Loading
Archives of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
ISSN: 2692-787X
2023
Volume 4, Issue 2, p28-55
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Can the Systemic Immune Inflammation Index Predict the Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy?
Sevcan Sarikaya, Emre Uysal, Oğuzhan Günenç
Objective: The aim of this study was to predict the selection of treatment for ectopic pregnancy (EP) using the values of platelet/lymphocyte ratio (PLR), neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR), monocyte/lymphocyte ratio (MLR) and systemic immune inflammation index (SII) obtained from hematological parameters routinely used in clinical practice.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p28-33 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.039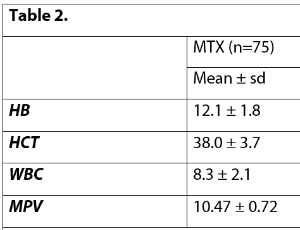
Association between Maternal Serum Leptin Level and Preterm Birth among Parturients in Lagos, Nigeria
Olubunmi Olufunke Ogein, Adeyemi Adebola Okunowo, Gbenga Olorunfemi, Benedetto Osunwusi, Omololu Adegbola
Preterm birth is one of the major causes of neonatal morbidity and mortality worldwide. The association between occurrence of preterm birth and biomarkers measured in the maternal serum maybe helpful in predicting preterm birth especially in low resource settings.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p34-40 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.040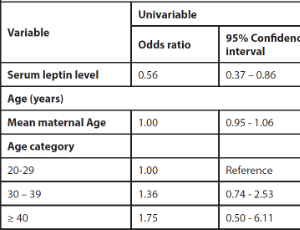
Utero-Vesical Fistula Closure after 3 Weeks Treatment with Intravenous Mesenchymal Stem Cells Infusion: Case Report
Di Silvio Mauricio, Luján-Irastorza Jesús Estuardo, Durand-Montaño Carlos, Henández-Ramos Roberto, Barrón-Vallejo Jesús, Ávila-Rebollar Daniela, Myslabodski Julio, Pariente-Fernández Maruxa, Tagle-Rodríguez Jorge Mario, Ramírez-Amezcua Miguel Ángel, Paredes-Núñez María Angélica, Vargas-Hernández Víctor Manuel
Objective: To describe the evolution of Utero-Vesical Fistula (UVF) of one patient who received conservative treatment using intravenous (IV) infusion of 120x106 Adipose tissue Mesenchymal Stem Cells (ADMSCs). Clinical case report: A 36-year-old female presented with postcesarean hematuria 3 hours after an emergency c-section was performed consequently to placental abruption during labor.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p41-45 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.041
Hemostatic Pelvic Irradiation: A Rarely Reported Approach to Benign Gynecological Bleeding
Bouguerra F, Boudhina E, Chahdoura H, Souissi M, Tbessi S, Bouzid N, Belajouza S, Tebra S
Background: Ovarian cysts are usually treated using medical or surgical interventions. However, in some cases, these treatments may not be feasible or effective, and alternative options need to be considered. Case presentation: We report a case of a 43-year-old woman with a history of recurrent hemorrhagic ovarian cysts, who was on anticoagulant therapy due to tight mitral stenosis and had multiple autoimmune disorders.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p46-49 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.042
Early Cumulus Cell Removal Increases Cumulative Live Birth Rate while Having No Negative Effect on the Malformation Rate in In vitro Fertilization: A Propensity Score-Matched Cohort Study
Li Juan Sun, Shan Shan Liang, Min Hao Liu, Jia Ping Pan, Mei Yuan Huang, Xiao Ming Teng, Hai Xia Wu
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy and safety of early cumulus cell removal (ECCR) during human in vitro fertilization (IVF). Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed between January 2011 and December 2019. The study enrolled 1,131 couples who underwent IVF treatment with ECCR. After propensity score matching at a 1:1 ratio, 1,131 couples who underwent overnight coincubation of gametes were selected.
Arch Obstet Gynecol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 2, p50-55 | DOI: 10.33696/Gynaecology.4.043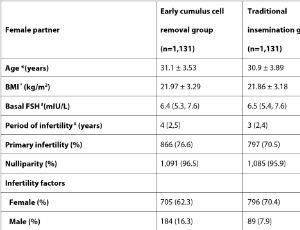
Recommended Articles
pMB FLASH - Status and Perspectives of Combining Proton Minibeam with FLASH Radiotherapy
Proton minibeam radiotherapy (pMBRT) is an external beam radiotherapy method with reduced side effects by taking advantage of spatial fractionation in the normal tissue. Due to scattering, the delivered small beams widen in the tissue ensuring a homogeneous dose distribution in the tumor. In this review, the physical and biological principles regarding dose distribution and healing effects are explained. In the last decade, several preclinical studies have been conducted addressing normal tissue sparing and tumor control in-vitro and in-vivo, using human skin tissue and mouse or rat models. The major results acquired in these studies are summarized. A further newly emerging therapy method is FLASH radiotherapy, i.e. the treatment using ultra-high dose rates. The possibility of combining these methods in proton minibeam FLASH therapy (pMB FLASH) is worked out. Additionally, technical feasibility and limitations will be discussed by looking at simulations as well as preclinical studies and also pointing out new ways of delivering the desired tumor dose, such as interlacing. We will also highlight the opportunities that emerge regarding high dose radiation, hypofractionation and the combination with immunotherapy.
Impact of Estradiol Supplementation during Luteal Phase Support on the In vitro Fertilization Clinical Outcome: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
At present, progesterone administration is widely used. There is no agreement on whether estradiol (E2) addition should be supplement to progesterone (P) as luteal phase support (LPS).
Radical Radiotherapy of Locally Advanced Cervix Uteri Carcinoma
Cervix uteri carcinoma is the most common gynecological cancer worldwide. In addition, it is the fourth most common malignancy and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death in women [1]. The most common histopathological subtype is squamous cell carcinoma (85%).
The Role of Anemia in Term and Preterm Pregnancies: Evidence from the Brazilian Multicenter Study on Preterm Birth (EMIP)
Evaluate the prevalence of anemia in term and preterm pregnancies and compare maternal and perinatal outcomes among groups.
Health Workers’ Perspectives on the Outcomes, Enablers, and Barriers to the Implementation of HIV “Test and Treat” Guidelines in Abuja, Nigeria
HIV/AIDS continues to be a major public health disease accounting for 35 million deaths across the world. In 2016 alone, there were 1.8 million new HIV infections and 1 million deaths worldwide.
News About the Extracellular Vesicles from Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Functions, Therapy and Protection from COVID-19
The present Commentary is a critical follow-up of a previous review about “Extracellular vesicles, news about their role in immune cells: physiology, pathology and diseases”, appeared in Clinical and Experimental Immunology last June 2019 [1].
HGF/MET Signalling and DNA Damage Response: Strategies to Conquer Radiotherapy Resistance in Head and Neck Cancer
Head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCCs) are a group of aggressive and genetically complex cancers, derived from the mucosal epithelium in the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx. Radiotherapy, often combined with chemotherapy remains the mainstay treatment options for patients.
Cancer Stem Cells, Together with Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Other Cooperative Cells, Govern the Initiation and Development of Cancer
Until the end of last century, the origin and development of cancers were mostly attributed to the proliferation of their active cells, operative in collaboration with non-cancer cells of the patients. In particular, an important role was attributed to cells now recognized as mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), first considered a few decades ago. Initially, however, the role attributed to these cells was only limited.
Ectopic Pregnancy: Vascularity Index as a Novel Diagnostic Criterion
Since the medical management of ectopic pregnancy (EP) was introduced by Dr. Steven Ory, and published in 1986 in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, diagnostic criteria have been established to predict its successful medical treatment with methotrexate (MTX), including its maximum diameter (MaxDia), its associated human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) level, and whether there was identified cardiac motion (CM).
Can the Systemic Immune Inflammation Index Predict the Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy?
Objective: The aim of this study was to predict the selection of treatment for ectopic pregnancy (EP) using the values of platelet/lymphocyte ratio (PLR), neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR), monocyte/lymphocyte ratio (MLR) and systemic immune inflammation index (SII) obtained from hematological parameters routinely used in clinical practice.
Association between Maternal Serum Leptin Level and Preterm Birth among Parturients in Lagos, Nigeria
Preterm birth is one of the major causes of neonatal morbidity and mortality worldwide. The association between occurrence of preterm birth and biomarkers measured in the maternal serum maybe helpful in predicting preterm birth especially in low resource settings.
Utero-Vesical Fistula Closure after 3 Weeks Treatment with Intravenous Mesenchymal Stem Cells Infusion: Case Report
Objective: To describe the evolution of Utero-Vesical Fistula (UVF) of one patient who received conservative treatment using intravenous (IV) infusion of 120x106 Adipose tissue Mesenchymal Stem Cells (ADMSCs). Clinical case report: A 36-year-old female presented with postcesarean hematuria 3 hours after an emergency c-section was performed consequently to placental abruption during labor.
Early Cumulus Cell Removal Increases Cumulative Live Birth Rate while Having No Negative Effect on the Malformation Rate in In vitro Fertilization: A Propensity Score-Matched Cohort Study
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy and safety of early cumulus cell removal (ECCR) during human in vitro fertilization (IVF). Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed between January 2011 and December 2019. The study enrolled 1,131 couples who underwent IVF treatment with ECCR. After propensity score matching at a 1:1 ratio, 1,131 couples who underwent overnight coincubation of gametes were selected.
Monitoring Transcription of miR-15a and miR-124 in Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Adipose Tissue Origin Differentiated into Pancreatic Beta-cells
MicroRNAs are small, noncoding pieces of nucleic acid with the potential to control mRNA translation. These sequences participate in the regulation of cell dynamic growth and differentiation. In this study, the expression of miR-15a and miR-124 was monitored in adipose-derived tissue stem cells committed to pancreatic β cells in vitro over 28 days. In the current experiment, adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells were incubated in an induction medium to accelerate differentiation toward the endocrine pancreatic lineage for 28 days with a three-stage protocol.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
