Loading
Journal of Diabetes and Clinical Research
ISSN: 2689-2839
Most Read Articles
Can Vitamin D Supplementation Reduce Insulin Resistance and Hence the Risks of Type 2 Diabetes?
Barbara J Boucher
The question of whether or not correction of vitamin D deficiency might reduce the risks of later type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has been under debate for many decades. The necessity of vitamin D for normal insulin secretion was first identified experimentally in the 1980s.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 1, p1-8 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.011
Validation of a New Test for Assessing the Quality of Life Perceived in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
Pala L , Cosentino C , Acciaioli S , Dicembrini I , Lazzeretti L , Rotella F , Mannucci E
The World Health Organization defines quality of life (QoL) as “the perception that an individual has of his life, in the context of the culture in which he lives, integrating personal goals, expectations and concerns, well-being and discomfort”.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 1, p9-16 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.032
Vitamin D and Insulin Resistance in Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia-a Commentary and Natural Expansion
Alan Sacerdote
In our previous focused review, the journal emphasized Type 2 diabetes (T2DM), excluding intimately associated disorders that should be considered integral components of the insulin resistance (IR) syndrome e.g., polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH), and gout.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 1, p17-27 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.033
Altered Peak C-peptide and Fasting Blood Glucose in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Mengxiang Zhang , Rui Ding , Zuqun Wang , Juan Zhang , Jing Liu , Juan Wang
ASD refers to a group of complex neurodevelopmental disorders, characterized by deficits in social communication, interaction and demonstrating restricted, repetitive, and stereotyped patterns of behavior. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention forecasted that the prevalence of ASD would be 1 in 45 in USA.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p43-52 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.008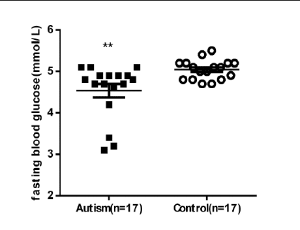
Plasma Non-Esterified Fatty Acids (NEFA) in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Evidence on Pathophysiology
Kailash Chandra , Vineet Jain , Swatantra Kumar Jain
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a metabolic dysfunction characterized by elevated levels of blood glucose as well as impaired lipid and protein metabolism. The mobilization of fatty acids is augmented in insulin resistance due to the failure of lipolysis inhibition by the hormone that further augments the increase in plasma NEFA levels.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 2, p46-50 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.3.037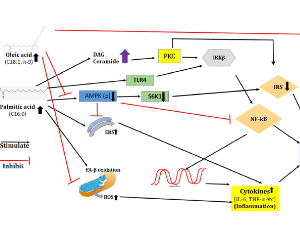
The Diabetic Shoulder – A Literature Review
Sana’a A. Alsubheen , Joy C. MacDermid , Tom J. Overend , Kenneth J. Faber
The shoulder complex is composed of three bony structures: the clavicle, scapula, and humerus, which are connected to form three synovial (glenohumeral, acromioclavicular, and sternoclavicular) and two functional (scapulothoracic and subacromial) joints.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p59-70 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.010
Risks and Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy in Children and Young People with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Rebecca Louise Thomas , Sze May Ng
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is associated with microvascular and macrovascular complications.Duration of diabetes, poor glycaemic control, high blood pressure and proteinuria are reported risk factors contributing to the development of diabetes related complications.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 3, p68-74 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.021
Improved Wound Closure Rates and Mechanical Properties Resembling Native Skin in Murine Diabetic Wounds Treated with a Tropoelastin and Collagen Wound Healing Device
Robert S. Kellar , Robert B. Diller , Aaron J. Tabor , Dominic D. Dominguez , Robert G. Audet , Tatum A. Bardsley , Alyssa J. Talbert , Nathan D. Cruz , Alison L. Ingraldi , Burt D. Ensley
Chronic, non-healing, or slow to heal wounds present a significant and growing health problem in the United States, with an estimated 6.5 million people affected, at an annual cost of US $20 billion, with the highest risk groups represented by the elderly and the increasing prevalence of lifestyle diseases such as diabetes and obesity.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 3, p86-99 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.024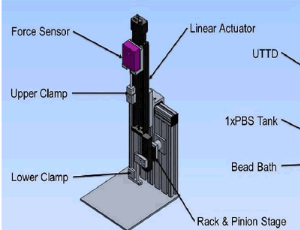
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
