Loading
Archives of Pharmacology and Therapeutics
ISSN: 2688-9609
Most Cited Articles
Why Do Patients Not Meet the Pharmacological Treatment?
Jose Luis Turabian
Therapeutic compliance has been defined as the degree to which the behaviour of a person corresponds with the recommendations of the health professional [1].
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 1, p1-7 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.1.001
Pharmacogenetic Variants in the DPYD and TYMS Genes are Clinically Significant Predictors of Fluoropyrimidine Toxicity: Are We Ready for Use in our Clinical Practice
Muhammad Wasif Saif, Hilal Hachem, Sneha Purvey, Ruchi Hamal, Lulu Zhang, Nauman Saleem Siddiqui, Amandeep Godara, Robert B. Diasio
Fluoropyrimidines have been extensively used for almost 6 decades to treat a variety of solid cancers, especially colon, gastric, anal, rectal, head & neck and breast. However, 31–34% of patients encountered grade 3–4 adverse events (AEs) with 0.5% mortality oftennecessitating dose reduction or discontinuation. A significant proportion of these AEs are likely to be the result of inter-individual genetic variation, in particularly such as dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPYD). DPYD gene encodes DPD, the rate-limiting enzyme responsible for catabolism of 5-FU and is responsible for >85% of 5-FU elimination.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 1, p6-8 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.2.012
Domination of Nephrotic Problems among Diabetic Patients of Bangladesh
Mohiuddin AK
Nearly 80% of people with diabetes live in low and middle-income countries. It increases healthcare use and expenditure and imposes a huge economic burden on the healthcare systems. The International Diabetes Federation estimated 7.1 million people with diabetes in Bangladesh and almost an equal number with undetected diabetes. This number is estimated to double by 2025.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 1, p8-13 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.1.002
Beta-Sitosterol: As Immunostimulant, Antioxidant and Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein
Sharuk L. Khan, Falak A. Siddiqui
This article is an extension to our recently published article in Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, entitled “Β-Sitosterol: Isolation from Muntingia Calabura Linn. Bark Extract, Structural Elucidation, and Molecular Docking Studies as Potential Inhibitor of SARSCoV-2 Mpro (COVID-19)”[1].
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 1, p12-16 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.2.014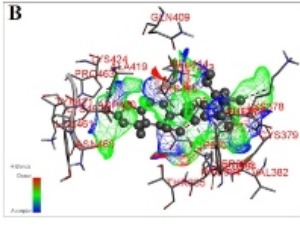
Pharmacologic Therapies for Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: Current and Future Treatments
Ilana P. Goldberg, Benjamin Lichtbroun, Eric A. Singer, Saum Ghodoussipour
Bladder cancer is the sixth most common malignancy in the United States and 70% of cases are non-muscle invasive at the time of diagnosis. Effective treatment is crucial to prevent progression, which occurs in about 30% of patients. The American Urological Association (AUA) guidelines recommend treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) with intravesical Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) and chemotherapy.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2022, Volume 4, Issue 1, p13-22 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.030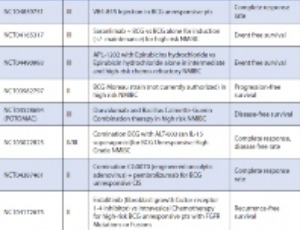
Diverse Therapeutic Applications of Onion
Preetismita Borah, Bimal Krishna Banik
Onion has been a very useful vegetable for human. The organic molecules present in onion are extremely diverse and exert numerous pharmacological pathways to prevent diseases. Although, mechanism of action of the compounds present in onion has been investigated, clearly there remains enough scope to study this subject further. In general, many scientists believe that the medicinal values of onion are because of a series of oxidation processes of the molecules present in it.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 1, p14-16 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.1.003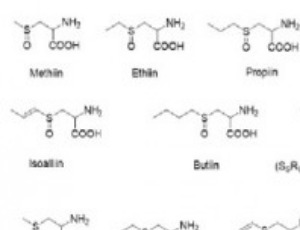
Molecular Detection of Plasmid - Mediated Quinolone Resistant Genes in Uropathogenic E. coli from Tertiary Referral Hospital in Tehran , Iran
Ali Badamchi, Shima Javadinia, Reza Farahani, Hamid Solgi, Azardokht Tabatabaei
Fluoroquinolone antibiotics are usually used for the treatment of urinary tract infections. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence and molecular characterization of Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance (PMQR) genes among ESBL-producing Escherichia coli isolates obtained from tertiary referral hospital in Tehran, Iran.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 1, p19-24 | DOI: doi.org/10.33696/Pharmacol.1.005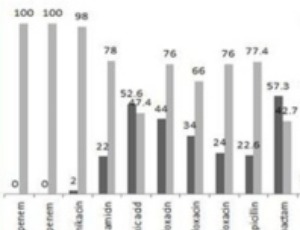
Artificial Intelligence in Pharma: Positive Trends but More Investment Needed to Drive a Transformation
Peter Henstock
Pharmaceutical companies have been actively adopting artificial intelligence (AI) approaches for drug discovery and are starting to focus this technology on clinical trials. The shift from large-scale collaborations to smaller strategic partnerships and recently to internal teams has led to increased headcounts that are being organized to deliver AI across the enterprise. Although the urgency of the COVID-19 could have been a perfect test case for leveraging AI, it drew awareness to the obstacles of data access.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 2, p24-28 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.2.017
Platelet Hyperactivity and Dysfunction in Diabetes and Cancer
Bahram Alamdary Badlou
However, the entire coagulation cascade is dysfunctional, in progressed chronic diabetes and cancer patients. Platelets (PLTs) in type 2 diabetic (DT2) involved in Thrombosis and Haemostasis (T&H) of individuals adhere to vascular endothelium and aggregate more voluntarily than those in healthy individuals, as are abnormalities in the microvascular and macrovascular circulations. However it is already known that the circulating PLTs are essential for T&H, inflammation growth factors delivery, regeneration; and knowledge of their function is fundamental to understanding the pathophysiology of vascular disease in diabetes and cancer-related diseases.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p25-26 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.1.006
Psychosocial Aspects of Drug Prescription: Recognizing These Phenomena to Improve the Quality of Clinical Practice
Jose Luis Turabian
The psychosocial aspects of pharmacological prescription are the factors that intervene in ways of reacting of the doctor and the patient to the prescription of a drug, as well as the role of social structures that determine it. The role of psychosocial factors in pharmacologic treatment of patients remains unclear and is notably absent in the literature of the discipline of general medicine. Biological (specific) and psychosocial (nonspecific) effects of drugs are not simply additive, but interact with each other.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p27-34 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.1.007
Is There a Simple and Easy Way to Detect Singlet Oxygen? Comparison of Methods for Detecting Singlet Oxygen and Application to Measure Scavenging Activity of Various Compounds
Tokuko Takajo, Kazunori Anzai
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are known to exert both beneficial and harmful effects in the human body. Singlet oxygen (1O2), is highly reactive and considered as one of the ROS, although it is not a radical molecule. 1O2 reacts with many kinds of biological components such as lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. 1O2 is short lived because it reacts with biomolecules and collisions with water molecules rapidly causing the return of 1O2 to the ground state, and is therefore not easy to quantify. Antioxidants, such as β-carotene, lycopene and astaxanthin, are quenchers of 1O2.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 2, p29-33 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.2.018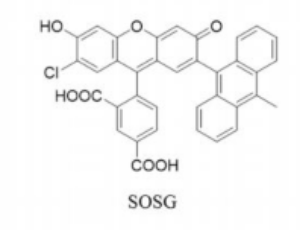
How Traditional Healers Diagnose and Treat Diabetes Mellitus in the Pretoria Mamelodi Area and How Do These Purported Medications Comply with Complementary and Alternative Medicine Regulations
Ondo Z.G
In South Africa, new amended regulations required a review of complementary and alternative medicine (CAMs) call-up for registration from November 2013. This impacted traditional healers (THs)’ compliance with the regulatory authorities’ on the good manufacturing practice which in return affected the public’s access to CAMs. This investigation embraces methods, THs use to diagnose and treat diabetes (DM) in Mamelodi. Furthermore, it assesses what their purported medications comprise of.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p33-45 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.1.008
ProLung™-budesonide Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Replication and Reduces Lung Inflammation
Kameswari S. Konduri, Ram Pattisapu, Jogi Pattisapu, Girija G. Konduri, John Zwetchkenbaum, Bidhan Roy, Monalisa Barman, Adria Frazier, Brett L. Hurst, Nejat Duzgunes
Inhaled budesonide benefits patients with COVID-19. ProLung™-budesonide enables the sustained, low dose administration of budesonide within a delivery vehicle similar to lung surfactant. ProLung™-budesonide may offer anti-inflammatory and protective effects to the lung in COVID-19, yet it’s effect on SARS-CoV-2 replication is unknown.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2, p52-65 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.3.028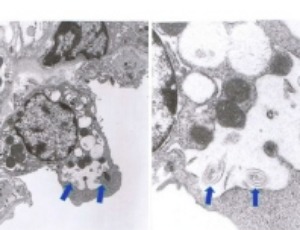
Recent Advances in Diagnosing and Treating Helicobacter pylori through Botanical Extracts and Advanced Technologies
Tamer A. Addissouky, Majeed M. A. Ali, Ibrahim El Tantawy El Sayed, Yuliang Wang
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is a major global health concern, with an estimated 50% of the world's population infected. The bacterium colonizes the stomach and is associated with a range of gastrointestinal diseases, including chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and gastric cancer. The current standard of care for H. pylori infection involves a combination of antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), but the widespread use of antibiotics has led to the development of antibiotic-resistant strains of H. pylori, making treatment more difficult. Recent advances in diagnostic strategies include the use of non-invasive tests and serological biomarkers.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p53-66 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.4.045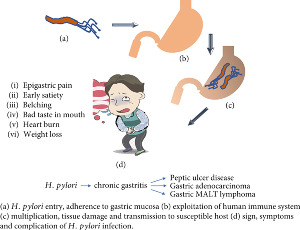
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
