Loading
Journal of Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials
ISSN: 2692-630X
Most Cited Articles
In Silico Proteome Analysis of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)
Chittaranjan Baruah, Saurov Mahanta, Papari Devi, Dhirendra K. Sharma
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARSCoV- 2) is a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA with genome size 26.2, and 31.7 kb coronavirus, covered by an enveloped structure, which is a major source of disaster in the 21st century. A typical CoV contains at least six ORFs in its genome. SARS-CoV-2 is the seventh coronavirus that is known to cause human disease.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p1-19 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.2.016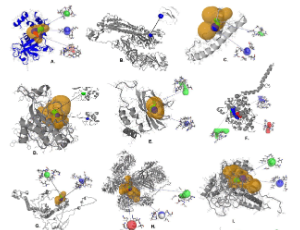
Development of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Semiconductors
Ahmed M. Abu-Dief
The variety of methods employed during the fabrication of MONPs can alter the characteristics and control the properties of the obtained nano-oxides. The reaction mechanisms and, therefore, the functionality of nanostructured MOx depend on their composition
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p5-10 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.1.002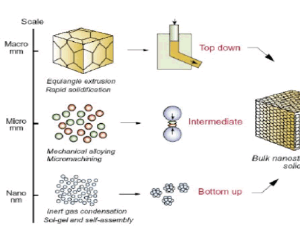
Exploiting Nanotechnology to Target Viruses
Sérgio Antunes Filho, Otávio Augusto Leitão dos Santos, Mayara Santana dos Santos, Bianca Pizzorno Backx
Infectious diseases caused by microorganisms of the most varied natures and by viral entities cause millions of deaths every year. Around the world, viral infections have impacted civilizations’ circumstances since the earliest times, including the current panorama of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic known as coronavirus disease in 2019 (COVID-19). In this sense, in the last century,
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p11-15 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.1.003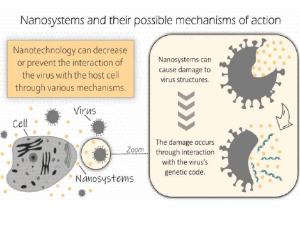
Structural Characterization of Commercial Graphite and Graphene Materials
It-Meng Low, Hani Manssor Albetran, Michael Degiorgio
The most important elemental-carbon-based materials include zero-, one-, two-, and three-dimensionalstructured fullerenes, carbon nanotubes, graphene, and graphite, respectively. These non-metallic carbon materials have properties that are similar to semiconducting metals.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p23-30 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.1.005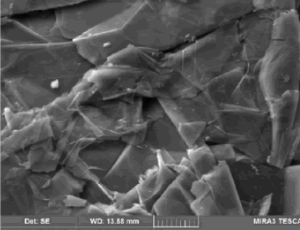
A Review on Nanotechnology: Applications in Food Industry, Future Opportunities, Challenges and Potential Risks
Monalisha Sahoo, Chirasmita Panigrahi, Siddharth Vishwakarma, Jayant Kumar
Nanotechnology is an evolving revolution with enormous promise in a variety of fields, including mechanics, medicine, and the food business. Nanoparticles owing to having greater surface area and enhanced rates of mass transfer seem to pose higher biological and chemical activities, penetrability, catalytic behaviour, enzymatic reactivity, and quantum
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 1, p28-33 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.3.029
Multidirectional Benefits of Nanotechnology in the Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Tuberculosis
Monika Gupta, Shivangi, Laxman S. Meena
Despite the curious advancement in medical science and therapeutics, tuberculosis (TB) persist the primary factor of mortality than any other infectious disease and socioeconomic disaster for millions of people around the world. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), World’s One-third of the population is infected with this disease and of these, 8 to 10 million people develop active disease and 2 million people die each year and the rest of the infected people remain asymptomatic.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 2, p46-56 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.1.008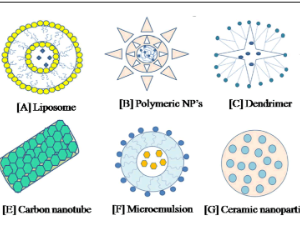
Nanotechnology in Water Treatment: An Optimistic Perspective for the Near Future
Bruna Maria Praun Pereira, Bianca Pizzorno Backx
Unequal access to drinking water and basic sanitation are old issues in Brazil and worldwide. Besides, this situation foments the proliferation of infectious parasitic diseases. Moreover, mainly in underdeveloped countries, it victimizes socioeconomically vulnerable people. The degree of water contamination analysis, usually by fecal matter, is made by the number of microorganisms present in the sample, including Escherichia coli or thermotolerant coliforms. In addition, several
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p51-56 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.2.020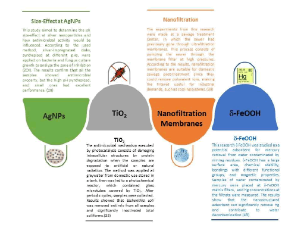
Ligand-free Few Atoms Ag Nanoclusters Synthesis and Their Potential Application as Photocatalytic Agents
Jesica M. J. Santillán, David Muñetón Arboleda, Diego Muraca, Daniel C. Schinca, Lucía B. Scaffardi
Reducing the size of a metal from macroscopic to the nanoscale generates a scaling behavior in physical and chemical properties due to the large surface-to-volume fraction. While a further size reduction to small clusters under 2 nm (<~100 atoms) yield geometric and electronic structurwhich are still different from their nanoparticle (NP) counterpart.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 2, p65-71 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.1.009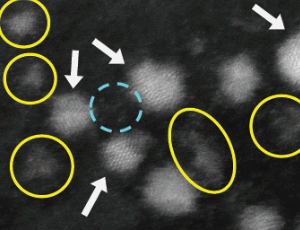
Detection of Viruses and Development of New treatments: Insights into Antibody-Antigen Interactions and Multifunctional Lab-On-Particle for SARS CoV-2
Martin Amé, Esraa Samy Abu Serea, Ahmed Esmail Shalan, A. Guillermo Bracamonte
The Corona Virus disease is a severe respiratory problem generated via severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS CoV-2). The latest strain of the disease was deadly enough to halt the global routines of human development. In this context, a number of research studies have been conducted to provide knowledge and to combat with this severe illness.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p67-75 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.2.022
Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dyes Using Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) and Mg-TiO2 Nanoparticles
Sandesh Jaybhaye, Nikita Shinde, Shrutika Jaybhaye, Himanshu Narayan
Titanium dioxide (TiO2 ) based nano-sized photocatalysts (NPCs) were synthesized following a green method from the extract of Peepal (Ficus religiosa) leaves and titanium tetrachloride as precursors. Doping of TiO2 with Magnesium (Mg) was done using magnesium chloride through the method of chemical precipitation. Size of the NPC samples were estimated and characterized by CPS Disc Centrifuge, Diffracted Light Scattering (DLS) and Field Emission Gun Scanning Electron Microscopy (FEG-SEM) techniques.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 2, p67-76 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.3.032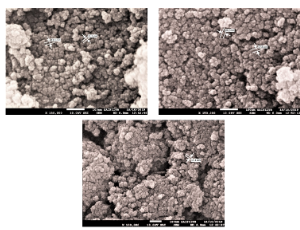
Developing Neo-bioplastics for the Realization of Carbon Sustainable Society
Akihito Nakanishi, Kohei Iritani, Yuri Sakihama
Plastic is a composite material made from organic polymers and can be freely molded into a film, fiber, or plate by heat or pressure processing. In 1839, Goodyear proposed the vulcanization of natural rubbers, while E. Simon discovered polystyrene
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 2, p72-85 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.1.010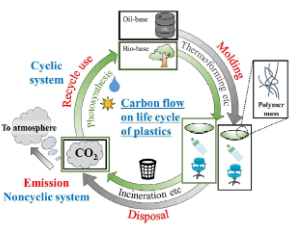
Biological and Non-Conventional Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs): Their Potential Applications
Bhabesh Deka, Chittaranjan Baruah, Azariah Babu, Pankaj Kalita
In nature, nanoparticles can be found as natural or synthetic. Nanoparticles may form either physically or chemically. Nanoparticles are uniform types of common material whose dimensions are less than 100 nm. Volcanic ash, ocean spray, fine sand, and dust are some examples of natural nanoparticles.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 2, p79-89 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.3.034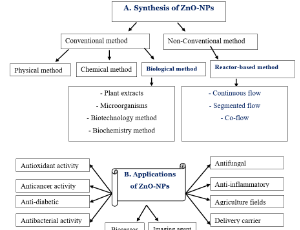
Nanotechnology for Water Purification – Current Trends and Challenges
M. P. Ajith, Paulraj Rajamani
Environmental pollution is a significant concern in both developing and developed countries. The pollution load in the environment accumulates as a result of anthropogenic activity. Both organic and inorganic contaminants are hazardous to living things, and their incidence and persistence have risen dramatically in current years.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p88-91 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.2.025
Current Progress in Vanadium Oxide Nanostructures and Its Composites as Supercapacitor Electrodes
Raktima Basu, Sandip Dhara
In recent time, supercapacitors (SCs) are one of the emerging technologies used for clean energy prospect. The higher power density, low specific energy, longer cycle life, and environmental affability made the SCs superior compared to conventional batteries. However, the scientific community is working towards increasing the specific energy of SCs by finding a suitable electrode material. Carbon materials, conducting polymers, and metal oxide or hydroxides are
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p92-103 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.1.012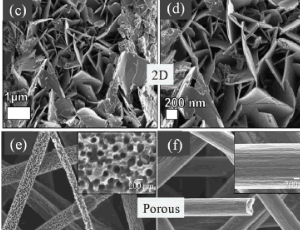
Green Nanotechnology: The Influence of Intermolecular and Supramolecular Interactions
Otávio Augusto Leitão dos Santos, Bianca Pizzorno Backx
In the last decade, the study of nanometer-scale particles has grown exponentially worldwide. This growth is due to the broad field of nanostructures applications, which, due to their dimensions in nanometric sizes, have new properties not found in micro and macro scale. These properties result from the increase in the ratio between the surface area and volume, and the nanostructures’ size directly influences these. Tolerance to temperature, variety of colors, changes in chemical reactivity,
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p104-108 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.1.013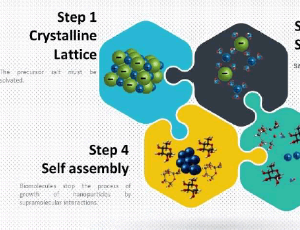
Rapid Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 by Coupling Tungsten Trioxide (WO3) Photocatalyst with Copper Nanoclusters
Silvia Ghezzi, Isabel Pagani, Guido Poli, Sudipto Pal, Antonio Licciulli, Stefano Perboni, Elisa Vicenzi
At the end of 2019, a novel severe respiratory disease (coronavirus disease 2019, COVID-19) spread to Wuhan, China, it became pandemic in few months, with more than 41 million people infected worldwide as of October 2020. COVID-19 is caused by a novel virus called severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) CoV-2 to distinguish it from SARS-CoV that emerged in Guangdong province in China in 2003 and caused the severe clinical condition known as SARS. Like SARS-CoV, SARS- CoV-2 causes a severe inter
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p109-115 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.1.014
Quantifying Respiratory Airborne Particle Dispersion Control Through Improvised Reusable Masks: The Physics of Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions for Reducing SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Airborne Transmission
Nathan J. Edwards, Rebecca Widrick, Richard Potember, Mike Gerschefske
In light of the current pandemic from rapid transmission of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2 or COVID-19) and significant morbidity, there has been inconsistent medical guidance given to the public regarding the wearing of non-medical improvised fabric masks or face coverings to reduce the transmission of COVID-19.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p116-128 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.1.015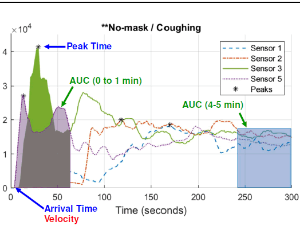
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
