Loading
2025
Volume 7, Issue 4, p166-182
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Should You Be Afraid of the Big Bad Wolf? A Practical Real-world Review for the Comfortable Use of Bosutinib in the Therapy of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Jeffrey H Lipton
Bosutinib is a second generation (2G) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) for the therapy of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). It is effective, as other 2g TKIs and long term, is likely the safest, with few significant issues. Short term adverse events which have inhibited their use in the past can be overcome with some simple maneuvers which will be reviewed here. The background for bosutinib, patient selection, and a process for successfully starting patients on therapy will be outlined.
J Cancer Immunol, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 4, p166-173 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.7.115
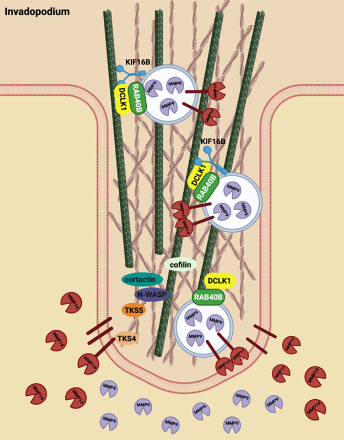
Highlighting the Role of DCLK1 in Tumor Invasion and Potential for Therapeutic Intervention
Molly E. Muehlebach, Sufi Mary Thomas
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) accounts for nearly 5% of global cancer deaths per year, with epidemiological studies suggesting an expected 30% increase in cases by 2030 due to rising incidence of viral infection (i.e. huma papilloma virus [HPV]). Treatment consists primarily of surgical tumor removal accompanied by post-operative chemoradiation therapy; however, disease recurrence is still an issue amongst 10–26% of patients. Doublecortin-like kinase 1 (DCLK1) is a microtubule-associated protein with dual kinase activity, and upregulation has been associated with poor prognosis in multiple solid tumors.
J Cancer Immunol, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 4, p174-180 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.7.116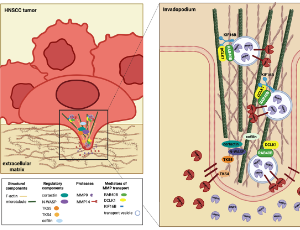
Re-engineering the Tumor–Immune Interface—Emerging Frontiers in Cancer Immunology and Immunotherapy
Sanjay K. Srivastava
Cancer immunology continues to redefine the landscape of oncology, shifting the therapeutic paradigm from direct cytotoxicity toward immune modulation and re-education. The latest publications in the Journal of Cancer Immunology capture this evolution with remarkable clarity—highlighting how manipulating both the tumor microenvironment (TME) and the immune effector landscape can unlock durable anti-tumor immunity
J Cancer Immunol, 2025, Volume 7, Issue 4, p181-182 | DOI: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.7.117
Recommended Articles
Prevalence of Symptom Clusters in Cancer Patients at First Presentation in Palliative Care Clinic as per Different Disease Groups
Cancer has its own disease burden and patients usually suffer from symptom clusters when they are referred for palliative treatment. Identification of symptom cluster trajectories will help clinician to take into account measures that can optimize quality of life of palliative patients. Therefore the aim of this paper is to determine the overall prevalence of symptoms and symptoms clusters in different disease groups according to etiology at the time of first visit to Palliative care clinic by using HIS Palliative First Assessment note indicating Edmonton symptom scale.
Chimeric Antigen Receptor CAR NK Cells Emerging Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Cancer
Although NK cells are recognized as effector lymphocytes of the innate immune system, they also regulate the adaptive immune response by releasing inflammatory cytokines and developing immunological memory. Unlike other lymphocytes such as T or B cells, NK cells do not express rearrangeable, antigen-specific receptors.
pMB FLASH - Status and Perspectives of Combining Proton Minibeam with FLASH Radiotherapy
Proton minibeam radiotherapy (pMBRT) is an external beam radiotherapy method with reduced side effects by taking advantage of spatial fractionation in the normal tissue. Due to scattering, the delivered small beams widen in the tissue ensuring a homogeneous dose distribution in the tumor. In this review, the physical and biological principles regarding dose distribution and healing effects are explained. In the last decade, several preclinical studies have been conducted addressing normal tissue sparing and tumor control in-vitro and in-vivo, using human skin tissue and mouse or rat models. The major results acquired in these studies are summarized. A further newly emerging therapy method is FLASH radiotherapy, i.e. the treatment using ultra-high dose rates. The possibility of combining these methods in proton minibeam FLASH therapy (pMB FLASH) is worked out. Additionally, technical feasibility and limitations will be discussed by looking at simulations as well as preclinical studies and also pointing out new ways of delivering the desired tumor dose, such as interlacing. We will also highlight the opportunities that emerge regarding high dose radiation, hypofractionation and the combination with immunotherapy.
Salivary Protein Antigens for Breast Cancer Biomarkers
Breast Cancer is the most regularly diagnosed type of cancer in women in the world, making up on its own 25% of all cases, or nearly 2 million new cases in 2018, and 15% of all cancer related deaths, or around 626,700 deaths for that same year.
Commentary on "The Gene Master Regulators GMR Approach Provides Legitimate Targets for Personalized, Time-Sensitive Cancer Gene Therapy"
For decades, the scientific community tried hard to identify the gene biomarkers whose mutations or regulations cause (better say are associated with) specific forms of cancer. For instance, the September 17th 2019 release of the Genomic Data Commons Data Portal includes 3,142,246 mutations detected in 22,872 genes sequenced from 37,075 cases of cancers localized in 67 primary sites.
Leucocyte-Tumor Cell Hybridization Can Initiate Cancer Metastasis
According to estimates from the International Agency for Research on Cancer, by the year 2030 there will be 22 million new cancer cases and 13 million deaths per year. The main reason for death from cancer is not the initial tumor but it’s metastasis to distant parts of the body, yet this process has remained poorly understood for quite some time.
CTLA-4 and PD-L1 or PD-1 Pathways: Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Cancer Immunotherapy
The immune system developed certain checks and balance to control or inhibit the reactivity against normal cells of the body. Uncontrolled immune responses to the non-self entities such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, or mutated self-antigens can cause an inflammatory reaction and autoimmune diseases.
Autophagy: When to strike?
Autophagy was originally viewed as a widely conserved multistep lysosomal degradation pathway in eukaryotes. It includes the formation of autophagosomes, doublemembrane structures engulfing cytoplasm with damaged organelles during the degradation process.
Combination Therapies with Anti-angiogenesis and B7-H3 Blockade in Cancers
Tumor angiogenesis, a hallmark of cancer, is a critical step in the tumorigenesis of solid cancers. The process of tumor angiogenesis is orchestrated by a range of secreted factors, signaling pathways as well as nonendothelial cells.
Relationship of lncRNA to Breast Cancer
At present, breast cancer is more frequently diagnosed in women than in men. According to global cancer statistics, each year more than 1,675,000 women are diagnosed and more than 500,000 of them die. Some subtypes of breast cancer have been described.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cancer Care: Current Applications and Future Perspectives
Cancer is the second most common cause of death worldwide, accounting for an estimated 9.6 million deaths in the year 2018, a number that is expected to grow to more than 13 million by 2030. In the past decade, we have witnessed unprecedented scientific advancement in the understanding of cancer etiology, prevention, diagnosis and development of new therapeutic strategies.
Aerosol Distribution Pattern of a Single-port Device: New Perspective Treatment for Peritoneal Carcinomatosis in Brazil
The local and peritoneal recurrence play a vital role in the natural history of the evolution of gastrointestinal and ovarian neoplasms. Different methods of applying intraperitoneal chemotherapy were used perioperatively to consolidate or control peritoneal carcinomatosis [1]. The use of chemotherapy directly in the peritoneal cavity allows the direct action of the therapeutic agent in the metastatic nodules, increasing the local concentration with a limited increase in the systemic concentration.
Protein Therapeutics from Monolayer to Spheroids- A Model for Preclinical Investigations
The arrival of recombinant insulin in the pharmaceutical market paved a new direction for the clinical potential of proteins. Thus, the pharmaceutical industry underwent a paradigm shift towards proteins as therapeutic moieties. A number of recombinant protein drugs are available and many more are in pipeline to target major diseases, such as cancer, viral diseases, cardiovascular diseases and endocrine disease.
Verrucous Carcinoma of the Esophagus: Its Unique Etiology and Association with Human Papilloma Virus
Verrucous carcinoma of the esophagus (VCE) is a rare variant of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Most cases of VCE presents as an exophytic, slow-growing mass with a superficial growth pattern. Even when VCE exhibits a characteristic pattern during an endoscopic examination, it is very difficult to make a definitive diagnosis of VCE preoperatively, because biopsy specimens are
only characterized by nonspecific acanthosis and hyperkeratosis or parakeratosis associated with inflammation.
Involvement of D-Loop Mutations in the Occurrence of Ovarian Carcinoma
Cancer mortality is proportionally higher in Africa than elsewhere in the world. In Senegal, ovarian cancer is responsible for 2.8% of deaths and is one of the most fatal gynaecological cancers. This work is therefore being carried out in order to better understand the impact of D-Loop mutations in the evolution of ovarian cancer in Senegalese women.
Cellular Response to Stress: At the Crossroads between Immunosenescence and Cancer
Aging is a complicated process not yet fully understood. Driven by a variety of stressors such as infectious agents, radiation, intracellular stress, and stressing metabolic conditions, molecular damage occurs over time [1]. Among many consequences, age-related unchecked molecular damage leads to immunosenescence, a hallmark of aging. Traditionally defined as a declining function of the immune system, immunosenescence is a term that includes the effect of aging on adaptive and innate immunity [2].
Purinergic System and Cervical Cancer: Perspectives
We have recently published an article entitled “Purinergic signaling and tumor microenvironment in cervical Cancer”. In this paper, we reviewed the last studies about purinergic signaling and cervical cancer, highlighting the intrinsic factors related to the inflammatory process, such as extracellular nucleotides and adenosine - components of the purinergic system.
Inference of Clonal Copy Number Alterations from RNASequencing Data
Tissues are composed of various types of interacting cells [1]. To understand the cellular organization and function in tissues, it is necessary to identify all of the different cell types and the locations of these different cell types within tissue structures. The transformative advances in experimental and computational methods will help us to build the complex map of the tissues and study how tissue organization influences the cell’s molecular state and interactions in healthy and diseased tissue.
Inhibition of Autophagy and Immune Response: Alpha-fetoprotein Stimulates Initiation of Liver Cancer
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a tumorous marker for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), it is synthesized mainly by the embryo yolk sac, fetal liver and the gastrointestinal tract. AFP belongs to the family of protein products of albuminoid genes, which are located in tandem arrangement in chromosome 4 (region 4q11-q13).
Methylation Status of Tumor Suppressor Genes in Circulating DNA of PDAC Patients: Facts and Hopes
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most lethal solid tumor malignancies and it is projected to become a leading cause of cancer related deaths in coming years. It is often diagnosed at an advanced stage owing to the lack of specific symptoms and rapid invasion.
