Loading
Journal of Diabetes and Clinical Research
ISSN: 2689-2839
Latest Articles
Discriminatory Ability of Adiposity Phenotypes in Identifying Cardiometabolic Disorders in Indigenous and Non-indigenous African Populations
Clement Nyuyki Kufe , Jean Claude Mbanya
A population-based cross-sectional study recruited 1921 participants from the settled Fulani, nomadic pastoral Fulani and the general population. Body weight (BW), height, waist circumference (WC), and hip circumference (HC) were measured and body mass index (BMI), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), waist-to-height ratio (WHtR), Conicity Index (Cindex), body adiposity index (BAI), body roundness index (BRI) and body shape index (ABSI) were determined. The associations of anthropometric indices with cardiometabolic disorders were assessed by multivariable adjusted logistic regression and the area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve compared the predictive abilities.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 1, p1-18 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.065
Enhancing Clinical Collaboration: Interface Linking between Laboratories and Clinics for Translational Healthcare
Pradeep Kumar Dabla , Harleen Kaur Sethi
Clinical laboratories are pivotal in modern healthcare, providing essential diagnostic information that influences patient management and healthcare efficiency. Technological advancements and economic pressures have continuously shaped laboratory medicine, leading to significant transformations in diagnostic capabilities. This article explores the evolving role of clinical laboratories, emphasizing their impact on disease prevention, early diagnosis, and patient safety.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 1, p19-21 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.066
Decline in Physical Activity after Age 35 Increases the Risk of Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Diabetes: A Cross-sectional Analysis of the MIDUS Study
Tomoya Sato
Data were analyzed from 1,395 participants in the Midlife in the United States (MIDUS) study, including biomarker subsamples. Participants reported their physical activity levels during young adulthood and currently (≥ 20 min, three times per week). Participants were categorized as persistently active, increased, decreased, or persistently inactive. Obesity was defined as body mass index (BMI) ≥ 30 kg/m², insulin resistance by HOMA-IR ≥ 2.8, and diabetes by self-reported diagnosis. Multivariable logistic regression was used to assess associations.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 1, p27-37 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.068
Inhibition of Sortilin Improves Retinal Function in Diabetic Mice Through Decreased Inflammatory Mediators
Li Liu , Youde Jiang , Robert Wright , Mohamed Al-Shabrawey , Jena J. Steinle
Inflammation is a key factor in retinal damage in response to diabetes. Sortilin represents a new regulator of retinal inflammation. Sortilin is involved in over 50 different signaling cascades. To investigate sortilin in the diabetic retina, we first measured protein levels in retinal lysates from diabetic humans and diabetic mice. We then inhibited sortilin using a small molecule inhibitor, AF38469, and evaluated retinal function using electroretinogram (ERG) and fluorescein angiography.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 1, p44-51 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.070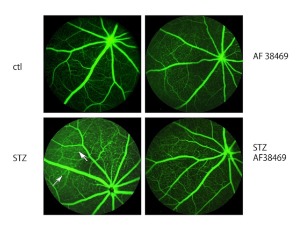
BCG Immunotherapy: Promising Protection from COVID-19 and Other Infectious Diseases in Type 1 Diabetics
Denise L Faustman , Miriam Davis , Willem M Kuhtreiber
Individuals with type 1 diabetes are more vulnerable than the general population to morbidity and mortality from infectious disease, including COVID-19. Over the last 20 years, the >100-year-old tuberculosis vaccine, known as Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG), has been observed in global populations to protect from viral, bacterial and parasitic infections, among others.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 1, p38-43 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.069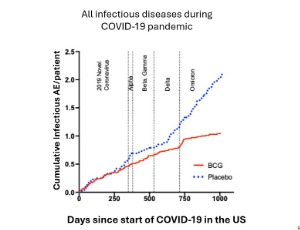
From Seed to Solution: Expert Insights on Sesame’s Role in Diabetes and Beyond
Ali Jafari
Sesame (Sesamum indicum L) has garnered attention for its potential in diabetes management due to its rich bioactive compounds, including sesamin, sesamolin, and unsaturated fatty acids. This commentary explores recent advances in sesame research, emphasizing its role in improving glycemic control, lipid profiles, inflammation, and oxidative stress, as evidenced by a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mechanistic insights reveal sesame’s effects on PPARα activation, Nrf2 signaling, and NF-κB suppression, which underpin its metabolic benefits.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 1, p52-59 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.071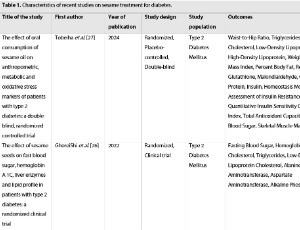
Management of Metabolic Diseases: From Reactive Care to Preventive Strategies
Gundu H. R. Rao
Metabolic diseases such as hypertension, obesity, diabetes, and vascular disorders have reached epidemic proportions worldwide [1–6]. Despite major advances in medicine, cardiovascular disease has remained the leading cause of death for more than a century. Among these disorders, diabetes mellitus stands out as a major contributor to morbidity and mortality, placing a heavy burden on patients, healthcare systems, and economies.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 1, p60-62 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.6.072
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
