Loading
Journal of Experimental Neurology
ISSN: 2692-2819
2023
Volume 4, Issue 2, p43-86
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Generation of Human Oligodendrocyte Progenitors for Treatment of Demyelinating Diseases and Spinal Cord Injury
Thomas Hazel, Michael Hefferan, Kateryna Schwartz, Ningpu Yu, Karl Johe, Michael Levy
Glial cells play a critical role in the development and function of the mammalian central nervous system (CNS). Among other roles, these cells provide the myelin sheath needed for the efficient propagation of impulses along nerve fibers, provide trophic support for neuronal cells, and remove toxins and excess neurotransmitters from the interstitial space. Transplantation of glial cells or glial progenitors into the diseased or injured CNS can provide therapeutic benefits.
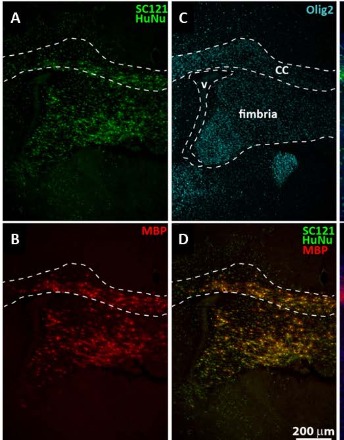
J Exp Neurol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p43-54 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.4.072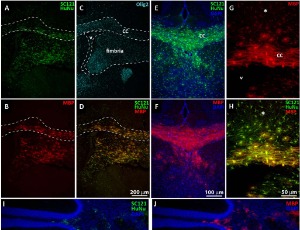
Daily Activity Restriction Quantification in Older Population via Using Activity Frequency: Dual Roles in Preventing Falls
Xia Shen, Lin Yu Chen, Jing Xin Wang, Yan Na Jiang
Daily activity restriction is an expected physical behavior aiming to prevent falls in the older population. However, it plays dual roles in preventing falls, both positive and harmful. Therefore, the degree of daily activity restriction is proposed as a critical factor influencing the weight ratio of the positive and negative roles and finally determining the efficacy of fall prevention. Thus, quantification of daily activity restriction is essential to learn its efficacy.
J Exp Neurol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p55-57 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.4.073
Late Decrease in Cerebral Blood Flow in Bacterial Meningitis: More than a Simple Normalization of Acute Inflammatory Vessel Wall Architecture?
Vivig Shantha Kumar, Vignarth Shantha Kumar
Acute bacterial meningitis is a disease with an overwhelmingly high mortality rate and high incidence of adverse neurological sequelae and poor neurological recovery amongst survivors. Amongst the numerous complications of bacterial meningitis, the presence of cerebrovascular disease represents a severe disease form. Vascular involvement during bacterial meningitis has long been established by numerous pathological and angiographic studies.
J Exp Neurol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p58-75 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.4.074
Glypican-2 as the Regeneration-Associated Gene (RAG)
Kazuma Sakamoto, Yuji Suzuki, Kenji Kadomatsu
We recently reported that glypican-2, a neuronal cell surface glycoprotein, is involved in age-dependent differences in axonal regenerative capacity in the mammalian central nervous systems (CNS). While several extrinsic inhibitory factors expressed or deposited in the lesion after trauma hinder axonal regeneration, our understanding of intrinsic factors expressed in neurons that regulate axonal regeneration is still limited.
J Exp Neurol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p84-86 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.4.076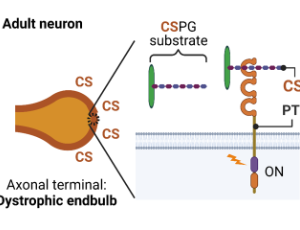
Recommended Articles
Influence of Clinical Risk Factors on Outcomes in Men with Stage I Non-Seminomatous Germ Cell Tumor Undergoing Robot-Assisted Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection
Retroperitoneal lymph nodes are often the first landing site of metastatic disease in men with testicular cancer. Primary retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) for clinical stage I NSGCT can accurately surgically stage patients who may have nodal micrometastases, and in some cases, can serve as the primary therapy when volume of metastasis is low.
Gastric Cancer: A Brief Review, from Risk Factors to Treatment
Gastric cancer (GC), also known as stomach cancer, is a worldwide health problem. Anatomically, it can occur from the gastroesophageal junction to distal portions of the stomach. Considering both sexes, worldwide, it is the 5th most common neoplasm (5.7%) and the 3rd cause of mortality among malignancies, leading to approximately 782,000 deaths in 2018. The incidence varies geographically but 50% of new cases are diagnosed in developed countries. High incidence is observed in Asia, Latin America, and in the central and eastern parts of Europe. There are several ways to classify GC, but the most used is Lauren’s Classification, which proposes two main histological groups: intestinal and diffuse. This classification is important because there are marked etiological, pathological, and epidemiological differences between the subgroups, guiding the clinical approach for each patient.
Cardiac Stem Cell Therapy, Quo Vadis
Cardiovascular disease causes 30% of global mortality and is still the number one cause of death worldwide. A main patho-physiological process is the coronary disease leading to malperfusion and ischemic cardiac disease as well as cardiac infarction.
Long-Term Use of Oral Bisphosphonates and Fracture Risk in Men with Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury
Lower extremity fractures in individuals with a spinal cord injury (SCI) cause significant morbidity [1] and contribute to excess mortality [2]. Early identification of persons at highest risk for fracture is possible using bone mineral density (BMD) testing by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) imaging
Risks and Countermeasures for the Musculoskeletal systems in the Extreme Environment of Aviators and Astronauts
Resistive Exercise in Astronauts on Prolonged Spaceflights provides partial Protection against Spaceflight-induced Bone Loss showed very promising data on measures that can be employed to preserve the bone and muscular health of astronauts. The value of the information from these measures of bone and muscular health is how the
Are We Close to Achieving a HBV Cure? Risk for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Persists Despite Long-term HBV Suppression: An Update on Our Experience
Since the discovery of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) by Blumberg et al., great progress has been made in understanding the pathogenesis of the virus and its role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). It is estimated that hepatitis B is responsible for about 50% of the HCC cases worldwide. Because of geographic variations in HBV incidence, the burden of HBV-related HCC (HBV-HCC) is highest in endemic areas such as Asian-Pacific and sub- Saharan Africa and lowest in the United States and the West. The hepatitis B vaccines, developed in the 1980s, transformed the evolution of hepatitis B in the modern era. This was followed by high effective anti-viral that reduced HBV infections and HBV-HCC.
Obesity, Family History of Diabetes, and Consanguineous Marriages are Risk Factors among Urban Population in South Indian City of Bengaluru
In 2017, approximately 424.9 million adults (age 20- 79 yrs) were affected by diabetes, with 4 million deaths. Global diabetes burden is estimated to increase up to 628.9 million people. Moreover, diabetes care costed approximately $727 billion in 2017.
Commentary on Association between Birth Weight and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: Evidence from UK Biobank
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is one of the major causes of death worldwide and poses a huge public health burden [1,2]. Early identification of individuals at risk of cardiovascular disease is crucial to develop effective preventions. The DOHAD hypothesis proposed by Professor Barker et al. states that an abnormal environment
Pregnancy and Hepatitis B Immunization: A Commentary on Maternal Knowledge and Vertical Transmission Risks
The paper Maternal knowledge of the risk of vertical transmission and offspring acquisition of hepatitis B, recently published in Annals of Hepatology, provides unique insight on a topic not previously studied in the USA. The research paper discusses important topics on maternal hepatitis B infections.
Can Vitamin D Supplementation Reduce Insulin Resistance and Hence the Risks of Type 2 Diabetes?
The question of whether or not correction of vitamin D deficiency might reduce the risks of later type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has been under debate for many decades. The necessity of vitamin D for normal insulin secretion was first identified experimentally in the 1980s.
A Review on Nanotechnology: Applications in Food Industry, Future Opportunities, Challenges and Potential Risks
Nanotechnology is an evolving revolution with enormous promise in a variety of fields, including mechanics, medicine, and the food business. Nanoparticles owing to having greater surface area and enhanced rates of mass transfer seem to pose higher biological and chemical activities, penetrability, catalytic behaviour, enzymatic reactivity, and quantum
Identification of Risk Markers for Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study with Focus on Quality Assurance Based on Real World Data
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a metabolic disease defined by hyperglycemia. If not treated, chronic and even short periods (i.e. weeks) of undesirable hyperglycemia increases the risk for developing diabetic microvascular complications such as retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy, foot ulcers and amputations, and macrovascular complications such as cardiovascular disease including stroke
Risks and Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy in Children and Young People with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is associated with microvascular and macrovascular complications.Duration of diabetes, poor glycaemic control, high blood pressure and proteinuria are reported risk factors contributing to the development of diabetes related complications.
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Mammary Cancer Risk: Does Obesity Matter too?
Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in women in the United States. Breast cancer incidence rates, particularly among younger women, have been increasing since the 1930s, and are only partially explained by changes in parity, age at first birth, and improved screening and detection. Many questions remain unanswered regarding the mechanisms that underlie current risk.
The Association of PRKRAP1 Pseudogene with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Risk
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the deterioration of the maturation period of lymphoblasts, and the uncontrolled excessive reproduction of the abnormal cells. In addition to gene rearrangements, chromosome number abormalities (Down syndrome, etc.), and genetic locations, being male, Caucasian ethnicity, having a sibling diagnosed with leukemia, exposure to radiation, having received chemotherapy or radiotherapy, and exposure to some toxins and chemical substances such as benzene may be counted as the ALL risk factors.
A Review of Testing Strategies for Bacterial Risk Control in Platelets Recommended by the FDA
Platelet transfusion is associated with the risk of sepsis from bacterial contamination due to the need to store units at room temperature in oxygen-permeable bags. This risk associated with platelet transfusion is highest among all transfusable blood components. Measures applied in the past several decades have significantly reduced the occurrence of patient morbidity and mortality but have not eliminated it totally. Sampling of processed platelets for bacterial culture after 24 hours post-collection lowered the rate of infection but still allowed contaminated transfusions to occur due to low levels of bacteria being missed during sampling. Bacteria entering log phase growth after 24 hours may not be detected.
Neuroprotective Effects of Khaya Anthotheca (Welw.) C.DC (Meliaceae) Decoction on Neurodegeneration Induced by Estrogen Depletion in Rats
The cortex, hippocampus, and amygdala are among the brain regions where estrogens may act to improve cognition, memory and mood. In these regions, estrogens have many beneficial effects, including neuroprotection, neurogenesis, as well as neurotrophic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects [1-2].
Prevalence of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Osteoarthritis Patients Derived from Primary Care Records: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies
Health intelligence on the frequency of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and its risk factors identifies targets and populations for preventative strategies and allows evaluation of health outcomes, behaviors and interventions in populations and health care settings.
Review of the COVID-19 Risk in Multiple Sclerosis
Severe respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARSCoV- 2) is the virus responsible for the novel coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) and has resulted in the death of over one million people around the world. COVID- 19’s presentation is highly heterogeneous as cases range from asymptomatic to rapidly progressive resulting in low survival rates.
A Machine Learning Study of 534,023 Medicare Beneficiaries with COVID-19: Implications for Personalized Risk Prediction for People Over 65
The global outbreak of COVID-19 has resulted in over 378 million infections and worldwide deaths have surpassed 5.6 million. In the United States, there have been over 75 million confirmed cases and over 886,000 deaths as of February 1, 2022.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
