Loading
Journal of Cellular Immunology
ISSN: 2689-2812
2021
Volume 3, Issue 3, p133-200
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Efferocytosis and Anthrax: Implications for Bacterial Sepsis?
Joshua S. Mytych, Zijian Pan, A. Darise Farris
Bacillus anthracis (Ba) is a gram-positive, rod-shaped, spore- and toxin-forming bacterium. While mainly an herbivore pathogen, human infection with Ba spores can occur through a number of routes including cutaneous, gastrointestinal, injectional, or inhalational.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 3, p133-139 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.090
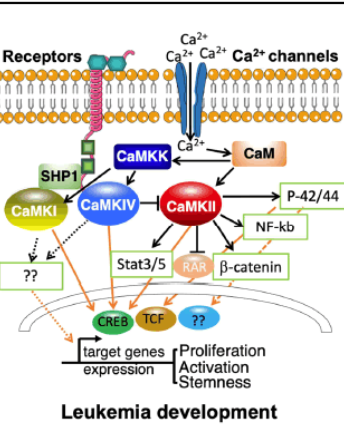
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinases in Leukemia Development
Changhao Cui, Chen Wang, Min Cao, Xunlei Kang
Calcium (Ca2+) is an intracellular universal second messenger that regulates a variety of cellular processes. Many biological processes, including gene transcription, cell cycle, migration, and apoptosis, are affected by changes in intracellular Ca2+ signaling. Disruption of normal Ca2+ signaling can cause tumorigenic phenotypes.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 3, p144-150 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.091
Promoter Reporter Systems for Imaging of Cells Transplanted into Post-infarcted Heart
Katarzyna Fiedorowicz, Maciej Kurpisz
Recently, stem/progenitor cell therapies have been intensively pursued. An increasing body of evidence has shown the promising results with respect to transient recovery of cardiac function in a variety of animal models with the use of stem cells interventions.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 3, p151-155 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.092
Duration of SARS-CoV-2 Infectivity
Seitz Tamara, Kelani Hasan, Wenisch Christoph, Laferl Hermann
The ongoing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic led to a high number of deaths worldwide as well as an overload of healthcare systems and an economic collapse. One of the reasons can be attributed to the lack of knowledge about the duration of infectivity at the beginning of the pandemic, resulting in hospital isolation of patients and
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 3, p156-163 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.093
Unconventional Approaches to Direct Detection of Borreliosis and Other Tick Borne Illnesses: A Path Forward
Lance Liotta, Alessandra Luchini
The current COVID-19 pandemic has brought to public attention the conceptual difference between a test for COVID-19 derived RNA or proteins indicating the presence of an active infection, versus COVID-19 serology testing indicating pathogen infection. Only the former test for molecules derived from COVID-19 provides reliable
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 3, p164-172 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.094
Increased Binding Affinity of Furin to D614G Mutant S-glycoprotein May Augment Infectivity of the Predominating SARS-CoV-2 Variant
Sardar Sindhu, Rasheed Ahmad, Fahd Al-Mulla
The coronavirus disease (COVID)-19 pandemic has profoundly devastated human health and wellbeing all over the world, along with colossal setback to global economy in terms of soaring new infections, hospitalizations, ICU admissions, work losses, closures of businesses and institutions, bankruptcies, and precautionary measures
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 3, p173-176 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.095
Murine Models of Alcohol Consumption: Imperfect but Still Potential Source of Novel Biomarkers and Therapeutic Drug Discovery for Alcoholic Liver Disease
Khaled Alharshawi, Costica Aloman
Improving our knowledge regarding the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying murine models of alcoholic liver injury should enhance the management and therapies of alcoholic liver disease (ALD) seen in humans [1]. Although none of the animal models available reproduce all main aspects of human ALD, they still provide very
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 3, p177-181 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.096
The Variable Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Potential Treatment with Combination IL-15 and IL-21
Stephen William Wilz
SARS-Cov-2 is the virus that causes the disease COVID-19. The disease has led to the worst worldwide health crisis in 100 years. While many patients remain asymptomatic, most patients develop a mild respiratory infection. Symptoms include cough, fever and chills, fatigue and body aches, headache and loss of the sense of taste or
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 3, p182-190 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.097
Sleep Disturbances are a Significant Predictor of Chikungunya Arthritis Flare Severity
Sarah Renee Tritsch, Richard Amdur, Liliana Encinales, Andres Cadena Bonfanti, Paige Fierbaugh, Geraldine Avendaño, Carlos Andres Herrera Gomez, Karol Suchowiecki, Evelyn Mendoza-Torres, Wendy Rosales, Dennys Jimenez, Carlos Alberto Perez Hernandez, Alfonso Sucerquia Hernández, Paula Bruges Silvera, Yerlenis Galvis Crespo, Alberto David Cabana Jimenez, Jennifer Carolina Martinez Zapata, Christopher N. Mores, Gary Steven Firestein, Gary Leonard Simon, Aileen Yu-hen Chang
Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) is an alphavirus transmitted by mosquitoes that causes debilitating arthritis. In a cohort of 500 Colombian patients, one quarter reported joint pain 20 months after infection, and further, 1 out of 8 had joint pain three years after infection.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 3, p191-197 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.098
The Potential of Combination Therapies and Patient Stratification to Improve CCR2 Inhibition Therapeutics
Jason E. Duex, Dan Theodorescu
Chemokines and their receptors are the communication mechanism used by cells of the immune system, allowing them to identify and eliminate pathogens and cancerous cells. However, it is becoming clear that chemokines and their receptors are also playing a role in tumor progression and metastasis.
J Cell Immunol, 2021, Volume 3, Issue 3, p198-200 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.3.099
Recommended Articles
Karyotypic Profile of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Patients Diagnosed at Tertiary Level in Afghanistan
Balanced translocation resulting in fusion of the Abelson gene (ABL1) from chromosome 9q34 with the breakpoint cluster region (BCR) gene on chromosome 22q11.2 is the pathognomonic molecular driver of CML. The resulting BCRABL 1 fusion gene is both the diagnostic as well as therapeutic target of CML. The first agent with tyrosine kinase inhibitor activity that was licenced in 2000 for treatment of CML patients, was Imatinib, gradually followed by multiple agents with higher efficacy.
Chimeric Antigen Receptor CAR NK Cells Emerging Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Cancer
Although NK cells are recognized as effector lymphocytes of the innate immune system, they also regulate the adaptive immune response by releasing inflammatory cytokines and developing immunological memory. Unlike other lymphocytes such as T or B cells, NK cells do not express rearrangeable, antigen-specific receptors.
Cyclic Nucleotide Signaling Pathways in Apicomplexan Parasites Provide a Valuable Source for Novel Drug Targets
Malaria is one of the most important disabling human, tropical disease caused by different Plasmodium species, which are protozoan parasites belonging to the Apicomplexa. The Apicomplexan parasites have a plastid like structure the “apicoplast” and comprise the genera Plasmodium, Toxoplasma and Cryptosporidium causing malaria, toxoplasmosis, and cryptosporidiosis.
COVID-19 Clinical Research
While the global COVID-19 pandemic has challenged the entire humanity and health systems, it also triggered researchers to urgently perform clinical trials to assess the safety and efficacy of many agents and modalities to combat COVID-19. As of April 22, over 650 clinical studies have been registered both in USA and internationally. Results from these studies are also coming at a brisk pace in this unprecedented emergency.
Chest Pain in Repeated Emergency Department Visitors
Chest pain is the leading symptom in 5 to 8% of all emergency department (ED) visits and is also one of the major reasons of repeated ED visits, causing around 6% of these cases [1]. Generally, in 15 to 25% of patients with chest pain, acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is the underlying cause.
Deubiquitinase as Potential Targets for Cancer Immunotherapy
During the last few decades, immunotherapy is considered to be an important approach to help our immune system to fight various kinds of diseases, such as tumor. Sometimes, it works very well for some types of cancers, for example: bladder cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer and lymphoma.
Role of the Gut Microbiome in the Modulation of Cancer Immunotherapy Response
The gut microbiome or gut flora is a vast community of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and fungi that inhabit the digestive tract of the human and other animals [1,2]. In the human body, bacterial species colonize into the oral cavity, skin, vagina, and placenta, however, the largest population of microorganisms resides in the intestine.
In silico Analysis for the Repurposing of Broad-spectrum Antiviral Drugs against Multiple Targets from SARS-CoV-2: A Molecular Docking and ADMET Approach
SARS-CoV-2 belongs to the genus Beta of the Coronaviridae family of enveloped single-stranded, positive-sense ribonucleic acid (RNA) with a genome length of 30,000bp. The virion is composed of various non-structural (RNA dependent RNA polymerase also known as RdRp) and structural proteins such as Spike (S), Nucleocapsid (N), Matrix (M), and Envelope (E) proteins.
Is Citrate A Critical Signal in Immunity and Inflammation?
When immune cells are activated, they undergo metabolic change in order to have sufficient energy to function effectively. The Krebs cycle is one of the most important pathways involved in this response and citrate, a critical component of this pathway, regulates carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Molecular Biology for BCR-ABL1 Quantification for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Monitorization and Evaluation
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) is a clonal disorder originated by a pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell, which presents the translocation t(9;22) (q34;q11) in 90% of the cases.
The Pathogenesis of Continuous Spike and Waves during Slow Sleep Syndrome: Short Communication
Continuous spikes during slow wave sleep (CSWS) syndrome is an age-related and self-limited severe epileptic encephalopathy characterized by electrical status epilepticus in sleep (ESES) on electroencephalogram, seizures, and developmental regression
Pain Outcomes with an Elliptical Regimen (POWER) Study: Identifying the Proper Dosage of Exercise for Therapeutic Effect in Persons with Chronic Back Pain
Low back pain (LBP) is one of the most prevalent conditions that will affect 70-85% of individuals at some point in their life [1]. LBP accounts for 2.3% of all visits to the physician, and is the most common area of the body to experience pain [2]. Exercise has been a mainstay for managing persons with chronic low back pain for almost 40
Dendorbium Nobile Lindl. Alkaloids Suppress NF-κB and NLRP3 Signaling Pathways to Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-induced Neuroinflammation
The important immune cells in the brain are called microglia acting as the central junction between neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. In patients of cognitive disorders and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) animal models, amoebic morphology and inflammatory pathways are activated to release numerous cells in the inflammatory factors by active microglia.
TNFAIP8: Inflammation, Immunity and Human Diseases
Inflammation can be caused by various environmental factors, including microbial infection and toxic chemical exposure. In response to inflammation, immune cells like macrophages, B and T lymphocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and various stromal cells secrete soluble polypeptide cytokine Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF?)
CTLA-4 and PD-L1 or PD-1 Pathways: Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Cancer Immunotherapy
The immune system developed certain checks and balance to control or inhibit the reactivity against normal cells of the body. Uncontrolled immune responses to the non-self entities such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, or mutated self-antigens can cause an inflammatory reaction and autoimmune diseases.
Cancer Nanomedicine: Strategies to Enhance Tumor Delivery and Immunotherapy
Cancer nanomedicine was originally developed for more efficient delivery of chemotherapeutic agents into tumor, and has been extensively employed as a therapeutic for cancer treatment owing to its unique features in drug delivery, diagnosis and imaging, as well as the therapeutic nature of some nanomaterials themselves.
Beta-Sitosterol: As Immunostimulant, Antioxidant and Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein
This article is an extension to our recently published article in Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, entitled “Β-Sitosterol: Isolation from Muntingia Calabura Linn. Bark Extract, Structural Elucidation, and Molecular Docking Studies as Potential Inhibitor of SARSCoV-2 Mpro (COVID-19)”[1].
Rapid Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 by Coupling Tungsten Trioxide (WO3) Photocatalyst with Copper Nanoclusters
At the end of 2019, a novel severe respiratory disease (coronavirus disease 2019, COVID-19) spread to Wuhan, China, it became pandemic in few months, with more than 41 million people infected worldwide as of October 2020. COVID-19 is caused by a novel virus called severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) CoV-2 to distinguish it from SARS-CoV that emerged in Guangdong province in China in 2003 and caused the severe clinical condition known as SARS. Like SARS-CoV, SARS- CoV-2 causes a severe inter
Targeting "Do Not Eat Me" Signal CD47 in Cancer Immunotherapy
Cells of the innate and adaptive arm of the immune system including macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells, neutrophils, T cells, and B cells, etc. are crucial for the maintenance of the body’s homeostatic balance and prevention of multiple diseases including cancer.
Quantifying Respiratory Airborne Particle Dispersion Control Through Improvised Reusable Masks: The Physics of Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions for Reducing SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Airborne Transmission
In light of the current pandemic from rapid transmission of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2 or COVID-19) and significant morbidity, there has been inconsistent medical guidance given to the public regarding the wearing of non-medical improvised fabric masks or face coverings to reduce the transmission of COVID-19.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
