Loading
Journal of Cellular Immunology
ISSN: 2689-2812
2023
Volume 5, Issue 4, p97-140
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
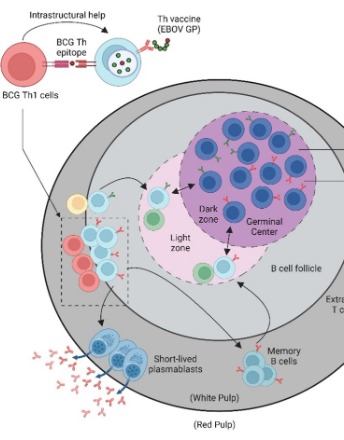
Designing Anti-Viral Vaccines that Harness Intrastructural Help from Prior BCG Vaccination
Tony W. Ng, Steven A. Porcelli
Vaccines are among the most effective tools for combatting the impact and spread of infectious diseases. However, the effectiveness of a vaccine can be diminished by vaccine inequality, particularly during severe outbreaks of infectious diseases in resource-poor areas. As seen in many developing countries that lack adequate healthcare infrastructure and economic resources, the acquisition and distribution of potentially life-saving vaccines may be limited, leading to prolonged suffering and increased deaths.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 4, p97-102 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.174
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis in Lymphoma by Chemotherapy Regimen
Kamen W. Kossow, Joseph G. Bennett, Marc S Hoffmann
Treatment of lymphomas involves a wide variety of chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted-agents tailored to disease biology and patient characteristics. Each of these regimens carry their own risk of opportunistic infections in an immunocompromised population. In addition to the treatment associated immunosuppression, lymphoma itself is immunosuppressive. Lymphoma associated immunosuppression is secondary to increased production of abnormal lymphocytes
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 4, p103-115 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.175
Commentary on Updated Insight into the Role of Th2-Associated Immunity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Xinyue Hou, Jinjin Chu, Shuhao Liu, Shuyu Jin, Jiamei Sun, Hui Wang, Haibo Li, Wei Liu, Chunxiang Chai, Sue Zhang, Donghua Xu
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a common autoimmune disease caused by multiple factors. The pathogenesis of SLE remains unclear. Helper T cell 2 (Th2 cell) is essential for humoral immunity, which participates in regulating type 2 immune response by producing typical cytokines of interleukin (IL)-4, IL-5, and IL-13. It is well known that Th2-associated immunity plays a vital role in autoimmune diseases, including SLE.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 4, p116-119 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.176
Type 1 Diabetes: A Disorder of the Exocrine and Endocrine Pancreas
Brittany S. Bruggeman, Desmond A. Schatz
Type 1 diabetes has historically been described as an endocrine (β-cell) specific autoimmune disease. However, a substantial reduction (20-50%) in pancreas organ size and subclinical to symptomatic exocrine pancreatic insufficiency are present at diagnosis and may begin even prior to the development of islet autoimmunity. The mechanisms of exocrine loss in type 1 diabetes are not well understood, but leading hypotheses include developmental defects, β-cell loss resulting in exocrine atrophy, or autoimmune or inflammatory destruction of exocrine cells.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 4, p120-126 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.177
Can Vaccines Stop Cancer Before It Starts? Assessing the Promise of Prophylactic Immunization Against High-Risk Preneoplastic Lesions
Tamer A. Addissouky, Ibrahim El Tantawy El Sayed, Majeed M. A. Ali, Yuliang Wang, Ayman El Baz, Ahmed A. Khalil, Naglaa Elarabany
Background: Cancer remains a leading cause of mortality with modest declines, highlighting the need for more efficacious prevention strategies like early immunological intervention against premalignant disease.
J Cell Immunol, 2023, Volume 5, Issue 4, p127-140 | DOI: 10.33696/immunology.5.178
Recommended Articles
Angioimmunoblastic T cell Lymphoma Microenvironment
Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL) is one of the most common T-cell lymphomas, second only to peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS). Initially AITL was considered a non-malignant lymphadenopathy with immune hyperactivation, nowadays being classified as a PTCL.
Exploiting Nanotechnology to Target Viruses
Infectious diseases caused by microorganisms of the most varied natures and by viral entities cause millions of deaths every year. Around the world, viral infections have impacted civilizations’ circumstances since the earliest times, including the current panorama of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic known as coronavirus disease in 2019 (COVID-19). In this sense, in the last century,
Reduced BCR Signaling and a Metabolic Shift Accompanies Malignant Progression of Follicular Lymphoma: A Lesson from Transcriptomics
Lymphoma represents the most common form of hematological malignancy in the developed world, accounting for 3.6% of all cancers and 55.6% of all blood cancers in Europe, with non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL) representing 90% of cases.
Bioconjugation of AuNPs with HPV 16/18 E6 Antibody through Physical Adsorption Technique
HPV 16/18 E6 oncoprotein has been evaluated as a useful biomarker with prognostic abilities as it can detect pre-cancer and cancerous states of cervical cancer progression. A positive E6 assay indicates a high correlation to the cervical cancerous phenotype, not the potential for cervical cancer, thus high specificity in triaging patients during screening. E6 levels of expression associate directly with the severity of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) lesions and the risk of
The Dual Role of Macrophages during Hepatitis B Infection
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) chronically infects more than 250 million individuals worldwide and is responsible for more than 800,000 deaths per year by promoting end-stage liver diseases, among which decompensated cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (WHO, July 2020) are prominent. Studies performed in chimpanzees or in animalversion of HBV (woodchuck HBV: WHBV) highlighted the lack of immune responses against the virus upon primary infection. Thus, HBV has been described as a “stealth” virus (i.e. a virus that does not modify/induce immune response in the cell). However, a growing number of studies describe that HBV is able to rapidly and efficiently counteract the innate immune response in a large variety of cells (hepatocytes, macrophages, Natural Killer cell…). Hereby, we focus on the role of macrophages (Mφ) during HBV infection.
What Can Go Wrong When Applying Immune Modulation Therapies to Target Persistent Bacterial Infections
Persistence is a transient phenotypic adaptation that confers survival to a small percentage of cells (between 0.01 and 10%) in genetically identical bacterial populations. Nevertheless, persistence greatly affects the evolution of acquired drug resistance mutations by decreasing antibiotic efficacy and generating a reservoir of surviving cells that can contribute to the onset of chronic infectious disease.
Verrucous Carcinoma of the Esophagus: Its Unique Etiology and Association with Human Papilloma Virus
Verrucous carcinoma is an extremely rare disease, and it is unique in terms of its appearance, growth pattern, and etiology. In 1948, Ackerman first described verrucous squamous cell carcinoma (VSC) as a variant of oral squamous cell carcinoma, and he collected 31 cases of oral neoplasms under the name, “Verrucous Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity.”
In Silico Proteome Analysis of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARSCoV- 2) is a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA with genome size 26.2, and 31.7 kb coronavirus, covered by an enveloped structure, which is a major source of disaster in the 21st century. A typical CoV contains at least six ORFs in its genome. SARS-CoV-2 is the seventh coronavirus that is known to cause human disease.
Kinetin/N6-furfuryladenine: A New Neurodegenerative Disease Lead from an Old Plant Cytokine
N6-fufuryladenine (N6FFA), or kinetin, has a long history as a plant cytokine with practical applications in agriculture. This adenosine analog is now commonplace in natural product small molecule chemical screening libraries, and as such has been discovered as active in mammalian disease pathways that include Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease (HD) and Familial Dysautonomia.
Tenofovir at the Crossroad of the Therapy and Prophylaxis of HIV and HBV Infections
Tenofovir, alias (R)-PMPA, was first divulged as an anti- HIV agent in 1993 [1]. That it would in 2012, become the first antiretroviral agent, approved by the US FDA (Food and Drug Administration) to prevent HIV infection, could have been predicted from the findings of Tsai et al.
Detection of Viruses and Development of New treatments: Insights into Antibody-Antigen Interactions and Multifunctional Lab-On-Particle for SARS CoV-2
The Corona Virus disease is a severe respiratory problem generated via severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS CoV-2). The latest strain of the disease was deadly enough to halt the global routines of human development. In this context, a number of research studies have been conducted to provide knowledge and to combat with this severe illness.
A New Isolated Local Varicella Virus: Isolation, Identification, Comparative Growth Characteristics and Immunological Evaluation in an Animal Model
A panel of 4 different cell lines was optimized for isolation, identification, and authentication of a varicella zoster virus from a swab sample of an 8-year-old boy suspected to varicella zoster infection. The system enabled highly efficient and rapid isolation of viruses in 33°C by serial sub culturing to more than 25 passages.
Extragastric Manifestations of Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Commentary
Helicobacter pylori (Hp) is characterized as a gram-negative bacterium with microaerophilic metabolism, flagellated and helix-shaped that affects approximately 50% of the world population and, in some regions, this rate can exceed 80%. Hp infection is well known to infect the epithelial tissue of the stomach, being involved with development of many stomach diseases, including gastric carcinoma.
CCR5 Inhibitors and HIV-1 Infection
Cellular components are attractive targets for antiviral therapy because they do not mutate as readily as do viral proteins do [1-3]. The identification of CCR5 as an HIV-1 coreceptor [4-7], facilitated by the discovery of the antiviral activities of CCR5 ligand ?-chemokines [8], resulted in the development of new viral entry inhibitors to block CCR5 binding, including both- small molecules and CCR5 antibodies
Anti-HIV-1 Activity of Crocodylus mindorensis (Philippine Crocodile) Serum in Cell-free and Cell-associated Virus Interactions to Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
Highly-Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART) is the recommended treatment and management strategy for HIV infection. Although the existing antiretroviral drugs are indispensably significant in improving the quality and extending the lives of HIV/ AIDS individuals, the drugs still have many limitations including development of resistance, production of toxicity, and their limited availability.
Lack of Prognostic Significance of Pretreatment Total Metabolic Tumor Volume on Event-free Survival at 24 Months in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a heterogeneous disease with variable outcomes. The majority of patients benefit from chemo-immunotherapy; however, 30 to 40% relapse after first-line treatment, and 10% are refractory to first-line treatment. This variability in outcome has led to the identification of prognostic factors to stratify patients based on their risk of relapse. The five-factor international prognostic index (IPI) was formulated for such risk stratification more than 20 years ago, based on clinical information obtained from patients with aggressive lymphomas treated with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP)-like chemotherapy. The addition of rituximab to CHOP chemotherapy led to improved outcomes, diminishing the discriminatory capacity of IPI amongst risk groups. Efforts to enhance the prognostic model by adding or defining new factors have only led to minor improvements without the ability to identify patients at risk of an inferior outcome.
Photodynamic Therapy for the Prevention of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Dental Office: Could be Possible?
In January 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) identified a novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 in the Wuhan province of China, which has since caused a worldwide pandemic, with more than 21.2 million confirmed cases and over 760,200 confirmed deaths as of 14 August 2020. SARS-CoV-2 is a single-stranded RNA virus classified in
Antifungal Effects of PC945, a Novel Inhaled Triazole, on Candida albicans Pulmonary Infection in Immunocompromised Mice
Candida spp. are often detected from fungal cultures or mycobiome analysis of respiratory secretions, but are not usually treated since, even if detected persistently, the presence is assumed to be benign colonization unless invasive candidiasis in deeply immunocompromised subjects is suspected.
Dental Practice Covid-19 Infection Control Precautions
In the end of 2019, a large number of patients started suffering from a disease that includes symptoms which can be displayed as a severe pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome, in addition to multi organ dysfunction. These symptoms were detected in Wuhan, which is considered the capital city of Hubei province, with
Epidemiologic, Clinical, and Biological Characteristics of Adult T-cell Leukemia/Lymphoma in Martinique (1983- 2013)
Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL) was first described in the Southwest islands of Japan in 1977 [1]. Then, the HTLV-1 (human T-lymphotropic virustype 1) was isolated in the United States in 1981 in two patients, one with mycosis fungoïdes and the other with Sezary syndrome [2,3], which have been consequently renamed.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
