Loading
Archives of Clinical Ophthalmology
ISSN: 2771-7925

Christophe P Ribelayga
Bernice Weingarten Chair in Ophthalmology, USA
Featured Article
Repeatability of Scheimpflug Corneal Tomography in Patients with Keratoconus and Different Body Mass Indices

Featured Article
Uhthoff ’s Phenomenon as Presentation of COVID-19 Infection
Featured Article
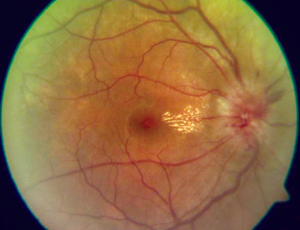
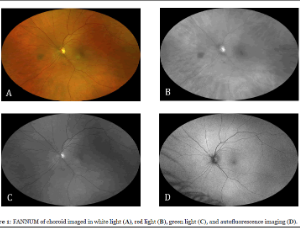
Focal Aggregates of Normal or Near Normal Uveal Melanocytes (FANNUMs) in the Choroid. A Practical Clinical Category of Small Ophthalmoscopically Evident Discrete Melanocytic Choroidal Lesions
About this Journal
Archives of Clinical Ophthalmology is an international publication primarily dedicated to publish original research and novel findings in the field of Ophthalmology. This online scientific journal provides a great opportunity to ophthalmologists and vision scientists to discuss and exchange their ideas and major advances in Ophthalmology and Vision Science.
Articles
Repeatability of Scheimpflug Corneal Tomography in Patients with Keratoconus and Different Body Mass Indices
To evaluate the repeatability of corneal tomographic parameters in keratoconus patients across different body mass index (BMI) categories. This prospective study was conducted at the University of Auckland, New Zealand, from June 2021 to June 2022. A total of 243 eyes from keratoconus patients aged 18-45 years were categorized into normal (BMI ≤24.9; n=55), overweight (BMI 25.0-29.9; n=58), and obese (BMI ≥30.0; n=130) groups. Patients underwent three consecutive scans using the Pentacam AXL.
Lens Clarity and Visual Fatigue in Children: The Role of Eyewear Hygiene and Healthcare Professionals
Visual fatigue, also known as digital eye strain (DES), has become a growing concern among children due to increased exposure to digital screens, especially after the global shift to remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. Although prolonged screen time and poor ergonomics are well-recognized contributors, the influence of eyewear hygiene-specifically lens cleanliness-on visual discomfort is less explored.
Gabapentin for Ocular Surface Disorders: Bridging Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Innovation
This commentary critically evaluates Rusciano's (2024) comprehensive review on gabapentin (GBP) as a multifaceted therapy for ocular surface diseases, emphasizing its transition from systemic to topical applications. We highlight the review's synthesis of GBP's polypharmacology—spanning calcium channel modulation, anti-inflammatory effects, and neuroprotection—and its innovative integration with nanotechnology (e.g., nanoceria platforms) to overcome corneal delivery challenges while potentially reducing systemic side effects associated with oral administration.
Generating Awareness and a Planned Multidisciplinary Treatment Approach Can Save Both the Sight and Life in Retinoblastoma in Developing Countries
While rare, retinoblastoma is the most common (1:16000 – 18000 live births) intraocular and life threatening tumor of childhood. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 66% of children present with symptoms before 2 years of age and 95% before 5 years of age. About 8000 new cases are detected annually with the highest incidence in Africa and India. In fact, more than 1400 cases each year are from India. According to Mukesh et al., 43% of the global burden lives in 6 countries of Asia (India, China, Indonesia, Pakistan, Bangladesh & Philippines).
Multidisciplinary Acute Care of Central Retinal Artery Occlusion with a Stroke Paradigm: A Call to Action
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is an ophthalmologic emergency that can result in permanent vision loss. Over 25% of CRAO are associated with acute cerebral ischemia, and there are many parallels between CRAO and acute ischemic stroke. There are no definitive treatment algorithms for CRAO, however there may be opportunities to treat CRAO as an “eye stroke”. Given the similarities to acute ischemic stroke, multidisciplinary involvement and stroke algorithms should be considered and tested for this disease.
Mega-Dose Dietary Riboflavin in Treatment in Keratoconus, Post-Refractive Cornea Ectasia and Migraine. Has Its Time Arrived?
Recently, several studies and investigators have shown the beneficial effects of high dose dietary riboflavin (vitamin B2) in the treatment of keratoconus, post-refractive (LASIK, PRK & Radial Keratotomy) ectasia (with sunlight exposure) and patients treated with our own protocol (NIH Clinical Study – www.clinicaltrials.gov - # NCT 03095235) discovered significant relief for intractable migraine headaches and/or ophthalmic migraine (classic migraine visual symptoms without headache).
Assessment of Visual Function for Education: A Commentary on ‘VEP Visual Acuity in Children with Cortical Visual Impairment’
Last year’s article In the International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology [1] highlighted that Cortical Visual Impairment (CVI) is now the leading cause of visual impairment in the developed world [2]. It also provided a definition of CVI [3,4], and summarized its functional deficits, and methods of assessment.
Uhthoff ’s Phenomenon as Presentation of COVID-19 Infection
This is the first reported case of COVID-19 associated optic neuritis (ON) presenting with classic Uhtoff’s phenomenon typically associated with multiple sclerosis (MS). Uhthoff phenomenon, also known as Uhthoff sign or syndrome, is a transient worsening of neurological function lasting less than 24 hours that can occur in multiple sclerosis patients due to increases in core body temperature.
Macular Microcirculation after Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment Repair Evaluated by OCT-Angiography
In the process of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD), retinal homeostasis may be adversely affected with resultant modifications in retinal and choroidal tissue. Hypoxia and nutrient deprivation along with inflammation at the detached retina may lead to morphological and microvascularity alterations. These changes imply that the functional status of the macula may not be entirely restored despite anatomical repair.
Repeatability of Scheimpflug Corneal Tomography in Patients with Keratoconus and Different Body Mass Indices
To evaluate the repeatability of corneal tomographic parameters in keratoconus patients across different body mass index (BMI) categories. This prospective study was conducted at the University of Auckland, New Zealand, from June 2021 to June 2022. A total of 243 eyes from keratoconus patients aged 18-45 years were categorized into normal (BMI ≤24.9; n=55), overweight (BMI 25.0-29.9; n=58), and obese (BMI ≥30.0; n=130) groups. Patients underwent three consecutive scans using the Pentacam AXL.
Stroke and Visual Loss in a Young Girl with Dengue Fever – Report of a Case and a Mini Review
The case of a young girl with Dengue fever presenting with seizures and bilateral visual loss is presented. At the time of presentation, she had right hemiplegia and dysarthria but was not dysphasic. Fundoscopy revealed presence of macular and disc oedema in the right eye and vitreous haemorrhage in the left eye.
Comment on “Retinitis Pigmentosa and Molar Tooth Sign Caused by Novel AHI1 Compound Heterozygote Pathogenic Variants: A Case Report”
Joubert syndrome (JS) is a rare congenital neurodevelopmental disease which is basically a primary Ciliopathy. It’s characteristic manifestation on imaging is so called ‘molar tooth sign’ in the brainstem and cerebellum. JS can involve multiple organs, mainly including retina, kidney, bone and liver. Clinical signs of early onset JS include hypotonia, developmental delay, breathing abnormalities, and ocular motor apraxia.
Multidisciplinary Acute Care of Central Retinal Artery Occlusion with a Stroke Paradigm: A Call to Action
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is an ophthalmologic emergency that can result in permanent vision loss. Over 25% of CRAO are associated with acute cerebral ischemia, and there are many parallels between CRAO and acute ischemic stroke. There are no definitive treatment algorithms for CRAO, however there may be opportunities to treat CRAO as an “eye stroke”. Given the similarities to acute ischemic stroke, multidisciplinary involvement and stroke algorithms should be considered and tested for this disease.
Focal Aggregates of Normal or Near Normal Uveal Melanocytes (FANNUMs) in the Choroid. A Practical Clinical Category of Small Ophthalmoscopically Evident Discrete Melanocytic Choroidal Lesions
Focal aggregate of normal or near normal uveal melanocytes (FANNUM) of the choroid is a term the author has proposed to categorize small melanocytic choroidal lesions that are not detectably thicker than surrounding normal choroid by B-scan ocular ultrasonography. In this article, the author describes the clinical features of small melanotic choroidal lesions he categorizes clinically as FANNUMs and discusses the presumed compositional spectrum of such lesions.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
