Loading
Journal of Cellular Signaling
ISSN: 2692-0638
2022
Volume 3, Issue 3, p129-166
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Phosphoinositide-Specific Phospholipases C in Psychiatric Diseases and Suicide
Vincenza Rita Lo Vasco
Mood disorders represent a major medical need requiring chronic treatment. About one million people die by suicide worldwide each year, both as a consequence of major depression or not. Multiple deficits, including cell atrophy and loss, were described in the brains of mood disorders affected patients and in experimental animal models. Numerous changes in gene expression and activity were described in limbic and cortical brain regions.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 3, p129-140 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.075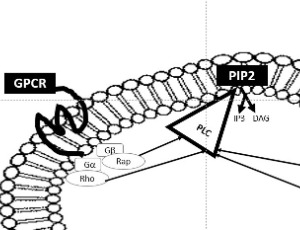
MAGIs: Junctional Scaffolds Linking Inter-Cellular Junction Architecture, Actin Cytoskeleton Dynamics, and Signaling Pathways
Lisa Heron-Milhavet, Alexandre Djiane
MAGIs (membrane-associated guanylate-kinases (MAGUK) inverted) are apical scaffolds conserved across evolution, which regulate cellular junctions. Low expression of MAGIs has been associated with tumorigenesis in a wide variety of cancers. This “tumor-suppressive” function of MAGIs has stimulated many studies to better understand the processes they control, and how their misregulation could contribute to cancer progression.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 3, p141-147 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.076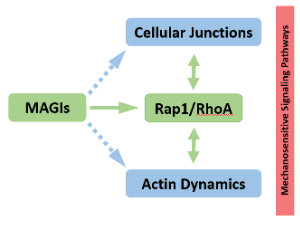
Repurposed Anti-IL-6 Therapeutics, Another Way to Quell the Cytokine Storm in Tuberculosis
Funmilayo Grâce Boni, Insaf Hamdi, Liadrine Moukendza Koundi, Lamine Baba-Moussa
Study on ‘‘cytokine storms’’ has been braced up in infectious diseases. The pertinence of this research begins to be evident in tuberculosis as it was observed that increased levels of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) were connected with disease severity. The IL-6 blockers therapeutics approaches for tuberculosis are currently a key line of research, with many in progress clinical trials, as IL-6 has become an important factor of the immune response to tuberculosis.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 3, p148-152 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.077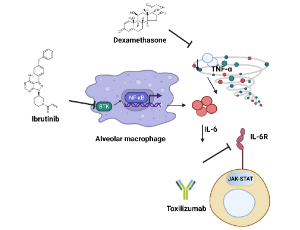
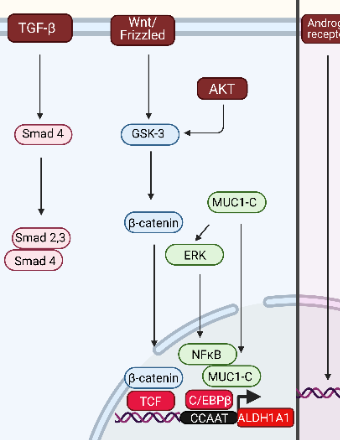
New Aspects in the Mechanism of Action of ALDH1A1 and 1A3 Isoforms in Carcinogenesis
Martina Poturnajova, Miroslava Matuskova
The ALDH gene superfamily encodes a group of evolutionarily-related proteins catalyzing the irreversible oxidation of aldehyde substrates to their corresponding carboxylic acids. Aldehyde dehydrogenases (ALDH) isoforms 1A1 and 1A3 belong to intracellular enzymes with a broad spectrum of functions linked with an advanced stage of solid tumors and the stemness potential of the neoplastic cells.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 3, p153-159 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.078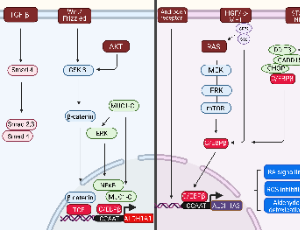
Oxidative DNA Damage: A Role in Altering Neuronal Function
Adib Behrouzi, Mark R. Kelley, Jill C. Fehrenbacher
A role for oxidative stress in the etiology of myriad neuropathologies is well accepted. However, the specific effects of oxidative DNA damage in the onset or promotion of neuronal dysfunction have been less studied. In our recent publication by Behrouzi et al. (Oxidative DNA Damage and Cisplatin Neurotoxicity Is Exacerbated by Inhibition of OGG1 Glycosylase Activity and APE1 Endonuclease Activity in Sensory Neurons), inhibition of enzymes that play a role in repairing oxidative DNA damage exacerbated neurotoxic effects of the chemotherapeutic agent, cisplatin.
J Cell Signal, 2022, Volume 3, Issue 3, p160-166 | DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.3.079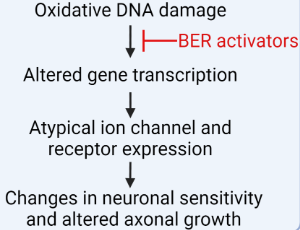
Recommended Articles
Ubiquitin Proteasome System Regulates Biological Particles Interaction in Particle Disease (PD) via NF-κB Signaling
Considering their outstanding mechanical character, it is inevitable to utilize titanium and titanium composite for biomedical engineering application [1-6]. However, the particles releasing from these bulks or composites of biomaterials after long term implanting in human body will cause cell apoptosis or cell death, inflammation, bone
Searching for Easy Reliable Prognostic Parametres in Colorectal Cancer Patients Evaluation
Despite the advances in diagnostic and therapeutic field, colorectal cancer (CRC) still remains the third most common cause of death worldwide, with more than 600,000 cancer-related deaths per year.
Safety and Efficacy of s-MOX Regimen in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Who Developed Cardiotoxicity Following Fluoropyrimidine Administration: A Case Series
5-fluorouracil (5-FU), an antimetabolite in the fluoropyrimidine class, is the third most commonly used chemotherapeutic agent worldwide for the treatment of solid malignancies [1]. Despite advances in novel cancer therapies, commonly used in combination with fluoropyrimidines, 5-FU remains one of the most effective and safe chemotherapy agents to manage colorectal cancer (CRC).
The Link of Nutrient Fluxes to Hepatic Insulin Resistance at Gene Expression
Insulin resistance has been studied extensively at systemic, organ, tissue and cellular and molecular levels. Overnutrition plays an essential role in the development of chronic metabolic diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. For subjects without genetic defects, the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes is a graduate process. How the transition from an insulinsensitive state to an insulin-resistant state occurs, and what the roles of nutrients are in the process have not been fully understood. Here, we try to summarize the current understanding of insulin-regulate gene expression in the liver, and describe a phenomenon of hepatic insulin resistance at gene expression (HIRAGE), which may be linked to overnutrition.
Dexamethasone: The First Drug to be Shown to Decrease Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19
The precise role of corticosteroids for treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is unclear due to lack of randomized trials.
No Studies in Stroke Regarding Brain fMRI Activity and Pelvic Floor Muscle Training/Activation - Only Studies in Non-stroke Population: A Review of Neuroimaging Studies
Neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction (NLUTD) is highly prevalent in poststroke patients, leading to major impact on the quality of life (QoL) and healthcare resources. Pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) has, over the past two decades, been recommended as first-line treatment for neurologically healthy patients with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS).
Design of a Peptide Against the Interaction Between Immune Response Protein TRAF5 and the Oncoprotein E6 from HPV
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the human papillomavirus (HPV) affects more than 600 million people worldwide, being the most common sexually transmitted disease (STD). There were over 250,000 deaths due to cervical cancer worldwide and most of them took place in developing countries (WHO). There are more than 80 HPV types and more than 40 infect the genital tract
Role of PI3K/Akt/GSK-3 Pathway in Emesis and Potential New Antiemetics
Nausea and vomiting are protective defense mechanisms by which vomit competent species avoid ingestion of potentially toxic substances. More specifically, vomiting is the act of forceful expulsion of gastrointestinal contents through the mouth, whereas nausea is an unpleasant painless subjective feeling that one will imminently vomit.
The Dual Role of Macrophages during Hepatitis B Infection
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) chronically infects more than 250 million individuals worldwide and is responsible for more than 800,000 deaths per year by promoting end-stage liver diseases, among which decompensated cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (WHO, July 2020) are prominent. Studies performed in chimpanzees or in animalversion of HBV (woodchuck HBV: WHBV) highlighted the lack of immune responses against the virus upon primary infection. Thus, HBV has been described as a “stealth” virus (i.e. a virus that does not modify/induce immune response in the cell). However, a growing number of studies describe that HBV is able to rapidly and efficiently counteract the innate immune response in a large variety of cells (hepatocytes, macrophages, Natural Killer cell…). Hereby, we focus on the role of macrophages (Mφ) during HBV infection.
Exercise Benefits on Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is an age-related neurodegenerative disorder [1] and the most common cause of human dementia, accounting for approximately 60%?80% of cases. It is estimated that more than 30 million AD patients, and the number likely to increase to over 100 million by 2050 because of the increase of the elderly population [2].
Inhibition of Autophagy and Immune Response: Alpha-fetoprotein Stimulates Initiation of Liver Cancer
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a tumorous marker for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), it is synthesized mainly by the embryo yolk sac, fetal liver and the gastrointestinal tract. AFP belongs to the family of protein products of albuminoid genes, which are located in tandem arrangement in chromosome 4 (region 4q11-q13).
Immunological Features with DNA Microsatellite Alterations in Patients with Colorectal Cancer
DNA microsatellites are tandemly repeating short (1-6 base pairs) DNA motifs, such as mononucleotide (A)n, dinucleotide (CA)n, trinucleotide (CAG)n, and tetranucleotide (AAAG)n, with each motif potentially repeating up to 50 times.
Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/NFkB Axis in Ovarian Cancer
Phosphoinositol 3 kinase (PI3K) defines a class of lipid kinases that have the ability to phosphorylate the inositol ring 3?-OH group in inositol phospholipids and therefore produce phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PIP3) [1]. PI3K encompasses a family of enzymes divided into: Class IA PI3K which includes three isomers (?, ?, ?) and Class IB which include the group (?).
Insulin Signal Transduction is Impaired in the Type 2 Diabetic Retina
With increasing rates of obesity, rates of type 2 diabetes and diabetic complications are expected to rise exponentially over the next few decades (American Diabetic Association). A key feature of type 2 diabetes is a resistance to insulin. Insulin signaling is key to a number of physiological processes, including glucose metabolism, cell growth, general gene expression, and apoptosis.
S1P Generation by Sphingosine Kinase-2 in Recruited Macrophages Resolves Lung Inflammation by Blocking STING Signaling in Alveolar Macrophages
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is the major cause of mortality among hospitalized acute lung injury (ALI) patients. Lung macrophages play an important role in maintaining the tissue-fluid homeostasis following injury. We recently showed that circulating monocytes recruited into the alveolar space suppressed the stimulator of type 1 interferon genes (STING) signaling in alveolar macrophages through sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P).
Study on Imaging Findings, Pathology and Treatment of Cerebellar Infarction
To explore the pathological mechanism and clinical treatment of cerebellar infarction through the clinical imaging changes of cerebellar infarction.
A New Player in an Old Story: FBXO16 Prevents Breast Cancer Tumorigenesis through Disrupting Cellular Function of Nuclear β-Catenin
β-Catenin is the central modulator of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Upon Wnt on state, β-Catenin is translocated to the nucleus and function as a transcription coactivator for several oncogenes. In Wnt off state, β-catenin is mostly localized in the cytoplasm and sequestered by the destruction complex, the negative regulator of β-catenin expression [2,3].
Physiotherapy Exercise Program for Managing Adhesive Capsulitis in Patients with and without Diabetes: A Pilot Randomized Trial
Adhesive capsulitis (AC), also known as ‘frozen shoulder’, is characterized by the development of dense adhesions and capsular thickening leading to a progressive and painful restriction of shoulder range of motion (ROM) and functional disability [1]. The onset is gradual, usually occurs between the ages of 40 and 60 years and is more common in females and diabetics.
New Trends in Interrelation of Infectious Colorectal Cancer with Intestinal Microbiota
The intestinal microbiota creates a bodily barrier for invading pathogen by using aggressive exclusion. Pathogens and immune cells can interact directly and dynamically with symbiotic bacteria, determining the pathophysiology and outcome of an infection. They can defend the host through a variety of processes, including attachment site occupancy, nutrition intake, metabolite competition, and the synthesis of antimicrobial compounds including bacteriocins that influence pathogen survival (a process referred to as colonization resistance).
Managing Acute Urinary Dysfunction for Neurologic Injury Patients
Damage to the nervous system can have direct and indirect impact on the lower urinary tract. Broadly speaking, damage can be grouped into three categories: problems with bladder storage, stress incontinence, and problems with bladder emptying [1].
Trending Special Issues
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.