Loading
Archives of Pharmacology and Therapeutics
ISSN: 2688-9609
2020
Volume 2, Issue 2, p17-33
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Drugs and Family Medicine: Form and Content
Jose Luis Turabian
Choosing an individual medication for a particular patient is one of the most important clinical decisions in family medicine (FM). Prescription of drugs is currently the main tool of FM and that’s the main source of prescription of drugs.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 2, p17-20 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.2.015
Biological Activity of Miscanthus capensis Root Extract
Idowu Jonas Sagbo, Wilfred Otang-Mbeng
Miscanthus capensis is a hardy, evergreen, medium-high, clump-forming grass that belongs to the Poaceae family. It is used in South Africa for the treatment of pimples, wounds, eczema, and acne.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 2, p21-23 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.2.016
Artificial Intelligence in Pharma: Positive Trends but More Investment Needed to Drive a Transformation
Peter Henstock
Over the past few years, pharmaceutical R&D has become aware of the potential benefits of leveraging artificial intelligence and its collective subfields including machine learning, deep learning, data science and advanced analytics.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 2, p24-28 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.2.017
Is There a Simple and Easy Way to Detect Singlet Oxygen? Comparison of Methods for Detecting Singlet Oxygen and Application to Measure Scavenging Activity of Various Compounds
Tokuko Takajo, Kazunori Anzai
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are known to exert both beneficial and harmful effects in the human body. Singlet oxygen (1O2), is highly reactive and considered as one of the ROS, although it is not a radical molecule.
Arch Pharmacol Ther, 2020, Volume 2, Issue 2, p29-33 | DOI: 10.33696/Pharmacol.2.018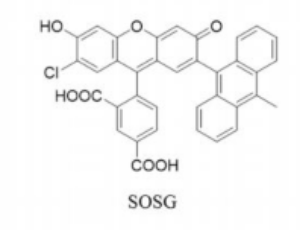
Recommended Articles
Why Do Patients Not Meet the Pharmacological Treatment?
Therapeutic compliance has been defined as the degree to which the behaviour of a person corresponds with the recommendations of the health professional [1].
Machine Learning for Healthcare: Emerging Challenges and Opportunities in Disease Diagnosis
Diagnosis is a process that identifies, explains, or establishes the individual’s disease from its symptoms and signs. Early and precise diagnosis is crucial since it influences the efficacy of treatment and avoids longterm complications for the infected person. Further, in the case of infectious diseases, undiagnosed patients can transmit the disease to a healthy population unknowingly. Besides, most of the diseases evolve with the time that significantly affects the clinical outcomes.
Diet and Exercise: A Novel Cure for Asthma? - A Short Communications on a Non-Pharmacological Strategy
Behavioral interventions with regular physical activity, weight loss and diet have repeatedly demonstrated preventive effects in a wide range of diseases. Furthermore, an unhealthy lifestyle is a known predictor for increased use of medication and also the leading risk factor for global mortality.
Dexamethasone: The First Drug to be Shown to Decrease Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19
The precise role of corticosteroids for treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is unclear due to lack of randomized trials.
How to Prevent Rehospitalization in Patients with COVID-19
Since December 2019, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) caused by 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) has resulted in 89,000 cases of Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), formerly known as Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (NCP) in China, including 2,450 deaths.
Pharmacogenetic Variants in the DPYD and TYMS Genes are Clinically Significant Predictors of Fluoropyrimidine Toxicity: Are We Ready for Use in our Clinical Practice
Fluoropyrimidines have been extensively used for almost 6 decades to treat a variety of solid cancers, especially colon, gastric, anal, rectal, head & neck and breast. However, 31–34% of patients encountered grade 3–4 adverse events (AEs) with 0.5% mortality oftennecessitating dose reduction or discontinuation.
Pharmacologic Therapy with Niacin for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Emerging Evidence
In pharmacologic doses niacin (nicotinic acid) has been used clinically for over six decades for atherogenic dyslipidemia and reduction of cardiovascular event risk. In combination with statin therapy, it effects regression of coronary atherosclerosis. Emerging evidence indicates a new potential use for niacin for the treatment of NAFLD and its complications. Despite this enormous amount of data on niacin, there is confusion and misconceptions about its use of a drug rather than as a vitamin, its formulations, and how it can be used in clinical practice. The purpose of this invited brief communication is to update and summarize this emerging evidence. We comment on how it may be valuable in the context of other drugs-in-development for NAFLD, especially for combination therapy for synergistic efficacy.
Preparing for a More Public Health-Aware Practice of Medicine in Response to COVID-19
After one year in a pandemic, we mourn the loss of over half a million lives in the United States, and over four million worldwide, and remain concerned over the challenges facing the families of 35 million people in the United States, and 200 million worldwide, who have suffered from cases of COVID-19.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cancer Care: Current Applications and Future Perspectives
Cancer is the second most common cause of death worldwide, accounting for an estimated 9.6 million deaths in the year 2018, a number that is expected to grow to more than 13 million by 2030. In the past decade, we have witnessed unprecedented scientific advancement in the understanding of cancer etiology, prevention, diagnosis and development of new therapeutic strategies.
Quantifying Respiratory Airborne Particle Dispersion Control Through Improvised Reusable Masks: The Physics of Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions for Reducing SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Airborne Transmission
In light of the current pandemic from rapid transmission of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2 or COVID-19) and significant morbidity, there has been inconsistent medical guidance given to the public regarding the wearing of non-medical improvised fabric masks or face coverings to reduce the transmission of COVID-19.
Artificial Intelligence in Pharma: Positive Trends but More Investment Needed to Drive a Transformation
Over the past few years, pharmaceutical R&D has become aware of the potential benefits of leveraging artificial intelligence and its collective subfields including machine learning, deep learning, data science and advanced analytics.
The Use of Hydroxychloroquine and Interferons for the Prophylaxis of COVID-19
At the beginning of Covid-19 pandemic, we proposed to use hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) and intranasal interferon (IFN) a-2b spray to prevent SARS-CoV-2.
Pharmacologic Therapies for Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: Current and Future Treatments
Bladder cancer is the sixth most common malignancy in the United States and 70% of cases are non-muscle invasive at the time of diagnosis. Effective treatment is crucial to prevent progression, which occurs in about 30% of patients. The American Urological Association (AUA) guidelines recommend treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) with intravesical Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) and chemotherapy.
EMG Signal Processing for Hand Motion Pattern Recognition Using Machine Learning Algorithms
Stroke is a major cause of death and disability in the world. There were approximately 25.7 million stroke survivors and 6.5 million deaths from stroke [1]. Stroke can result in arm disability and reduce daily life activity via weak arm muscle activity [2]. Studies have been performed to discover therapeutic and assistive approaches to compensate for disabilities and restore functions.
Hyperglycemia and diabetes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19
The prevalence of diabetes in COVID-19 patients ranges from 5.3% to 58% representing the second comorbidity after hypertension. However, when adjusted for age, diabetes prevalence among COVID-19 patients is similar to its prevalence in the general population.
Management of Diagnostic and Treatment Centers in the Second Wave of COVID-19
COVID-19 has challenged global health and affected many countries. The disease had infected more than 16 million people and killed over 650,000 ones by the end of July 2020. According to Sahu et al., COVID-19 epidemic is the third most common coronavirus in the 21st century, resulting in numerous deaths all over the world. It has caused severe psychological stress and increased hospital visits along with increased tiredness and burnout of medical staff. The disease has also raised many problems for the management of hospitals and diagnostic-treatment centers, so that many of them have no capacity to receive patients.
Scalable 3D Screen Printing Technology in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing - High Degree of Freedom in Terms of Drug Choice
Additive manufacturing has the potential to revolutionize the pharmaceutical industry, enabling the production of customized drugs for the mass market. However, concerns over scalability, low mechanical resistance, low printing resolution and limited material choices have so far hindered the practical application of current 3D printing (3DP)
News About the Extracellular Vesicles from Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Functions, Therapy and Protection from COVID-19
The present Commentary is a critical follow-up of a previous review about “Extracellular vesicles, news about their role in immune cells: physiology, pathology and diseases”, appeared in Clinical and Experimental Immunology last June 2019 [1].
Possible Therapeutic Use of Natural Compounds Against COVID-19
The outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) has led to coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19); a pandemic disease that has resulted in devastating social, economic, morbidity and mortality burdens. SARS-CoV-2 infects cells following receptor-mediated endocytosis and priming by cellular proteases.
Ectodomain Shedding May Play a Pivotal Role in Disease Severity in COVID-19
Ectodomain shedding mediated by a disintegrin and metalloprotease 10/17 (ADAM10/17) modulates the function of immune effector cells and may be involved in the novel coronavirus disease COVID-19. Toll-like receptor 7/8 (TLR7/8) recognizes single-strand RNA from viruses such as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19) during the innate immune response
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
