M (IgM) and immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies are produced during the initial acute period of infection and the recovery period from the period of onset of symptoms.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 4, p176-182 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.123
Optogenetics Sheds Light on Brown and Beige Adipocytes
Aaron Clifford Brown
Excessive food intake leads to lipid accumulation in white adipose tissue, triggering inflammation, cellular stress, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. In contrast, the dynamic energy expenditure and heat generation of brown and beige adipose tissue, driven by specialized mitochondria, render it an appealing candidate for therapeutic strategies aimed at addressing metabolic disorders.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 4, p178-186 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.105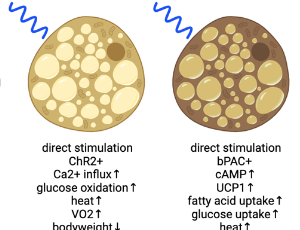
Redox Homeostasis in Well-differentiated Primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells
Ayaho Yamamoto, Peter D. Sly, Anna Henningham, Nelufa Begum, Abrey J. Yeo, Emmanuelle Fantino
Oxidative stress (OS) in the airway epithelium is associated with inflammation, cell damage, and mitochondrial dysfunction that may initiate or worsen respiratory disease. Redox regulation maintains the equilibrium of pro-oxidant/antioxidant reactions but can be disturbed by environmental exposures. The mechanism(s) underlying the induction and impact of OS on airway epithelium and how these influences on respiratory disease is poorly understood.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 4, p193-206 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.083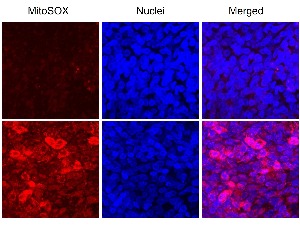
Indole Family and Neomycin Sulfate: Inductors of Differentiation in C2C12 and RD cell Lines
Lorena Milanesi, Andrea Vasconsuelo, Lucía Pronsato, Natalia Frattini, Nicolás Blanco
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a highly aggressive tumor primarily affecting the pediatric population, that generally originates from a failure in the embryonic differentiation of myogenic precursor cells. Standard treatment involves surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy, with a poor prognosis, especially when it spreads to other parts of the body, highlighting the need for new treatment approaches.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 4, p195-207 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.125
Hydrogen Peroxide-induced Cell Death in Mammalian Cells
Tamutenda Chidawanyika, Surachai Supattapone
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is an important intra- and extra-cellular signaling molecule that can determine cell fate. At low concentrations, H2O2 plays roles in proliferation, immunity, and metabolism. Cellular exposure to higher non-physiologic concentrations of H2O2 can result in oxidative stress.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p206-211 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.052
Resveratrol and Astaxanthin Protect Primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells Cultured at an Air-liquid Interface from an Acute Oxidant Exposure
Ayaho Yamamoto, Peter D. Sly, Nelufa Begum, Abrey J. Yeo, Emmanuelle Fantino
Oxidative stress (OS) in the airway epithelium is associated with cell damage, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction that may initiate or worsen respiratory disease. However, it is unclear whether exogenous antioxidants can provide protection to the airway epithelium from OS. Resveratrol and astaxanthin are nutritional compounds that have shown diverse benefits including protection against OS and inflammation in various situations.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 4, p207-217 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.084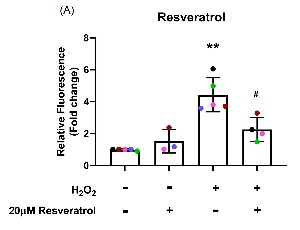
Combating PDAC Drug Resistance: The Role of Ref-1 Inhibitors in Accelerating Progress in Pancreatic Cancer Research
Eyram K. Kpenu, Mark R. Kelley
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains one of the most lethal solid tumor diagnoses given its limited treatment options and dismal prognosis. Its complex tumor microenvironment (TME), heterogeneity, and high propensity for drug resistance are major obstacles in developing effective therapies. Here, we highlight the critical role of Redox effector 1 (Ref-1) in PDAC progression and drug resistance, focusing on its redox regulation of key transcription factors (TFs) such as STAT3, HIF1α, and NF-κB, which are pivotal for tumor survival, proliferation, and immune evasion.
J Cell Signal, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 4, p208-216 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.5.126
Chronic IL-1 Exposed AR+ PCa Cell Lines Show Conserved Loss of IL-1 Sensitivity and Evolve Both Conserved and Unique Differential Gene Expression Profiles
Shayna E. Thomas-Jardin, Mohammed S. Kanchwala, Haley Dahl, Vivian Liu, Rohan Ahuja, Reshma Soundharrajan, Nicole Roos, Sydney Diep, Amrit Sandhu, Chao Xing, Nikki A. Delk
Inflammation drives prostate cancer (PCa) progression. While inflammation is a cancer hallmark, the underlying mechanisms mediating inflammation-induced PCa are still under investigation. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) is an inflammatory cytokine that promotes cancer progression, including PCa metastasis and castration resistance. We previously found that acute IL-1 exposure represses PCa androgen receptor (AR) expression concomitant with the upregulation of pro-survival proteins, causing de novo accumulation of castration-resistant PCa cells.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 4, p248-260 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.058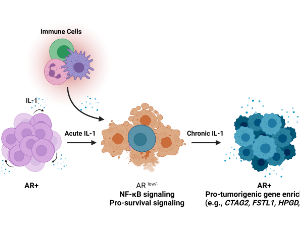
Trending Special Issues
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.