Loading
Archives of Gastroenterology Research
ISSN: 2692-5427

Francesco Giuseppe Foschi
Faenza Hospital, Ausl Romagna, Italy
Featured Article
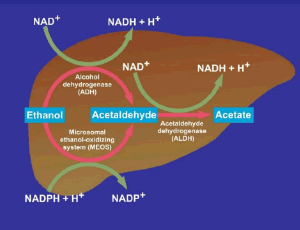
Alcoholic Liver Disease and the co-triggering Role of MEOS with Its CYP 2E1 Catalytic Cycle and ROS
Featured Article
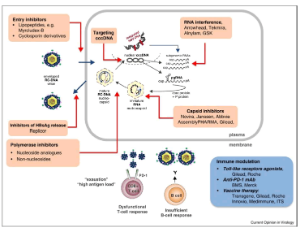
Are We Close to Achieving a HBV Cure? Risk for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Persists Despite Long-term HBV Suppression: An Update on Our Experience
Featured Article
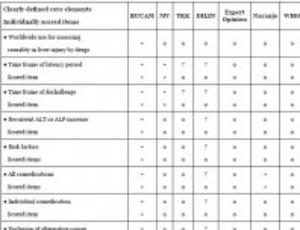
DILI, HILI, RUCAM Algorithm, and AI, the Artificial Intelligence: Provocative issues, Progress, and Proposals
About this Journal
Archives of Gastroenterology Research is a peer reviewed online journal devoted to publish articles related to gastrointestinal diseases. Archives of Gastroenterology Research is fully dedicated to deliver significant facts and findings related to clinical gastroenterology, and other relevant fields such as hepatology
Articles
Gastrointestinal Reflux Related Aspiration (GRASP) and Airway Injury after Lung Transplantation: Insights into Pathophysiology and Role of Airway Biomarkers for Risk Stratification
Lung transplantation remains the only long term treatment for end-stage pulmonary disease. The main limitation to allograft survival beyond the first year post transplant is development of chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD). Among survivors, CLAD will develop in virtually all recipients and often will show signs of airway injury before any clinical manifestations appear. There is currently no specific treatment available and management depends largely on modification of risk factors. Recent efforts by our group and others have focused on understanding the underlying pathophysiology and development of clinical biomarkers to diagnose CLAD early and allow risk stratification before irreversible allograft injury.
Disease Resolution after Cessation of Treatment in Patients with Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic inflammatory condition of the esophagus. EoE is triggered in most patients by dietary allergens and mediated by type 2 immune responses. Over the past 3 decades, substantial progresses have been made in understanding EoE pathogenesis, management, and natural history. EoE affects children and adults, and the incidence and prevalence have increased over time. Untreated EoE can lead to severe complications including food impaction, small caliber esophagus, esophageal stricture, and esophageal perforation.
Food Protein-Induced Allergic Proctocolitis (FPIAP): New Insights into Pathogenesis and Implications
Food protein induced allergic proctocolitis (FPIAP) is one of the earliest presentations of food allergies in infancy. It is a non-immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated condition. Although the inflammation is located at the rectosigmoid colon, clinical symptoms are not limited to mucousy, bloody stools and often include gastroesophageal reflux (GER), feeding difficulties, irritability and poor sleep.
Abdominal Migraine in Children and Adolescents at a Single Tertiary Pediatric Gastroenterology Center: A Twelve-yea Experience on Clinical and Therapeutic Findings
Observational, retrospective cohort single-center study in consecutive cases of children and adolescents, referred for initial evaluation of chronic abdominal pain at the Pediatric Gastroenterology Outpatient Clinic. Inclusion criteria: Age between 4 and 17 years; Diagnosis of AM defined from structured questionnaires according to three consensus criteria (Rome III, Rome IV criteria, and The International Classification of Headache Disorders).
norUDCA, a Novel Therapeutic Approach to the Disposal of A1- antitrypsin Mutant Z Proteins
α1-antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) is a well-known genetic disease. No effective medical therapy is currently available for the liver disease. 24-norursodeoxycholic acid (norUDCA) has shown potent anti-cholestatic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic properties in experimental and human cholestatic liver diseases. In this minireview, we discuss the role of exogenous norUDCA in reducing accumulation of a1-antitrypsin mutant Z proteins (AATZ) in the livers of PiZ mice and the in vitro model, HTOZ cells.
A Case Series of Rapid Resolution of Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis with Dupilumab Treatment as Demonstrated by Sedation-Free Transnasal Esophagoscopy (TN-Eso)
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the esophagus. Dupilumab, a treatment for EoE, requires an initial endoscopic evaluation no sooner than 12 weeks after initiation. As it is costly and pediatric patients often experience fear and pain associated with the injection, this could lead to non-adherence or premature cessation of therapy. Here, we report a case series, as part of a larger ongoing study, in which subjects demonstrated an earlier response to dupilumab.
Cholestatic Pruritus: Current Management Approach and Emerging Therapies – Mini Review
Cholestatic Pruritus is a phenomenon that occurs in disease processes that impair bile flow. This condition poses significant challenges to quality of life and is often underdiagnosed and undertreated. While the direct cause of cholestatic pruritus remains unclear, it likely involves a complex interplay between multiple biochemical pathways. Due to recent advances in diagnostic tools, more biochemical pathways of cholestatic pruritis have been discovered.
Multifaceted Strategies for Managing Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Study of Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Interventions
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a chronic condition characterized by the retrograde flow of gastric contents into the esophagus, leading to symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and potential esophageal injury. The pathophysiology of GERD primarily involves dysfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), impaired esophageal clearance, delayed gastric emptying, and transient LES relaxations. Additional contributing factors include hiatal hernia and obesity. The pharmacological management of GERD focuses on acid suppression and includes the use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), H2-receptor antagonists, antacids, and prokinetic agents.
Upregulation of Downstream Angiogenic Genes Using mRNA for the Transfection of Transcription Factor Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1 Alpha: A Short Communication
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α) plays a critical role in regulating cellular responses to low oxygen levels. In our study, we transfected HIF-1α mRNA into human dermal fibroblasts and assessed its biological activity by measuring the upregulation of downstream angiogenic genes, aiming to investigate the delivery mechanism of HIF-1α mRNA and its functional impact. In this short communication, we will describe our transfection methodology, present the results we obtained, and discuss the potential implications of these findings for future therapeutic applications.
A Dual Mechanism Hypothesis for Celiac Disease: Intraluminal Pressure-Induced Villous Compression and Nitrate-Driven Motility Impairment
Celiac disease (CD) is an immune-mediated enteropathy triggered by gluten ingestion in genetically predisposed individuals, resulting in villous atrophy, crypt hyperplasia, and mucosal inflammation. While immunologic mechanisms are well characterized, the role of mechanical and biochemical factors in disease onset remains underexplored.
Endoscopic Palliation Therapy with Esophageal SEMS in a Case of Malignant Esophageal Stricture with Trachea-Esophageal Fistula
Esophageal cancer, a highly aggressive malignancy, frequently presents with advanced-stage dysphagia, significantly impacting patient quality of life. While surgical resection offers the best chance for cure in early stages, many patients are diagnosed with unresectable or metastatic disease, necessitating palliative interventions to alleviate symptoms.
Food Protein-induced Allergic Proctocolitis with Breastfeeding or Formula Feeding at Symptoms Onset—A Ten-Year Experience at a Single Tertiary Center
Aim: This study evaluates the sociodemographic, clinical, and anthropometric data of infants diagnosed with Food Protein-Induced Allergic Proctocolitis (FPIAP), categorized as exclusively breastfeeding or formula feeding at the onset of symptoms. This division allows us to compare the effects of different feeding on the development of FPIAP. Methods: This retrospective, observational, single-center study included infants ≤36 months diagnosed with FPIAP. Exclusion criteria were chronic morbidities to ensure a focused study population.
Liver Transplantation in an Adolescent Patient Post Extended Right Hepatectomy for Undifferentiated Sarcoma
Undifferentiated embryonal sarcoma of the liver (UESL) is an uncommon malignant neoplasm in the pediatric population, accounting for a small fraction of primary hepatic tumors but associated with an aggressive clinical course and poor prognosis. Surgical resection remains the mainstay of treatment; however, extended hepatectomy can leave patients with limited functional reserve and predispose them to hepatic failure, making liver transplantation (LT) a therapeutic alternative in selected cases.
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernias: An Update on Management Strategies and Outcomes
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) is a developmental defect of the diaphragm, occurring in approximately 1 in 3,000 live births with a high mortality rate of between 30 and 50%. This narrative review provides an update on antenatal and postnatal management strategies and current outcomes emphasizing where further research is required. Fetal endotracheal obstruction (FETO) has been demonstrated in a large RCT to improve survival in the most severe CDH and is now adopted into clinical practice.
Females with Autoimmune Liver Diseases are at Increased Risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Nationwide Matched Cohort Study
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains a leading cause of death in women. Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease score does not encompass inflammatory diseases, which is associated with increased CVD risk. This score may underestimate risk in women with autoimmune liver diseases (AILD) such as autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). We investigated if women with AILD had increased CVD risk compared to female and male controls.
Treatment and Drug Resistance to Helicobacter Pylori: A Brief Review
Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative, spiral-shaped bacterium that inhabits the gastric environment of 60.3% of the global population. Though most individuals infected with the bacterium remain asymptomatic, it is known that this infection plays a pivotal role in the development of diseases such as chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer, gastric cancer and gastric MALT lymphoma. Hence, eradication of H. pylori is associated with the potential prevention of many gastric and extra gastric diseases, such as gastric cancer.
Alcoholic Liver Disease and the co-triggering Role of MEOS with Its CYP 2E1 Catalytic Cycle and ROS
Until the early sixties, the concept prevailed that alcoholic liver disease (ALD), also termed alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), results from malnutrition commonly observed among individuals consuming chronically high amounts of alcohol rather than being causally related to the use of alcoholic beverages. However, the malnutrition concept became a matter of debate because of the clinical observation that humans, even on a normal diet and without signs of underweight or malnutrition
Conversion Surgery for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Lenvatinb
Multidisciplinary treatment is widely applied for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Systemic therapy is recommended and can provide a modest prognosis for HCC in Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging C. Lenvatinib is a newly developed multityrosine kinase inhibitor and has become a more preferred targeted drug than sorafenib to achieve conversion surgery due to its higher tumor necrosis effect.
Are We Close to Achieving a HBV Cure? Risk for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Persists Despite Long-term HBV Suppression: An Update on Our Experience
Since the discovery of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) by Blumberg et al., great progress has been made in understanding the pathogenesis of the virus and its role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). It is estimated that hepatitis B is responsible for about 50% of the HCC cases worldwide. Because of geographic variations in HBV incidence, the burden of HBV-related HCC (HBV-HCC) is highest in endemic areas such as Asian-Pacific and sub- Saharan Africa and lowest in the United States and the West.
The Dual Role of Macrophages during Hepatitis B Infection
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) chronically infects more than 250 million individuals worldwide and is responsible for more than 800,000 deaths per year by promoting end-stage liver diseases, among which decompensated cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (WHO, July 2020) are prominent. Studies performed in chimpanzees or in animalversion of HBV (woodchuck HBV: WHBV) highlighted the lack of immune responses against the virus upon primary infection.
Gastric Cancer: A Brief Review, from Risk Factors to Treatment
Gastric cancer (GC), also known as stomach cancer, is a worldwide health problem. Anatomically, it can occur from the gastroesophageal junction to distal portions of the stomach. Considering both sexes, worldwide, it is the 5th most common neoplasm (5.7%) and the 3rd cause of mortality among malignancies, leading to approximately 782,000 deaths in 2018. The incidence varies geographically but 50% of new cases are diagnosed in developed countries. High incidence is observed in Asia, Latin America, and in the central and eastern parts of Europe. There are several ways to classify GC, but the most used is Lauren’s Classification, which proposes two main histological groups: intestinal and diffuse. This classification is important because there are marked etiological, pathological, and epidemiological differences between the subgroups, guiding the clinical approach for each patient.
Preclinical Promise and Clinical Challenges for Innovative Therapies Targeting Liver Fibrogenesis
Liver fibrosis resulting from chronic liver injury can progress to cirrhosis and liver failure. Current treatments are limited, creating an urgent need for novel antifibrotic therapies. Multiple emerging approaches have shown preclinical promise in inhibiting liver fibrogenesis or stimulating regeneration, including artificial liver support, stem cell therapy, cell/gene therapy, nanomedicines, immunotherapy, and herbal medicines.
Elucidating the Role of Chemokines in Infectious Diseases and Gastric Cancer
Although the prevalence of gastric cancer is decreasing in many developed nations, it is the fourth most prevalent cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally. Around 8 percent of recently diagnosed malignant tumors are stomach cancer, more than 7,00,000 individuals die from gastric cancer yearly. Despite extensive research into new diagnostic and therapeutic methods, the prognosis for individuals with advanced stomach cancer remains dismal, and survival rates have hardly improved. In recent years, many latest innovations have improved our understanding of the molecular mechanisms and modifications that contribute to gastric cancer’s beginning and progression, including several genetic and molecular modifications and mutations.
New Trends in Interrelation of Infectious Colorectal Cancer with Intestinal Microbiota
The intestinal microbiota creates a bodily barrier for invading pathogen by using aggressive exclusion. Pathogens and immune cells can interact directly and dynamically with symbiotic bacteria, determining the pathophysiology and outcome of an infection. They can defend the host through a variety of processes, including attachment site occupancy, nutrition intake, metabolite competition, and the synthesis of antimicrobial compounds including bacteriocins that influence pathogen survival (a process referred to as colonization resistance).
Survival Disparity Between Antiviral-Treated and Antiviral-Naïve Patients Who Develop Their First HBV-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a public health problem, accounting for more than 257 million cases of chronic infection and a major cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) worldwide. With the vaccination and the advent of nucleos(t)ide analogues (NAs) as antiviral therapy, chronic HBV infection currently accounts for approximately 50% of HCC cases worldwide, a significant decrease from >80% in the 1980’s. The reduced incidence of HBV-related HCC (HBV-HCC) with NAs with lamivudine, entecavir, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is well documented.
Advances in Functionalized Hybrid Biopolymer Augmented Lipid-based Systems: A Spotlight on Their Role in Design of Gastro Retentive Delivery Systems
Biopolymers have earmarked their importance in the biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. Researchers are still working for the facilitation of better therapeutic effects and medical benefits. In this context, several strategies are on a play like functionalization of biopolymers with physicochemical modification, functionalization of lipids with biopolymers, development of composites or hybrid systems for bringing together the benefits of individual moieties/systems
Alcoholic Liver Disease and the co-triggering Role of MEOS with Its CYP 2E1 Catalytic Cycle and ROS
Until the early sixties, the concept prevailed that alcoholic liver disease (ALD), also termed alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), results from malnutrition commonly observed among individuals consuming chronically high amounts of alcohol rather than being causally related to the use of alcoholic beverages. However, the malnutrition concept became a matter of debate because of the clinical observation that humans, even on a normal diet and without signs of underweight or malnutrition
The Inappropriate Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors: An Internal Medicine Residency Clinics Effort to Deprescribe
Since 1989, PPIs have become among the top-selling drug classes in the country. It is estimated that in the United States alone, about a quarter of the country suffers from acid related conditions. Their versatility and popularity have prompted the World Health Organization to add PPIs to their list of essential medications. The low cost of PPIs and over the counter (OTC) availability of these medications have made their use ubiquitous in outpatient care.
Updates in the Treatment of Superficial Gastric Neoplasms by Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Gastric cancer is one of the neoplasms with the highest degree of mortality worldwide, responsible for more than 780,000 deaths in 2018 and whose incidence has been increasing over the last few years, mainly in Asian and Latin American countries. The technological imaging advances in digestive endoscopy such as virtual chromoendoscopy and magnification associated with a systematic and comprehensive endoscopic examination of the entire gastric mucosa by a trained operator have optimized the early detection of pre-malignant and malignant lesions, which have favoured the high rate of curability through the use of endoscopic resection techniques such as endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD).
Alcoholic Liver Disease and the co-triggering Role of MEOS with Its CYP 2E1 Catalytic Cycle and ROS
Until the early sixties, the concept prevailed that alcoholic liver disease (ALD), also termed alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), results from malnutrition commonly observed among individuals consuming chronically high amounts of alcohol rather than being causally related to the use of alcoholic beverages. However, the malnutrition concept became a matter of debate because of the clinical observation that humans, even on a normal diet and without signs of underweight or malnutrition
Are We Close to Achieving a HBV Cure? Risk for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Persists Despite Long-term HBV Suppression: An Update on Our Experience
Since the discovery of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) by Blumberg et al., great progress has been made in understanding the pathogenesis of the virus and its role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). It is estimated that hepatitis B is responsible for about 50% of the HCC cases worldwide. Because of geographic variations in HBV incidence, the burden of HBV-related HCC (HBV-HCC) is highest in endemic areas such as Asian-Pacific and sub- Saharan Africa and lowest in the United States and the West.
The Dual Role of Macrophages during Hepatitis B Infection
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) chronically infects more than 250 million individuals worldwide and is responsible for more than 800,000 deaths per year by promoting end-stage liver diseases, among which decompensated cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (WHO, July 2020) are prominent. Studies performed in chimpanzees or in animalversion of HBV (woodchuck HBV: WHBV) highlighted the lack of immune responses against the virus upon primary infection.
DILI, HILI, RUCAM Algorithm, and AI, the Artificial Intelligence: Provocative issues, Progress, and Proposals
Artificial Intelligence (AI) principles published in 1956 included the recommendation to use algorithms for solving complex processes. The creation of the Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM) was published in 1993 with integration of an intelligent algorithm to solve issues of causality assessment in cases of complex suspected drug induced liver injury (DILI) cases. Other causality assessment methods (CAMs) published before the era of AI and RUCAM followed rather general principles without precise and valid algorithm.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
