Loading

2025
Volume 3, Issue 1, p1-13
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Exploring Cell Differentiation, Induced by Inhibition of Phospholipase C/Protein Kinase C Cascade, as a Potential Therapeutic Strategy against Rhabdomyosarcoma
Nicolás Blanco, Natalia Frattini, Lucía Pronsato, Lorena Milanesi, Andrea Vasconsuelo
Among the reasons of childhood mortality, cancer is the leading cause of death. Of all paediatric cancers diagnosed, soft tissue sarcomas account for 7%, of which approximately 50% are rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS), with an incidence of 4.71 per million children and adolescents. Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is the most common soft-tissue tumour in children and adolescents. This aggressive childhood cancer originates in normal skeletal muscle from myogenic cells that have failed to fully differentiate.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p1-4 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.3.027
Pseudoaneurysm of the Breast after Diagnostic Core-Needle Biopsy: Contextualizing Impact on Treatment
Caroline Lommer, Brandy M. Griffith, Ashley P Davenport, Gary Tozbikian, Doreen M. Agnese, Sara P. Myers
This case report considers an iatrogenic pseudoaneurysm (PSA), a rare event occurring in fewer than 2% of patients, after a core-needle biopsy of the breast in a 46-year-old with stage IIIC triple negative invasive breast carcinoma on preoperative chemoimmunotherapy with the PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab. A post-biopsy MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) demonstrated a well-defined, contrast-enhancing lesion with pulsatile flow consistent with PSA.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p5-9 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.3.028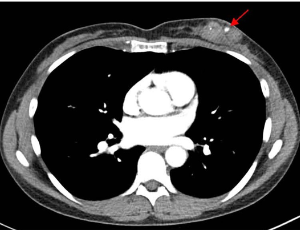
From Tiny Fish to Big Impact: Automating Zebrafish Microinjections for Cancer Research and Beyond
Yi Ding, Lasse D. Jensen, Jan de Sonneville
Zebrafish xenograft models have become indispensable in cancer biology for their capacity to recapitulate key aspects of human tumor progression in a live vertebrate system. However, widespread adoption has been constrained by the technical demands of microinjection, which require extensive training, result in operator variability, and limit scalability.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p10-13 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.3.029
Recommended Articles
Uniportal VATS Lobectomy for Lung Cancer: Feasibility and Cost Effectiveness in a Single Center Experience
In last decades, video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) together with robotic-assisted thoracic surgery (RATS) can be considered the biggest innovation in thoracic surgery. This approach drastically changed the way of performing surgical operations, improving patient’s outcome undergoing thoracic surgery.
Angioimmunoblastic T cell Lymphoma Microenvironment
Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL) is one of the most common T-cell lymphomas, second only to peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS). Initially AITL was considered a non-malignant lymphadenopathy with immune hyperactivation, nowadays being classified as a PTCL.
Searching for Easy Reliable Prognostic Parametres in Colorectal Cancer Patients Evaluation
Tumor node metastasis (TNM) staging system is the most useful method in predicting prognosis of colorectal cancer (CRC), the third most common cause of death worldwide, even if other biological markers are currently under evaluation to assess their role in affecting CRC outcome and planning the best tailored therapeutic approach. Several molecular factors are being demonstrated to be effective in influencing both overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) in CRC, acting on different aspects of tumor promoting and progression.
Impact of Cisplatin Dosing Regimens on Mammary Tumor Growth in an Animal Model
In a recent paper, we introduced a variant of the classical Simeoni tumor growth model, and illustrated its value in assessing tumor growth in a reproducible mouse model for mammary tumors. Our modification consisted of incorporating delay differential equations in the mathematical formulation of the Simeoni model, to represent the delay in drug action often observed under chemotherapeutic or immunotherapeutic regimens.
Lessons Learnt from COVID-19: How Can We Prepare for Another Pandemic?
Five months into the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. death toll from the virus has now surpassed 100,000 people. Many more cases remain nationwide, while an unknown number of patients currently harbor the virus asymptomatically. While health officials are now optimistic regarding the decline in prevalence and number of deaths due to COVID-19 and the possibility of a vaccine by the fall, we cannot lose sight of the bigger picture: the next pandemic.
VA-Radiation Oncology Quality Surveillance Program: Enhancing Quality Measure Data Capture, Measuring Quality Benchmarks and Ensuring Long Term Sustainability of Quality Improvements in Community Care
Delivery of high-quality cancer care improves oncologic outcomes, including survival and quality of life. The VA National Radiation Oncology (NROP) established the VA Radiation Oncology Quality Surveillance Program (VAROQS) which has developed clinical quality measures (QM) as a measure of quality indices in radiation oncology. We sought to measure quality in community care, assess barriers to data capture, and develop solutions to ensure long term sustainability of continuous quality improvement for veterans that receive dual care, both within the VA and in non-VA community care (NVCC).
Reduced BCR Signaling and a Metabolic Shift Accompanies Malignant Progression of Follicular Lymphoma: A Lesson from Transcriptomics
In the manuscript entitled “The ion channels and transporters gene expression profile indicates a shift in excitability and metabolisms during malignant progression of Follicular Lymphoma”, we reported recent advances in our understanding of how the gene expression profile of ion channels and transporters (ICT-GEP) contributes to identify specific signatures associated with Follicular Lymphoma (FL), with those FL that acquire chemoresistance after a relapsing-remitting course, and with the more aggressive Diffuse Large Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL), which in some cases represent the evolution of FLs.
The Challenge of Cognitive Dissonance in the Delivery of Precision Medicine in Veterinary Oncology
The use of molecular and genomic analysis of a cancer as a means to define a patient-specific treatment is interchangeably referred to as Precision Medicine, Personalized Medicine, or Genomically-directed medicine (herein, collectively PMED). In the foregoing commentary we have focused on PMED approaches related to treatment selection and do not prioritize the development of novel molecular assays used to guide patient diagnostics or prognostication.
Synthetic Lethal Drug Combinations Targeting Proteasome and Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in TP53-Mutated Cancers
Background: We have recently published SL-BioDP, a web resource for querying, exploration and visualization of potential synthetic lethal targets and possible synergistic drug combinations for 18 cancer types. Methods: From our predictive synthetic lethality model used in SL-BioDP, we inferred TP53 mutation lead to potential synergistic drug combination of Bortezomib and Vorinostat. Here we show, how to extrapolate the drug combination results by combining drug screening data from cancer cell lines and showed the potential synergy of the drug targets, proteasome, and histone deacetylase (HDAC) pathways respectively, for patient survival advantage.
Prognosis and Survival of Medullary Carcinoma of the Breast
Medullary breast carcinoma (MBC) is a rare tumor, representing 3% to 5% of invasive breast carcinomas. The World Health Organization defines it as a well-circumscribed invasive tumor, composed of poorly differentiated cells, arranged in sheets, without gland formation and a scarce collagen stroma with the presence of a very prominent lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate.
Role of the Gut Microbiome in the Modulation of Cancer Immunotherapy Response
The gut microbiome or gut flora is a vast community of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and fungi that inhabit the digestive tract of the human and other animals. In the human body, bacterial species colonize into the oral cavity, skin, vagina, and placenta, however, the largest population of microorganisms resides in the intestine. The majority of gut microbiota belong to the phyla Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria.
Prognostic Role of Human Epididymis Protein 4 (HE4) in Ovarian Cancer Treatment: Our Point of View
In the last 10 years, the marker “Human Epididymis protein 4 (HE4)” for the management of gynecological tumors has entered powerfully in the world literature. At the moment, carrying out an accurate research in the main scientific portals such as PubMed, we can find more than 2,000 works concerning Cancer antigen-125 (Ca125), but those concerning HE4 are less than 400. The assessment of the prognostic significance of Ca125 has been described in more than 1000 scientific papers, whereas in the case of HE4 such works are only about 100.
Can Filtration Technology Advance Culture of Circulating Tumor Cells towards Precision Medicine?
Expansion of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTC), the metastatic seeds of cancer in the blood stream, holds great potential in clinical application, especially towards precision medicine. Given the relatively rare nature of CTCs, their culture remains to be a significant challenge. When developing technologies for CTC culture, there are key elements that need careful consideration, including the speed of culture, compatibility with downstream analysis, and the implementation of the technology into established clinical daily routines. Herein, we briefly discuss the implications of our recent report of an ultrathin filter for the capture and culture of circulating colon cancer cells.
Influence of Clinical Risk Factors on Outcomes in Men with Stage I Non-Seminomatous Germ Cell Tumor Undergoing Robot-Assisted Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection
We recently published our multi-institutional experience performing primary robot-assisted retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RA-RPLND) for men with non-seminomatous germ cell tumor (NSGCT). We concluded that primary RA-RPLND for NSGCT can be performed safely with low complication rates, acceptable early oncologic outcomes, and lower overall theoretical chemotherapy burden. In this commentary, we explore outcomes in clinical stage I patients stratified by clinical risk factors (RF) and estimate reductions in chemotherapy burden.
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer worldwide, affecting nearly one in eight women. Accurate cancer staging is essential for determining the patient’s prognosis and for choosing the appropriate treatment. The staging system most often used is the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM system, where T refers to the size of the tumor, N refers to spread of the primary cancer to nearby lymph nodes, and M refers to the spread of metastasis to distant sites in the body.
Forces, Chromosomal Configurations, and Carcinogenesis: Towards Another Therapeutic Approach
Previous studies of in vitro and in vivo morphogenesis may suggest a more inclusive principle governing biological processes. In this regard, methylglyoxal (MG) in very low, non-toxic concentrations and ascorbic acid have been shown to promote in vitro morphogenesis in various types of plants. Forces of cohesion and adhesion might be involved in such development. These are conveyed through the electronic desaturation of protein by means of MG and ascorbic acid.
Botulinum Toxin: The Promising Future of Prostate Cancer Treatment
Peripheral nerves have been shown to modulate the growth and spread of tumours in the prostate, feeding both cancer cells and the stroma in the tumour environment. Several in vitro and in vivo studies have reported the effect of botulinum toxin (BT) on tumour tissue in the prostate. BT in humans has been observed to cause increased apoptosis of cancer cells, with morphological changes characterized by extensive degenerative and atrophic areas of cancer, reduced cytoplasm, and pyknotic nuclei, compared to the characteristics of cancer tissues injected with saline solution.
Radical Radiotherapy of Locally Advanced Cervix Uteri Carcinoma
External beam radiotherapy with concomitant platinum-based chemotherapy followed by brachytherapy is defined as radical radiotherapy of cervix uteri carcinoma. Radical radiotherapy is the gold standard treatment for locally advanced cervix uteri carcinoma. The rates of survival and treatment-related adverse events in patients with cervix uteri carcinoma are affected by both stage of disease and treatment. Both should be optimal in proportion to the available facilities. Here, recommendations from the current literature are presented.
The Emerging Role of Pyruvate Kinase M2 in Regulating Glutaminolysis via c-Myc
The dimer form Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) possesses lower glycolytic ability compared to its terameter form. This is of great importance for cancer cells since dimer PKM2 increases the levels of glycolytic intermediates for cell proliferation and growth. Accumulating evidence has also revealed that dimer PKM2 has many non-glycolytic functions including acting as a transcription factor and protein kinase. Our recent work has uncovered a novel non-glycolytic function of dimer PKM2. PKM2 coordinates the switch between glycolysis and glutaminolysis in cancer cells.
Surgery Versus Radiation Therapy for Early-Stage Lung Cancer: Patient Selection is Crucial
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer related death in the United States with mortality rates surpassing breast, prostate, brain, and colorectal cancers combined. Recent data shows that susceptibility for both men and women for developing invasive lung and bronchogenic carcinoma peak after the age of 70 years.
