Loading
Journal of Cellular Signaling
ISSN: 2692-0638
Most Cited Articles
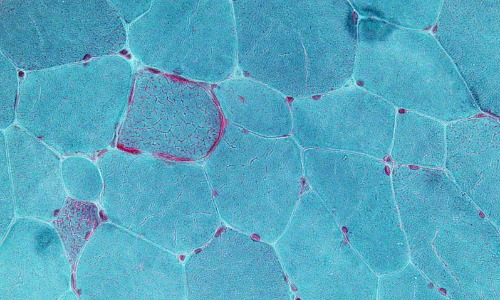
Flow Cytometric Characterization of Accidental Cell Death Highlights Connections to Regulated Cell Death
Gary Warnes
Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs) are known by their nature to cause inflammatory responses in numerous disease states from cancer, trauma to age related diseases (e.g. atherosclerosis, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases), these molecules are released by cells undergoing cell death.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.001
Augmenting Venetoclax Activity Through Signal Transduction in AML
Ian Michael Bouligny, Keri Renee Maher, Steven Grant
Venetoclax, a small-molecule B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) inhibitor, selectively eradicates leukemic stem cells (LSCs). While venetoclax has revolutionized the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), treatment failure and disease relapse are common. Mechanisms underlying venetoclax resistance are surprisingly heterogeneous.
J Cell Signal, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 1, p1-12 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.4.085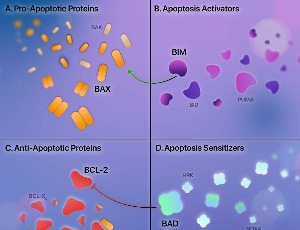
Manipulating Oxidative Stress Following Ionizing Radiation
Adriana Haimovitz-Friedman, Aviram Mizrachi, Edgar A. Jaimes
It is now well accepted that the ionizing radiation-generated reactive oxygen species (ROS), that constitute ~2/3 of the effects of external beam radiation, do not only produce direct tumor cell death, but also affect the surrounding microenvironment. Moreover, this indirect effect of radiation may result in systemic effects, specifically the initiation of an inflammatory response.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p8-13 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.003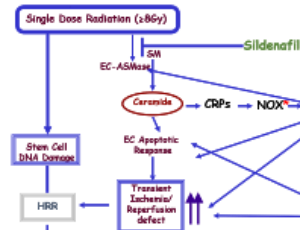
Prospective Evaluation of Effect of Metformin on Activation of AMP-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) and Disease Control in a Sub-group Analysis of Patients with GI Malignancies
Amandeep Godara, Nauman S. Siddiqui, Hilal Hachem, Philip N. Tsichlis, Robert E. Martell, Muhammad Wasif Saif
Observational studies have demonstrated association of metformin with reduced cancer incidence and mortality in multiple cancer types, including gastrointestinal (GI) malignancies. Anti-neoplastic effects of metformin are believed through many mechanisms including activation of AMP-activated protein kinase, which controls mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) growth regulatory pathway.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 2, p35-41 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.008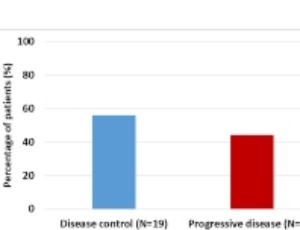
The Effect of Glucocorticoids on Angiogenesis in the Treatment of Solid Tumors
Bing Liu, Julie E. Goodwin
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are defined by their role in maintaining glucose homeostasis and natural GCs are a class of corticosteroids secreted by the adrenal cortex. Cortisol is the most important natural GC in humans. Cellular cortisol levels are regulated by the tissue-specific metabolic enzymes 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 and 2 (11β-HSD 1 and 2); 11β-HSD 1 converts inactive cortisone to active cortisol, while 11β-HSD 2 has the opposite function.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p42-49 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.011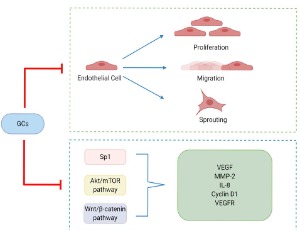
Expression and Localization of Phosphoinositide-Specific Phospholipases C in Cultured, Differentiating and Stimulated Human Osteoblasts
Sara Daisy Casoni, Alessia Romanelli, Marta Checchi, Serena Truocchio, Marzia Ferretti, Carla Palumbo, Vincenza Rita Lo Vasco
The osteoblasts contribute to bone homeostasis maintaining the bone mass, and intervene in bone injuries repair. Insights in the events leading to the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts might allow uncover potential molecular targets to control the complex mechanisms underlying bone remodeling. Signal transduction pathways contribute to the differentiation and metabolic activities of osteoblasts, with special regard to calcium-related signaling, including the Phosphoinositide (PI) pathway.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 1, p44-61 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.067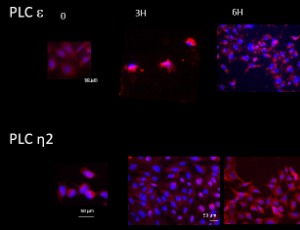
Wnt Signaling Cascades and Their Role in Coronary Artery Health and Disease
Nadisha Weerackoon, Kushan L. Gunawardhana, Arya Mani
The Wnt signaling is classified as two distinct pathways of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling, and the non-canonical pathways of planar cell polarity and Wnt/Ca2+ pathways. However, the scientific discoveries in recent years have shown that canonical and noncanonical Wnts pathways are intertwined and have complex interaction with other major signaling pathways such as hedgehog, Hippo and TOR signaling.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p52-62 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.035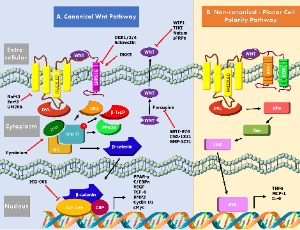
Role of Sphingolipid Signaling in Glomerular Diseases: Focus on DKD and FSGS
Alla Mitrofanova, Yelena Drexler, Sandra Merscher, Alessia Fornoni
Being a sophisticated and highly organized living system, mammals harbor a large number of biomolecular machineries which represent a dynamic and complex network of interconnections responsible for the effective operation, development and survivability of their body cells. Sphingolipids are a special class of lipids in eukaryotic cells, which have recently gained the attention of researchers because of their involvement in several fundamental processes of living cells, including proliferation
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p56-69 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.013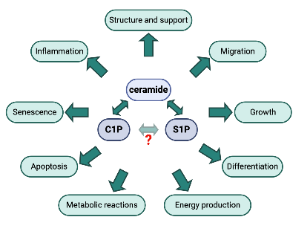
Metabolic Syndrome is an Important Cornerstone in the Health-disease Line and Pathological Organ Interaction
Ferah Armutcu, Suheyla Akyol, Huseyin Vural
Today, metabolic syndrome (MS) has been regarded as a very important disease due to its complex multifactorial etiology and damage to different organs. In general, obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, hyperglycemia, and insulin resistance are the main metabolic abnormalities of the MS. Compared with the others; in particular, insulin resistance and central obesity are considered the main causes in the pathogenesis
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p70-75 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.014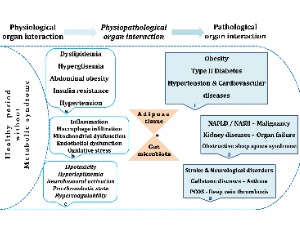
Machine Learning for Healthcare: Emerging Challenges and Opportunities in Disease Diagnosis
Sachin Kumar Deshmukh
Diagnosis is a process that identifies, explains, or establishes the individual’s disease from its symptoms and signs. Early and precise diagnosis is crucial since it influences the efficacy of treatment and avoids longterm complications for the infected person. Further, in the case of infectious diseases, undiagnosed patients can transmit the disease to a healthy population unknowingly. Besides, most of the diseases evolve with the time that significantly affects the clinical outcomes.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p76-78 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.015
Is Citrate A Critical Signal in Immunity and Inflammation?
Alessia Zotta, Zbigniew Zaslona, Luke A. O’Neill
When immune cells are activated, they undergo metabolic change in order to have sufficient energy to function effectively. The Krebs cycle is one of the most important pathways involved in this response and citrate, a critical component of this pathway, regulates carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p87-96 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.017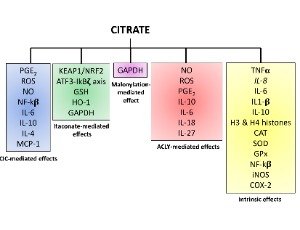
Using Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein Deficiency to Understand Maternal Health
Jason W. Miklas, Hannele Ruohola-Baker
Fatty acid oxidation disorders unfortunately can result in the sudden unexplained death of infants. Mitochondrial trifunctional protein (MTP) deficiency is one such disease where long-chain fatty acids cannot be fully oxidized through beta-oxidation which, can lead to cardiac arrythmias in an infant.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 3, p97-101 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.018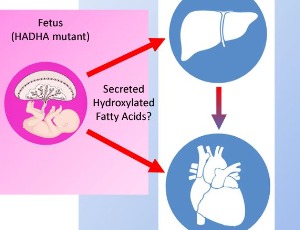
Dendorbium Nobile Lindl. Alkaloids Suppress NF-κB and NLRP3 Signaling Pathways to Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-induced Neuroinflammation
Jiaojiao Liu, Bo Liu, Xi He, Wu Qin, Jingshan Shi
The important immune cells in the brain are called microglia acting as the central junction between neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. In patients of cognitive disorders and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) animal models, amoebic morphology and inflammatory pathways are activated to release numerous cells in the inflammatory factors by active microglia.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p102-114 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.019
The Effect of Diet Induced Obesity on Serotonin in Zebrafish
Leen Uyttebroek, Samuel Van Remoortel, Laura Buyssens, Nastasia Popowycz, Guy Hubens, Jean-Pierre Timmermans, Luc van Nassauw
Obesity is a worldwide epidemic and a major risk factor for numerous diseases. The regulation of feeding behavior and body weight depends on a wide range of neuronal pathways influencing satiety and hunger. Serotonin (5-HT) is one of those players identified to have a profound effect on energy homeostasis. The effect of obesity on 5-HT metabolism in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and its underlying mechanisms still needs to be further elaborated.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 2, p115-128 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.074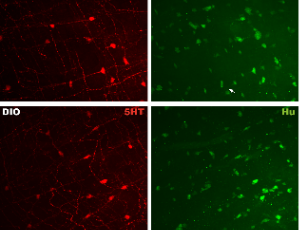
APE1/Ref-1 as a Novel Target for Retinal Diseases
Curtis Heisel, Jonah Yousif, Mahmut Mijiti, Kostas Charizanis, Mitchel Brigell, Timothy W. Corson, Mark R. Kelley
APE1/Ref-1 (also called Ref-1) has been extensively studied for its role in DNA repair and reduction-oxidation (redox) signaling. The review titled: “The multifunctional APE1 DNA repair-redox signaling protein as a drug target in human disease” by Caston et. al. summarizes the molecular functions of Ref-1 and the role it plays in a number of diseases, with a specific focus on various types of cancer.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p133-138 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.044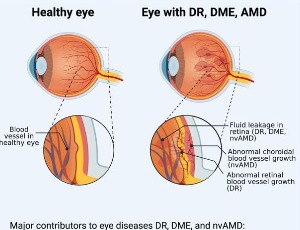
APE1/Ref-1 – One Target with Multiple Indications: Emerging Aspects and New Directions
Mahmut Mijiti, Rachel Caston, Silpa Gampala, Melissa L. Fishel, Jill C. Fehrenbacher, Mark R. Kelley
In the realm of DNA repair, base excision repair (BER) protein, APE1/Ref-1 (Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1/Redox Effector - 1, also called APE1) has been studied for decades. However, over the past decade, APE1 has been established as a key player in reduction-oxidation (redox) signaling. In the review by Caston et al. (The multifunctional APE1 DNA repair-redox signaling protein as a drug target in human disease), multiple roles of APE1 in cancer and other diseases are summarized.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p151-161 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.047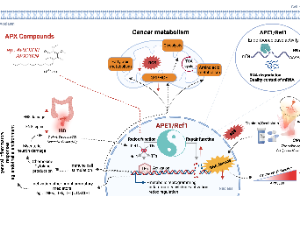
Improving Obesity and Insulin Resistance by Targeting Skeletal Muscle MKP-1
Anton M. Bennett, Ahmed Lawan
Obesity has reached a global epidemic and it predisposes to the development of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and related metabolic diseases. Current interventions against obesity and/or type 2 diabetes such as calorie restriction, exercise, genetic manipulations or established pharmacological treatments have not been successful for many patients with obesity and/or type 2 diabetes.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p160-168 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.025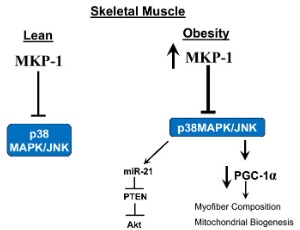
Oxidative DNA Damage: A Role in Altering Neuronal Function
Adib Behrouzi, Mark R. Kelley, Jill C. Fehrenbacher
A role for oxidative stress in the etiology of myriad neuropathologies is well accepted. However, the specific effects of oxidative DNA damage in the onset or promotion of neuronal dysfunction have been less studied. In our recent publication by Behrouzi et al. (Oxidative DNA Damage and Cisplatin Neurotoxicity Is Exacerbated by Inhibition of OGG1 Glycosylase Activity and APE1 Endonuclease Activity in Sensory Neurons), inhibition of enzymes that play a role in repairing oxidative DNA damage exacerbated neurotoxic effects of the chemotherapeutic agent, cisplatin.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 3, p160-166 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.079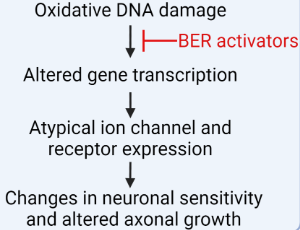
NH2-Terminal Cleavage of Cardiac Troponin I Signals Adaptive Response to Cardiac Stressors
Chad M. Warren, Monika Halas, Han-Zhong Feng, Beata M. Wolska, Jian-Ping Jin, R. John Solaro
Cardiac sarcomeres express a variant of troponin I (cTnI) that contains a unique N-terminal extension of ~30 amino acids with regulatory phosphorylation sites. The extension is important in the control of myofilament response to Ca2+, which contributes to the neuro-humoral regulation of the dynamics of cardiac contraction and relaxation.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p162-171 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.048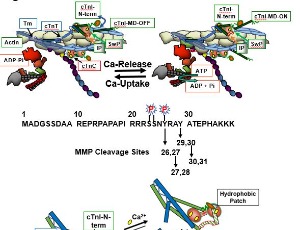
The Possible Role of Molecular Vibration in Intracellular Signalling
Werner Jaross
The exchange of information within the cell is extremely complex. Besides the well-studied chemical signalling, physical signalling is required to fulfil spatial and temporal aspects. The Golgi apparatus and the microtubule skeleton system are the decisive structures for numerous intracellular transport tasks.
J Cell Signal, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p180-186 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.027
Hydrogen Peroxide-induced Cell Death in Mammalian Cells
Tamutenda Chidawanyika, Surachai Supattapone
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is an important intra- and extra-cellular signaling molecule that can determine cell fate. At low concentrations, H2O2 plays roles in proliferation, immunity, and metabolism. Cellular exposure to higher non-physiologic concentrations of H2O2 can result in oxidative stress.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p206-211 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.052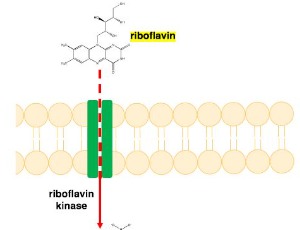
Resveratrol and Astaxanthin Protect Primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells Cultured at an Air-liquid Interface from an Acute Oxidant Exposure
Ayaho Yamamoto, Peter D. Sly, Nelufa Begum, Abrey J. Yeo, Emmanuelle Fantino
Oxidative stress (OS) in the airway epithelium is associated with cell damage, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction that may initiate or worsen respiratory disease. However, it is unclear whether exogenous antioxidants can provide protection to the airway epithelium from OS. Resveratrol and astaxanthin are nutritional compounds that have shown diverse benefits including protection against OS and inflammation in various situations.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 4, p207-217 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.084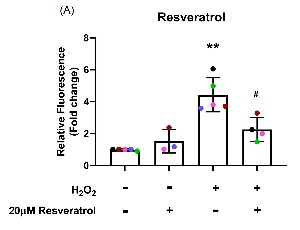
Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 and Oncogenesis in the Liver Disease
Da-eun Nam, Hae Chang Seong, Young S. Hahn
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a significant cause of cancer mortality worldwide. Chronic hepatic inflammation and fibrosis play a critical role in the development of HCC. Liver fibrosis develops as a result of response to injury such that a persistent and excessive wound healing response induces extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition leading to HCC.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p221-227 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.054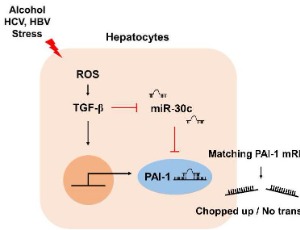
Novel Treatments Targeting the Dysregulated Cell Signaling Pathway during Sepsis
Justin H. Franco, Xiaohuan Chen, Zhixing K. Pan
Previously characterized as a purely immune mediated disease, sepsis is now recognized as a dysregulated multisystem response against a pathogen. Recognition of the infectious agent by pathogen recognition receptors (PRRs) can initiate activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway and promote the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines. During sepsis, the activation of NF-κB is dysregulated and results in cytokine storm, or the pathologic release of cytokines.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 4, p228-234 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.055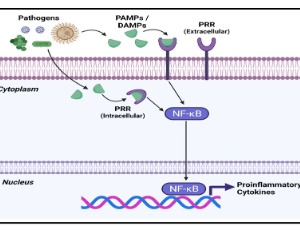
Guanylin Peptides Signaling: Insights into Guanylate Cyclase C Dependent and Independent Signaling Pathways
Ivan Strinic, Nikola Habek, Aleksandra Dugandžic
Guanylin peptides (GPs) and their receptor, guanylate cyclase C (GC-C), have recently become a topic of great interest in metabolic research. Guanylin and uroguanylin are the most investigated GPs and they belong to a larger family of natriuretic peptides. GPs play a physiological role in regulation of electrolyte balance via the intestine and the kidney by regulating the energy balance via their action in the brain.
J Cell Signal, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 4, p261-268 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.2.059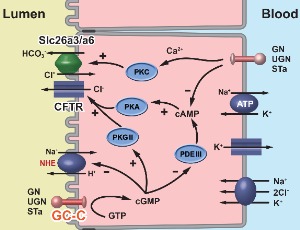
Trending Special Issues
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.