Loading
Journal of Cellular Signaling
ISSN: 2692-0638
2020
Volume 1, Issue 4, p102-205
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
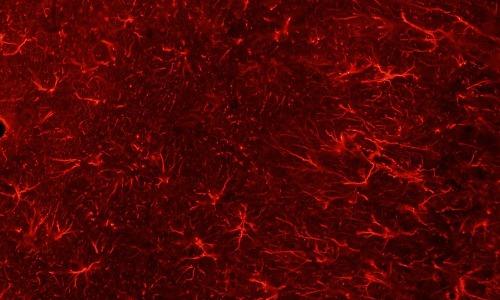
Dendorbium Nobile Lindl. Alkaloids Suppress NF-κB and NLRP3 Signaling Pathways to Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-induced Neuroinflammation
Jiaojiao Liu, Bo Liu, Xi He, Wu Qin, Jingshan Shi
The important immune cells in the brain are called microglia acting as the central junction between neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. In patients of cognitive disorders and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) animal models, amoebic morphology and inflammatory pathways are activated to release numerous cells in the inflammatory factors by active microglia.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p102-114 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.019
Galectin 3 and Glial Cells of the CNS: A Fruitful Crosstalk with Remyelinating Potential
Laura A. Pasquini
Galectin-3 (Gal-3), the only chimera-like galectin, has three structural domains: (a) the NH2 terminal domain containing serine phosphorylation, important for nuclear localization, secretion and oligomerization; (b) a sequence susceptible to metalloprotease (MMP) cleavage; and (c) a C-terminal domain containing the carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD) and an anti-death motif.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p115-126 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.020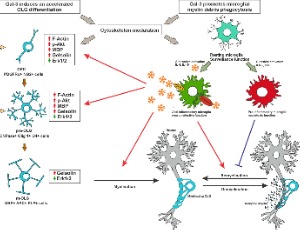
NOXA the BCL-2 Family Member behind the Scenes in Cancer Treatment
Alison Dumont, Steven Lohard, Laurent Maillet, Philippe P Juin, Sophie Barillé-Nion
NOXA is a critical mediator of stress responses to anticancer drugs. This BH3-only protein sets the apoptotic threshold in cancer cells in response to chemotherapies by counteracting the prosurvival BCL-2 family protein MCL-1. A complex and dynamic network relying on both highly controlled gene transcription activity and protein degradation by proteasome, regulates cellular NOXA levels from low in steady state to rapidly enhanced upon stressful condition.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p127-143 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.021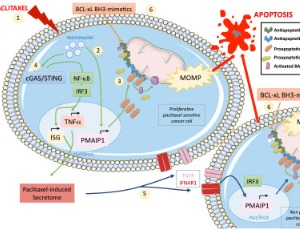
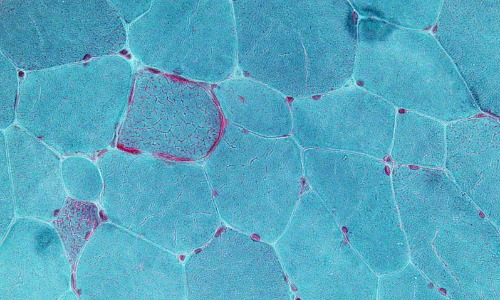
Refining the Class IIa HDAC/MEF2 Paradigm in Muscle Biology: More than Meets the Eye
F. Dequiedt, Thomas Cherrier
For several decades, the transcription factor MEF2 (myocyte enhancer factor-2) has been known as a master regulator of myogenesis that orchestrates the first step in muscle formation: the differentiation of myoblasts into myocytes. Because of its importance during myoblast differentiation, the potential roles of MEF2 during later steps of myogenesis, in particular myocyte fusion, could not be properly investigated.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p144-150 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.022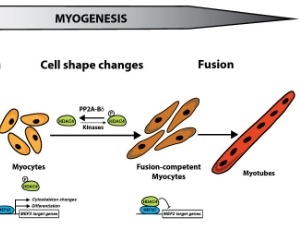
A Novel Regulatory Mechanism to Regulate the Deubiquitinating Activity of USP25 by Oligomerization
Ying Li, Bing Liu, David Reverter
Protein ubiquitination is a major post-translational mechanism that regulates fate and function of many proteins in the cell, either by regulating their abundance by the 26S-proteasome-ubiquitin system or by modulating protein activity by the attachment of the ubiquitin modifier
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p151-154 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.023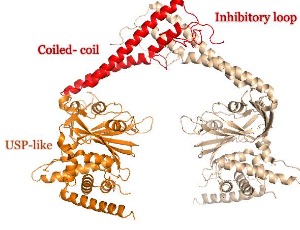
Role of PI3K/Akt/GSK-3 Pathway in Emesis and Potential New Antiemetics
Weixia Zhong, Darmani NA
Nausea and vomiting are protective defense mechanisms by which vomit competent species avoid ingestion of potentially toxic substances. More specifically, vomiting is the act of forceful expulsion of gastrointestinal contents through the mouth, whereas nausea is an unpleasant painless subjective feeling that one will imminently vomit.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p155-159 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.024
Improving Obesity and Insulin Resistance by Targeting Skeletal Muscle MKP-1
Anton M. Bennett, Ahmed Lawan
Obesity has reached a global epidemic and it predisposes to the development of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and related metabolic diseases. Current interventions against obesity and/or type 2 diabetes such as calorie restriction, exercise, genetic manipulations or established pharmacological treatments have not been successful for many patients with obesity and/or type 2 diabetes.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p160-168 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.025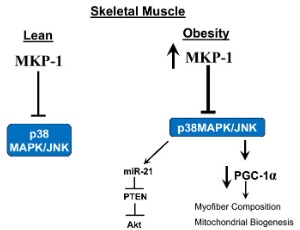
A Novel Regulatory Pathway of Desmoglein-3 in Keratinocyte Stress Response
Ambreen Rehman, Hong Wan
The desmosomal cadherin Desmoglein-3 (Dsg3) is a core adhesion component in desmosome junctions that occur with high frequency in the stratified squamous epithelial membrane lining the skin and mucous membrane. Dsg3 is identified as a major target of the circulating autoantibodies in Pemphigus Vulgaris (PV), an autoimmune blistering skin disease, and many signaling pathways have been demonstrated to be activated by PV-IgG targeting Dsg3, highlighting its role as a surface regulator in cell signa
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p169-179 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.026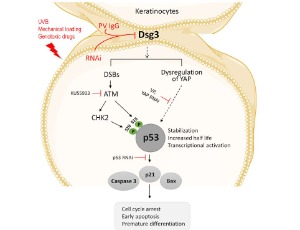
The Possible Role of Molecular Vibration in Intracellular Signalling
Werner Jaross
The exchange of information within the cell is extremely complex. Besides the well-studied chemical signalling, physical signalling is required to fulfil spatial and temporal aspects. The Golgi apparatus and the microtubule skeleton system are the decisive structures for numerous intracellular transport tasks.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p180-186 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.027
The Role of TIGAR-mediated Metabolic Processes in Autophagy and Cell Survival
Dingmei Zhang, Mei Li, Zheng-Hong Qin
Autophagy is the one of the essential pathways for maintaining homeostasis of cells and plays an important regulatory role in cell survival and death. Tp53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR) is a Tp53 target protein and is not only involved in the regulation of metabolism, cell cycle progression and radiation response, but also plays a role in autophagy.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p187-194 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.028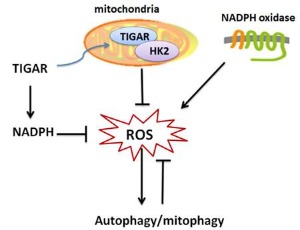
Kinetin/N6-furfuryladenine: A New Neurodegenerative Disease Lead from an Old Plant Cytokine
Tamara Maiuri, Ray Truant
N6-fufuryladenine (N6FFA), or kinetin, has a long history as a plant cytokine with practical applications in agriculture. This adenosine analog is now commonplace in natural product small molecule chemical screening libraries, and as such has been discovered as active in mammalian disease pathways that include Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease (HD) and Familial Dysautonomia.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p195-199 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.029
PRMT1-catalyzed SMAD7 Arginine Methylation Bridges EMT and Stemness
Jian Qin, Jian Xu
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a lineage transition from epithelium to mesenchyme, is induced by a convergence of signaling pathways and often driven by TGFß/SMAD signaling. Except for its critical roles on cell shape and motility during cancer invasion and metastasis, TGFß/SMAD activation-induced EMT has also been reported to be involved in cancer stem cell (CSC) generation.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p200-205 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.030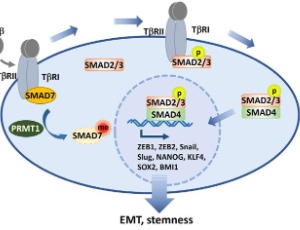
Recommended Articles
The Nature of Radiation-induced Inherited Recessive Gene Mutations in Drosophila Melanogaster
The nature of gene mutations induced by ionizing radiation in germ cells and transmitted to offspring remains one of the most important problems in radiation genetics of higher eukaryotes. The data accumulated in this field were obtained by different authors under different experimental conditions which does not give a complete insight about the nature of radiation-induced inherited mutations at different genome levels (chromosome, gene, DNA).
Constitutively Active Death Receptor Induces Apoptosis in Mammalian Cells
Apoptosis is a physiological response in development and homeostasis of metazoans. Apoptosis is triggered during pathological events as a means to renew affected tissues and eliminate cancer cells. The immune system regulates the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis, where signals such as TNFα or displayed ligands on the surface of immune cells trigger signal cascades by death receptors present on targeted cells.
Prevalence of Symptom Clusters in Cancer Patients at First Presentation in Palliative Care Clinic as per Different Disease Groups
Cancer has its own disease burden and patients usually suffer from symptom clusters when they are referred for palliative treatment. Identification of symptom cluster trajectories will help clinician to take into account measures that can optimize quality of life of palliative patients. Therefore the aim of this paper is to determine the overall prevalence of symptoms and symptoms clusters in different disease groups according to etiology at the time of first visit to Palliative care clinic by using HIS Palliative First Assessment note indicating Edmonton symptom scale.
Chimeric Antigen Receptor CAR NK Cells Emerging Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Cancer
Although NK cells are recognized as effector lymphocytes of the innate immune system, they also regulate the adaptive immune response by releasing inflammatory cytokines and developing immunological memory. Unlike other lymphocytes such as T or B cells, NK cells do not express rearrangeable, antigen-specific receptors.
Emerging Role of TRPML1 Mucolipin Endolysosomal Channel in Cancer
The transient receptor potential mucolipin 1 (TRPML1) is an endolysosomal channel belonging to the TRP family. Clinically, mutations of TRPML1 have been responsible for a severe lysosomal storage disorder called mucolipidosis type IV.
Activation of NLRP3 Inflammosome by N4-Acetyl Cytidine and Its Consequences
N4-acetylcytidine (N4A) is an organic compound and a metabolite of transferrable ribonucleic acid. Its molecular formula is C11H15N3O6. Earlier studies suggest that N4A was mainly found on tRNA and 18S rRNA, while recent studies have shown that there is also a large amount of N4A on mRNA, whose abundance is not even lower than the m7G cap modification carried by mRNA.
Cyclic Nucleotide Signaling Pathways in Apicomplexan Parasites Provide a Valuable Source for Novel Drug Targets
Malaria is one of the most important disabling human, tropical disease caused by different Plasmodium species, which are protozoan parasites belonging to the Apicomplexa. The Apicomplexan parasites have a plastid like structure the “apicoplast” and comprise the genera Plasmodium, Toxoplasma and Cryptosporidium causing malaria, toxoplasmosis, and cryptosporidiosis.
Ubiquitin Proteasome System Regulates Biological Particles Interaction in Particle Disease (PD) via NF-κB Signaling
Considering their outstanding mechanical character, it is inevitable to utilize titanium and titanium composite for biomedical engineering application [1-6]. However, the particles releasing from these bulks or composites of biomaterials after long term implanting in human body will cause cell apoptosis or cell death, inflammation, bone
Uniportal VATS Lobectomy for Lung Cancer: Feasibility and Cost Effectiveness in a Single Center Experience
In last decades, video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) together with robotic-assisted thoracic surgery (RATS) can be considered the biggest innovation in thoracic surgery. This approach drastically changed the way of performing surgical operations, improving patient’s outcome undergoing thoracic surgery.
Gender Disparities in Outcomes Following Pulmonary Embolism Treatment in the Intensive Care Unit; A Multi-center Retrospective Cohort Study
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of blood flow in the pulmonary artery bed that can result in a life-threatening and potentially reversible right ventricular failure [1]. PE remains one of the leading causes of poor prognosis and death, particularly when a shock or right ventricular failure occurs [2]. According to studies, PE is generally manifested in a nonspecific manner
Prospective Evaluation of Effect of Metformin on Activation of AMP-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) and Disease Control in a Sub-group Analysis of Patients with GI Malignancies
Observational studies have demonstrated association of metformin with reduced cancer incidence and mortality in multiple cancer types, including gastrointestinal (GI) malignancies. Anti-neoplastic effects of metformin are believed through many mechanisms including activation of AMP-activated protein kinase, which controls mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) growth regulatory pathway.
Circulating Cell-Free RNA: A New Perspective for Endometrial Cancer
In order to implement the knowledge of cancer to monitor its evolution and setting, in the last decade, new minimally invasive and repeatable samples collection have been developed such as liquid biopsy.
Searching for Easy Reliable Prognostic Parametres in Colorectal Cancer Patients Evaluation
Despite the advances in diagnostic and therapeutic field, colorectal cancer (CRC) still remains the third most common cause of death worldwide, with more than 600,000 cancer-related deaths per year.
Impact of Cisplatin Dosing Regimens on Mammary Tumor Growth in an Animal Model
In a recent paper, we introduced a variant of the classical Simeoni tumor growth model, and illustrated its value in assessing tumor growth in a reproducible mouse model for mammary tumors. Our modification consisted of incorporating delay differential equations in the mathematical formulation of the Simeoni model, to represent the delay in drug action often observed under chemotherapeutic or immunotherapeutic regimens.
Deubiquitinase as Potential Targets for Cancer Immunotherapy
During the last few decades, immunotherapy is considered to be an important approach to help our immune system to fight various kinds of diseases, such as tumor. Sometimes, it works very well for some types of cancers, for example: bladder cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer and lymphoma.
The Effect of Glucocorticoids on Angiogenesis in the Treatment of Solid Tumors
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are defined by their role in maintaining glucose homeostasis and natural GCs are a class of corticosteroids secreted by the adrenal cortex. Cortisol is the most important natural GC in humans. Cellular cortisol levels are regulated by the tissue-specific metabolic enzymes 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 and 2 (11β-HSD 1 and 2); 11β-HSD 1 converts inactive cortisone to active cortisol, while 11β-HSD 2 has the opposite function.
Spontaneous Resolution of Infected Pancreatic Necrosis after Fistulization into Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
A 67-year-old female with a history of arterial hypertension and previous hysterectomy, was recovered, in July 2019, for moderately-severe acute biliary pancreatitis with evidence of stones in gallbladder and bile duct and pancreatic necrosis on imaging (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography. A contrast enhanced CT, a week after the admission, showed necrotic areas in the pancreas and a large peripancreatic fluid collection (60 mm long) with air pockets within (acute necrotic collection, with signs of infection. Since she was haemodynamically stable and there was no evidence of organ failure, according to “step-up approach”, she was managed medically with antibiotics (piperacillin-tazobactam + metronidazole) and fluids.
The Potential Role of SEPT6 in Liver Fibrosis and Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Liver fibrosis is a reversible wound-healing response in which a variety of cells and factors are involved in and results in excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM). Cirrhosis is one of the significant causes of portal hypertension and end-stage liver disease, and it is the 14th most common cause of death around the world. Approximately 1.03 million people worldwide die from liver cirrhosis every year.
Synthetic Lethal Drug Combinations Targeting Proteasome and Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in TP53-Mutated Cancers
Tumors harboring mutations in certain oncogenes are often dependent on activation of certain pathways which becomes essential for the survival of the cancer cells. This condition is formally known as synthetic lethality, a state when simultaneous loss of two genes is lethal to a cancer cell, while the loss of the individual genes is not.
Physiotherapy Research in a Danish University Hospital: A Retrospective Review, 2010-2018
Patients of all ages with motor disorders expect highquality assessments and evidence- based treatment [1]. In university hospitals, alongside medical training and treatment of patients, research [2] is an integral part of the skills for medical professionals e.g. doctors, nurses, occupational therapists and physiotherapists.
Trending Special Issues
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.