Loading
Journal of Cellular Immunology
ISSN: 2689-2812
2022
Volume 4, Issue 6, p194-224
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
The Importance of C5aR2 in Neutrophil Function and Its Impact on Neutrophil-mediated Diseases
Daniel Leonard Seiler, Marie Kleingarn, Syeda Zoela Gilani, Paula Emily Reichel, Jörg Köhl, Christian Marcel Karsten
C5aR2 serves as the second receptor for the anaphylatoxin C5a. It was identified about 10 years after identification of the first cognate receptor, C5aR1. Initially, C5aR2 was considered a mere decoy receptor for C5a. According to this view, its function was to scavenge excess C5a from C5aR1 and thereby exert anti-inflammatory effects. However, this initial view of C5aR2 had been oversimplified.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume 4, Issue 6, p194-201 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.150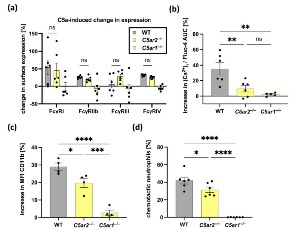
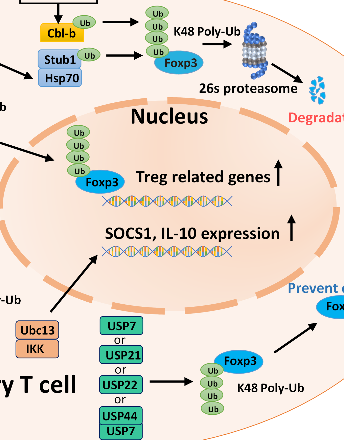
Ubiquitin-Dependent Regulation of Treg Function and Plasticity
Yikui Li, Ping Wei, Fan Pan
Delicately, our immune system eliminates exogenous and endogenous threats and prevents harmful immune responses against the host. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are indispensable in controlling immune responses and inducing immune tolerance; thus, immune homeostasis is maintained [1]. As a subset of CD4+ T cells, Tregs have been extensively studied for decades. They are best known for their ability to suppress immune responses, induce self-tolerance and help tumor cells escape immune surveillance [2-5]. Tregs mediate immune suppression via several mechanisms: They constitutively express cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4), which competes with the costimulatory molecule CD28 for binding CD80/86 to downregulate T cell activation [6].
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume 4, Issue 6, p202-210 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.151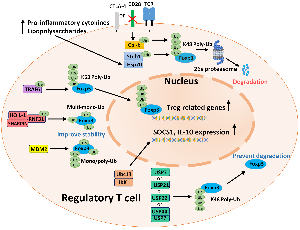
Preliminary Evidence of Differentially Induced Immune Responses by Microparticle-adsorbed LPS in Patients with Crohn’s Disease
P Ashwood
Inorganic microparticles are ubiquitous in the modern Western diet present as food additives and are actively scavenged by microfold (M) cells overlying human intestinal lymphoid aggregates. In Crohn’s disease (CD), inflammation is caused by the inability of the intestinal mucosa to sustain tolerance to gut luminal factors including bacteria and their by-products.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume 4, Issue 6, p211-218 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.152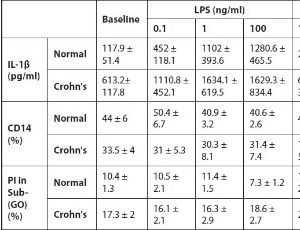
Vγ2+ γδ T Cells and Their Regulatory Potential in Skin Allograft Survival
Shilpi Giri, Girdhari Lal
Our recently published research article “Vγ2+ γδ T cells in the presence of anti-CD40L control surgical inflammation and promote skin allograft survival” revealed that the Vγ2+ subset of γδ T cells, which otherwise are known primarily for its proinflammatory function, regulate the survival of skin allografts in the presence of anti-CD40L.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume 4, Issue 6, p219-222 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.153
Is Omicron Variant of COVID-19 Threatening Health Like Other Variants?
Mousa Ghelichi-Ghojogh, Hamed Ghasemloo, Hamid Hosseinpour, Rohollah Valizadeh, Tella Sadighpour
World health organization (WHO) designated the variant B.1.1.529 a variant of concern, named Omicron, as a fastspreading SARS-CoV-2 variant, on 26 November 2021 which started from Southern Africa. In addition to the new mutations (more than 30 mutations in the spike protein), Omicron also carries mutations similar to the alpha, beta, gamma, and delta variants of coronavirus, and is collectively known as the fifth most disturbing variant.
J Cell Immunol, 2022, Volume 4, Issue 6, p223-224 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.4.154
Recommended Articles
Chimeric Antigen Receptor CAR NK Cells Emerging Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Cancer
Although NK cells are recognized as effector lymphocytes of the innate immune system, they also regulate the adaptive immune response by releasing inflammatory cytokines and developing immunological memory. Unlike other lymphocytes such as T or B cells, NK cells do not express rearrangeable, antigen-specific receptors.
COVID-19 Clinical Research
While the global COVID-19 pandemic has challenged the entire humanity and health systems, it also triggered researchers to urgently perform clinical trials to assess the safety and efficacy of many agents and modalities to combat COVID-19. As of April 22, over 650 clinical studies have been registered both in USA and internationally. Results from these studies are also coming at a brisk pace in this unprecedented emergency.
Deubiquitinase as Potential Targets for Cancer Immunotherapy
During the last few decades, immunotherapy is considered to be an important approach to help our immune system to fight various kinds of diseases, such as tumor. Sometimes, it works very well for some types of cancers, for example: bladder cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer and lymphoma.
Role of the Gut Microbiome in the Modulation of Cancer Immunotherapy Response
The gut microbiome or gut flora is a vast community of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and fungi that inhabit the digestive tract of the human and other animals [1,2]. In the human body, bacterial species colonize into the oral cavity, skin, vagina, and placenta, however, the largest population of microorganisms resides in the intestine.
In silico Analysis for the Repurposing of Broad-spectrum Antiviral Drugs against Multiple Targets from SARS-CoV-2: A Molecular Docking and ADMET Approach
SARS-CoV-2 belongs to the genus Beta of the Coronaviridae family of enveloped single-stranded, positive-sense ribonucleic acid (RNA) with a genome length of 30,000bp. The virion is composed of various non-structural (RNA dependent RNA polymerase also known as RdRp) and structural proteins such as Spike (S), Nucleocapsid (N), Matrix (M), and Envelope (E) proteins.
Is Citrate A Critical Signal in Immunity and Inflammation?
When immune cells are activated, they undergo metabolic change in order to have sufficient energy to function effectively. The Krebs cycle is one of the most important pathways involved in this response and citrate, a critical component of this pathway, regulates carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Dendorbium Nobile Lindl. Alkaloids Suppress NF-κB and NLRP3 Signaling Pathways to Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-induced Neuroinflammation
The important immune cells in the brain are called microglia acting as the central junction between neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. In patients of cognitive disorders and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) animal models, amoebic morphology and inflammatory pathways are activated to release numerous cells in the inflammatory factors by active microglia.
TNFAIP8: Inflammation, Immunity and Human Diseases
Inflammation can be caused by various environmental factors, including microbial infection and toxic chemical exposure. In response to inflammation, immune cells like macrophages, B and T lymphocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and various stromal cells secrete soluble polypeptide cytokine Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF?)
CTLA-4 and PD-L1 or PD-1 Pathways: Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Cancer Immunotherapy
The immune system developed certain checks and balance to control or inhibit the reactivity against normal cells of the body. Uncontrolled immune responses to the non-self entities such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, or mutated self-antigens can cause an inflammatory reaction and autoimmune diseases.
Cancer Nanomedicine: Strategies to Enhance Tumor Delivery and Immunotherapy
Cancer nanomedicine was originally developed for more efficient delivery of chemotherapeutic agents into tumor, and has been extensively employed as a therapeutic for cancer treatment owing to its unique features in drug delivery, diagnosis and imaging, as well as the therapeutic nature of some nanomaterials themselves.
Practical Considerations Regarding Recommendations for an Educational Program in Robot Assisted Gynaecological Surgery
Robot assisted gynaecological surgery is exponentially expanding its field and gynaecologists need to be prepared to implement this new approach in clinical practice.
Beta-Sitosterol: As Immunostimulant, Antioxidant and Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein
This article is an extension to our recently published article in Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, entitled “Β-Sitosterol: Isolation from Muntingia Calabura Linn. Bark Extract, Structural Elucidation, and Molecular Docking Studies as Potential Inhibitor of SARSCoV-2 Mpro (COVID-19)”[1].
Rapid Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 by Coupling Tungsten Trioxide (WO3) Photocatalyst with Copper Nanoclusters
At the end of 2019, a novel severe respiratory disease (coronavirus disease 2019, COVID-19) spread to Wuhan, China, it became pandemic in few months, with more than 41 million people infected worldwide as of October 2020. COVID-19 is caused by a novel virus called severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) CoV-2 to distinguish it from SARS-CoV that emerged in Guangdong province in China in 2003 and caused the severe clinical condition known as SARS. Like SARS-CoV, SARS- CoV-2 causes a severe inter
Targeting "Do Not Eat Me" Signal CD47 in Cancer Immunotherapy
Cells of the innate and adaptive arm of the immune system including macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells, neutrophils, T cells, and B cells, etc. are crucial for the maintenance of the body’s homeostatic balance and prevention of multiple diseases including cancer.
Quantifying Respiratory Airborne Particle Dispersion Control Through Improvised Reusable Masks: The Physics of Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions for Reducing SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Airborne Transmission
In light of the current pandemic from rapid transmission of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2 or COVID-19) and significant morbidity, there has been inconsistent medical guidance given to the public regarding the wearing of non-medical improvised fabric masks or face coverings to reduce the transmission of COVID-19.
In Silico Proteome Analysis of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARSCoV- 2) is a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA with genome size 26.2, and 31.7 kb coronavirus, covered by an enveloped structure, which is a major source of disaster in the 21st century. A typical CoV contains at least six ORFs in its genome. SARS-CoV-2 is the seventh coronavirus that is known to cause human disease.
COVID-19 Disease and SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Patients with Cancer
Since the declaration of COVID-19 as a pandemic in March 2020 [1], there have been more than 100 million reported cases of COVID-19 worldwide and more than 2.1 million deaths [2].
COVID-19 and the Health of Illicit Substance Users: Preliminary Analysis from Illicit Drug Transaction Data
While much attention has been given to how COVID-19 patients are treated (or fail to be treated), the impact of the pandemic on illicit drug users remains largely undiscussed
COVID-19 Rapid Diagnostic Test Results and their Associations with Certain Factors Among the Residents of Balochistan
This paper analyses any possible association of various factors like gender, last COVID-19 PCR test results, BCG Vaccination, Seasonal Flu vaccination, occupation and confirmed case contact history with COVID-19 RDT results of the participants.
ProLung™-budesonide Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Replication and Reduces Lung Inflammation
Inhaled budesonide benefits patients with COVID-19. ProLung™-budesonide enables the sustained, low dose administration of budesonide within a delivery vehicle similar to lung surfactant.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
