Loading
Journal of Diabetes and Clinical Research
ISSN: 2689-2839
2019
Volume 1, Issue 2, p37-70
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Commentary: A Herbal Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes – The Dangers of Adulterated and Falsified Products
David W Holt, Atholl Johnston
In 2018, our group published a letter in The Lancet detailing a case in which a patient had taken a herbal preparation to treat her diabetes [1]. In essence, our laboratory was approached by the treating physician after the patient, a 58 year old lady of south Asian origin with a 30 year history of type 2 diabetes said that, during the previous two years, she had replaced some of her prescribed anti-diabetic medication with a herbal remedy purchased in India.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p37-39 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.006
Obesity, Family History of Diabetes, and Consanguineous Marriages are Risk Factors among Urban Population in South Indian City of Bengaluru
Aravinda Jagadeesha
In 2017, approximately 424.9 million adults (age 20- 79 yrs) were affected by diabetes, with 4 million deaths. Global diabetes burden is estimated to increase up to 628.9 million people. Moreover, diabetes care costed approximately $727 billion in 2017.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p40-42 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.007
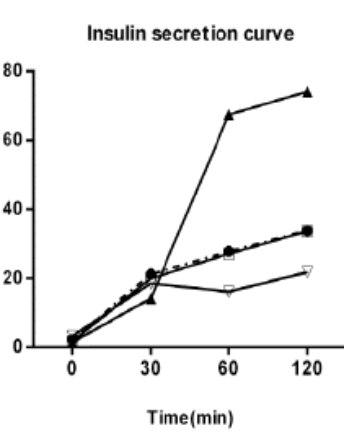
Altered Peak C-peptide and Fasting Blood Glucose in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Mengxiang Zhang, Rui Ding, Zuqun Wang, Juan Zhang, Jing Liu, Juan Wang
ASD refers to a group of complex neurodevelopmental disorders, characterized by deficits in social communication, interaction and demonstrating restricted, repetitive, and stereotyped patterns of behavior. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention forecasted that the prevalence of ASD would be 1 in 45 in USA.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p43-52 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.008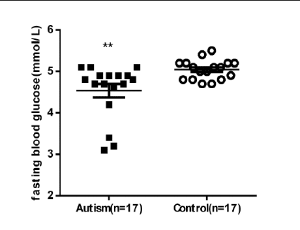
Cut-off Value of Random Blood Glucose among Asian Indians for Preliminary Screening of Persons with Prediabetes and Undetected Type 2 Diabetes Defined by the Glycosylated Haemoglobin Criteria
Priscilla Susairaj, Chamukuttan Snehalatha, Arun Raghavan, Arun Nanditha, Ramachandran Vinitha, Krishnamoorthy Satheesh, Desmond G Johnston, Nicholas J Wareham, Ambady Ramachandran
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) remains undiagnosed for many years in large number of persons living in developing countries. The cost of diagnostic tests and the invasive procedures involved in conventional screening methods remain a major setback to timely testing
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p53-58 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.009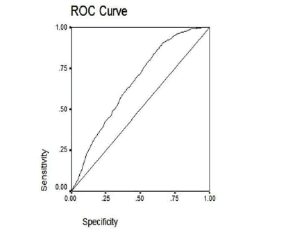
The Diabetic Shoulder – A Literature Review
Sana’a A. Alsubheen, Joy C. MacDermid, Tom J. Overend, Kenneth J. Faber
The shoulder complex is composed of three bony structures: the clavicle, scapula, and humerus, which are connected to form three synovial (glenohumeral, acromioclavicular, and sternoclavicular) and two functional (scapulothoracic and subacromial) joints.
J Diabetes Clin Res, 2019, Volume 1, Issue 2, p59-70 | DOI: 10.33696/diabetes.1.010
Recommended Articles
Role of Topical Insulin in Venous Ulcer Management
Wound healing is a dynamic process whereby cellular structures and the tissue layers are reconstructed. Adult wound healing can be categorized into three stages: inflammatory phase, proliferative phase, and remodelling phase. Blood cells like macrophages, neutrophils, extracellular matrix and mediators, various proteins, and various genes play an important role in these phases.
The Link of Nutrient Fluxes to Hepatic Insulin Resistance at Gene Expression
Insulin resistance has been studied extensively at systemic, organ, tissue and cellular and molecular levels. Overnutrition plays an essential role in the development of chronic metabolic diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. For subjects without genetic defects, the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes is a graduate process. How the transition from an insulinsensitive state to an insulin-resistant state occurs, and what the roles of nutrients are in the process have not been fully understood. Here, we try to summarize the current understanding of insulin-regulate gene expression in the liver, and describe a phenomenon of hepatic insulin resistance at gene expression (HIRAGE), which may be linked to overnutrition.
Improving Obesity and Insulin Resistance by Targeting Skeletal Muscle MKP-1
Obesity has reached a global epidemic and it predisposes to the development of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and related metabolic diseases. Current interventions against obesity and/or type 2 diabetes such as calorie restriction, exercise, genetic manipulations or established pharmacological treatments have not been successful for many patients with obesity and/or type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes Mellitus and Dengue
Diabetes mellitus is a common metabolic disorder that present with abnormal glucose metabolism. This metabolic disease is prevalent in many countries, worldwide. It is no doubt there might be a chance that diabetes mellitus might co-occur with other medical problems.
The Clinical Utility of Outpatient Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Establishing Insulinoma Diagnosis in a Patient with Impaired Nocturnal Hypoglycemia Awareness
Insulinomas are insulin secreting tumors arising from spontaneous mutations of the ductal, acinar, or islet cells of the pancreas. They are rare, having an incidence of only four cases per million people per year. Patients typically present with fasting hypoglycemia, experiencing neurologic symptoms like confusion, changes in vision, or abnormal behavior and autonomic symptoms like palpitations, diaphoresis, or tremulousness.
Altered Peak C-peptide and Fasting Blood Glucose in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
ASD refers to a group of complex neurodevelopmental disorders, characterized by deficits in social communication, interaction and demonstrating restricted, repetitive, and stereotyped patterns of behavior. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention forecasted that the prevalence of ASD would be 1 in 45 in USA.
Cut-off Value of Random Blood Glucose among Asian Indians for Preliminary Screening of Persons with Prediabetes and Undetected Type 2 Diabetes Defined by the Glycosylated Haemoglobin Criteria
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) remains undiagnosed for many years in large number of persons living in developing countries. The cost of diagnostic tests and the invasive procedures involved in conventional screening methods remain a major setback to timely testing
Can Vitamin D Supplementation Reduce Insulin Resistance and Hence the Risks of Type 2 Diabetes?
The question of whether or not correction of vitamin D deficiency might reduce the risks of later type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has been under debate for many decades. The necessity of vitamin D for normal insulin secretion was first identified experimentally in the 1980s.
Investigation of Regimen Adjustment for T2DM Patients Inadequately Controlled on Basal Insulin – Interpretation of the 4200 Study
Epidemiological survey indicated that majority of Chinese T2DM patients were with postprandial hyperglycemia, which may be related to more significant decline of ? cell function and more carbohydrates in dietary structure.
Insulin Signal Transduction is Impaired in the Type 2 Diabetic Retina
With increasing rates of obesity, rates of type 2 diabetes and diabetic complications are expected to rise exponentially over the next few decades (American Diabetic Association). A key feature of type 2 diabetes is a resistance to insulin. Insulin signaling is key to a number of physiological processes, including glucose metabolism, cell growth, general gene expression, and apoptosis.
Vitamin D and Insulin Resistance in Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia-a Commentary and Natural Expansion
In our previous focused review, the journal emphasized Type 2 diabetes (T2DM), excluding intimately associated disorders that should be considered integral components of the insulin resistance (IR) syndrome e.g., polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH), and gout.
Short Commentary on African Cuisine-Centered Insulin Therapy: Expert Opinion on the Management of Hyperglycaemia in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
The traditional African diet is considered a very rich source of nutrition being largely whole with minimal processing [1]. There are unique challenges when managing Diabetes in Africa especially when making nutritional recommendations. An appropriate diet protects organ (heart, liver, pancreas etc.) health and vice versa.
Insulin-like Growth Factor 2: Beyond its Role in Hippocampal-dependent Memory
The insulin-like peptides family is composed of insulin, insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1), and insulin-like growth factor (IGF2), together with IGF binding proteins (IGFBP1- IGFBP6) [1]. IGF2 is a single-chain secreted protein of 67 amino acids with important functions in fetal growth and development. IGF2 is the less characterized member of this family, and in mice and rats its expression in the brain occurs during embryonic development and adulthood but declines during aging [2].
A Commentary on “Better TIR, HbA1c, and Less Hypoglycemia in Closed-loop Insulin System in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Meta-analysis”
Our team’s previous meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of closed-loop insulin system (CLS) in non-pregnant individuals with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). In this study, we aim to discuss the broader application of CLS in a more diverse population and address the current challenges and future development directions.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
