Loading
Journal of Cellular Immunology
ISSN: 2689-2812
2019
Volume 1, Issue 2, p25-52
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Proteomic Functional Signatures during the Priming of Human Th17 Cells
Mohd Moin Khan, Robert Moulder, Riitta Lahesmaa
A combination of regulated responses toward pathogens and minimized autoimmune reactions is needed for the balanced function of the immune system. Amongst the immunologically important CD4+ lymphocytes, T helper 17 (Th17) cells help maintain homeostasis and provide protection against pathogens of fungal or bacterial origins
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p25-28 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.006
TNFAIP8: Inflammation, Immunity and Human Diseases
Suryakant Niture, John Moore, Deepak Kumar
Inflammation can be caused by various environmental factors, including microbial infection and toxic chemical exposure. In response to inflammation, immune cells like macrophages, B and T lymphocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and various stromal cells secrete soluble polypeptide cytokine Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF?)
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p29-34 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.007
The Role of NETosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Ryan Salemme, Lauren N. Peralta, Sri Harika Meka, Nivetha Pushpanathan, Jessy J Alexander
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a devastating autoimmune disease that affects women to men at a ratio of 9:1 and is predominant in those of African ancestry. In SLE, the presence of autoantigens results in aberrant immune activation leading to systemic inflammation that predominantly affects the brain, kidneys, blood, and skin. Current guidelines recommend treatment with immunosuppressive drugs like prednisone, cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, and even some antimalarial drugs
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p35-44 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.008
Dual Expression of GARP in Immune and Glioma Cells: Yet Another Mechanism of Cancer Immune Escape
Emily Trzeciak, Niklas Zimmer, Ella Kim, Jonathan Schupp, Bettina Sprang, Petra Leukel, Fatemeh Khafaji, Florian Ringel, Clemens Sommer, Jochen Tuettenberg, Andrea Tuettenberg
Glioblastomas (GB) are amongst the most lethal human tumors exhibiting a highly aggressive behavior manifested by tumor cell infiltration into surrounding tissue. Furthermore, GBs are notorious for their high degree of resistance to cytotoxic treatments [1-3].
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p45-49 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.009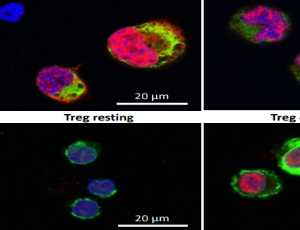
Targeting "Do Not Eat Me" Signal CD47 in Cancer Immunotherapy
Sachin Kumar Deshmukh
Cells of the innate and adaptive arm of the immune system including macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells, neutrophils, T cells, and B cells, etc. are crucial for the maintenance of the body’s homeostatic balance and prevention of multiple diseases including cancer.
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p50-52 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.010
Recommended Articles
Deubiquitinase as Potential Targets for Cancer Immunotherapy
During the last few decades, immunotherapy is considered to be an important approach to help our immune system to fight various kinds of diseases, such as tumor. Sometimes, it works very well for some types of cancers, for example: bladder cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer and lymphoma.
Is Citrate A Critical Signal in Immunity and Inflammation?
When immune cells are activated, they undergo metabolic change in order to have sufficient energy to function effectively. The Krebs cycle is one of the most important pathways involved in this response and citrate, a critical component of this pathway, regulates carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Dendorbium Nobile Lindl. Alkaloids Suppress NF-κB and NLRP3 Signaling Pathways to Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-induced Neuroinflammation
The important immune cells in the brain are called microglia acting as the central junction between neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. In patients of cognitive disorders and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) animal models, amoebic morphology and inflammatory pathways are activated to release numerous cells in the inflammatory factors by active microglia.
TNFAIP8: Inflammation, Immunity and Human Diseases
Inflammation can be caused by various environmental factors, including microbial infection and toxic chemical exposure. In response to inflammation, immune cells like macrophages, B and T lymphocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and various stromal cells secrete soluble polypeptide cytokine Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF?)
CTLA-4 and PD-L1 or PD-1 Pathways: Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Cancer Immunotherapy
The immune system developed certain checks and balance to control or inhibit the reactivity against normal cells of the body. Uncontrolled immune responses to the non-self entities such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, or mutated self-antigens can cause an inflammatory reaction and autoimmune diseases.
Cancer Nanomedicine: Strategies to Enhance Tumor Delivery and Immunotherapy
Cancer nanomedicine was originally developed for more efficient delivery of chemotherapeutic agents into tumor, and has been extensively employed as a therapeutic for cancer treatment owing to its unique features in drug delivery, diagnosis and imaging, as well as the therapeutic nature of some nanomaterials themselves.
Targeting "Do Not Eat Me" Signal CD47 in Cancer Immunotherapy
Cells of the innate and adaptive arm of the immune system including macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells, neutrophils, T cells, and B cells, etc. are crucial for the maintenance of the body’s homeostatic balance and prevention of multiple diseases including cancer.
The Dual Role of Macrophages during Hepatitis B Infection
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) chronically infects more than 250 million individuals worldwide and is responsible for more than 800,000 deaths per year by promoting end-stage liver diseases, among which decompensated cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (WHO, July 2020) are prominent. Studies performed in chimpanzees or in animalversion of HBV (woodchuck HBV: WHBV) highlighted the lack of immune responses against the virus upon primary infection. Thus, HBV has been described as a “stealth” virus (i.e. a virus that does not modify/induce immune response in the cell). However, a growing number of studies describe that HBV is able to rapidly and efficiently counteract the innate immune response in a large variety of cells (hepatocytes, macrophages, Natural Killer cell…). Hereby, we focus on the role of macrophages (Mφ) during HBV infection.
ProLung™-budesonide Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Replication and Reduces Lung Inflammation
Inhaled budesonide benefits patients with COVID-19. ProLung™-budesonide enables the sustained, low dose administration of budesonide within a delivery vehicle similar to lung surfactant.
S1P Generation by Sphingosine Kinase-2 in Recruited Macrophages Resolves Lung Inflammation by Blocking STING Signaling in Alveolar Macrophages
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is the major cause of mortality among hospitalized acute lung injury (ALI) patients. Lung macrophages play an important role in maintaining the tissue-fluid homeostasis following injury. We recently showed that circulating monocytes recruited into the alveolar space suppressed the stimulator of type 1 interferon genes (STING) signaling in alveolar macrophages through sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P).
Arid5a Inroads to Immunity, Inflammation, and Cancer
The immune system is essential to host defense because it senses attacking pathogens and elicits protective immune responses. Although immune responses can protect against pathogens, uncontrolled immune responses cause tissue damage and other pathological consequences through their inflammatory mediators.
Emerging Roles of Pseudogene RNAs in Antitumor and Antiviral Immunity
Tumor immunity and immunotherapy have become increasingly important in treatment strategies for a variety of malignancies including advanced triple negative breast cancer.
Gemcitabine in the Era of Cancer Immunotherapy
Gemcitabine is a synthetic pyrimidine nucleoside analogue which is administered intravenously as a chemotherapeutic to treat numerous cancers. Gemcitabine requires transport into cells and activation by phosphorylation, the resulting gemcitabine triphosphate is incorporated into newly synthesized DNA during cell division, inhibiting further DNA synthesis and causing cell death. Gemcitabine is used to treat cancers including those of the pancreas, lung, breast, colon, and ovary either as first or second line treatments as a single agent or in combination.
CART Cells: A New Dawn in Cancer Immunotherapy
Over the last 10 to 15 years the treatment of patients with hematologic malignancies has seen the blossom of a large number of new agents and even new treatment strategies. Monoclonal antibodies (MoAb), TKI inhibitors, checkpoint inhibitors have been introduced in the daily clinical practice and contributed significantly to the improvement of the outcome of hematologic patients. Along with the development of these new drugs, cellular therapies, namely chimeric antigen receptor-engineered T (CART) cells, have revolutionized the therapeutic paradigm of patients with B-cell lymphoid malignancies and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
OGR1-a Novel Modulator Target of Tumor Immunotherapy
Tumors mainly utilize glucose to promote aerobic glycolysis for their survival (Warburg effect). The highly glycolytic environment is not suitable for the survival and function of effector T cells, and leads to the decline of antitumor immunity.
Friend or Foe? Opposing Functions of O-GlcNAc in Regulating Inflammation
Effector CD4+ T cells (i.e. Th1, Th2, Th17) are essential in the adaptive immune system’s specific elimination of different classes of pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, and parasites, while regulatory T cells shut these inflammatory responses off once a pathogen has been cleared [1]. Interestingly, effector T cells preferentially utilize
CRISPR Taking the Front Seat in Immunotherapy
CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) technology has dramatically simplified genome editing and is widely applicable in both basic research and therapeutic areas.
M1 and M2 Macrophages Polarization via mTORC1 Influences Innate Immunity and Outcome of Ehrlichia Infection
Macrophages are innate immune cells that play a key role in regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses against infections with several pathogens as they respond to pathogens and tissue injury, serve as antigen presenting cells priming the adaptive immune response, drive inflammation and host defense as well as repairing
Macrophages in Oral Tissues
The balance between cell removal following tissue damage and new cell formation to facilitate repair has long been linked to the behaviour of inflammatory macrophages and their interactions with tissue-resident non-immune cells. The main aim of the inflammatory response is to modulate the tissue environment by removing unwanted cells and recruiting cells and soluble factors from the bloodstream to help protect the damaged tissue against infective foreign bodies.
Is Cellular Senescence of Dopaminergic Neurons the Cause of Local Inflammation in the Midbrain Observed in Parkinson’s Disease?
Current research investigating the pathomechanisms of neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system (CNS), such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), or Parkinson’s disease (PD), led to the understanding that these diseases have to be seen in the context of immune responses [1]. In other words,
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
