Loading
Archives of Pharmacology and Therapeutics
ISSN: 2688-9609
2023
Volume 5, Issue 1, p1-81
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Off Label Use as an Indicator of Therapeutic Need in Pediatrics
Silvia Miriam Cammarata
Unapproved use of an approved drug is called “off-label” use. In line with European Medicine Agency’s pharmacovigilance directive, off-label use “relates to situations where a medicinal product is intentionally used for a medical purpose not in accordance with the authorised product information (SmPC).
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p1-4 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.036
The Role of the General Practitioner in Vaccination against COVID-19
Jose Luis Turabian
The SARS-CoV-2 virus, responsible for covid-19, had an animal origin and jumped to humans in 2019. In 2020 alone, COVID-19 infected almost 100 million people around the planet and ended with the lives of 2 million people. The development in a very short space of time, of vaccines against COVID-19, in response to the urgency of the pandemic, is a transcendental milestone in the history of medicine.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p5-7 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.037
POSTCOVID-19WAR Era, Interaction between Cancer-Hematologic Disorders- Diabetes Significantly Increased by COVID-19 Variants, Aggressively
Bahram Alamdary Badlou
Understanding the mechanism of bidirectional interaction between different angles of the death triangle is a lifesaving novel idea that I invented in 2018. Platelet hyperactivity and dysfunction in diabetes and cancer patients were already known facts [1] but whether different COVID-19 variants could activate and/or accelerate death triangle machinery?
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p8-10 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.038
Keeping Ready against Omicron and Future Variants: Can Ivermectin Prophylactic Effects Improve the Vaccination Effects against COVID-19?
Hamidreza Zalpoor, Mohsen Nabi-Afjadi, Fatemeh Aziziyan, Chanour Tavakol
The standard treatment options for Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) remain challenging despite community vaccinations and reduced mortality. As the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus continues to evolve and new strains emerge, diversity in the use of existing antiviral drugs has become a crucial therapeutic tool in combating the COVID-19 epidemic.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p11-17 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.039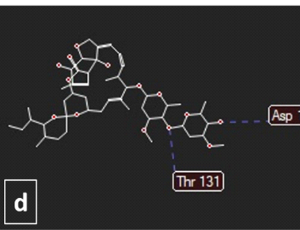
Proto-oncogenes Crosstalk, Feedback and Expression, and Anticancer Drugs Resistance
Mahmoud M. Elalfy, Mona G. Elhadidy, Eman Mohamed El Nashar
Proto-oncogenes like C-MYC, EGFR and others have physiological function in regeneration, wound and any stressfully injury to maintain tissue echotexture and healing. Notably, these growth factors work together and had life span to retain to basal level after tissue remodeling and retain its function like what happen in partial hepatectomy.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p18-21 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.040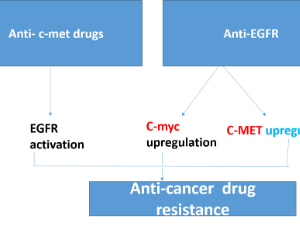
Reflections on COVID-19 Pharmacological Treatment and Beyond: Beware of “Salads” with Many Ingredients but Low Scientific Content
Jose Luis Turabian
The pandemic triggered by SARS-CoV-2 has changed since that first case in Wuhan in 2019. We currently have efficient vaccines that have allowed us to return to our daily activities. But, SARS-CoV-2 remains a public health emergency of international concern.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p22-24 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.041
Application of Halides Complexes of Ruthenium (II) in Metallopharmaceuticals and in Material Science: Part-I
Vishnu Kumar Sahu, Anil Kumar Soni, Kavindra Kumar Mishra, Rajesh Kumar Singh
Ruthenium readily forms coordinate-complexes and these complexes have their applications in diverse fields. A survey of literature shows that designing of new ligands that can be complexed with Ruthenium (Ru) in various oxidation states can lead to development of new materials with diverse applications.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p25-35 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.042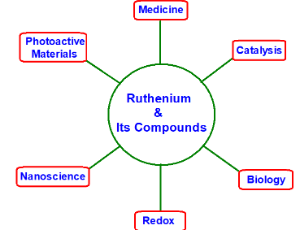
From Data to Knowledge: A Mini-Review on Molecular Network Modeling and Analysis for Therapeutic Target Discovery
Mustafa Ozen, Effat S. Emamian, Ali Abdi
Successful drug development is a risky and lengthy process that can take over ten years and consume billions of dollars. Target discovery is a critical stage of drug development for the identification of key molecules and pathways that can be targeted by novel therapeutics to find more effective treatments. Due to the rapid development in artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques over the past decade
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p36-43 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.043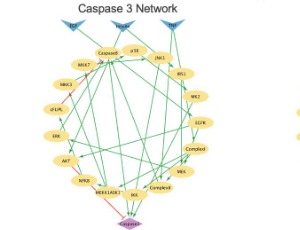
Dose-dependent Oxidative Damage of Molnupiravir (Antiviral Drug for Treatment of COVID-19) in Lung, Liver, Heart, and Kidney Tissues in Rats
Kevser TANBEK, Suleyman SANDAL
Molnupiravir (MOL) is an orally absorbed prodrug of the ribonucleoside analogue N-hydroxycytidine, which has in vitro activity against several coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-1 and 2. It remains to be seen whether long term MOL has serious side effects. The side effects of MOL, which was the first to be allowed for oral use during the pandemic process, are not yet fully known. In this study, it was aimed to investigate the the mechanisms of possible dose-dependent damage on liver, lung, heart, and kidney tissues.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p44-52 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.044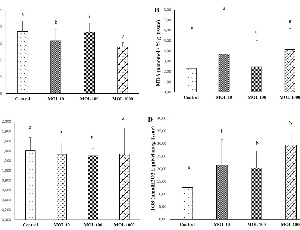
Recent Advances in Diagnosing and Treating Helicobacter pylori through Botanical Extracts and Advanced Technologies
Tamer A. Addissouky, Majeed M. A. Ali, Ibrahim El Tantawy El Sayed, Yuliang Wang
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is a major global health concern, with an estimated 50% of the world's population infected. The bacterium colonizes the stomach and is associated with a range of gastrointestinal diseases, including chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and gastric cancer. The current standard of care for H. pylori infection involves a combination of antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), but the widespread use of antibiotics has led to the development of antibiotic-resistant strains of H. pylori, making treatment more difficult. Recent advances in diagnostic strategies include the use of non-invasive tests and serological biomarkers.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p53-66 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.045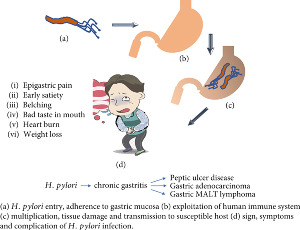
Pharmacology of Berberine and Its Metabolites, Is It the Natures Ozempic or Imatinib?
Naresh Kumar Singh, Muralikrishnan Dhanasekaran, Arun HS Kumar
Berberine, a naturally occurring alkaloid, is widely explored for several health benefits, including weight management and metabolic disorders. The major pharmacological action of berberine is reported to be by activation of AMP-activated protein kinase, while its other clinical outcomes are devoid of clear mechanism of action/s. Hence in this study a detailed pharmacology of berberine and its two major metabolites (berberrubine, and jatrorrhizine) in humans was evaluated using well established Insilco tools.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p67-81 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.046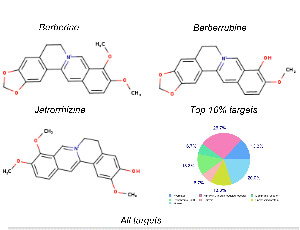
Recommended Articles
Prevalence of Symptom Clusters in Cancer Patients at First Presentation in Palliative Care Clinic as per Different Disease Groups
Cancer has its own disease burden and patients usually suffer from symptom clusters when they are referred for palliative treatment. Identification of symptom cluster trajectories will help clinician to take into account measures that can optimize quality of life of palliative patients. Therefore the aim of this paper is to determine the overall prevalence of symptoms and symptoms clusters in different disease groups according to etiology at the time of first visit to Palliative care clinic by using HIS Palliative First Assessment note indicating Edmonton symptom scale.
Chimeric Antigen Receptor CAR NK Cells Emerging Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Cancer
Although NK cells are recognized as effector lymphocytes of the innate immune system, they also regulate the adaptive immune response by releasing inflammatory cytokines and developing immunological memory. Unlike other lymphocytes such as T or B cells, NK cells do not express rearrangeable, antigen-specific receptors.
pMB FLASH - Status and Perspectives of Combining Proton Minibeam with FLASH Radiotherapy
Proton minibeam radiotherapy (pMBRT) is an external beam radiotherapy method with reduced side effects by taking advantage of spatial fractionation in the normal tissue. Due to scattering, the delivered small beams widen in the tissue ensuring a homogeneous dose distribution in the tumor. In this review, the physical and biological principles regarding dose distribution and healing effects are explained. In the last decade, several preclinical studies have been conducted addressing normal tissue sparing and tumor control in-vitro and in-vivo, using human skin tissue and mouse or rat models. The major results acquired in these studies are summarized. A further newly emerging therapy method is FLASH radiotherapy, i.e. the treatment using ultra-high dose rates. The possibility of combining these methods in proton minibeam FLASH therapy (pMB FLASH) is worked out. Additionally, technical feasibility and limitations will be discussed by looking at simulations as well as preclinical studies and also pointing out new ways of delivering the desired tumor dose, such as interlacing. We will also highlight the opportunities that emerge regarding high dose radiation, hypofractionation and the combination with immunotherapy.
Emerging Role of TRPML1 Mucolipin Endolysosomal Channel in Cancer
The transient receptor potential mucolipin 1 (TRPML1) is an endolysosomal channel belonging to the TRP family. Clinically, mutations of TRPML1 have been responsible for a severe lysosomal storage disorder called mucolipidosis type IV.
Cyclic Nucleotide Signaling Pathways in Apicomplexan Parasites Provide a Valuable Source for Novel Drug Targets
Malaria is one of the most important disabling human, tropical disease caused by different Plasmodium species, which are protozoan parasites belonging to the Apicomplexa. The Apicomplexan parasites have a plastid like structure the “apicoplast” and comprise the genera Plasmodium, Toxoplasma and Cryptosporidium causing malaria, toxoplasmosis, and cryptosporidiosis.
COVID-19 Clinical Research
While the global COVID-19 pandemic has challenged the entire humanity and health systems, it also triggered researchers to urgently perform clinical trials to assess the safety and efficacy of many agents and modalities to combat COVID-19. As of April 22, over 650 clinical studies have been registered both in USA and internationally. Results from these studies are also coming at a brisk pace in this unprecedented emergency.
Uniportal VATS Lobectomy for Lung Cancer: Feasibility and Cost Effectiveness in a Single Center Experience
In last decades, video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) together with robotic-assisted thoracic surgery (RATS) can be considered the biggest innovation in thoracic surgery. This approach drastically changed the way of performing surgical operations, improving patient’s outcome undergoing thoracic surgery.
A Bioinformatics Protocol for Rational Design of Peptide Vaccines and the COVID-19 Rampage
The currently ongoing coronavirus pandemic, the SARSCOV- 2, interchangeably referred to as the COVID-19 infection, has in a short span of time altered the ways and means of almost all of mankind. So strong has been its effect that all human activity ceased in one way or another for a considerable time, led to significant loss of life and economic drain of.
Circulating Cell-Free RNA: A New Perspective for Endometrial Cancer
In order to implement the knowledge of cancer to monitor its evolution and setting, in the last decade, new minimally invasive and repeatable samples collection have been developed such as liquid biopsy.
Searching for Easy Reliable Prognostic Parametres in Colorectal Cancer Patients Evaluation
Despite the advances in diagnostic and therapeutic field, colorectal cancer (CRC) still remains the third most common cause of death worldwide, with more than 600,000 cancer-related deaths per year.
Identification of the Molecular Basis of Anti-fibrotic Effects of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Activator Using the Human Lung Fibroblast
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is an irreversible fibrotic lung disease with unknown etiology [1-3]. Although two approved medications, pirfenidone and nintedanib, are able to slow down lung function decline in IPF patients, many other chronic pathologic conditions such as dyspnea and pulmonary hypertension (PH) and overall disease progression,
Safety of Using Rituximab Therapy During COVID-19 Pandemic
Rituximab is a chimeric (20% rodent and 80% human) monoclonal antibody that binds to the CD20 antigen present on the cell surface and leads to depletion of mature B-cells [1,2]. It is the first approved monoclonal antibody to be used in the therapy of indolent B-cell non- Hodgkin’s lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Deubiquitinase as Potential Targets for Cancer Immunotherapy
During the last few decades, immunotherapy is considered to be an important approach to help our immune system to fight various kinds of diseases, such as tumor. Sometimes, it works very well for some types of cancers, for example: bladder cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer and lymphoma.
Acute Success and Long-term Follow-up of Catheter Ablation of Isthmus-dependent Atrial Flutter; A Comparison of 10 mm Tip Standard, 6 mm Tip Irrigated Radiofrequency, and Cryotherapy Catheters
Various catheter ablation technologies have evolved to improve the procedural success and safety of cavotricuspid isthmus (CTI) block. Numerous studies have compared the different energy types, catheter tip sizes, and energy settings.
The Role of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease – Questions and Future directions
With the advent of the direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), patients requiring anticoagulation for common conditions such as atrial fibrillation and venous thromboembolism no longer need to worry about dietary restrictions or regular monitoring of the international normalized ratio which complicated warfarin treatment.
How Well Do Hemodialysis Patients Respond to the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine?
In January 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) classified COVID-19 to be a Public Health Emergency of International Concern and declared it a pandemic on March 11, 2020 [1]. Over one hundred and eighty-five million people have been infected by SARS-CoV-2 and roughly four million have died worldwide so far
The Potential Role of SEPT6 in Liver Fibrosis and Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Liver fibrosis is a reversible wound-healing response in which a variety of cells and factors are involved in and results in excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM). Cirrhosis is one of the significant causes of portal hypertension and end-stage liver disease, and it is the 14th most common cause of death around the world. Approximately 1.03 million people worldwide die from liver cirrhosis every year.
The Challenge of Cognitive Dissonance in the Delivery of Precision Medicine in Veterinary Oncology
The use of molecular and genomic analysis of a cancer as a means to define a patient-specific treatment is interchangeably referred to as Precision Medicine, Personalized Medicine, or Genomically-directed medicine (herein, collectively PMED).
Synthetic Lethal Drug Combinations Targeting Proteasome and Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in TP53-Mutated Cancers
Tumors harboring mutations in certain oncogenes are often dependent on activation of certain pathways which becomes essential for the survival of the cancer cells. This condition is formally known as synthetic lethality, a state when simultaneous loss of two genes is lethal to a cancer cell, while the loss of the individual genes is not.
Physiotherapy Research in a Danish University Hospital: A Retrospective Review, 2010-2018
Patients of all ages with motor disorders expect highquality assessments and evidence- based treatment [1]. In university hospitals, alongside medical training and treatment of patients, research [2] is an integral part of the skills for medical professionals e.g. doctors, nurses, occupational therapists and physiotherapists.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
