Loading
Journal of Experimental Neurology
ISSN: 2692-2819
2023
Volume 4, Issue 3, p87-122
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Therapeutic Effectiveness of Brain Computer Interfaces in Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review
Yordan P. Penev, Alice Beneke, Kevin Thomas Root, Emily Meisel, Sean Kwak, Michael Diaz, Julia Root, Mohammad R. Hosseini, Brandon Lucke-Wold
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are a rapidly advancing field which utilizes brain activity to control external devices for a myriad of functions, including the restoration of motor function. Clinically, BCIs have been especially impactful in patients who suffer from stroke-mediated damage. However, due to the rapid advancement in the field, there is a lack of accepted standards of practice.
J Exp Neurol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 3, p87-93 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.4.077
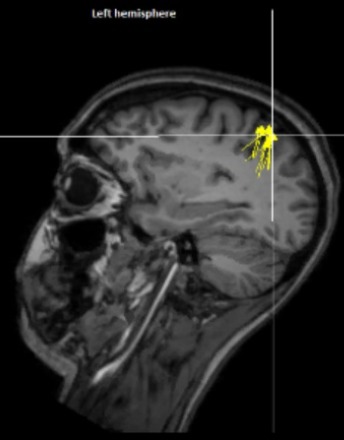
Responsive Neurostimulation for Management of Refractory Precuneus Onset Epilepsy: A Case Report
Arun Swaminathan
Posterior quadrant epilepsy is relatively uncommon and refractory seizures from these regions are difficult to diagnose and manage. A 28-year-old woman presented for evaluation of her seizures. Scalp Electroencephalogram (EEG) showed seizures with independent onset over the right posterior and left anterior regions.
J Exp Neurol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 3, p94-99 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.4.078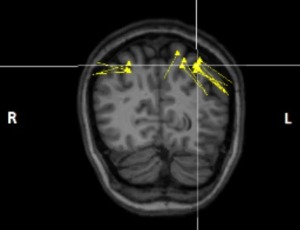
Change in Prevalence of Meningitis among Children with Febrile Seizure after the Pentavalent Vaccination
Shadi Shiva, Shokoufeh Khanzadeh, Vahid Shohanizad, Arshin Ghaedi, Brandon Lucke-Wold
Introduction: One of the most significant current discussions in pediatrics is whether lumbar puncture (LP) should be performed in children with febrile seizure (FS) as in the past. Objectives: We compared the prevalence of meningitis among FS children before and after the pentavalent vaccine to determine the importance of the LP in these children.
J Exp Neurol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 3, p100-108 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.4.079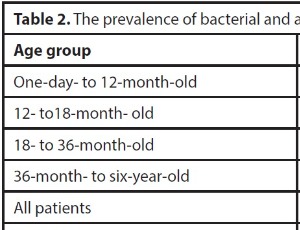
Association of Conformationally Altered Tau with α-1-antichymotrypsin in the Nuclei of Neurons in the Alzheimer's Disease Brain
Perla H. Horta-López, Jan Rícny, Benjamín Florán-Garduño, Francisco Garcia-Sierra
Conformational changes of Tau have been described to occur during its fibrillary and non-fibrillary aggregation inside neurons affected in the brain of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients. Two consecutive conformations have been described during the progression of the disease: an early conformation detected with the Alz-50 antibody, recognizing Tau molecules folding its amino terminus over its third repeated domain, and a later conformation involving the bending of the proline-rich region over the third repeated domain.
J Exp Neurol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 3, p100-108 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.4.080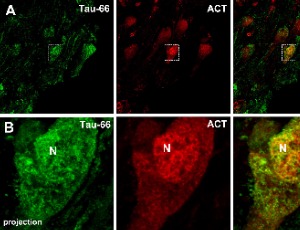
A Case Report of Rheumatoid Meningitis – A Rare Condition Presenting with Neurological Deficits
Arun Swaminathan, Arvind Ramesh
Rheumatoid meningitis (RM) is a rare condition seen in patients with longstanding rheumatoid arthritis (RA). It can present with a variety of neurological symptoms and is often mistaken for other neurological conditions, especially in the setting of immune suppression in these patients. We present a rare case of RM in an elderly woman with RA that presented with focal neurological symptoms and was eventually diagnosed on brain biopsy.
J Exp Neurol, 2023, Volume 4, Issue 3, p115-122 | DOI: 10.33696/Neurol.4.081
Recommended Articles
Commentary: Use of BACTRAC Proteomic Database-Uromodulin Protein Expression During Ischemic Stroke
Uromodulin (UMOD) is a glycoprotein expressed by the epithelial cells of the thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop in the kidney. Research has shown that increased uromodulin expression may be associated with lower risk of cardiovascular disease in adults.
Commentary – HIV-Induced Extracranial Carotid Ectasia and Stroke
HIV is a known risk factor for both ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Even with the widespread use of antiretroviral therapy, stroke incidence is higher in patients with HIV compared to non-HIV control subjects.
Body Iron Overload is a Determining Factor in Brain Damage in Acute Ischemic Stroke
Stroke is the second largest cause of death worldwide, with a world annual mortality incidence of about 5.5 million people, and it is also the leading cause of disability worldwide with 50% of survivors being chronically disabled.
Responsive Neurostimulation for Management of Refractory Precuneus Onset Epilepsy: A Case Report
Posterior quadrant epilepsy is relatively uncommon and refractory seizures from these regions are difficult to diagnose and manage. A 28-year-old woman presented for evaluation of her seizures. Scalp Electroencephalogram (EEG) showed seizures with independent onset over the right posterior and left anterior regions.
Change in Prevalence of Meningitis among Children with Febrile Seizure after the Pentavalent Vaccination
Introduction: One of the most significant current discussions in pediatrics is whether lumbar puncture (LP) should be performed in children with febrile seizure (FS) as in the past. Objectives: We compared the prevalence of meningitis among FS children before and after the pentavalent vaccine to determine the importance of the LP in these children.
Association of Conformationally Altered Tau with α-1-antichymotrypsin in the Nuclei of Neurons in the Alzheimer's Disease Brain
Conformational changes of Tau have been described to occur during its fibrillary and non-fibrillary aggregation inside neurons affected in the brain of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients. Two consecutive conformations have been described during the progression of the disease: an early conformation detected with the Alz-50 antibody, recognizing Tau molecules folding its amino terminus over its third repeated domain, and a later conformation involving the bending of the proline-rich region over the third repeated domain.
Macrophages in Bone and Synovial Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Macrophages are members of the innate immune system; that originate from monocyte cells from the myeloid stem cells. In response to the tissue environment, monocytes differentiate into two subtypes of macrophages, M1, or M2. The M1 or classically activated macrophages (CAM) aggravate immune responses by releasing reactive oxygen species (ROS), and pro-inflammatory cytokines.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
