Loading
Journal of Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials
ISSN: 2692-630X
2023
Volume 4, Issue 2, p38-93
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Theoretical Investigations of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Jing Chen, Andreas L. Vishart, Stephan P. A. Sauer, Kurt V. Mikkelsen
This presentation considers theoretical investigations of dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSC). Theoretical methods were applied to investigate the interactions between titanium dioxide nanoparticles and sensitizers. The ONIOM model was used to obtain the geometries of different conformers of dye molecules with TiO2 and their binding energies. TD-DFT calculations were carried out to obtain the absorption spectra and the relative orbital energy levels of sensitizers and TiO2.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p38-54 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.4.042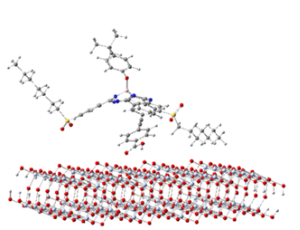
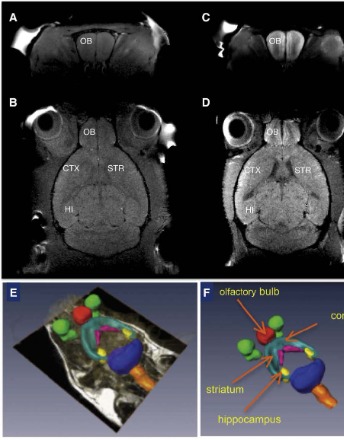
Key Features in the Design and Function of Nanocarriers for Intranasal Administration of Gene Therapy in Huntington Disease
Oksana Fihurka, Stephen Aradi, Vasyl Sava, Juan Sanchez-Ramos
A major obstacle to fulfilling the therapeutic promise of gene therapies for hereditary brain diseases, such as Huntington’ Disease (HD), is the requirement for viral vectors and/or an invasive delivery system (stereotaxic injection into brain or infusion into the intrathecal space). HD is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disease for which several clinical trials have demonstrated gene-lowering effects following intrathecal administration.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p55-69 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.4.043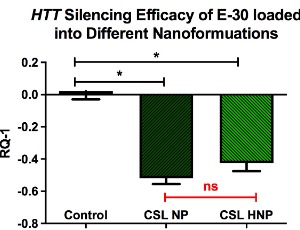
Immobilized Cell Bioreactor Industrialization in the Development of an Innovative Optical Biosensor Technology
Athanasios A. Koutinas, Theano Petsi, Athanasia Panitsa, Maria Kanellaki
This commentary shows the development of a new optical biosensor, based on cell immobilization of Pseudomonas Fluorescens HK44, in nano and micro-tubular cellulose (TC) and a mixture of carbohydrate nanotubes (CHNTs) and carbohydrate micro-tubes (CHMTs). Methodology follows, this biocatalyst can be industrialized with the use of a single tank immobilized cell bioreactor (ICB).
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p70-74 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.4.044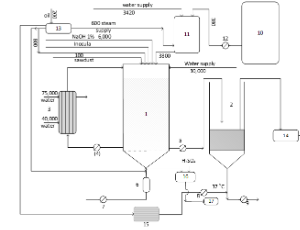
Oxidation and TD-DFT of Toxic Acriflavine Hydrochloride Dye by Potassium Permanganate in Neutral Media: Kinetics and Removal of Dyes from Wastewater
Samia M. Ibrahim, Ahmed F. Al-Hossainy, Hazim M. Ali, Mohamed Abd El Aal, Nasser Farhan
Fabrication of dye thin films is accomplished through physical vapor deposition with a thickness of 150 ± 5 nm. Kinetically, the reduction of permanganate ion as a multi-equivalent oxidant by acriflavine hydrochloride (ACFH) in a neutral medium has been studied spectrophotometrically. In the presence of a pseudo-first-order reaction, the experimental results suggest fractional first-order kinetics in [ACFH] and a first-order dependency in [MnO4-].
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p75-88 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.4.045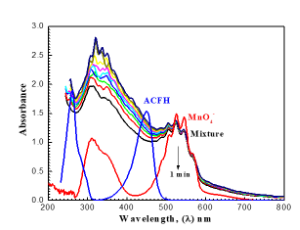
Enhanced Structural and Morphological Properties of Doped Cobalt Zinc Ferrite
Asmaa Reda Abd El-Salam, K. E. Rady, Ezzat A. ELFadaly, Mobarak Hassan Aly
In this study, Mn2+ substituted Co0.8−x Mnx Zn0.2 (where x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3) ferrites are prepared by a coprecipitation method to study the effect of Mn2+ions on the structural and morphological properties. These ferrites are characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), and Fourier transform infrared. X-ray diffraction patterns of the prepared samples confirm partial substitution of Mn2+ ions that does not change the basic structure of Co0.8 Zn0.2 Fe2O4.
J Nanotechnol Nanomaterials, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p89-93 | DOI: 10.33696/Nanotechnol.4.046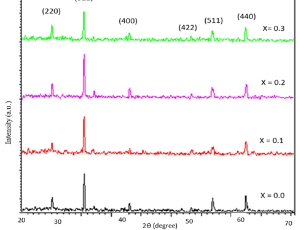
Recommended Articles
Escherichia coli Stress, Multi-cellularity, and the Generation of the Quorum Sensing Peptide EDF
Bacterial communication via quorum sensing (QS) molecules, as well as toxin-antitoxin (TA) gene modules located on bacterial chromosomes are well-studied mechanisms. Escherichia coli mazEF is a stress-induced TA system mediating cell death requiring a QS extracellular death factor (EDF), the pentapeptide NNWNN. MazF is an endoribonuclease specific for ACA sites. During adverse conditions, the activated MazF generates a stress induced translation machinery, composed of MazF-processed mRNAs and selective ribosomes that specifically translate these processed mRNAs.
Constitutively Active Death Receptor Induces Apoptosis in Mammalian Cells
Apoptosis is a physiological response in development and homeostasis of metazoans. Apoptosis is triggered during pathological events as a means to renew affected tissues and eliminate cancer cells. The immune system regulates the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis, where signals such as TNFα or displayed ligands on the surface of immune cells trigger signal cascades by death receptors present on targeted cells.
Chimeric Antigen Receptor CAR NK Cells Emerging Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Cancer
Although NK cells are recognized as effector lymphocytes of the innate immune system, they also regulate the adaptive immune response by releasing inflammatory cytokines and developing immunological memory. Unlike other lymphocytes such as T or B cells, NK cells do not express rearrangeable, antigen-specific receptors.
Flow Cytometric Characterization of Accidental Cell Death Highlights Connections to Regulated Cell Death
Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs) are known by their nature to cause inflammatory responses in numerous disease states from cancer, trauma to age related diseases (e.g. atherosclerosis, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases), these molecules are released by cells undergoing cell death.
Angioimmunoblastic T cell Lymphoma Microenvironment
Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL) is one of the most common T-cell lymphomas, second only to peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS). Initially AITL was considered a non-malignant lymphadenopathy with immune hyperactivation, nowadays being classified as a PTCL.
Circulating Cell-Free RNA: A New Perspective for Endometrial Cancer
In order to implement the knowledge of cancer to monitor its evolution and setting, in the last decade, new minimally invasive and repeatable samples collection have been developed such as liquid biopsy.
The Potential Role of SEPT6 in Liver Fibrosis and Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Liver fibrosis is a reversible wound-healing response in which a variety of cells and factors are involved in and results in excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM). Cirrhosis is one of the significant causes of portal hypertension and end-stage liver disease, and it is the 14th most common cause of death around the world. Approximately 1.03 million people worldwide die from liver cirrhosis every year.
Prognostic Utility of Ferritin Transferrin Ratio in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
There is growing body of literature to identify novel prognostic markers in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), including serum ferritin (SF), transferrin levels, alfa fetoprotein (AFP), and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR). Chronic inflammation and fibrogenesis are considered quite essential in the oncogenesis of HCC. The trigger for this inflammation could range from viral hepatitis, alcoholic cirrhosis, to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Also, iron overload as in hereditary hemochromatosis is linked to one of the factors for HCC oncogenesis.
Can Filtration Technology Advance Culture of Circulating Tumor Cells towards Precision Medicine?
Today, cancer is the second leading cause of death, with about 9.6 million deaths globally in 2018 [1]. At the end of the 19th century, Paul Ehrlich contributed a milestone to cancer research by introducing chemotherapy as a promising tumor treatment approach. Since then, cancer treatment has undergone tremendous advances, with chemotherapy still being a widely used cancer treatment method today, however, often associated with severe side effects.
Influence of Clinical Risk Factors on Outcomes in Men with Stage I Non-Seminomatous Germ Cell Tumor Undergoing Robot-Assisted Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection
Retroperitoneal lymph nodes are often the first landing site of metastatic disease in men with testicular cancer. Primary retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) for clinical stage I NSGCT can accurately surgically stage patients who may have nodal micrometastases, and in some cases, can serve as the primary therapy when volume of metastasis is low.
Commentary on “Integrative Transcriptomics, Proteomics, and Metabolomics Data Analysis Exploring the Injury Mechanism of Ricin on Human Lung Epithelial Cells”
Ricin toxin (RT) is classified as a potential bio-threat agent in assassinations and terrorism due to its extreme toxicity. Due to aerosol RT exposure is the most lethal route, it is urgent to study its injury mechanism.
Primary Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of Bladder – A Rare Diagnostic Entity
Primary small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the urinary bladder is a rare histological type shows poor differentiation and behaves in a highly aggressive manner. It accounts to 0.3- 0.7% of all bladder tumors [1,2]. Neuroendocrine carcinomas predominantly occur in respiratory and gastrointestinal tract and very rarely in the urinary bladder.
Pseudothrombocytosis Due to Red Blood Cell Fragmentation in Haemoglobin-H Disease
Red cell membrane in patients with haemoglobin H (Hb-H) disease and other haemoglobinopathies is rigid and thus red blood cells are fragmented during passage through narrow capillary beds, especially through the splenic sinusoids and the liver [1,2]. These fragments are frequently seen in peripheral blood films.
Cardiac Stem Cell Therapy, Quo Vadis
Cardiovascular disease causes 30% of global mortality and is still the number one cause of death worldwide. A main patho-physiological process is the coronary disease leading to malperfusion and ischemic cardiac disease as well as cardiac infarction.
Commentary on “Epigenetically Altered T Cells Contribute to Lupus Flares”
The recently published manuscript entitled “Epigenetically Altered T Cells Contribute to Lupus Flares” summarizes recent advances in our understanding of how the environment alters the immune system to cause flares of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in genetically predisposed people, and why it affects women approximately 9 times more often than men
Galectin 3 and Glial Cells of the CNS: A Fruitful Crosstalk with Remyelinating Potential
Galectin-3 (Gal-3), the only chimera-like galectin, has three structural domains: (a) the NH2 terminal domain containing serine phosphorylation, important for nuclear localization, secretion and oligomerization; (b) a sequence susceptible to metalloprotease (MMP) cleavage; and (c) a C-terminal domain containing the carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD) and an anti-death motif.
Leucocyte-Tumor Cell Hybridization Can Initiate Cancer Metastasis
According to estimates from the International Agency for Research on Cancer, by the year 2030 there will be 22 million new cancer cases and 13 million deaths per year. The main reason for death from cancer is not the initial tumor but it’s metastasis to distant parts of the body, yet this process has remained poorly understood for quite some time.
Proteomic Functional Signatures during the Priming of Human Th17 Cells
A combination of regulated responses toward pathogens and minimized autoimmune reactions is needed for the balanced function of the immune system. Amongst the immunologically important CD4+ lymphocytes, T helper 17 (Th17) cells help maintain homeostasis and provide protection against pathogens of fungal or bacterial origins
Gene Therapy for Sickle Cell Disease: Start of a New Era
This manuscript reviews treatment of Sickle Cell disease over time. The application of allogeneic stem cells proved the sickle cell disease could be permanently corrected and cured but limited to those with a compatible donor.
Dual Expression of GARP in Immune and Glioma Cells: Yet Another Mechanism of Cancer Immune Escape
Glioblastomas (GB) are amongst the most lethal human tumors exhibiting a highly aggressive behavior manifested by tumor cell infiltration into surrounding tissue. Furthermore, GBs are notorious for their high degree of resistance to cytotoxic treatments [1-3].
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
