Loading
Archives of Cancer Biology and Therapy
ISSN: 2692-8302
2021
Volume 2, Issue 2, p29-53
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Exosome to Promote Cancer Progression via Its Bioactive Cargoes
Austin McMasters, Kelly M McMasters, Hongying Hao
Exosomes are membranous vesicles ranging in size from 30–100 nm in diameter. They are secreted from multiple cell types into the body fluids through exocytosis, a process commonly used for receptor discharge and intercellular communications.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p29-34 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.2.021
Genetic Predisposition of Breast Cancer in the United Arab Emirates
Ajda Altino, Ahmed Abdel-Aziz, Mouza Al Ameri
This commentary refers to our published article, as highlighted in this article most common gene causing breast cancer in the population living in the United Arab Emirates is BRCA2 followed by BRCA1. This is the first publication discussing about clinical and pathological features of breast cancer in woman with a positive genetic mutation in the United Arab Emirates.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p35-36 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.2.022
Primary Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of Bladder – A Rare Diagnostic Entity
Prachi, Gaurav Sharma
Primary small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the urinary bladder is a rare histological type shows poor differentiation and behaves in a highly aggressive manner. It accounts to 0.3- 0.7% of all bladder tumors [1,2]. Neuroendocrine carcinomas predominantly occur in respiratory and gastrointestinal tract and very rarely in the urinary bladder.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p37-39 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.2.023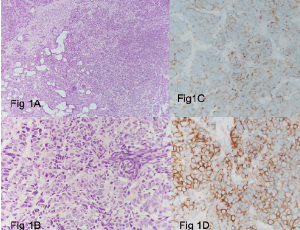
Molecular Biology for BCR-ABL1 Quantification for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Monitorization and Evaluation
Anelis Maria Marin, Gabriela Silva Soares, Dalila Luciola Zanette, Mateus Nóbrega Aoki
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) is a clonal disorder originated by a pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell, which presents the translocation t(9;22) (q34;q11) in 90% of the cases.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p40-42 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.2.024
The Impact of Dido on the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
Agnes Fütterer, Amaia Talavera-Gutiérrez, Carlos Martínez-A
The human body is constituted by more than 200 committed cell types [1], all of which derive from the zygote, a single totipotent cell that divides and differentiates into all the cells of an organism throughout its development. Out of this diversity, we focus our interest here on the epithelial and the mesenchymal cells.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p43-49 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.2.025
SorLA Targeting - A Method to Overcome Therapy Resistance in Breast Cancer
Hussein Al-Akhrass, Nicolas Pasquier, Johanna Ivaska
Tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER2- targeted therapies have dramatically improved breast cancer patients’ outcome compared to conventional chemotherapies. In the clinic, HER2 monoclonal antibody trastuzumab with chemotherapy represent the gold standard treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 2, p50-53 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.2.026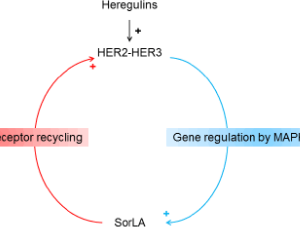
Recommended Articles
Acute Abdomen due to Perforation of Small Bowel Malignant Melanoma Metastasis
Primary tumors of the small bowel are a rare condition, accounting for 2 to 3% of gastrointestinal tumors. Malignant melanoma is the most common metastatic tumor found in the gastrointestinal tract [1]. It can be localized in different sites, from the oral cavity to the anus. It can also be present as a primary lesion.
Exosome to Promote Cancer Progression via Its Bioactive Cargoes
Exosomes are membranous vesicles ranging in size from 30–100 nm in diameter. They are secreted from multiple cell types into the body fluids through exocytosis, a process commonly used for receptor discharge and intercellular communications.
Primary Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of Bladder – A Rare Diagnostic Entity
Primary small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the urinary bladder is a rare histological type shows poor differentiation and behaves in a highly aggressive manner. It accounts to 0.3- 0.7% of all bladder tumors [1,2]. Neuroendocrine carcinomas predominantly occur in respiratory and gastrointestinal tract and very rarely in the urinary bladder.
The Link of Nutrient Fluxes to Hepatic Insulin Resistance at Gene Expression
Insulin resistance has been studied extensively at systemic, organ, tissue and cellular and molecular levels. Overnutrition plays an essential role in the development of chronic metabolic diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. For subjects without genetic defects, the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes is a graduate process. How the transition from an insulinsensitive state to an insulin-resistant state occurs, and what the roles of nutrients are in the process have not been fully understood. Here, we try to summarize the current understanding of insulin-regulate gene expression in the liver, and describe a phenomenon of hepatic insulin resistance at gene expression (HIRAGE), which may be linked to overnutrition.
Leucocyte-Tumor Cell Hybridization Can Initiate Cancer Metastasis
According to estimates from the International Agency for Research on Cancer, by the year 2030 there will be 22 million new cancer cases and 13 million deaths per year. The main reason for death from cancer is not the initial tumor but it’s metastasis to distant parts of the body, yet this process has remained poorly understood for quite some time.
The Role of ERO1α in Modulating Cancer Progression and Immune Escape
The failure to eradicate minimal residual disease often located at metastatic sites and/or the bone marrow niche continues to be a clinical barrier for successful treatments in cancer.
MicroRNA Signature Targeting Transient Receptor Potential Channels in the Prognosis and Therapy of Cancer
This short communication would to be the continuation of the Santoni’s paper entitled “Targeting Transient Receptor Potential Channels by MicroRNAs drives tumor development and progression” published in: Calcium Signaling, Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology
Pharmacologic Therapies for Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: Current and Future Treatments
Bladder cancer is the sixth most common malignancy in the United States and 70% of cases are non-muscle invasive at the time of diagnosis. Effective treatment is crucial to prevent progression, which occurs in about 30% of patients. The American Urological Association (AUA) guidelines recommend treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) with intravesical Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) and chemotherapy.
Primary Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of Bladder – A Rare Diagnostic Entity
A 75-year-old male patient presented with gross haematuria and pelvic pain since a month. He is a chronic smoker with 40-pack year index. His family history is insignificant. Ultrasonography showed 2 × 2 cm broad based solid heteroechoic mass along the left lateral wall of urinary bladder.
Control of CD4 Helper and CD8 Cytotoxic T cell Differentiation
Engagement of mature T cell receptor (TCR), a multiprotein complex consisting of an αβ heterodimer associated with invariant CD3 signaling proteins, on CD4+CD8+ double positive (DP) thymocytes by selfpeptide/ self-MHC complex on thymic stromal cells results in negative selection of thymocytes expressing strong affinity TCRs and
Chronic IL-1 Exposed AR+ PCa Cell Lines Show Conserved Loss of IL-1 Sensitivity and Evolve Both Conserved and Unique Differential Gene Expression Profiles
Inflammation drives prostate cancer (PCa) progression. While inflammation is a cancer hallmark, the underlying mechanisms mediating inflammation-induced PCa are still under investigation. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) is an inflammatory cytokine that promotes cancer progression, including PCa metastasis and castration resistance. We previously found that acute IL-1 exposure represses PCa androgen receptor (AR) expression concomitant with the upregulation of pro-survival proteins, causing de novo accumulation of castration-resistant PCa cells.
Right Atrial Metastasis from Melanoma Treated with Immunotherapy
It is long known that melanoma has the ability to metastasize widely. Unusual sites of metastases are seen including intracardiac. The literature reports cases of cardiac metastases however, most reports pre-date the more recent era of immunotherapy and targeted agent use and do not describe systemic treatment responses.
Purinergic P2X7 Receptor as a Potential Targeted Therapy for COVID-19-associated Lung Cancer Progression
Severe acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection is a serious threat to lung cancer patients. Hereby, we hypothesize that Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) may contribute to lung cancer progression by increasing extracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels and hyperactivating the purinergic P2X purinoceptor 7 receptor (P2X7R).
Potential Mechanism of CDC42 Promoting HCC Metastasis
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an aggressive malignancy with increasing morbidity and mortality worldwide. The migration and motility of HCC tumor cells are enhanced by the formation of invadopodia, which comprise membrane protrusions at the leading edge. Previous studies have showed that cell division cycle 42 (CDC42) plays an essential role in remodeling the cytoskeleton, which is associated with invadopodia formation and thus mediates cellular movement.
Small Cell Carcinoma of the Cervix: A Case Report and Literature Review
Cervical small cell carcinoma (SCC) is a rare disease, with a high degree of malignancy and a poor prognosis. Para-aortic lymph nodes (PALN) are frequent sites of recurrence after pelvic chemoradiotherapy. In the present study, we report the case of a 26-year-old female patient with cervical SCC who suffered for two times PALN relapses.
The Interplay of Interferon-Beta, Cobalamin, and MicroRNA Regulation in Multiple Sclerosis Therapy
Multiple Sclerosis (MS), a chronic inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system, is a complex disorder affecting millions globally, which necessitates innovative therapeutic strategies. In the quest for novel treatments, we have conducted a recent study that has provided crucial insights into the potential synergistic effects of interferonbeta (IFN-β) and cobalamin (Vitamin B12) in MS therapy, targeting interleukin-10 (IL-10), osteopontin (OPN), and specific microRNAs (miR-106a, let-7c, and miR-146a]
Examination of the Association between Periodontal Disease, Tooth Loss, and Risk of Gallbladder Carcinoma : A Case- Control Study in Greek Adults
Objective: To estimate the possible association between periodontal disease (PD) clinical indices, and number of missing teeth and the risk of developing gallbladder carcinoma (GBC) in Greek adults using data from a population based case-control study.
Role of Exosomal MicroRNAs in Modulating the Response of Cancer Cells to Paclitaxel Treatment
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles in gene regulation and have been implicated in various human diseases, including cancer. MiRNAs can be packaged in exosomes and transferred between cells. These exosomal miRNAs regulate intercellular communication and influence almost all aspects of cancer biology, including proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis.
Perioperative Immune Checkpoint Blockade for Muscle-Invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer
Checkpoint inhibitors offer promise in treating muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer, but the optimal timing of their administration—neoadjuvant or adjuvant—remains unclear. To determine the efficacy of combining checkpoint inhibition with standard cisplatin-based chemotherapy, we conducted a phase II trial of neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 (αPD-1) and anti-CTLA-4 (αCTLA-4), in combination with cisplatin-gemcitabine, for patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer prior to radical cystectomy.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
