Loading
2025
Volume 6, Issue 4, p158-187
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Integrating Psychotherapy into Clinical Care for Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease
Andreas-Antonios Roussakis, Rima Hawkins, Cara Mackley, Paola Piccini
Psychotherapy has historically played a limited role in Parkinson’s disease (PD) care, despite the high prevalence of neuropsychiatric and psychological conditions in this population. With sporadic evidence for the benefits of psychotherapy in PD, a clear pathway for psychotherapeutic intervention is still in development.
J Exp Neurol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 4, p158-161 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.6.119
A Commentary on “Suppressive Effect of Topical Moxifloxacin on Imiquimod-Induced Model of Psoriasis in Mice”
Alaa Hamza Abbas
The Journal of Experimental Neurology frequently highlights studies that bridge the gap between neurological disorders and systemic conditions, particularly those with an immunological component. The recent article, "Suppressive Effect of Topical Moxifloxacin on Imiquimod-Induced Model of Psoriasis in Mice," by Abbas et al., presents intriguing data suggesting a potential role for the fluoroquinolone antibiotic moxifloxacin in the treatment of psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory skin disorder.
J Exp Neurol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 4, p162-165 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.6.120
Extraforaminal Spinal Nerve Stimulation: A Practical Surgical Guide Based on Clinical Experience
Danielle Kohr, Alaa Abd-Elsayed, Sudhir Diwan, Michael Kugler
Extraforaminal spinal nerve stimulation (SNS) is an emerging neuromodulation technique for treating neuropathic pain. Targeting the spinal nerve distal to the intervertebral foramen enables anatomically precise stimulation, distinguishing it from conventional spinal cord or dorsal root ganglion stimulation. This article provides the first comprehensive description of the extraforaminal SNS approach, including technical refinements, anatomical insights, and clinical experience.
J Exp Neurol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 4, p166-180 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.6.121
From Atmospheric Forecasting to Neurological Inspiration: The Emerging Role of Brain Emotional Learning in Environmental Modeling
Alireza Hakimi
The intersection of computational neuroscience and environmental modeling has birthed novel algorithms that emulate brain-inspired emotional learning. One such contribution is the BELBFM (Brain Emotional Learning Based on Basic and Functional Memories) model, recently proposed for dual-height wind speed forecasting. While designed for meteorological applications, the structure and function of BELBFM echo principles long studied in neurobiology.
J Exp Neurol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 4, p181-182 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.6.122
Hypoplastic Internal Carotid Artery in a Young Stroke Patient
Farid Ullah, Muhammad Osama, Salman Khan, Imran Ullah, Abdullah, Aizaz Ali, Hafsa Salim
Hypoplastic internal carotid artery (HICA) is a rare congenital vascular anomaly, typically asymptomatic due to collateral circulation. However, in certain cases, it may present with ischemic stroke. We report a 17-year-old male with a history of smoking and illicit drug use who presented with acute left-sided weakness. Imaging revealed an infarct in the right middle cerebral artery territory and a hypoplastic right internal carotid artery.
J Exp Neurol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 4, p183-187 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.6.123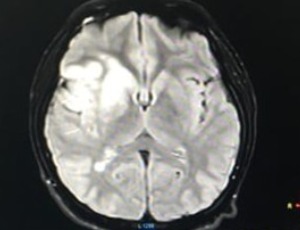
Recommended Articles
Study on Imaging Findings, Pathology and Treatment of Cerebellar Infarction
To explore the pathological mechanism and clinical treatment of cerebellar infarction through the clinical imaging changes of cerebellar infarction.
Prevention of Suicide in Persons with Progressive Neurological Diseases
People suffering with neurological diseases are at risk of committing suicide. A case-control study found increased risk of attempted suicide in patients with nine chronic neurological diseases [1]
Epilepsy in Neurodegenerative Disease: A Commentary
Case Summary - We published a case report of a 22-year-old woman who presented to our university hospital with encephalopathy and left hemiparesis of a few weeks duration.
What is the Time Necessary to be Able to Place Transpedicular Screws According to the Chosen Technique?
Transpedicular screw placement techniques are technically plaintiffs have relied on navigation intraoperative which is limited by its high cost, limited use of a fluoroscope with the radiological overexposure of the personnel of health and patient offers limited help when placing screws, and vertebral anatomical modifications especially in patients with degenerative pathology result an index of placement-related complications suboptimal of the screws [1,2].
Since its introduction by Roy-Camille [3] and Louis [4] in the seventies, the use of screws pedicle has increased markedly to the present day
Commentary on "Dysfunction of the Magnocellular Stream in Alzheimer Disease Evaluated by Pattern Electroretinograms and Visual Evoked Potentials"
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) represents the most common cause of dementia. Even if AD is commonly viewed as a disorder primarily of memory, there are several other additional domains, including visual function.
Should Food Cravings be Controlled or Understood?
Food Cravings (FC) is the term commonly used to describe sensations related to an intense desire for specific consumption [1], and there are features that we separate into internal and external aspects related to FC [2]
Skeletal Muscle Weakness Often Occurs in Patients with Myalgic Encephalomyelitis / Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS)
This commentary complements data reported in Clinical Biomechanics [1] reporting reduced maximal handgrip strength in numerous patients with myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) in proportion to their lowered maximal physical performances.
Managing Acute Urinary Dysfunction for Neurologic Injury Patients
Damage to the nervous system can have direct and indirect impact on the lower urinary tract. Broadly speaking, damage can be grouped into three categories: problems with bladder storage, stress incontinence, and problems with bladder emptying [1].
To Stick or Not to Stick? Scalp and Intracranial EEG Evaluation Both Help Achieve Good Surgical and Neuropsychiatric Outcomes in Epilepsy Surgery up to 20 Years Post-Surgery
Epilepsy has a worldwide prevalence of about 50 million [1]. Seizure medications provide adequate control in two thirds of these patients but about a third are refractory to multiple medications and need surgery or other treatments [2].
Intracranial Pressure Monitoring in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -Current Practices and Challenges
The annual incidence of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) in the United States is 6-16 cases per 100,000 population, with approximately 30,000 cases occurring each year.
Treatment of Neurological Manifestations of Mucopolysaccharidoses: Translational Considerations in Drug Development
Since the development of Ceredase® and Cerezyme® for the treatment of Gaucher disease in the early 1990s, treatment of lysosomal storage disorders via enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) has provided life-changing benefit to patients and their families.
Commentary to the Newly Rising Aquatic Exercise: Ai Chi
As aquatic therapy has become an important rehabilitative option, more exercise programs have emerged. Ai Chi, is one of the therapeutic aquatic exercise concepts with growing potential.
Microptofluidic Technology for Biodiagnostics of Traumatic Brain Injury: A Commentary
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a leading cause of death and neurological disability worldwide with millions of people sustaining and living with its long-term effects []. TBI is often categorized as mild, moderate and severe with primary injuries separated as either focal or diffuse, with the latter including contusions, intracranial hematomas and brain herniation.
Alzheimers Disease: A Brief Review
The worldwide prevalence of dementia is estimated to be over 45 million people. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common cause of dementia, responsible for 60-80% of cases.
Effect of Exosomes on Alzheimer’s Disease
AD is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive cognitive impairment, behavioral changes, memory loss and executive dysfunction, all of which present serious threats to the health of older people.
Neurocysticercosis: Autoantibodies, Another Cog in the Wheel of Its Variable Pathogenicity
Neurological diseases are a major cause of disability and the second cause of death today. This reality has stimulated the search for predictive biomarkers facilitating early diagnosis and the design of appropriate treatments.
Comment On: Modulatory Effects of Magnetic Vestibular Stimulation on Resting-State Networks Can be Explained by Subject-Specific Orientation of Inner Ear Anatomy in the MR Static Magnetic Field
It was recently demonstrated that modulations in resting-state networks (RSNs) can be introduced via the stimulation of the vestibular inner ear by a strong magnetic field (>1 tesla) as used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Alzheimer and It’s Possible Therapy: A Review
It is one of the most prevalent neurodegenerative disorder in the world, first described by a German Scientist, Alois Alzheimer, in 1906.
Retroviral Elements in Human Evolution and Neural Development
Human embryogenesis and the development of its most unique product, the human brain, are believed to be precisely regulated by factors adopted during human
evolution that differentiate us from other species.
Resolving the Molecular Steps in Clostridial Neurotoxin Light Chain Translocation
Due to use as human vaccines and therapies, the clostridial neurotoxins (CNTs) have been subjected to decades of scientific investigation using biophysical, electrophysiological, and pharmacological approaches to establish mechanisms of toxin action.
