Loading
Journal of Experimental Pathology
ISSN: 2694-5061
2023
Volume 4, Issue 1, p1-44
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
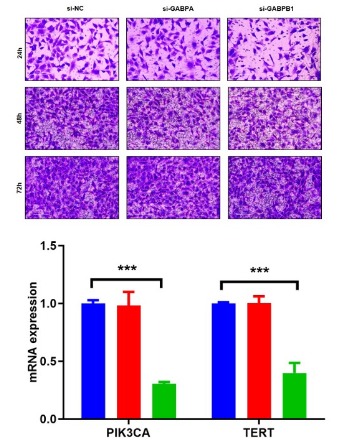
Concurrent PIK3CA and TERT Mutation Promote the Proliferation and Invasion of Thyroid Carcinoma Cells and may be Caused by Up-regulating the Expression of GABPA/GABPB1
Huanli Duan, Qiang Ma, Leiming Wang, Shengnan Wang, Yanlei Xiong, Lianghong Teng
Our previous research demonstrated that TERT and concurrent PIK3CA mutations predict worse overall survival in patients with poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma and anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. However, the molecular mechanism underlying the synergistic oncogenic operations of the two oncogenes is unclear.
J Exp Pathol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 1, p1-8 | DOI: 10.33696/pathology.4.041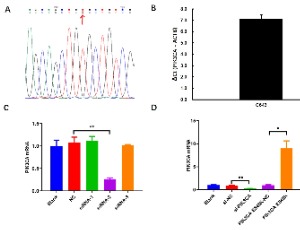
Current Understanding and Gaps in Knowledge of Chlamydia trachomatis Infection
G Bastidas, D Bastidas, G Bastidas-Delgado
Chlamydia trachomatis is a bacterial infection that most frequently causes sexually transmitted infection in the world, therefore, it is considered a serious public health problem. The objective of this commentary is to describe in a condensed but sufficient manner what has been reported by researchers on the subject based on the documentary review available in digital repositories on aspects of the infection.
J Exp Pathol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 1, p9-15 | DOI: 10.33696/pathology.4.042
Evaluation of Antimicrobial Potential of Endophytic Fungi and GC-MS Metabolic Profiling of Cephalosporium sp., and Fusarium moniliforme
Hafiza Farhat, Faizah Urooj, Nida Sohail, Shahid Ullah, Muhammad Aamer
From last few decades, microbes gained special attention residing inside plant tissues, now called endophyte. Studies proved that these microbes are able to produce biologically active metabolites and effective candidates against various pathogens. Endophytic fungi are a source of natural therapeutic products. Therefore, endophytic Fusarium species are isolated from different plants.
J Exp Pathol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 1, p16-33 | DOI: 10.33696/pathology.4.043
- Abstract |
- Full Text |
- Cite |
- Supplementary File
Evaluation of Breast, Lymph Node, and Thyroid Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology by Liquid Based Smears and Conventional Smears
Rajesh Reddy, Shailaja Prabhala, Shrinivas B Somalwar, Ashok Kumar Deshpande
Introduction: Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a first-line investigation for palpable lumps and is a highly cost-effective and accurate investigative technique. It is a safe, simple, rapid, minimally invasive technique. Liquid-based cytology (LBC) has been used in gynecologic-cytology for over three decades. Many laboratories have adopted LBC technique for exfoliative and FNA samples. We undertook the present study to compare the advantages and disadvantages of conventional and liquid based cytology preparations.
J Exp Pathol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 1, p34-44 | DOI: 10.33696/pathology.4.044
Recommended Articles
Karyotypic Profile of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Patients Diagnosed at Tertiary Level in Afghanistan
Balanced translocation resulting in fusion of the Abelson gene (ABL1) from chromosome 9q34 with the breakpoint cluster region (BCR) gene on chromosome 22q11.2 is the pathognomonic molecular driver of CML. The resulting BCRABL 1 fusion gene is both the diagnostic as well as therapeutic target of CML. The first agent with tyrosine kinase inhibitor activity that was licenced in 2000 for treatment of CML patients, was Imatinib, gradually followed by multiple agents with higher efficacy.
Prognosis and Survival of Medullary Carcinoma of the Breast
Medullary breast carcinoma (MBC) is a rare tumor, representing 3% to 5% of invasive breast carcinomas. The World Health Organization defines it as a well-circumscribed invasive tumor, composed of poorly differentiated cells, arranged in sheets, without gland formation and a scarce collagen stroma with the presence of a very prominent lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate.
Molecular Detection of Plasmid - Mediated Quinolone Resistant Genes in Uropathogenic E. coli from Tertiary Referral Hospital in Tehran , Iran
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) due to Escherichia coli is the most common bacterial infection. Fluoroquinolones are commonly used for the treatment of UTI because isolated microorganisms are frequently resistant to aminopenicillins and trimethoprim- sulfamethoxazole and fluoroquinolones are given orally [1].
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer worldwide, affecting nearly one in eight women. Accurate cancer staging is essential for determining the patient’s prognosis and for choosing the appropriate treatment.
Genetic Predisposition of Breast Cancer in the United Arab Emirates
This commentary refers to our published article, as highlighted in this article most common gene causing breast cancer in the population living in the United Arab Emirates is BRCA2 followed by BRCA1. This is the first publication discussing about clinical and pathological features of breast cancer in woman with a positive genetic mutation in the United Arab Emirates.
SorLA Targeting - A Method to Overcome Therapy Resistance in Breast Cancer
Tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER2- targeted therapies have dramatically improved breast cancer patients’ outcome compared to conventional chemotherapies. In the clinic, HER2 monoclonal antibody trastuzumab with chemotherapy represent the gold standard treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer.
Salivary Protein Antigens for Breast Cancer Biomarkers
Breast Cancer is the most regularly diagnosed type of cancer in women in the world, making up on its own 25% of all cases, or nearly 2 million new cases in 2018, and 15% of all cancer related deaths, or around 626,700 deaths for that same year.
Relationship of lncRNA to Breast Cancer
At present, breast cancer is more frequently diagnosed in women than in men. According to global cancer statistics, each year more than 1,675,000 women are diagnosed and more than 500,000 of them die. Some subtypes of breast cancer have been described.
Preparing for a More Public Health-Aware Practice of Medicine in Response to COVID-19
After one year in a pandemic, we mourn the loss of over half a million lives in the United States, and over four million worldwide, and remain concerned over the challenges facing the families of 35 million people in the United States, and 200 million worldwide, who have suffered from cases of COVID-19.
Protein Therapeutics from Monolayer to Spheroids- A Model for Preclinical Investigations
The arrival of recombinant insulin in the pharmaceutical market paved a new direction for the clinical potential of proteins. Thus, the pharmaceutical industry underwent a paradigm shift towards proteins as therapeutic moieties.
Multiple Roles of the Interleukin IL-17 Members in Breast Cancer and Beyond
Worldwide, breast cancer is the most-common invasive cancer in women. Commonly used treatments include surgery, hormonal therapy, radiotherapy, chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Failure of these treatments is often due to intrinsic or acquired resistances and is responsible for most relapses of cancer [1]. Heterogeneity among patients and tumors, together with the versatility of cancer make drug resistance more challenging to deal with.
Mitochondria Autoimmunity and MNRR1 in Breast Carcinogenesis: A Review
Recently, Aras et al. reported that MNRR1, a nuclear DNA (nDNA)-encoded mitochondrial antigen, promotes cancer cell migration and the development of metastasis as a proof of concept supporting the participation of mitochondrial autoimmunity in breast carcinogenesis.
Ovarian Function Suppression Plus Aromatase Inhibitors or Tamoxifen in Premenopausal HR-positive Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common type of malignant tumor in women, accounting for 30% of women’s cancer, while the mortality rate ranks second among women’s cancer. Twenty-five percent of all breast cancer patients are premenopausal patients, and 7% of patients are younger than 40 years old.
A New Player in an Old Story: FBXO16 Prevents Breast Cancer Tumorigenesis through Disrupting Cellular Function of Nuclear β-Catenin
β-Catenin is the central modulator of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Upon Wnt on state, β-Catenin is translocated to the nucleus and function as a transcription coactivator for several oncogenes. In Wnt off state, β-catenin is mostly localized in the cytoplasm and sequestered by the destruction complex, the negative regulator of β-catenin expression [2,3].
Acellular Dermal Matrix in Prosthetic Breast Reconstructive Surgery with Prepectoral Technique: A Literature Review
Breast cancer is the second most commonly diagnosed cancer worldwide, with an incidence of 2.088.850 and a mortality rate of 627,000. Incidence and mortality rate in Europe were 522,513 and 92,000, respectively, while in Italy accounted for 53,000 diagnoses and 12,000 deaths.
Cervical Cancer Prevalence in sub-Saharan Africa and HPV Vaccination Policy: A Public Health Grand Challenge?
“Women are not dying because of diseases we cannot treat. They are dying because societies have yet to make the decision that their lives are worth saving.”
Breast Implant-associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: A Review with Emphasis on the Role of Brentuximab Vedotin
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) represents a heterogeneous group of T-cell lymphomas, which characteristically express CD30 and are associated with translocations involving the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene on chromosome 2p23 [1]. Systemic ALCL, which may be subclassified by the presence or absence of
Continuing Medical Education Rarely Addresses Leading Public Health Problems Including Diabetes and Obesity
Medical schools sponsor continuing medical education (CME) to help fulfill their mission of improving the health of the community. CME programs can help physicians stay up-to-date with the best practices associated with disease prevention and treatment.
Patient-Reported Health Outcomes among HIV-Infected Patients on Antiretroviral Therapy in a Tertiary Hospital in Dar Es Salaam, Tanzania: A Cross Sectional Study
The use of antiretroviral therapy (ART) has resulted into HIV-infected patients living longer than it was the case in the pre-ART era [1]. Surviving patients are concerned not only with the treatment ability to extend their lives but also that their quality of life is improved on the course.
Anti-tumor Mechanisms of Short-chain Fatty Acids, and the Relationship between the Gut Microbiome, Carcinogenesis, Tumor Growth, and Proliferation in Colorectal Carcinoma
We reviewed the anti-tumor mechanisms of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) as well as the relationship between the gut microbiome and the pathology of colorectal carcinoma (CRC). According to our in silico analysis of human CRC cell lines, it was shown that SCFAs suppress various genes and transcription factors that participate in tumor growth/proliferation and cell turnover, and butyric acid displayed the strongest inhibitory effects among SCFAs.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
