Loading
Journal of Experimental Neurology
ISSN: 2692-2819
Featured Articles
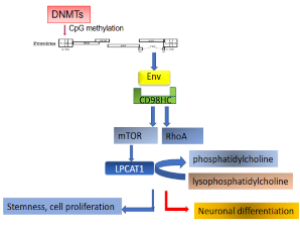
Retroviral Elements in Human Evolution and Neural Development
Tongguang Wang, Tara T. Doucet-O’Hare, Lisa Henderson, Rachel P. M. Abrams, Avindra Nath
Human embryogenesis and the development of its most unique product, the human brain, are believed to be precisely regulated by factors adopted during human
evolution that differentiate us from other species.
Cathepsin D: A Candidate Link between Amyloid β-protein and Tauopathy in Alzheimer Disease
Caitlin N. Suire, Malcolm A. Leissring
Alzheimer disease (AD) is a debilitating neurodegenerative disorder characterized by extracellular deposition of the amyloid β-protein (Aβ) and intraneuronal accumulation of the microtubule-associated protein, tau
J Exp Neurol, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p10-15 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.2.029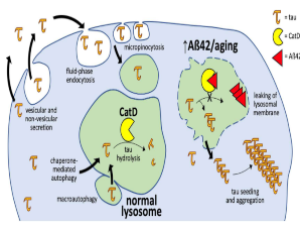
Commentary on Vulnerability and Resilience to Activity- Based Anorexia and the Role of Dopamine
Jeff A. Beeler, Nesha S. Burghardt
Anorexia nervosa (AN) is an eating disorder characterized by a fear of gaining weight and self-starvation, leading to life-threatening weight loss [1]. It occurs predominately in women and frequently begins during adolescence.
J Exp Neurol, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p21-28 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.2.031
Commentary: Use of BACTRAC Proteomic Database-Uromodulin Protein Expression During Ischemic Stroke
Gabriella-Salome K. Armstrong, Jacqueline A. Frank, Christopher J. McLouth, Ann Stowe, Jill M. Roberts, Amanda L. Trout, Justin F. Fraser, Keith Pennypacker
Uromodulin (UMOD) is a glycoprotein expressed by the epithelial cells of the thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop in the kidney. Research has shown that increased uromodulin expression may be associated with lower risk of cardiovascular disease in adults.
J Exp Neurol, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p29-33 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.2.032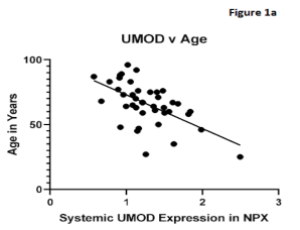
Combined Antiseizure Efficacy of Cannabidiol and Clonazepam in a Conditional Mouse Model of Dravet Syndrome
Shu-Hui Chuang, Ruth E. Westenbroek, Nephi Stella, William A. Catterall
Dravet syndrome (DS) is an intractable childhood epilepsy disorder affecting one in 15,000 to 20,000 births [1]. It is caused by de novo heterozygous lossof- function mutations in the SCN1A gene encoding the brain type-I voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.1
J Exp Neurol, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p81-85 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.2.040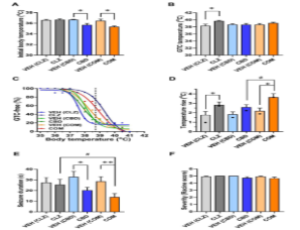
Differential Fecal Microbiome Dysbiosis after Equivalent Traumatic Brain Injury in Aged Versus Young Adult Mice
Booker T Davis IV, Mecca B.A.R. Islam, Promi Das, Jack A Gilbert, Karen J. Ho, Steven J. Schwulst
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) has a bimodal age distribution with peak incidence at age 24 and age 65 with worse outcomes developing in aged populations
J Exp Neurol, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p120-130 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.2.044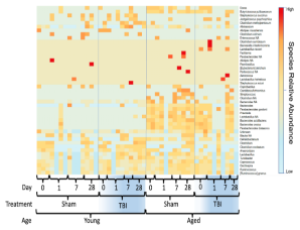
Resolving the Molecular Steps in Clostridial Neurotoxin Light Chain Translocation
Madison Zuverink, Joseph T. Barbieri
Due to use as human vaccines and therapies, the clostridial neurotoxins (CNTs) have been subjected to decades of scientific investigation using biophysical, electrophysiological, and pharmacological approaches to establish mechanisms of toxin action.
J Exp Neurol, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p123-134 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.1.020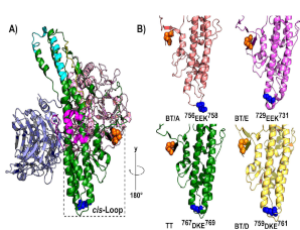
The Spread of Spectrin in Ataxia and Neurodegenerative Disease
Jon S. Morrow, Michael C. Stankewich
Experimental and hereditary defects in the ubiquitous scaffolding proteins of the spectrin gene family cause an array of neuropathologies
J Exp Neurol, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p131-139 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.2.045
Capillary Stalling: A Mechanism of Decreased Cerebral Blood Flow in AD/ADRD
Reece Crumpler, Richard J. Roman, Fan Fan
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) and Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Dementias (ADRD) are debilitating conditions that are highly associated with aging populations, especially those with comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertension.
J Exp Neurol, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 4, p149-153 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.2.048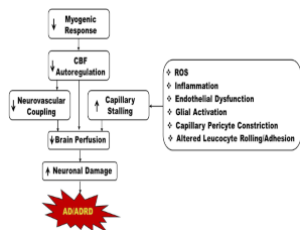
A Protocol for the Generation of Treatment-naïve Biopsy-derived Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma and Diffuse Midline Glioma Models
Matt C. Biery, Alyssa Noll, Carrie Myers, Shelli M. Morris, Conrad A. Winter, Fiona Pakiam, Bonnie L. Cole, Samuel R. Browd, James M. Olson, Nicholas A. Vitanza
Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) is an aggressive brain tumor that arises in the ventral pons during middle childhood.
J Exp Neurol, 2020, Volume 1, Issue 4, p158-167 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.1.025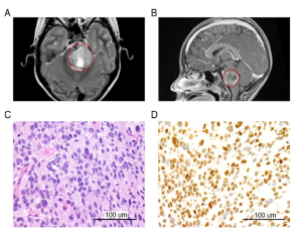
Protein Citrullination in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases
Issa O. Yusuf, Webb Camille, Paul R. Thompson, Zuoshang Xu
Protein citrullination (PC) is a posttranslational modification (PTM) that converts a peptidyl arginine into a peptidyl citrulline. Aberrant PC is a hallmark of neurodegenerative diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, prion disease, and multiple sclerosis. Common among these diseases is a dramatic increase of PC in reactive astrocytes. Some citrullinated proteins have been identified.
J Exp Neurol, 2024, Volume 5, Issue 4, p183-191 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.5.101
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
