Loading
Journal of Cellular Immunology
ISSN: 2689-2812
Featured Articles
Glucose Metabolism is a Better Marker for Predicting Clinical Alzheimer’s Disease than Amyloid or Tau
Tyler C. Hammond, Ai-Ling Lin
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) research has long been dominated with communications regarding the amyloid hypothesis and targeting amyloid clearance through pharmacological therapies from the brain. Unfortunately, this research strategy has yielded only one new FDA-accelerated approved therapeutic for early AD, and its clinical benefit still needs to be verified. It may be time to employ a new strategy in AD therapeutics research. Hammond et al. reported that diminished uptake of glucose in the brain is a better marker for classifying AD than beta-amyloid (Aβ) or phosphorylated tau deposition.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume 4, Issue 1, p15-18 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.128
Essentials of CAR-T Therapy and Associated Microbial Challenges in Long Run Immunotherapy
Muhammad Kalim, Rui Jing, Xin Li, Zhiwu Jiang, Ningbo Zheng, Ziyu Wang, Guo Wei, Yong Lu
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy has shown potential in improving outcomes for individuals with hematological malignancies. However, achieving long-term full remission for blood cancer remains challenging due to severe life-threatening toxicities such as limited anti-tumor efficacy, antigen escape, trafficking restrictions, and limited tumor invasion. Furthermore, the interactions between CAR-T cells and their host tumor microenvironments have a significant impact on CAR-T function.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume 6, Issue 1, p25-50 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.189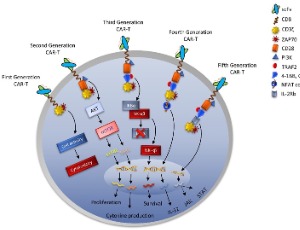
TNFAIP8: Inflammation, Immunity and Human Diseases
Suryakant Niture, John Moore, Deepak Kumar
Inflammation can be caused by various environmental factors, including microbial infection and toxic chemical exposure. In response to inflammation, immune cells like macrophages, B and T lymphocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and various stromal cells secrete soluble polypeptide cytokine Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF?)
J Cell Immunol, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p29-34 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.007
Naltrexone as a Novel Therapeutic for Diabetic Corneal Complications
Patricia J. McLaughlin, Joseph W. Sassani, Ian S. Zagon
Diabetes is a widespread autoimmune disorder that affects nearly 10% of the adult population in the United States. In addition to the primary disease, there are numerous complications associated with inflammation including abnormalities of the heart, visual system, and peripheral nervous system. More than half of the individuals with diabetes will have one or more ocular related complications such as dry eye disease (DED), keratopathy, or retinopathy.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 2, p42-46 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.018
Inulin Supplementation Mitigates Gut Dysbiosis and Brain Impairment Induced by Mild Traumatic Brain Injury during Chronic Phase
Lucille M. Yanckello, Brian Fanelli, Scott McCulloch, Xin Xing, McKenna Sun, Tyler C. Hammond, Rita Colwell, Zezong Gu, Aaron C. Ericsson, Ya-Hsuan Chang, Adam D. Bachstetter, Ai-Ling Lin
Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) has been shown to acutely alter the gut microbiome diversity and composition, known as dysbiosis, which can further exacerbate metabolic and vascular changes in the brain in both humans and rodents. However, it remains unknown how mTBI affects the gut microbiome in the chronic phase recovery (past one week post injury). It is also unknown if injury recovery can be improved by mitigating dysbiosis. The goal of the study is to fill the knowledge gap.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume 4, Issue 2, p50-64 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.132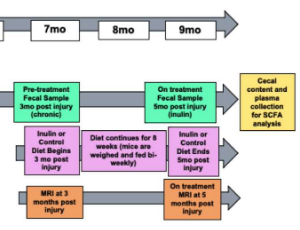
The Natural History of Post-Chikungunya Viral Arthritis Disease Activity and T-cell Immunology: A Cohort Study
Aileen Yu-hen Chang, Alfonso Sucerquia Hernández, Jose Forero-Mejía, Sarah Renee Tritsch, Evelyn Mendoza-Torres, Liliana Encinales, Andres Cadena Bonfanti, Abigale Marie Proctor, Gary Leonard Simon, Samuel Joseph Simmens, Gary Steven Firestein
Background: Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) is an alphavirus spread by mosquitos that causes arthralgias and arthritis that may last for years. The objective of this study was to describe the arthritis progression and T cell immunology over a two-year period. Methods: A cohort of 40 cases of serologically confirmed CHIKV from Magdalena and Atlántico, Colombia were followed in 2019 and again in 2021. Arthritis disease severity, disability, pain, stiffness, physical function, mobility, fatigue, anxiety, sleep disturbances and depression were assessed.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume 6, Issue 2, p64-75 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.191
Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/NFkB Axis in Ovarian Cancer
Alia Ghoneum, Ammar Yasser Abdulfattah, Neveen Said
Ovarian cancer stands as the most lethal gynecologic malignancy and remains the fifth most common gynecologic cancer. Poor prognosis and low five-year survival rate are attributed to nonspecific symptoms at early phases along with a lack of effective treatment at advanced stages. It is thus paramount, that ovarian carcinoma be viewed through several lenses in order to gain a thorough comprehension of its molecular pathogenesis, epidemiology, histological subtypes, hereditary factors, diagnostic approaches, and methods of treatment.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 2, p68-73 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.1.022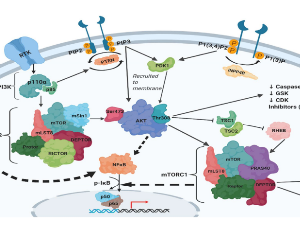
Can Molecular Biomarkers be Utilized to Determine Appropriate Adjuvant Therapy in Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)?
Prashanth Ashok Kumar, Alina Basnet, Stephen Graziano
Early-stage NSCLC, encompassing resectable stage I-III are curable, and represents 25% of all lung cancers. The management of non-metastatic NSCLC is a rapidly changing area of clinical oncology, where utilization of molecular biomarkers has become a cornerstone in informing appropriate management. In current clinical practice, adjuvant chemotherapy is recommended after surgical resection for tumors ≥ 4 cms in size (AJCC 7th stage IB, AJCC 8th stage IIA, and higher stage groups thereafter).
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume 6, Issue 2, p82-86 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.193
M1 Macrophages are More Susceptible to Necroptosis
Qin Hao, Steven Idell, Hua Tang
Macrophages play a crucial role in host innate immune defense against infection and tissue injury. Although macrophage activation and polarization has been well studied, we know less regarding the role of macrophage activation/polarization in inflammationassociated necrotic cell death. By using bone marrow-derived macrophages, we have recently demonstrated that M1 macrophages are much more susceptible than M0 and M2 subtypes of macrophages to necrotic cell death.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2, p97-102 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.084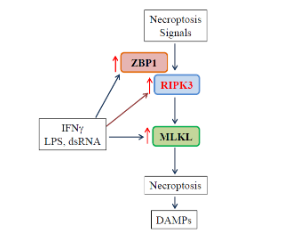
Structural Consequences of Variation in SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7
David A. Ostrov
New globally circulating SARS-CoV-2 strains are causing concern about evolution of virus transmissibility, fitness and immune evasion mechanisms. A variant emerging from the United Kingdom called SARS-CoV-2 VUI 202012/01, or B.1.1.7, is thought to exhibit increased transmissibility that results from replication 4-10 times faster than the original Wuhan virus (Wuhan-Hu-1).
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2, p103-108 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.085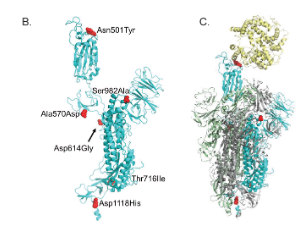
Ca2 /calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinases in Leukemia Development
Changhao Cui, Chen Wang, Min Cao, Xunlei Kang
Ca2+/ calmodulin (CaM) signaling is important for a wide range of cellular functions. It is not surprised the role of this signaling has been recognized in tumor progressions, such as proliferation, invasion, and migration. However, its role in leukemia has not been well appreciated. The multifunctional Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinases (CaMKs) are critical intermediates of this signaling and play key roles in cancer development.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 3, p144-150 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.091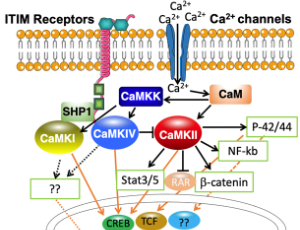
Cytoreductive Nephrectomy Following Immunotherapy: Evolution, Pearls, and Pitfalls of Treatment
Laura E. Davis, Adam Calaway, Eric A. Singer, Shawn Dason
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) is among the most frequently diagnosed malignancies in both genders with over 81,000 estimated cases in 2024. Despite increasing incidence of renal cell carcinomas <4 cm, up to 1/3 of patients diagnosed with RCC exhibit metastatic disease (mRCC) at time of diagnosis. Cytoreductive nephrectomy (CN), a procedure which encompasses the surgical removal of the primary tumor in patients with metastatic disease
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume 6, Issue 4, p163-170 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.202
The Issue of Monocyte Activation in ASD: Troubles with Translation
P Ashwood, R.J. Moreno
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) prevalence has increased year on year for the past two decades and currently affects 1 in 44 individuals in the US. An increasing number of studies have pointed to increased immune activation as both an etiological agent and also involved in the ongoing pathological process of ASD. Both adaptive and innate immune responses have been implicated. Evidence of innate dysregulation has so far included increased production of innate inflammatory cytokines, increased cell numbers, and altered activation in monocytes in the blood and microglia in the brain.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume 4, Issue 5, p167-170 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.146
Going above and Beyond: Using an Attenuated Herpes Viral Vaccine Vector to Elicit Protective Immune Responses Through Neutralizing and Non-neutralizing Functions of Antibodies
Katherine E. Kaugars, Angelo R. Retamal-Diaz, Anna Paula de Oliveira, Pablo A. Gonzalez, William R. Jacobs Jr.
The COVID-19 pandemic has made the development of novel vaccines a high priority for public health. While many vaccines have focused on the generation of neutralizing antibodies, we have discovered a novel herpes simplex virus (HSV) vaccine candidate, designated ΔgD-2, that can preferentially elicit non-neutralizing antibodies that function through Fcγ receptor (FcγR) activation
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume 4, Issue 5, p185-193 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.149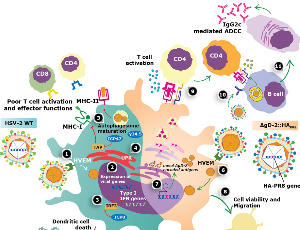
Polyamines: Key Players in Immunometabolism and Immune Regulation
Shanmuga S. Mahalingam, Pushpa Pandiyan
Polyamines are small organic molecules ubiquitously present in all living organisms and function as crucial regulators of biological processes ranging from fundamental cellular metabolism to immune regulation. Dysregulation of polyamine metabolism has been implicated in numerous diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders, inflammatory conditions, autoimmune diseases, and cancer. This review provides an overview of pathophysiology of these conditions, highlighting polyamines’ role in immunometabolic alterations in the context of immune regulation.
J Cell Immunol, 2024, Volume 6, Issue 5, p196-208 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.6.206
The Importance of miRNA Identification During Respiratory Viral Infections
Ivan Martinez-Espinoza, Ma Del Rocio Banos-Lara, Antonieta Guerrero-Plata
The expression of small non-coding RNA MicroRNAs (miRNAs) during respiratory viral infections is of critical importance as they are implicated in the viral replication, immune responses and severity of disease pathogenesis. Respiratory viral infections have an extensive impact on human health across the globe. For that is essential to understand the factors that regulate the host response against infections.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 4, p207-214 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.101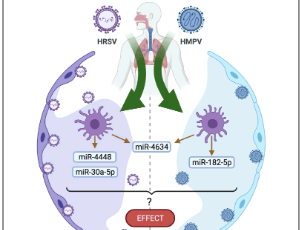
Preliminary Evidence of Differentially Induced Immune Responses by Microparticle-adsorbed LPS in Patients with Crohn’s Disease
P Ashwood
Inorganic microparticles are ubiquitous in the modern Western diet present as food additives and are actively scavenged by microfold (M) cells overlying human intestinal lymphoid aggregates. In Crohn’s disease (CD), inflammation is caused by the inability of the intestinal mucosa to sustain tolerance to gut luminal factors including bacteria and their by-products.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume 4, Issue 6, p211-218 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.152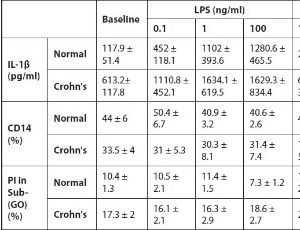
Hypomagnesemia and Outcomes in Hematologic Malignancies
Jennifer Gile, Joy Heimgartner, Gordon Ruan, M. Molly McMahon, Thomas Witzig
Magnesium, the fourth most abundant mineral in the human body, has several critically important functions in the body including cell growth, energy production and function of the immune system. There is an increasing interest in the role of magnesium in the pathology of different diseases including diabetes, cardiovascular disease and malignancies.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 5, p245-249 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.050
Exploring and Targeting the Tumor Immune Microenvironment of Neuroblastoma
Katherine E. Masih, Jun S. Wei, David Milewski, Javed Khan
Neuroblastoma is derived from the developing sympathetic nervous system and is the most common extracranial solid tumor of childhood.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 5, p305-316 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.111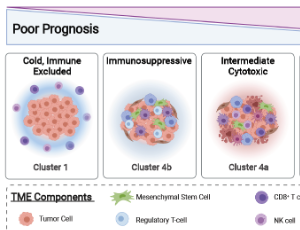
Potentials of Interferons and Hydroxychloroquine for the Prophylaxis and Early Treatment of COVID-19
Alexander Yang, Lakshmi S. Guduguntla, Bing Yang
The symptoms of the COVID-19 range from asymptomatic or mild disease to severe disease that results in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and eventually death. Understanding the molecular mechanisms responsible for the progression from mild to severe disease is the key to decreasing the mortality of COVID-19. Compared to mild cases, severe cases of the COVID-19 have decreased interferon (IFN) a, ß, λ production. Type I (IFN a/ß) and III IFNs (λ) work coordinately to induce inhibition of viral reproduction through the stimulation of interferon stimulated genes (ISGs).
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 6, p333-340 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.063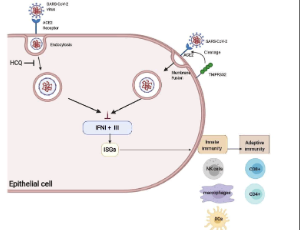
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
