Loading
Journal of Cellular Immunology
ISSN: 2689-2812
2023
Volume 5, Issue 1, p1-21
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Intracellular Hyaluronan Synthesis Impairs Hematopoiesis in Diabetes that can be Prevented by Heparin
Andrew Jun Wang, Vincent Charles Hascall
Hyperglycemia in diabetes induces impairment of hematopoiesis, an important consequence in bone marrow (BM) that contributes to chronic complications in advanced diabetes. The alterations to blood cells associated with diabetes mellitus (DM) pathologies have been carefully and extensively documented, but the underlying mechanism(s) is still unclear. Our recent publication indicates that aberrant intracellular synthesis of hyaluronan (HA) by hyperglycemic dividing BM progenitors is the central mechanism involved.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p1-6 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.155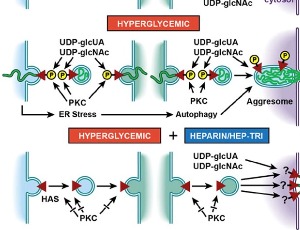
Role of Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) in Immune Regulation and Neuroprotection
John Dumbuya, Howard Prentice, Jang-Yen Wu
Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) has been in clinical use for over two decades to enhance hematopoiesis and granulopoiesis to increase the numbers of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells in patients with neutropenia and patients involved in bone marrow transplantation. G-CSF protein or G-CSF gene therapy has also been shown to have both neuroprotective and neurogenesis function and is quite effective in improving neurological functions in Parkinson’s disease [1], stroke [2-4] and Alzheimer’s disease [5].
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p7-9 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.156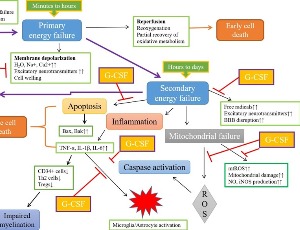
Importance of Ultrasensitive ELISA in Cancer Research
Daiki Makioka, Kanako Iha, Etsuro Ito
The ultrasensitive ELISA method developed by Watanabe and Ito combines sandwich ELISA and thio-NAD cycling to enable the quantitation of trace amounts of proteins. The ultra-traceability provided by this method makes it possible to quantify extremely small amounts of proteins in small extracellular vesicles called exosomes as well as in urine.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p10-13 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.157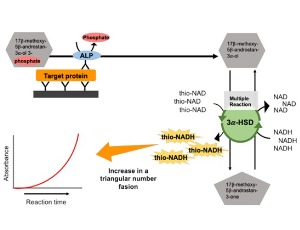
From Lipase Elevation to Diabetes – Pancreatic Involvement during Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
Sonja C. S. Simon, Jochen S. Utikal
Nowadays, as a standard of care treatment of several cancers, immune checkpoint inhibitors have changed the field of oncology. However, their empowerment of T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity bears the risk for injury of various organs as a side effect.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p14-18 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.158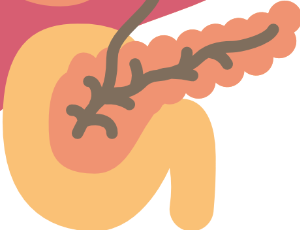
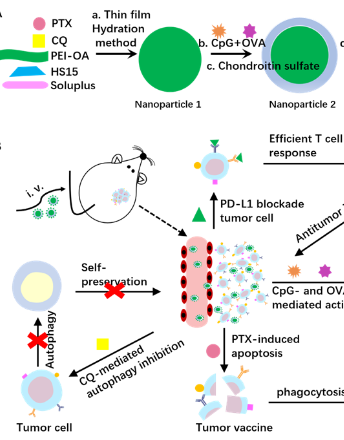
Towards a Chemo-immunotherapy to Improve Breast Cancer Immunotherapy
Xia Li, Lixin Ma, Yunhong Hu
Chemo-immunotherapy has shown great promise as a next-generation treatment strategy for established solid tumors. Cheng et al. first developed the PD-L1- and CD44-responsive multifunctional nanoparticles (MNPs) utilizing a polymer complex of polyethyleneimine and oleic acid (PEI-OA) and loaded with two chemotherapeutic drugs (paclitaxel and chloroquine), an antigen (ovalbumin), an immunopotentiator (CpG), and an immune checkpoint inhibitor (anti-PD-L1 antibody).
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 1, p19-21 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.159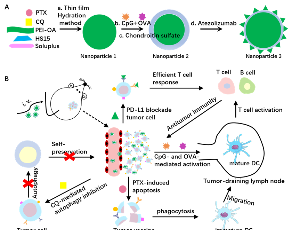
Recommended Articles
Prevalence of Symptom Clusters in Cancer Patients at First Presentation in Palliative Care Clinic as per Different Disease Groups
Cancer has its own disease burden and patients usually suffer from symptom clusters when they are referred for palliative treatment. Identification of symptom cluster trajectories will help clinician to take into account measures that can optimize quality of life of palliative patients. Therefore the aim of this paper is to determine the overall prevalence of symptoms and symptoms clusters in different disease groups according to etiology at the time of first visit to Palliative care clinic by using HIS Palliative First Assessment note indicating Edmonton symptom scale.
Chimeric Antigen Receptor CAR NK Cells Emerging Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Cancer
Although NK cells are recognized as effector lymphocytes of the innate immune system, they also regulate the adaptive immune response by releasing inflammatory cytokines and developing immunological memory. Unlike other lymphocytes such as T or B cells, NK cells do not express rearrangeable, antigen-specific receptors.
Emerging Role of TRPML1 Mucolipin Endolysosomal Channel in Cancer
The transient receptor potential mucolipin 1 (TRPML1) is an endolysosomal channel belonging to the TRP family. Clinically, mutations of TRPML1 have been responsible for a severe lysosomal storage disorder called mucolipidosis type IV.
Uniportal VATS Lobectomy for Lung Cancer: Feasibility and Cost Effectiveness in a Single Center Experience
In last decades, video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) together with robotic-assisted thoracic surgery (RATS) can be considered the biggest innovation in thoracic surgery. This approach drastically changed the way of performing surgical operations, improving patient’s outcome undergoing thoracic surgery.
Circulating Cell-Free RNA: A New Perspective for Endometrial Cancer
In order to implement the knowledge of cancer to monitor its evolution and setting, in the last decade, new minimally invasive and repeatable samples collection have been developed such as liquid biopsy.
Searching for Easy Reliable Prognostic Parametres in Colorectal Cancer Patients Evaluation
Despite the advances in diagnostic and therapeutic field, colorectal cancer (CRC) still remains the third most common cause of death worldwide, with more than 600,000 cancer-related deaths per year.
Multidisciplinary Acute Care of Central Retinal Artery Occlusion with a Stroke Paradigm: A Call to Action
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is a painless ophthalmologic emergency with potential for irreversible vision loss. Similar to ischemic stroke, CRAO occurs when there is sudden obstruction of the central retinal artery, leading to ischemic injury to the retina and subsequent cell death. Continuous occlusion and ischemia of the retina progresses to permanent damage to retinal cells and loss of vision.
Deubiquitinase as Potential Targets for Cancer Immunotherapy
During the last few decades, immunotherapy is considered to be an important approach to help our immune system to fight various kinds of diseases, such as tumor. Sometimes, it works very well for some types of cancers, for example: bladder cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer and lymphoma.
Synthetic Lethal Drug Combinations Targeting Proteasome and Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in TP53-Mutated Cancers
Tumors harboring mutations in certain oncogenes are often dependent on activation of certain pathways which becomes essential for the survival of the cancer cells. This condition is formally known as synthetic lethality, a state when simultaneous loss of two genes is lethal to a cancer cell, while the loss of the individual genes is not.
Role of the Gut Microbiome in the Modulation of Cancer Immunotherapy Response
The gut microbiome or gut flora is a vast community of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and fungi that inhabit the digestive tract of the human and other animals [1,2]. In the human body, bacterial species colonize into the oral cavity, skin, vagina, and placenta, however, the largest population of microorganisms resides in the intestine.
Do Support Vector Machines Play a Role in Stratifying Patient Population Based on Cancer Biomarkers
Cancer is a worldwide public health issue that affects millions of people every year. In 2018 there were 17 million newly documented cases of cancer globally (8.8 million in men and 8.2 million in women), leading to 9.6 million deaths. Cancer is a vastly heterogeneous disease, with over 100 different types of cancer currently identified in humans; the most common types of cancer are lung, female breast, bowel and prostate, these four types account for more than 40% of all new cancer case
Prognostic Role of Human Epididymis Protein 4 (HE4) in Ovarian Cancer Treatment: Our Point of View
In the last 10 years, the marker “Human Epididymis protein 4 (HE4)” for the management of gynecological tumors has entered powerfully in the world literature. At the moment, carrying out an accurate research in the main scientific portals such as PubMed, we can find more than 2,000 works concerning Cancer antigen-125 (Ca125), but those concerning HE4 are less than 400.
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer worldwide, affecting nearly one in eight women. Accurate cancer staging is essential for determining the patient’s prognosis and for choosing the appropriate treatment.
Platelet Hyperactivity and Dysfunction in Diabetes and Cancer
However, the entire coagulation cascade is dysfunctional, in progressed chronic diabetes and cancer patients.
Development of HPV 16/18 E6 Oncoprotein Paperbased Nanokit for Enhanced Detection of HPV 16/18 E6 Oncoprotein in Cervical Cancer Screening
According to global cancer statistics GLOBOCAN, carcinoma of cervix is ranked as the fourth most common malignancy among women worldwide with an estimation of 570,000 cases and 311,000 deaths in 2018. It is the second most common female malignancy in Lowand- Middle Income Countries (LMICs). In Kenya, the prevalence is 25 cases per 100,000 women. Approximately 75% cases of cervical cancer are caused by persistent infections of the cervical mucosal epithelium with carcinogenic types of human papillomaviruses (HPVs) mainly 16 and 18.
Gastric Cancer: A Brief Review, from Risk Factors to Treatment
Gastric cancer (GC), also known as stomach cancer, is a worldwide health problem. Anatomically, it can occur from the gastroesophageal junction to distal portions of the stomach. Considering both sexes, worldwide, it is the 5th most common neoplasm (5.7%) and the 3rd cause of mortality among malignancies, leading to approximately 782,000 deaths in 2018. The incidence varies geographically but 50% of new cases are diagnosed in developed countries. High incidence is observed in Asia, Latin America, and in the central and eastern parts of Europe. There are several ways to classify GC, but the most used is Lauren’s Classification, which proposes two main histological groups: intestinal and diffuse. This classification is important because there are marked etiological, pathological, and epidemiological differences between the subgroups, guiding the clinical approach for each patient.
Botulinum Toxin: The Promising Future of Prostate Cancer Treatment
Botulinum toxin (BT) is a potent poisonous neurotoxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum and related species [1]. Its action consists of inhibiting neuromuscular junctions by blocking the release of acetylcholine and desensitizing sensory nerves.
Safety and Efficacy of s-MOX Regimen in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Who Developed Cardiotoxicity Following Fluoropyrimidine Administration: A Case Series
5-fluorouracil (5-FU), an antimetabolite in the fluoropyrimidine class, is the third most commonly used chemotherapeutic agent worldwide for the treatment of solid malignancies [1]. Despite advances in novel cancer therapies, commonly used in combination with fluoropyrimidines, 5-FU remains one of the most effective and safe chemotherapy agents to manage colorectal cancer (CRC).
Is Citrate A Critical Signal in Immunity and Inflammation?
When immune cells are activated, they undergo metabolic change in order to have sufficient energy to function effectively. The Krebs cycle is one of the most important pathways involved in this response and citrate, a critical component of this pathway, regulates carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Surgery Versus Radiation Therapy for Early-Stage Lung Cancer: Patient Selection is Crucial
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer related death in the United States with mortality rates surpassing breast, prostate, brain, and colorectal cancers combined. Recent data shows that susceptibility for both men and women for developing invasive lung and bronchogenic carcinoma peak after the age of 70 years.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
