Loading
Journal of Clinical Haematology
ISSN: 2766-4686
Latest Articles
Diagnostic and Prognostic Challenges in Cytology for Multiple Myeloma: A Case Series in a Resource-limited Setting
Mame Ngone Coly , Mamadou Wague Guèye , Demba Makalou , Macoura Gadji , Alassane Diatta
Background: Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignancy of plasma cells characterized by clonal proliferation in the bone marrow and associated organ damage. In resource-limited settings, advanced diagnostic tools are often inaccessible, making conventional cytology a critical first-line diagnostic approach. Objectives: To assess the advantages and limitations of using bone marrow cytology as the primary diagnostic method for MM in a resource-constrained environment.
J Clin Haematol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p1-6 | DOI: 10.33696/haematology.6.062
The Effect of Food on the Pharmacokinetics of Unesbulin in Patients with Advanced Leiomyosarcoma
Lan Gao , Katsuyuki Murase , Diksha Kaushik , Nageswara Reddy , Brian A. Van Tine , Steven Attia , Dhiren D'Silva , Ronald Kong
Unesbulin is an orally bioavailable small molecule binding to the colchicine-binding site of tubulin and impeding tubulin polymerization and microtubule formation. It has been investigated as a monotherapy and in combination with other medications for the treatment of cancer, including leiomyosarcoma. This study investigated the effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of unesbulin. In total, eight leiomyosarcoma (LMS) patients (four males and four females) were enrolled in the food effect study during the phase 1b clinical study (NCT03761095).
J Clin Haematol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p12-16 | DOI: 10.33696/haematology.6.064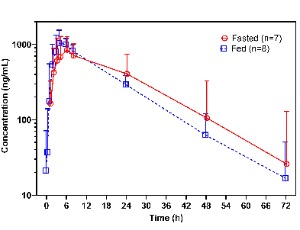
How to Provide a Sufficient Supply of Safe, Effective and Quality-assured Blood and Blood Components in Emergency Situations
Cees Th. Smit Sibinga
Background: Emergency situations can be personal and medical but also external and humanitarian (armed conflicts). In each situation a preparedness plan consisting of a risk assessment and gap analysis, emergency preparedness protocol, response and recovery protocol are needed. Objective: To discuss the question “how to provide a sufficient supply of safe, effective and quality blood and blood components in emergency situations?’”
J Clin Haematol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p17-27 | DOI: 10.33696/haematology.6.065
Lymphoid Blast Crisis in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Transformation to B cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Machrani Febriastry , Laila Miftakhul Jannah , Johanda Damanik
Background: Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is driven by the BCR-ABL1 fusion oncoprotein and is usually controllable with first- and second-generation tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKIs). However, ~5–7 % of patients eventually develop blast crisis, and a minority of these transform to B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL-B), a biologically aggressive state with a median overall survival of only 6–12 months despite therapy.
J Clin Haematol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p7-11 | DOI: 10.33696/haematology.6.063
Reduced Intensity Therapy for Primary Central Nervous System Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders is Associated with Preserved Survival Outcomes: A Twenty-Year Single-Institutional Experience
Bradley Uyemura , Zhanhai Li , David T. Yang , Michael J. Fallon , Jon S. Odorico , Kristin Bradley , Julie E. Chang
Primary central nervous system post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders (PCNS-PTLD) are rare complications of transplantation. Due to PCNS-PTLD’s scarcity, optimal treatments, risk factors, and outcomes are poorly characterized. By retrospective analysis of 20 patients treated at the University of Wisconsin between the years 2000–2022, we aimed to describe patient/disease characteristics, therapies received, and survival outcomes of PCNS-PTLD. Three separate clinical and pathological databases were reviewed to identify cases, with all patients having at least 2 years of long-term follow-up.
J Clin Haematol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p28-37 | DOI: 10.33696/haematology.6.066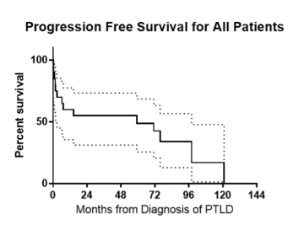
Repurposing Nilotinib as a Selective P38β Inhibitor in Hematopoietic Malignancies: Clinical Evidence and Mechanistic Insights
Xu Hannah Zhang , Jack Hsiang , Sangkil Nam , Hongzhi Li , Yate-Ching Yuan , Xiwei Wu , Susan Hmwe , Roger Moore , Steven T. Rosen
Background: Cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) is an incurable cancer characterized by elevated p38β and p38γ and downregulated tumor-suppressive p38α. Objectives: We aimed to identify selective p38β inhibitors and investigate their mechanisms and therapeutic implications in hematologic malignancies. Methods: A high-throughput screen of Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved compounds was conducted to identify p38β inhibitors. In vitro kinase assays, Western blots, scRNA-seq, synergy tests, and mass spectrometry were used. Clinical trial and public datasets were analyzed.
J Clin Haematol, 2025, Volume 6, Issue 1, p38-55 | DOI: 10.33696/haematology.6.067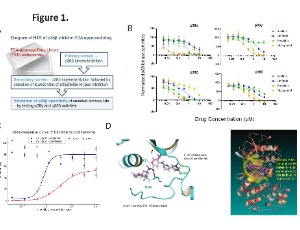
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
