Loading
Journal of Cellular Immunology
ISSN: 2689-2812
2020
Volume 2, Issue 5, p201-264
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Is Cellular Senescence of Dopaminergic Neurons the Cause of Local Inflammation in the Midbrain Observed in Parkinson’s Disease?
Markus Riessland
Current research investigating the pathomechanisms of neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system (CNS), such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), or Parkinson’s disease (PD), led to the understanding that these diseases have to be seen in the context of immune responses [1]. In other words,
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 5, p201-204 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.043
The Yin and the Yang of STAT1 Downstream of TLR4 Endocytosis: STAT1 beyond Interferon Signaling
Hozaifa Metwally, Tadamitsu Kishimoto
Developing defense mechanisms by the host is fundamental to ensure its survival against various microbial pathogens. At the heart of the host defense against microbes is its ability to initiate an immune response to detect and eliminate potential microbial threats. However, in many cases the aberrant immune response is the cause of the host’s clinical symptoms of infections rather than the microbe itself [1]. Therefore, understanding the
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 5, p205-210 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.044
Updates of Recent Vinpocetine Research in Treating Cardiovascular Diseases
Chongyang Zhang, Chen Yan
Vinpocetine was originally discovered and marketed under the trade name Cavinton around 1978. Vinpocetine is a synthetic derivative of the vincamine molecule which is an alkaloid extracted from the periwinkle plant, Vinca minor [1]. It has been clinically used in many Asian and Europe countries for preventing and treating neurological
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 5, p211-219 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.045
Control of CD4 Helper and CD8 Cytotoxic T cell Differentiation
Vibhuti P Dave
Engagement of mature T cell receptor (TCR), a multiprotein complex consisting of an αβ heterodimer associated with invariant CD3 signaling proteins, on CD4+CD8+ double positive (DP) thymocytes by selfpeptide/ self-MHC complex on thymic stromal cells results in negative selection of thymocytes expressing strong affinity TCRs and
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 5, p220-226 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.046
Pro-survival Bcl-2 Proteins are Modifiers of MYC-VX-680 Synthetic Lethality
Jing Zhang, Shenqiu Zhang, Qiong Shi, Dun Yang, Thaddeus D. Allen
The transcription factor encoded by the myelocytomatosis oncogene (MYC) is deregulated by distinct means in different human cancers. Aberrations include chromosomal translocation, amplification, mutation, enhancer activation and post-translational mechanisms that lead to MYC protein accumulation [1]. It is perhaps the most
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 5, p227-232 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.047
Culture nTAD: A New Avenue for Research in Late-stage Human Lung Development and Perinatal Lung Disease
Hongmei Mou
Primary cell culture is a laboratory process that has been practiced for more than a century by which the cells of interest are isolated from tissues and grown under the appropriate conditions to achieve a certain cell number. In conducting airway, basal cells function as stem cells that self-renew and differentiate to maintain tissue
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 5, p232-236 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.048
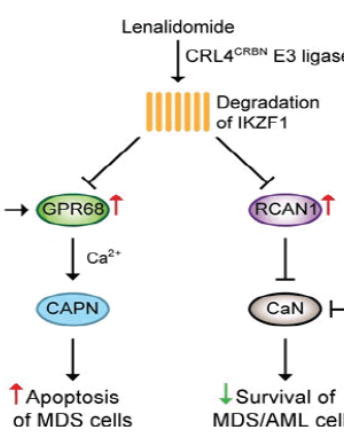
Cyclosporine Broadens the Therapeutic Potential of Lenalidomide in Myeloid Malignancies
Aixia Dou, Jing Fang
Thalidomide, lenalidomide and pomalidomide are synthetic immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) that have recently drawn attention in both clinics and basic research. Thalidomide was synthesized from glutamic acid and was banned due to its teratogenicity in pregnant women.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 5, p237-244 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.049
Hypomagnesemia and Outcomes in Hematologic Malignancies
Jennifer Gile, Joy Heimgartner, Gordon Ruan, M. Molly McMahon, Thomas Witzig
Magnesium is an essential mineral and cofactor for hundreds of enzymes and reactions. Magnesium is essential for the regulation of cell growth, division, and differentiation as well as protein synthesis, cell signaling and structural functions.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 5, p245-249 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.050
Emerging Functions of ICAM-1 in Macrophage Efferocytosis and Wound Healing
Prarthana J. Dalal, Ronen Sumagin
ICAM-1 is a transmembrane, cell surface glycoprotein expressed by a variety of cells, but has been best-studied in vascular endothelium. Structurally, ICAM-1 is composed of five extracellular IgG- like domains to help facilitate cell-cell interactions and has a short cytoplasmic tail anchored to the cytoskeleton to facilitate intracellular signal
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 5, p250-253 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.051
Juvenile-onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Accompanied by Secondary Thrombotic Microangiopathy
Eriko Tanaka, Tomoya Kaneda, Yuko Akutsu, Toru Kanamori, Mariko Mouri, Masaaki Mori
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects multiple organ systems. Juvenile-onset SLE (jSLE)?also called childhood-onset SLE?is usually defined as SLE with disease-onset before the 18th birthday. Patients with jSLE are reported to account for up to 20% of all SLE patients.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 5, p254-258 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.052
Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir/Voxilaprevir for Previously DAA-treated Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C?
Llaneras J, Riveiro-Barciela M, Esteban R, Buti M
Chronic hepatitis C infection is a global public health problem affecting more than 71 million people. Treatment of hepatitis C virus (HCV) has rapidly advanced with the introduction of oral direct-acting antivirals (DAAs).
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 5, p259-264 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.053
Recommended Articles
Constitutively Active Death Receptor Induces Apoptosis in Mammalian Cells
Apoptosis is a physiological response in development and homeostasis of metazoans. Apoptosis is triggered during pathological events as a means to renew affected tissues and eliminate cancer cells. The immune system regulates the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis, where signals such as TNFα or displayed ligands on the surface of immune cells trigger signal cascades by death receptors present on targeted cells.
Multidisciplinary Acute Care of Central Retinal Artery Occlusion with a Stroke Paradigm: A Call to Action
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is a painless ophthalmologic emergency with potential for irreversible vision loss. Similar to ischemic stroke, CRAO occurs when there is sudden obstruction of the central retinal artery, leading to ischemic injury to the retina and subsequent cell death. Continuous occlusion and ischemia of the retina progresses to permanent damage to retinal cells and loss of vision.
Is Citrate A Critical Signal in Immunity and Inflammation?
When immune cells are activated, they undergo metabolic change in order to have sufficient energy to function effectively. The Krebs cycle is one of the most important pathways involved in this response and citrate, a critical component of this pathway, regulates carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Modern Rehabilitation Strategies of Post-Stroke Motor Disfunctions: Functional Electrical Stimulation and Biofeedback-Stabilometric Postural Training
More than 80% of patients after a stroke have limited daily activity due to a complex polymorphic motor deficiency of various nature and severity, which leads to postural disorders (PD) [1]. Because of paresis, develops different changes in the musculoskeletal system (MSS) such as PD, restrictions of movements in the joints, impaired
Energy Expenditure and Nutrition in Neurogenic Obesity following Spinal Cord Injury
Worldwide, obesity is a public health concern and a metabolic ailment characterized by excessive adipose tissue accumulation resulting from an imbalance of energy expenditure and energy intake [1]. This disorder is a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and metabolic
No Studies in Stroke Regarding Brain fMRI Activity and Pelvic Floor Muscle Training/Activation - Only Studies in Non-stroke Population: A Review of Neuroimaging Studies
Neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction (NLUTD) is highly prevalent in poststroke patients, leading to major impact on the quality of life (QoL) and healthcare resources. Pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) has, over the past two decades, been recommended as first-line treatment for neurologically healthy patients with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS).
Dendorbium Nobile Lindl. Alkaloids Suppress NF-κB and NLRP3 Signaling Pathways to Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-induced Neuroinflammation
The important immune cells in the brain are called microglia acting as the central junction between neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. In patients of cognitive disorders and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) animal models, amoebic morphology and inflammatory pathways are activated to release numerous cells in the inflammatory factors by active microglia.
NOXA the BCL-2 Family Member behind the Scenes in Cancer Treatment
NOXA is a critical mediator of stress responses to anticancer drugs. This BH3-only protein sets the apoptotic threshold in cancer cells in response to chemotherapies by counteracting the prosurvival BCL-2 family protein MCL-1. A complex and dynamic network relying on both highly controlled gene transcription activity and protein degradation by proteasome, regulates cellular NOXA levels from low in steady state to rapidly enhanced upon stressful condition.
TNFAIP8: Inflammation, Immunity and Human Diseases
Inflammation can be caused by various environmental factors, including microbial infection and toxic chemical exposure. In response to inflammation, immune cells like macrophages, B and T lymphocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and various stromal cells secrete soluble polypeptide cytokine Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF?)
Autophagy: When to strike?
Autophagy was originally viewed as a widely conserved multistep lysosomal degradation pathway in eukaryotes. It includes the formation of autophagosomes, doublemembrane structures engulfing cytoplasm with damaged organelles during the degradation process.
The Role of TIGAR-mediated Metabolic Processes in Autophagy and Cell Survival
Autophagy is the one of the essential pathways for maintaining homeostasis of cells and plays an important regulatory role in cell survival and death. Tp53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR) is a Tp53 target protein and is not only involved in the regulation of metabolism, cell cycle progression and radiation response, but also plays a role in autophagy.
Inhibition of Autophagy and Immune Response: Alpha-fetoprotein Stimulates Initiation of Liver Cancer
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a tumorous marker for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), it is synthesized mainly by the embryo yolk sac, fetal liver and the gastrointestinal tract. AFP belongs to the family of protein products of albuminoid genes, which are located in tandem arrangement in chromosome 4 (region 4q11-q13).
Commentary on Association between Birth Weight and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: Evidence from UK Biobank
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is one of the major causes of death worldwide and poses a huge public health burden [1,2]. Early identification of individuals at risk of cardiovascular disease is crucial to develop effective preventions. The DOHAD hypothesis proposed by Professor Barker et al. states that an abnormal environment
ProLung™-budesonide Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Replication and Reduces Lung Inflammation
Inhaled budesonide benefits patients with COVID-19. ProLung™-budesonide enables the sustained, low dose administration of budesonide within a delivery vehicle similar to lung surfactant.
S1P Generation by Sphingosine Kinase-2 in Recruited Macrophages Resolves Lung Inflammation by Blocking STING Signaling in Alveolar Macrophages
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is the major cause of mortality among hospitalized acute lung injury (ALI) patients. Lung macrophages play an important role in maintaining the tissue-fluid homeostasis following injury. We recently showed that circulating monocytes recruited into the alveolar space suppressed the stimulator of type 1 interferon genes (STING) signaling in alveolar macrophages through sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P).
Arid5a Inroads to Immunity, Inflammation, and Cancer
The immune system is essential to host defense because it senses attacking pathogens and elicits protective immune responses. Although immune responses can protect against pathogens, uncontrolled immune responses cause tissue damage and other pathological consequences through their inflammatory mediators.
Immunogenic Cell Death: A Step Ahead of Autophagy in Cancer Therapy
Cell Death has long been considered to be an inevitable part of the life cycle of a cell and hence, considered a familiar consequence of cellular life.
Improved Wound Closure Rates and Mechanical Properties Resembling Native Skin in Murine Diabetic Wounds Treated with a Tropoelastin and Collagen Wound Healing Device
Chronic, non-healing, or slow to heal wounds present a significant and growing health problem in the United States, with an estimated 6.5 million people affected, at an annual cost of US $20 billion, with the highest risk groups represented by the elderly and the increasing prevalence of lifestyle diseases such as diabetes and obesity.
Friend or Foe? Opposing Functions of O-GlcNAc in Regulating Inflammation
Effector CD4+ T cells (i.e. Th1, Th2, Th17) are essential in the adaptive immune system’s specific elimination of different classes of pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, and parasites, while regulatory T cells shut these inflammatory responses off once a pathogen has been cleared [1]. Interestingly, effector T cells preferentially utilize
Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Cardiopathy and Cryptogenic Strokes
Cryptogenic stroke (CS) refers to the cerebral infarcts for which no definite cause is identified after adequate diagnostic evaluation. It accounts for 10-15% of all
strokes. Most of the cryptogenic strokes are embolicappearing non-lacunar infarcts based on the radiographic pattern.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
