Loading
Journal of Cellular Immunology
ISSN: 2689-2812
2020
Volume 2, Issue 4, p143-200
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
CRISPR Taking the Front Seat in Immunotherapy
Saad S. Kenderian, Andrew D. Badley
CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) technology has dramatically simplified genome editing and is widely applicable in both basic research and therapeutic areas.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 4, p143-148 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.032
Lung-targeted SERCA2a Gene Therapy: From Discovery to Therapeutic Application in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis
Malik Bisserier, Lahouaria Hadri
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic, progressive, devastating, and rare lung disease. IPF is characterized by usual interstitial pneumonia and represents the most common idiopathic interstitial lung disease.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 4, p149-156 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.033
TNF-alpha Inhibitors and Neutropenia: Current State of Art
Emmanuel Andrès, Noel Lorenzo Villalba, Abrar-Ahmad Zulfiqar, Yasmine Maouche, Khalid Serraj, Jacques-Eric Gottenberg
Drug-induced severe neutropenia, defined as an absolute neutrophil count (NC) ≤ 0.5 x 109/L or a complete lack of neutrophils in circulating blood, is a potentially severe complication that has been related to most classes of drugs. For the majority of drugs, the risk is likely to be very small.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 4, p157-164 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.034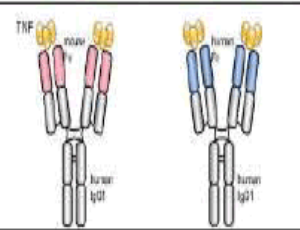
Autoantibodies in Overlapping Systemic Sclerosis and Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Autoimmune Diseases
Manuel M. Valdivia
Anticentromere antibodies (ACA) are considered an important diagnostic marker of scleroderma or systemic sclerosis (SSc), being CENP-B the major centromere auto-antigen recognized by sera from SSc patients. However, ACA can also be detected in patients with other connective tissue diseases.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 4, p165-167 | DOI: 10.33696//immunology.2.035
Sex Differences in Clinical Characteristics and Platelet Activation in Respiratory Syncytial Virus Bronchiolitis
Isabella Tarissi De Jacobis, Rosa Vona, Elisabetta Straface, Lucrezia Gambardella, Giulia Ceglie, Francesca de Gennaro, Ilenia Pontini, Anna Chiara Vittucci, Alessandra Carè, Camilla Cittadini, Alberto Villani, Donatella Pietraforte
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the most common cause of bronchiolitis. It is a single-stranded RNA virus of the Paramyxoviridae family that is transmitted through nasopharyngeal or conjunctival mucosa from infected individuals. The incubation period ranges from 2 to 8 days.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 4, p168-170 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.036
The status of Regulatory Cells/Molecules in Psoriatic Skin
Vadasz Zahava
In normal non-inflamed skin, the balance between the expression of pro-inflammatory cells/cytokines and regulatory/protective functions are extremely important for the maintenance of healthy skin. Normal skin T cells (mostly Th1 memory effector cells) have a remarkably diverse TCR repertoire and express high levels of CCR4, CCR6 and CCR8.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 4, p171-174 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.037
Are Cysteine-lipases Involved in the Immune System?
Qi Wu, Manfred T. Reetz
Lipases, esterases and proteases constitute superfamilies of hydrolases not only play an important role in the immune system, but also as catalysts in biotechnology and organic chemistry. Mechanistically, they all involve a similar catalytic triad.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 4, p175-177 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.038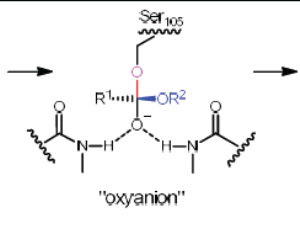
Allicin as an Adjunct Immunotherapy against Tuberculosis
Samreen Fatima, Ved Prakash Dwivedi
Allicin (diallylthiosulfinate) is a volatile, oxygenated, sulphur-containing compound, extracted from garlic (Allium sativum). It is responsible for the characteristic odor of garlic. Allicin is known to exert its effects as an antipathogenic agent mainly by targeting the thiol-containing proteins or enzymes in different microorganisms and also by regulating the key genes responsible for the virulence of the microorganism.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 4, p178-182 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.039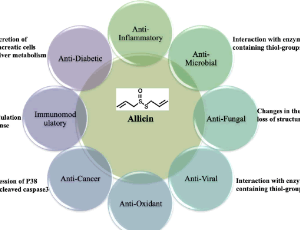
Cytokines (IL-1 β, IL-6, IL-18, TNF-α) in Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid in Neonatal Hypoxia/Ischemia)
Darinka Šumanovi?-Glamuzina, Marjana Jerkovi?-Raguž
Perinatal brain injury is an important clinical and socioeconomic entity. It is a syndrome of impaired brain function in the early days of life, and it is a consequence of inadequate brain oxygenation before, during or shortly after birth, with high mortality rates and early and late morbidity rates.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 4, p183-187 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.040
The Considerable Conundrum of NSAID-induced Melt
Basil Rigas, Wei Huang, Robert A. Honkanen
Over 20 years after the first description of NSAIDinduced Corneal Melt (NICM), a rare but potentially devastating visual complication induced by a topically applied medication, the optimal prevention and treatment for this condition remain unknown creating a clinical conundrum for eye care professionals and challenge for eye researchers.
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 4, p188-191 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.041
Current Advances in CAR T Cell Therapy for Malignant Mesothelioma
Astero Klampatsa, Steven M. Albelda
Malignant mesothelioma (MM) is an incurable primary tumor of the body’s serosal surfaces: the pleura, peritoneum, pericardium and the tunica vaginalis (in men).
J Cell Immunol, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 4, p192-200 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.2.042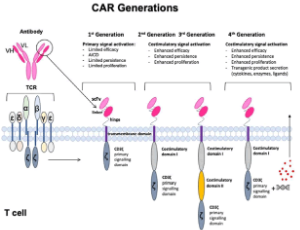
Recommended Articles
Multidirectional Benefits of Nanotechnology in the Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Tuberculosis
Despite the curious advancement in medical science and therapeutics, tuberculosis (TB) persist the primary factor of mortality than any other infectious disease and socioeconomic disaster for millions of people around the world. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), World’s One-third of the population is infected with this disease and of these, 8 to 10 million people develop active disease and 2 million people die each year and the rest of the infected people remain asymptomatic.
Commentary on “Epigenetically Altered T Cells Contribute to Lupus Flares”
The recently published manuscript entitled “Epigenetically Altered T Cells Contribute to Lupus Flares” summarizes recent advances in our understanding of how the environment alters the immune system to cause flares of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in genetically predisposed people, and why it affects women approximately 9 times more often than men
Humanized Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T cells
In 1989, researchers proposed an intricate strategy in the field of adoptive cell therapy (ACT). Using the T-cell receptor (TCR) as a template, they replaced the coding sequence for the Vα and Vβ chains with the antigen- recognition domains from an antibody (VH and VL chains).
CART Cells: A New Dawn in Cancer Immunotherapy
Over the last 10 to 15 years the treatment of patients with hematologic malignancies has seen the blossom of a large number of new agents and even new treatment strategies. Monoclonal antibodies (MoAb), TKI inhibitors, checkpoint inhibitors have been introduced in the daily clinical practice and contributed significantly to the improvement of the outcome of hematologic patients. Along with the development of these new drugs, cellular therapies, namely chimeric antigen receptor-engineered T (CART) cells, have revolutionized the therapeutic paradigm of patients with B-cell lymphoid malignancies and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Are Cysteine-lipases Involved in the Immune System?
Lipases, esterases and proteases constitute superfamilies of hydrolases not only play an important role in the immune system, but also as catalysts in biotechnology and organic chemistry. Mechanistically, they all involve a similar catalytic triad.
Allicin as an Adjunct Immunotherapy against Tuberculosis
Allicin (diallylthiosulfinate) is a volatile, oxygenated, sulphur-containing compound, extracted from garlic (Allium sativum). It is responsible for the characteristic odor of garlic. Allicin is known to exert its effects as an antipathogenic agent mainly by targeting the thiol-containing proteins or enzymes in different microorganisms and also by regulating the key genes responsible for the virulence of the microorganism.
Cytokines (IL-1 β, IL-6, IL-18, TNF-α) in Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid in Neonatal Hypoxia/Ischemia)
Perinatal brain injury is an important clinical and socioeconomic entity. It is a syndrome of impaired brain function in the early days of life, and it is a consequence of inadequate brain oxygenation before, during or shortly after birth, with high mortality rates and early and late morbidity rates.
Repurposed Anti-IL-6 Therapeutics, Another Way to Quell the Cytokine Storm in Tuberculosis
Study on ‘‘cytokine storms’’ has been braced up in infectious diseases. The pertinence of this research begins to be evident in tuberculosis as it was observed that increased levels of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) were connected with disease severity. The IL-6 blockers therapeutics approaches for tuberculosis are currently a key line of research, with many in progress clinical trials, as IL-6 has become an important factor of the immune response to tuberculosis.
Vγ2+ γδ T Cells and Their Regulatory Potential in Skin Allograft Survival
Our recently published research article “Vγ2+ γδ T cells in the presence of anti-CD40L control surgical inflammation and promote skin allograft survival” revealed that the Vγ2+ subset of γδ T cells, which otherwise are known primarily for its proinflammatory function, regulate the survival of skin allografts in the presence of anti-CD40L.
Role of Regulatory T cells in Prognosis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Kidney Transplant Recipients
The major issue in kidney transplantation remains the suppression of allograft rejection. Immunosuppressant decrease both donor-specific responsiveness and the risk of rejection in the months after transplantation and are maintained. The current immunosuppressant medications, although potent against short-time graft complications including acute renal rejection but are still less effective to ensure long-term graft survival.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
