Loading
Archives of Cancer Biology and Therapy
ISSN: 2692-8302
2021
Volume 2, Issue 1, p1-28
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Forces, Chromosomal Configurations, and Carcinogenesis: Towards Another Therapeutic Approach
Michael M. Lieber
Various types of forces, such as cohesive and adhesive forces, are involved in physical and biological processes. Many of these processes appear to have developmental features through different scales of nature, and such processes may reflect a universal dynamic of accommodation involving the universal dimensional constants
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p1-7 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.2.016
Radical Radiotherapy of Locally Advanced Cervix Uteri Carcinoma
Alparslan Serarslan, Deniz Meydan, Rana Elif Yildiz
Cervix uteri carcinoma is the most common gynecological cancer worldwide. In addition, it is the fourth most common malignancy and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death in women [1]. The most common histopathological subtype is squamous cell carcinoma (85%).
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p8-14 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.2.017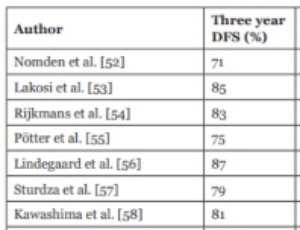
Botulinum Toxin: The Promising Future of Prostate Cancer Treatment
Alberto Piamo Morales
Botulinum toxin (BT) is a potent poisonous neurotoxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum and related species [1]. Its action consists of inhibiting neuromuscular junctions by blocking the release of acetylcholine and desensitizing sensory nerves.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p15-18 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.2.018
The Emerging Role of Pyruvate Kinase M2 in Regulating Glutaminolysis via c-Myc
Guangda Peng, Liangwei Li, Zhi-Ren Liu
Cancer cells reprogram their nutrition metabolism to meet their high bioenergetic and biosynthetic demands in support of rapid growth and continuous proliferation [1]. Both glycolysis and glutaminolysis are altered in cancer cells.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p19-24 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.2.019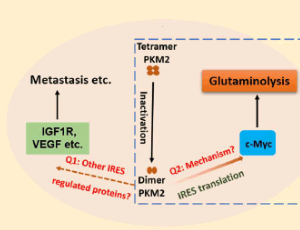
Surgery Versus Radiation Therapy for Early-Stage Lung Cancer: Patient Selection is Crucial
Matthew T. Hey, Hans E. Drawbert, Francisco Tarrazzi, Mark Block, Syed S. Razi
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer related death in the United States with mortality rates surpassing breast, prostate, brain, and colorectal cancers combined. Recent data shows that susceptibility for both men and women for developing invasive lung and bronchogenic carcinoma peak after the age of 70 years.
Arch Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p25-28 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerbiology.2.020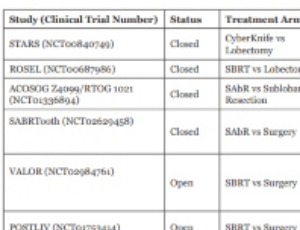
Recommended Articles
pMB FLASH - Status and Perspectives of Combining Proton Minibeam with FLASH Radiotherapy
Proton minibeam radiotherapy (pMBRT) is an external beam radiotherapy method with reduced side effects by taking advantage of spatial fractionation in the normal tissue. Due to scattering, the delivered small beams widen in the tissue ensuring a homogeneous dose distribution in the tumor. In this review, the physical and biological principles regarding dose distribution and healing effects are explained. In the last decade, several preclinical studies have been conducted addressing normal tissue sparing and tumor control in-vitro and in-vivo, using human skin tissue and mouse or rat models. The major results acquired in these studies are summarized. A further newly emerging therapy method is FLASH radiotherapy, i.e. the treatment using ultra-high dose rates. The possibility of combining these methods in proton minibeam FLASH therapy (pMB FLASH) is worked out. Additionally, technical feasibility and limitations will be discussed by looking at simulations as well as preclinical studies and also pointing out new ways of delivering the desired tumor dose, such as interlacing. We will also highlight the opportunities that emerge regarding high dose radiation, hypofractionation and the combination with immunotherapy.
Uniportal VATS Lobectomy for Lung Cancer: Feasibility and Cost Effectiveness in a Single Center Experience
In last decades, video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) together with robotic-assisted thoracic surgery (RATS) can be considered the biggest innovation in thoracic surgery. This approach drastically changed the way of performing surgical operations, improving patient’s outcome undergoing thoracic surgery.
Gender Disparities in Outcomes Following Pulmonary Embolism Treatment in the Intensive Care Unit; A Multi-center Retrospective Cohort Study
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of blood flow in the pulmonary artery bed that can result in a life-threatening and potentially reversible right ventricular failure [1]. PE remains one of the leading causes of poor prognosis and death, particularly when a shock or right ventricular failure occurs [2]. According to studies, PE is generally manifested in a nonspecific manner
Early Onset Fetal Growth Restriction: Does Path to Diagnosis Impact Outcomes and Pathology?
The etiology of fetal growth restriction is rooted in inadequate maternal-placental vascular malperfusion (MVM) of the placenta. Risk factors for MVM are broad and include maternal, fetal, and placental antecedent determinants.
Prognostic Role of Human Epididymis Protein 4 (HE4) in Ovarian Cancer Treatment: Our Point of View
In the last 10 years, the marker “Human Epididymis protein 4 (HE4)” for the management of gynecological tumors has entered powerfully in the world literature. At the moment, carrying out an accurate research in the main scientific portals such as PubMed, we can find more than 2,000 works concerning Cancer antigen-125 (Ca125), but those concerning HE4 are less than 400.
Healthy Fetal Outcomes Using A Novel Treatment For Maternal Lyme Disease And Babesiosis During Consecutive Pregnancies: A Case Study and Literature Review
The genus Babesia comprises over 100 species of tick-transmitted protozoal intraerythrocytic pathogens (piroplasms) [1], causing malarial-type illness. The most common human pathogens in the United States are B. microti [2] and Babesia duncani (WA- 1) [3]; Less common species include Babesia MO-1 [4] and KO-1 [5], as well as Babesia divergens and Babesia venatorum (EU-1) in Europe.
Influence of Clinical Risk Factors on Outcomes in Men with Stage I Non-Seminomatous Germ Cell Tumor Undergoing Robot-Assisted Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection
Retroperitoneal lymph nodes are often the first landing site of metastatic disease in men with testicular cancer. Primary retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) for clinical stage I NSGCT can accurately surgically stage patients who may have nodal micrometastases, and in some cases, can serve as the primary therapy when volume of metastasis is low.
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer worldwide, affecting nearly one in eight women. Accurate cancer staging is essential for determining the patient’s prognosis and for choosing the appropriate treatment.
Botulinum Toxin: The Promising Future of Prostate Cancer Treatment
Botulinum toxin (BT) is a potent poisonous neurotoxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum and related species [1]. Its action consists of inhibiting neuromuscular junctions by blocking the release of acetylcholine and desensitizing sensory nerves.
The Emerging Role of Pyruvate Kinase M2 in Regulating Glutaminolysis via c-Myc
Cancer cells reprogram their nutrition metabolism to meet their high bioenergetic and biosynthetic demands in support of rapid growth and continuous proliferation [1]. Both glycolysis and glutaminolysis are altered in cancer cells.
Pain Outcomes with an Elliptical Regimen (POWER) Study: Identifying the Proper Dosage of Exercise for Therapeutic Effect in Persons with Chronic Back Pain
Low back pain (LBP) is one of the most prevalent conditions that will affect 70-85% of individuals at some point in their life [1]. LBP accounts for 2.3% of all visits to the physician, and is the most common area of the body to experience pain [2]. Exercise has been a mainstay for managing persons with chronic low back pain for almost 40
NOXA the BCL-2 Family Member behind the Scenes in Cancer Treatment
NOXA is a critical mediator of stress responses to anticancer drugs. This BH3-only protein sets the apoptotic threshold in cancer cells in response to chemotherapies by counteracting the prosurvival BCL-2 family protein MCL-1. A complex and dynamic network relying on both highly controlled gene transcription activity and protein degradation by proteasome, regulates cellular NOXA levels from low in steady state to rapidly enhanced upon stressful condition.
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Followed by Fertility Sparing Surgery in Stage 1B2 Cervical Cancer
In 2020 we published a series of 18 patients who underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) and vaginal radical trachelectomy (VRT) as a fertility sparing alternative in stage 1B2 cervical cancer.
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia: An Update on Management Strategies and Outcomes
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) is a severe developmental anomaly with an estimated global prevalence at birth of about 2.3 in 10,000 live births. Despite recent advances in antenatal diagnosis, fetal interventions and postnatal management, the condition continues to have a high mortality due to pulmonary hypoplasia and pulmonary hypertension and affected infants can suffer long-term morbidity. In a prospective national population cohort study from the United Kingdom and Ireland,
The Effects of Vaginal Probiotic Administration on Perinatal Outcomes in Patients with Premature Preterm Rupture of Membrane
Preterm premature rupture of membrane is the rupture of the chorionic-amniotic membrane and leakage of amniotic fluid before the onset of labor pains and prior to the 37th week of pregnancy. Preterm premature rupture of membrane (PPROM) occurs in 3% of pregnancies and is the cause of about 25 to 30% of all preterm births. PPROM is an important contributor to perinatal morbidity.
Late ECG Changes after Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy in Testicular Cancer Survivors
Introducing cisplatin-based therapy into testicular cancer treatment represents a substantial progress in therapy leading to a longer survival of patients and less adverse effects; currently it represents the standard therapy.
Editorial Commentary for In Throwers with Posterior Instability, Rotator Cuff Tears are Common but Do Not Affect Surgical Outcomes
Superior labral pathology is an exceedingly common entity among throwers, and in recent years, a number of reports have elucidated the prevalence of posterior glenohumeral instability among overhead athletes (baseball, softball, volleyball.) However, within this unique patient population, these conditions should not be viewed as separate clinical entities, but, rather as findings that exist on a single pathomechanic spectrum.
Relevance of Neuropilin 1 and Neuropilin 2 Targeting for Cancer Treatment
Neuropilins (NRPs) are a class of transmembrane glycoprotein co-receptors including Neuropilin 1 (NRP1) and Neuropilin 2 (NRP2). They are the co-receptors of different families of receptors, thus they are involved in many hallmarks of cancer.
To Stick or Not to Stick? Scalp and Intracranial EEG Evaluation Both Help Achieve Good Surgical and Neuropsychiatric Outcomes in Epilepsy Surgery up to 20 Years Post-Surgery
Epilepsy has a worldwide prevalence of about 50 million [1]. Seizure medications provide adequate control in two thirds of these patients but about a third are refractory to multiple medications and need surgery or other treatments [2].
Health Workers’ Perspectives on the Outcomes, Enablers, and Barriers to the Implementation of HIV “Test and Treat” Guidelines in Abuja, Nigeria
HIV/AIDS continues to be a major public health disease accounting for 35 million deaths across the world. In 2016 alone, there were 1.8 million new HIV infections and 1 million deaths worldwide.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
