Loading
Archives of Gastroenterology Research
ISSN: 2692-5427
Editors Choice Articles
Hepatitis Treatment in the Last 20 Years: A Short Review
Abdurrahman Sagir
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) genome was isolated during the late 1980s using molecular cloning techniques. It is recognized as the cause of most cases of percutaneously transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis. It is estimated, that up to 200 million people worldwide are infected with the hepatitis C virus (HCV), more than 3% of the world population. The predominant risk factors for HCV are intravenous drug use, tattoos, exposure to blood products, occupational risk and ethnicity.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p1-3 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.1.001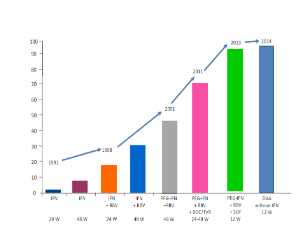
DILI, HILI, RUCAM Algorithm, and AI, the Artificial Intelligence: Provocative issues, Progress, and Proposals
Rolf Teschke
Artificial Intelligence (AI) principles published in 1956 included the recommendation to use algorithms for solving complex processes. The creation of the Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM) was published in 1993 with integration of an intelligent algorithm to solve issues of causality assessment in cases of complex suspected drug induced liver injury (DILI) cases. Other causality assessment methods (CAMs) published before the era of AI and RUCAM followed rather general principles without precise and valid algorithm.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 1, p4-11 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.1.002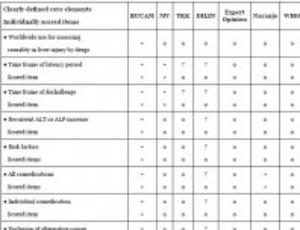
Alcoholic Liver Disease and the co-triggering Role of MEOS with Its CYP 2E1 Catalytic Cycle and ROS
Rolf Teschke, Manuela G. Neuman, Suthat Liangpunsakul, Helmut-Karl Seitz
Until the early sixties, the concept prevailed that alcoholic liver disease (ALD), also termed alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), results from malnutrition commonly observed among individuals consuming chronically high amounts of alcohol rather than being causally related to the use of alcoholic beverages. However, the malnutrition concept became a matter of debate because of the clinical observation that humans, even on a normal diet and without signs of underweight or malnutrition
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p9-25 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.2.022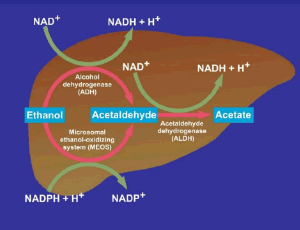
Updates in the Treatment of Superficial Gastric Neoplasms by Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Josue Aliaga Ramos, Vitor N. Arantes
Gastric cancer is one of the neoplasms with the highest degree of mortality worldwide, responsible for more than 780,000 deaths in 2018 and whose incidence has been increasing over the last few years, mainly in Asian and Latin American countries. The technological imaging advances in digestive endoscopy such as virtual chromoendoscopy and magnification associated with a systematic and comprehensive endoscopic examination of the entire gastric mucosa by a trained operator have optimized the early detection of pre-malignant and malignant lesions, which have favoured the high rate of curability through the use of endoscopic resection techniques such as endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD).
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p26-30 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.2.023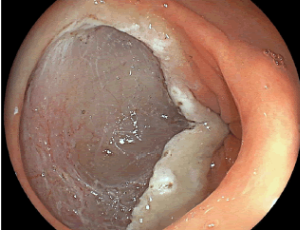
The Dual Role of Macrophages during Hepatitis B Infection
Suzanne Faure-Dupuy, Julie Lucifora, David Durantel
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) chronically infects more than 250 million individuals worldwide and is responsible for more than 800,000 deaths per year by promoting end-stage liver diseases, among which decompensated cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (WHO, July 2020) are prominent. Studies performed in chimpanzees or in animalversion of HBV (woodchuck HBV: WHBV) highlighted the lack of immune responses against the virus upon primary infection.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p89-94 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.1.016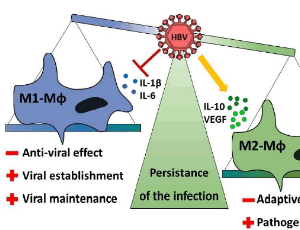
The Inappropriate Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors: An Internal Medicine Residency Clinics Effort to Deprescribe
Polina Gaisinskaya, Zed Seedat, Sanja Patino, Navneet Kaur, Oscar L. Hernandez, Eric Abkian, Jamie Fabricant, Mishah Azhar, Michael A. DeDonno, Nabil Benhayoun
Since 1989, PPIs have become among the top-selling drug classes in the country. It is estimated that in the United States alone, about a quarter of the country suffers from acid related conditions. Their versatility and popularity have prompted the World Health Organization to add PPIs to their list of essential medications. The low cost of PPIs and over the counter (OTC) availability of these medications have made their use ubiquitous in outpatient care.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p95-101 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.2.034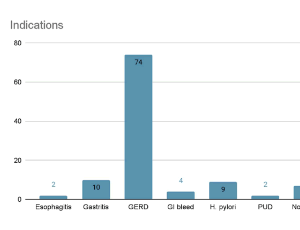
Are We Close to Achieving a HBV Cure? Risk for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Persists Despite Long-term HBV Suppression: An Update on Our Experience
Tina Boortalary, Brianna J Shinn, Robert M Coben, Mitchell I Conn, Jorge Prieto, Howard Kroop, Anthony J DiMarino, Hie-Won Hann
Since the discovery of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) by Blumberg et al., great progress has been made in understanding the pathogenesis of the virus and its role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). It is estimated that hepatitis B is responsible for about 50% of the HCC cases worldwide. Because of geographic variations in HBV incidence, the burden of HBV-related HCC (HBV-HCC) is highest in endemic areas such as Asian-Pacific and sub- Saharan Africa and lowest in the United States and the West.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p105-110 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.1.018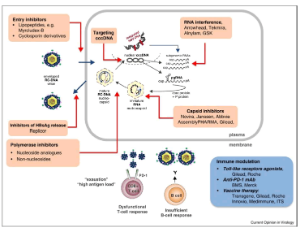
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
