Loading
Journal of Cellular Immunology
ISSN: 2689-2812
2021
Volume 3, Issue 2, p85-131
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Review of the COVID-19 Risk in Multiple Sclerosis
Farhan Chaudhry, Cristina Jageka, Phillip D. Levy, Mirela Cerghet, Robert P Lisak
Severe respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARSCoV- 2) is the virus responsible for the novel coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) and has resulted in the death of over one million people around the world. COVID- 19’s presentation is highly heterogeneous as cases range from asymptomatic to rapidly progressive resulting in low survival rates.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.080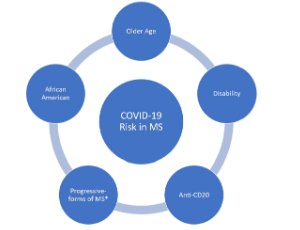
Syncytiotrophoblast Extracellular Microvesicles in Preeclampsia
Chirag Ram, Robert W. Hu, Laxminarayana Korutla, Andreas Habertheuer, Prashanth Vallabhajosyula
Preeclampsia is a major cause of mortality and morbidity in expecting mothers and is one of the most common causes of pregnancy complications and premature birth [2]. Along with eclampsia, it is directly associated with 10-15% of maternal deaths [2].
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.081
Immunomodulatory Effects of Cell Therapy after Myocardial Infarction
Joseph B Moore 4th, Marcin Wysoczynski
Myocardial infarction (MI) due to coronary artery stenosis compromises vascular endothelial integrity and increases vascular permeability. Concurrently, ensuing myocardial tissue death and necrosis results in the release of danger associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), cytokines, chemokines, bioactive lipids, as well as activation of the complement cascade.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2, p85-90 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.082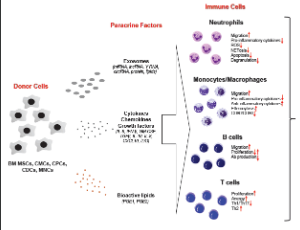
IL-10 Responsiveness and Anti-TNF Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Felicia M. Bloemendaal, Charlotte P. Peters, Anje A. te Velde, Cyriel Y. Ponsioen, Gijs R. van den Brink, Manon E. Wildenberg, Pim J. Koelink
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a multifactorial disease in which both genetic and environmental factors play an important role, although the precise cause remains obscure. It is clear that both the innate and adaptive immunity are involved in acquiring mucosal immune homeostasis in the intestine, which is dysregulated in IBD.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2, p91-96 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.083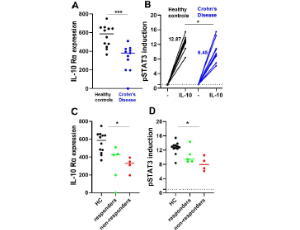
M1 Macrophages are More Susceptible to Necroptosis
Qin Hao, Steven Idell, Hua Tang
Macrophages are important cells of the innate immune system and play a crucial role in host immune defense against infection and injury [1-3]. Macrophages form the first line of defense against airborne particles and microbes through multiple functions including phagocytosis, production of cytokines and chemokines, and antigen presentation.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2, p97-102 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.084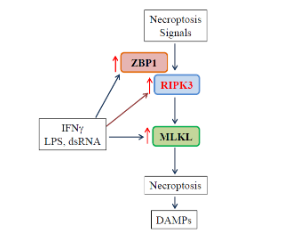
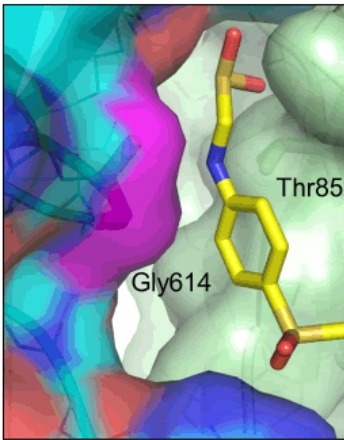
Structural Consequences of Variation in SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7
David A. Ostrov
New globally circulating SARS-CoV-2 strains are causing concern about evolution of virus transmissibility, fitness and immune evasion mechanisms. A variant emerging from the United Kingdom called SARS-CoV-2 VUI 202012/01, or B.1.1.7, is thought to exhibit increased transmissibility that results from replication 4-10 times faster than the original Wuhan virus (Wuhan-Hu-1).
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2, p103-108 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.085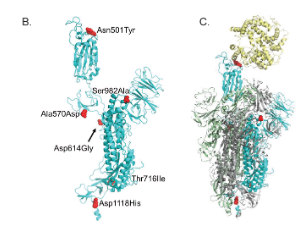
Pregnancy Specific Glycoproteins: A Possible Mediator of Immune Tolerance of Cancers
Junfei Zhao, Raul Rabadan, Arnold J. Levine
By the 1960’s there were a number of suggestions that the immune system played a role in detecting and rejecting cancerous cells. The next thirty to forty years saw a large number of attempts to identify the antigens found in a tumor that could lead to tumor rejection.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.086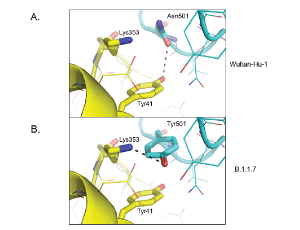
IL-22-mediates Cross-talk between Tumor Cells and Immune Cells Associated with Favorable Prognosis in Human Colorectal Cancer
Raoul André Droeser, Giandomenica Iezzi
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cause of cancer related death worldwide. Its outcome depends on different factors. On one hand there are cancer related features, including mutations, microsatellite status, and methylation alterations.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2, p118-121 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.087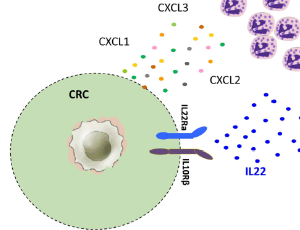
Understanding the Role of the Scabies Mite Microbiota in the Development of Novel Control Strategies
Sara Taylor, Katja Fischer
With a global prevalence of approximately 300 million people, scabies is one of the most common dermatological infectious diseases worldwide, and was recognised as a neglected tropical disease in 2017 by the World Health Organisation [1].
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2, p122-127 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.088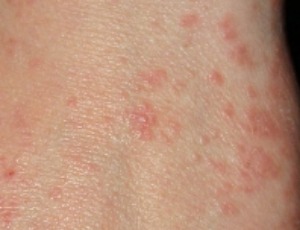
The First Viral Expression Model in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells to Observe Enteroviral Infections In vitro
Stefan Peischard, Huyen Tran Ho, Nathalie Strutz-Seebohm, Guiscard Seebohm
Viruses recently caused global outbreaks of potentially severe diseases. The newly recognized corona virus, which is causing SARS-CoV-2 is the most recent example for this scenario. Potentially severe but not as prominent as the corona virus is the Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3), which can cause fatal outcomes of myocarditis, meningitis, encephalitis and diabetes type 1 due to chronical infections of the heart, the brain, and the pancreas.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2, p128-131 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.089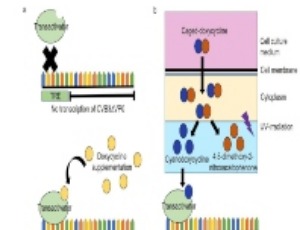
Recommended Articles
Prognosis and Survival of Medullary Carcinoma of the Breast
Medullary breast carcinoma (MBC) is a rare tumor, representing 3% to 5% of invasive breast carcinomas. The World Health Organization defines it as a well-circumscribed invasive tumor, composed of poorly differentiated cells, arranged in sheets, without gland formation and a scarce collagen stroma with the presence of a very prominent lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate.
Do Support Vector Machines Play a Role in Stratifying Patient Population Based on Cancer Biomarkers
Cancer is a worldwide public health issue that affects millions of people every year. In 2018 there were 17 million newly documented cases of cancer globally (8.8 million in men and 8.2 million in women), leading to 9.6 million deaths. Cancer is a vastly heterogeneous disease, with over 100 different types of cancer currently identified in humans; the most common types of cancer are lung, female breast, bowel and prostate, these four types account for more than 40% of all new cancer case
Is Citrate A Critical Signal in Immunity and Inflammation?
When immune cells are activated, they undergo metabolic change in order to have sufficient energy to function effectively. The Krebs cycle is one of the most important pathways involved in this response and citrate, a critical component of this pathway, regulates carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Salivary Protein Antigens for Breast Cancer Biomarkers
Breast Cancer is the most regularly diagnosed type of cancer in women in the world, making up on its own 25% of all cases, or nearly 2 million new cases in 2018, and 15% of all cancer related deaths, or around 626,700 deaths for that same year.
Dendorbium Nobile Lindl. Alkaloids Suppress NF-κB and NLRP3 Signaling Pathways to Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-induced Neuroinflammation
The important immune cells in the brain are called microglia acting as the central junction between neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. In patients of cognitive disorders and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) animal models, amoebic morphology and inflammatory pathways are activated to release numerous cells in the inflammatory factors by active microglia.
TNFAIP8: Inflammation, Immunity and Human Diseases
Inflammation can be caused by various environmental factors, including microbial infection and toxic chemical exposure. In response to inflammation, immune cells like macrophages, B and T lymphocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and various stromal cells secrete soluble polypeptide cytokine Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF?)
The Dual Role of Macrophages during Hepatitis B Infection
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) chronically infects more than 250 million individuals worldwide and is responsible for more than 800,000 deaths per year by promoting end-stage liver diseases, among which decompensated cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (WHO, July 2020) are prominent. Studies performed in chimpanzees or in animalversion of HBV (woodchuck HBV: WHBV) highlighted the lack of immune responses against the virus upon primary infection. Thus, HBV has been described as a “stealth” virus (i.e. a virus that does not modify/induce immune response in the cell). However, a growing number of studies describe that HBV is able to rapidly and efficiently counteract the innate immune response in a large variety of cells (hepatocytes, macrophages, Natural Killer cell…). Hereby, we focus on the role of macrophages (Mφ) during HBV infection.
Obeticholic Acid, FXR Agonists, Liver Disease and Plasma Biomarkers
How medications whose major biologic effect is to reduce bile acid synthesis favorably affect the course of a variety of cholestatic and metabolic liver diseases is not immediately apparent. Also, the most frequently used plasma biomarkers for evaluating benefit, alkaline phosphatase and conjugated bilirubin [1], provide different information. The former may be misleading with respect to the course of the disease and therefore it is important to focus on the pathophysiologic basis for its use.
ProLung™-budesonide Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Replication and Reduces Lung Inflammation
Inhaled budesonide benefits patients with COVID-19. ProLung™-budesonide enables the sustained, low dose administration of budesonide within a delivery vehicle similar to lung surfactant.
MicroRNA Signature Targeting Transient Receptor Potential Channels in the Prognosis and Therapy of Cancer
This short communication would to be the continuation of the Santoni’s paper entitled “Targeting Transient Receptor Potential Channels by MicroRNAs drives tumor development and progression” published in: Calcium Signaling, Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology
Prognosis of Patients with Advanced Liver Disease and Positive Stress Echocardiograms: Impact of Coronary Artery Disease, Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis, and Beta-blocker Therapy
Cardiac Complications are the leading cause of mortality after orthotopic liver transplantation. Advanced liver disease patients with positive DSE are at increased risk. CAD, beta blocker use and NASH are independently associated with cardiac events.
S1P Generation by Sphingosine Kinase-2 in Recruited Macrophages Resolves Lung Inflammation by Blocking STING Signaling in Alveolar Macrophages
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is the major cause of mortality among hospitalized acute lung injury (ALI) patients. Lung macrophages play an important role in maintaining the tissue-fluid homeostasis following injury. We recently showed that circulating monocytes recruited into the alveolar space suppressed the stimulator of type 1 interferon genes (STING) signaling in alveolar macrophages through sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P).
Arid5a Inroads to Immunity, Inflammation, and Cancer
The immune system is essential to host defense because it senses attacking pathogens and elicits protective immune responses. Although immune responses can protect against pathogens, uncontrolled immune responses cause tissue damage and other pathological consequences through their inflammatory mediators.
New Trends in Interrelation of Infectious Colorectal Cancer with Intestinal Microbiota
The intestinal microbiota creates a bodily barrier for invading pathogen by using aggressive exclusion. Pathogens and immune cells can interact directly and dynamically with symbiotic bacteria, determining the pathophysiology and outcome of an infection. They can defend the host through a variety of processes, including attachment site occupancy, nutrition intake, metabolite competition, and the synthesis of antimicrobial compounds including bacteriocins that influence pathogen survival (a process referred to as colonization resistance).
Exosomes, PD-L1 and aGvHD: Perspectives for WJMSCmediated Therapy
Tumor-derived small extracellular vesicles or exosomes which carry the checkpoint PD-L1 are directly involved in immune evasion and uncontrolled tumor growth. We have recently reported that PD-L1 is also enriched on Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stromal Cell (WJMSC)-associated exosomes.
The Role of Selected Habits, Periodontal Disease and Oral Hygiene Status on the Occurrence and Prognosis of Oral Mucosal Lesions
Patients with an array of benign oral mucosal diseases comprising fibro-epithelial polyps, lipomas and lichen planus commonly present to Oral & Maxillofacial units. While managing their specific conditions, it is important to assess for their risk habits such as betel chewing which is associated with a high burden of periodontal disease as
Biomarkers of Pembrolizumab Efficacy in First-Line Advanced PD-L1 ≥ 50% Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death worldwide. In 2020, a total of 19 million cancer patients were diagnosed, of which 11.4% were lung cancer, causing 18% of all cancer deaths. In 2020 in Spain, 29,638 cases were estimated.
Effect of Exosomes on Alzheimer’s Disease
AD is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive cognitive impairment, behavioral changes, memory loss and executive dysfunction, all of which present serious threats to the health of older people.
News About the Extracellular Vesicles from Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Functions, Therapy and Protection from COVID-19
The present Commentary is a critical follow-up of a previous review about “Extracellular vesicles, news about their role in immune cells: physiology, pathology and diseases”, appeared in Clinical and Experimental Immunology last June 2019 [1].
Faecal Microbiota Transplantation as Primary Treatment for Clostridioidoes difficile Infection-evidence for Change
Clostridioides difficile is an anaerobic spore-forming gram positive bacillus that infects the gut microbiota leading to gastrointestinal disease with varied severities ranging from self-limiting diarrhea to life-threatening pseudomembranous colitis,
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
