Loading
Archives of Gastroenterology Research
ISSN: 2692-5427
2021
Volume 2, Issue 3, p75-109
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Treatment and Drug Resistance to Helicobacter Pylori: A Brief Review
Vinícius Lima de Souza Gonçalves, Jonathan Santos Apolonio, Ronaldo Teixeira da Silva Junior, Maria Luísa Cordeiro Santos, Beatriz Rocha Cuzzuol, Marcel Silva Luz, Fabian Fellipe Bueno Lemos, Hanna Santos Marques, Camilo Santana Silva, Mariana Miranda Sampaio, Bruna Teixeira da Costa, Fabrício Freire de Melo
Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative, spiral-shaped bacterium that inhabits the gastric environment of 60.3% of the global population. Though most individuals infected with the bacterium remain asymptomatic, it is known that this infection plays a pivotal role in the development of diseases such as chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer, gastric cancer and gastric MALT lymphoma. Hence, eradication of H. pylori is associated with the potential prevention of many gastric and extra gastric diseases, such as gastric cancer.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p75-78 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.2.031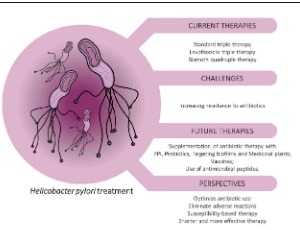
Creation of an Ex-vivo Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) Training Model Using a Perfused Non-cirrhotic Porcine Liver
Jorge E Lopera, Ryan Bitar, John Walker, James Elliott, Katie Strychalski, Harrison Pollard, Annie Dang, Luis Garza, Carlos Ortiz, Matthew Parker, Matthew Z Taon, Partha Mandal, Barrett O’Donnell, Rajeev Suri, Ho-Young Song
Liver cirrhosis is growing problem worldwide with serious adverse clinical manifestations secondary to portal hypertension, including ascites, hydrothorax, bleeding from gastric and esophageal varices among others. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) creation has demonstrated to be a very effective minimally invasive technique to treat portal hypertension largely supplanting surgical shunts. TIPS, however, is a highly technically demanding procedure with a steep learning curve.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p79-85 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.2.032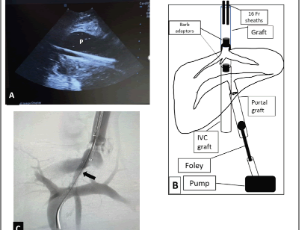
Survival Disparity Between Antiviral-Treated and Antiviral-Naïve Patients Who Develop Their First HBV-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Daniel Garrido, Peter Block, Selena Lin, Dina Halegoua-DeMarzio, Hie-Won Hann
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a public health problem, accounting for more than 257 million cases of chronic infection and a major cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) worldwide. With the vaccination and the advent of nucleos(t)ide analogues (NAs) as antiviral therapy, chronic HBV infection currently accounts for approximately 50% of HCC cases worldwide, a significant decrease from >80% in the 1980’s. The reduced incidence of HBV-related HCC (HBV-HCC) with NAs with lamivudine, entecavir, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is well documented.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p86-94 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.2.033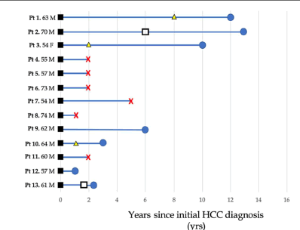
The Inappropriate Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors: An Internal Medicine Residency Clinics Effort to Deprescribe
Polina Gaisinskaya, Zed Seedat, Sanja Patino, Navneet Kaur, Oscar L. Hernandez, Eric Abkian, Jamie Fabricant, Mishah Azhar, Michael A. DeDonno, Nabil Benhayoun
Since 1989, PPIs have become among the top-selling drug classes in the country. It is estimated that in the United States alone, about a quarter of the country suffers from acid related conditions. Their versatility and popularity have prompted the World Health Organization to add PPIs to their list of essential medications. The low cost of PPIs and over the counter (OTC) availability of these medications have made their use ubiquitous in outpatient care.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p95-101 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.2.034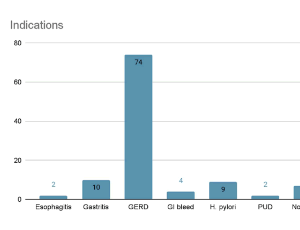
Extragastric Manifestations of Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Commentary
Camilo Santana Silva, Ronaldo Teixeira da Silva Junior, Luana Kauany de Sá Santos, Jonathan Santos Apolonio, Bruna Teixeira da Costa, Beatriz Rocha Cuzzuol, Marcel Silva Luz, Fabrício Freire de Melo
Helicobacter pylori (Hp) is characterized as a gram-negative bacterium with microaerophilic metabolism, flagellated and helix-shaped that affects approximately 50% of the world population and, in some regions, this rate can exceed 80%. Hp infection is well known to infect the epithelial tissue of the stomach, being involved with development of many stomach diseases, including gastric carcinoma.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 3, p102-109 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.2.035
Recommended Articles
Spontaneous Resolution of Infected Pancreatic Necrosis after Fistulization into Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
A 67-year-old female with a history of arterial hypertension and previous hysterectomy, was recovered, in July 2019, for moderately-severe acute biliary pancreatitis with evidence of stones in gallbladder and bile duct and pancreatic necrosis on imaging (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography. A contrast enhanced CT, a week after the admission, showed necrotic areas in the pancreas and a large peripancreatic fluid collection (60 mm long) with air pockets within (acute necrotic collection, with signs of infection. Since she was haemodynamically stable and there was no evidence of organ failure, according to “step-up approach”, she was managed medically with antibiotics (piperacillin-tazobactam + metronidazole) and fluids.
The Potential Role of SEPT6 in Liver Fibrosis and Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Liver fibrosis is a reversible wound-healing response in which a variety of cells and factors are involved in and results in excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM). Cirrhosis is one of the significant causes of portal hypertension and end-stage liver disease, and it is the 14th most common cause of death around the world. Approximately 1.03 million people worldwide die from liver cirrhosis every year.
Prognostic Utility of Ferritin Transferrin Ratio in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
There is growing body of literature to identify novel prognostic markers in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), including serum ferritin (SF), transferrin levels, alfa fetoprotein (AFP), and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR). Chronic inflammation and fibrogenesis are considered quite essential in the oncogenesis of HCC. The trigger for this inflammation could range from viral hepatitis, alcoholic cirrhosis, to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Also, iron overload as in hereditary hemochromatosis is linked to one of the factors for HCC oncogenesis.
Role of Topical Insulin in Venous Ulcer Management
Wound healing is a dynamic process whereby cellular structures and the tissue layers are reconstructed. Adult wound healing can be categorized into three stages: inflammatory phase, proliferative phase, and remodelling phase. Blood cells like macrophages, neutrophils, extracellular matrix and mediators, various proteins, and various genes play an important role in these phases.
Gastric Cancer: A Brief Review, from Risk Factors to Treatment
Gastric cancer (GC), also known as stomach cancer, is a worldwide health problem. Anatomically, it can occur from the gastroesophageal junction to distal portions of the stomach. Considering both sexes, worldwide, it is the 5th most common neoplasm (5.7%) and the 3rd cause of mortality among malignancies, leading to approximately 782,000 deaths in 2018. The incidence varies geographically but 50% of new cases are diagnosed in developed countries. High incidence is observed in Asia, Latin America, and in the central and eastern parts of Europe. There are several ways to classify GC, but the most used is Lauren’s Classification, which proposes two main histological groups: intestinal and diffuse. This classification is important because there are marked etiological, pathological, and epidemiological differences between the subgroups, guiding the clinical approach for each patient.
Botulinum Toxin: The Promising Future of Prostate Cancer Treatment
Botulinum toxin (BT) is a potent poisonous neurotoxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum and related species [1]. Its action consists of inhibiting neuromuscular junctions by blocking the release of acetylcholine and desensitizing sensory nerves.
Evaluation and Management of chronic Hypertension in Pregnancy
Chronic hypertension is present in 1-2% of pregnant women. Women with chronic hypertension are at an increased risk of maternal and perinatal complications when compared with normotensive women.
NOXA the BCL-2 Family Member behind the Scenes in Cancer Treatment
NOXA is a critical mediator of stress responses to anticancer drugs. This BH3-only protein sets the apoptotic threshold in cancer cells in response to chemotherapies by counteracting the prosurvival BCL-2 family protein MCL-1. A complex and dynamic network relying on both highly controlled gene transcription activity and protein degradation by proteasome, regulates cellular NOXA levels from low in steady state to rapidly enhanced upon stressful condition.
Pharmacologic Therapy with Niacin for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Emerging Evidence
In pharmacologic doses niacin (nicotinic acid) has been used clinically for over six decades for atherogenic dyslipidemia and reduction of cardiovascular event risk. In combination with statin therapy, it effects regression of coronary atherosclerosis. Emerging evidence indicates a new potential use for niacin for the treatment of NAFLD and its complications. Despite this enormous amount of data on niacin, there is confusion and misconceptions about its use of a drug rather than as a vitamin, its formulations, and how it can be used in clinical practice. The purpose of this invited brief communication is to update and summarize this emerging evidence. We comment on how it may be valuable in the context of other drugs-in-development for NAFLD, especially for combination therapy for synergistic efficacy.
Are We Close to Achieving a HBV Cure? Risk for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Persists Despite Long-term HBV Suppression: An Update on Our Experience
Since the discovery of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) by Blumberg et al., great progress has been made in understanding the pathogenesis of the virus and its role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). It is estimated that hepatitis B is responsible for about 50% of the HCC cases worldwide. Because of geographic variations in HBV incidence, the burden of HBV-related HCC (HBV-HCC) is highest in endemic areas such as Asian-Pacific and sub- Saharan Africa and lowest in the United States and the West. The hepatitis B vaccines, developed in the 1980s, transformed the evolution of hepatitis B in the modern era. This was followed by high effective anti-viral that reduced HBV infections and HBV-HCC.
The Role of TIGAR-mediated Metabolic Processes in Autophagy and Cell Survival
Autophagy is the one of the essential pathways for maintaining homeostasis of cells and plays an important regulatory role in cell survival and death. Tp53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR) is a Tp53 target protein and is not only involved in the regulation of metabolism, cell cycle progression and radiation response, but also plays a role in autophagy.
Fatty Liver and Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Fatty liver (FL) is the most common wide-world liver disease that is nowadays demonstrating an increasing prevalence trend. In sharp contrast, the most common causes of liver diseases, such as viral causes, are decreasing thanks to advances in antiviral therapies. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is characterized by hepatic fat accumulation, often associated with insulin resistance (IR), and defined by the presence of steatosis in at least 5% of hepatocytes in absence of relevant alcohol intake.
Conversion Surgery for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Lenvatinb
Multidisciplinary treatment is widely applied for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) using liver resection/ transplantation, local ablation therapy, transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), and systemic therapy. Systemic therapy is recommended and can provide a modest prognosis for HCC in Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging C.
Tenofovir at the Crossroad of the Therapy and Prophylaxis of HIV and HBV Infections
Tenofovir, alias (R)-PMPA, was first divulged as an anti- HIV agent in 1993 [1]. That it would in 2012, become the first antiretroviral agent, approved by the US FDA (Food and Drug Administration) to prevent HIV infection, could have been predicted from the findings of Tsai et al.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Animal Models Available to Characterize Tumor Immunology and Optimize Treatment Development
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the second cause of cancer-related death worldwide with almost 1 million new cases per year. At the diagnosis, 70% of patients have only access to a palliative treatment with few therapeutic options mostly represented by tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as sorafenib and lenvatinib in first line; regorafenib and cabozantinib in second line.
Treatment and Drug Resistance to Helicobacter Pylori: A Brief Review
Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative, spiral-shaped bacterium that inhabits the gastric environment of 60.3% of the global population. Though most individuals infected with the bacterium remain asymptomatic, it is known that this infection plays a pivotal role in the development of diseases such as chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer, gastric cancer and gastric MALT lymphoma. Hence, eradication of H. pylori is associated with the potential prevention of many gastric and extra gastric diseases, such as gastric cancer.
Creation of an Ex-vivo Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) Training Model Using a Perfused Non-cirrhotic Porcine Liver
Liver cirrhosis is growing problem worldwide with serious adverse clinical manifestations secondary to portal hypertension, including ascites, hydrothorax, bleeding from gastric and esophageal varices among others. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) creation has demonstrated to be a very effective minimally invasive technique to treat portal hypertension largely supplanting surgical shunts. TIPS, however, is a highly technically demanding procedure with a steep learning curve.
Survival Disparity Between Antiviral-Treated and Antiviral-Naïve Patients Who Develop Their First HBV-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a public health problem, accounting for more than 257 million cases of chronic infection and a major cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) worldwide. With the vaccination and the advent of nucleos(t)ide analogues (NAs) as antiviral therapy, chronic HBV infection currently accounts for approximately 50% of HCC cases worldwide, a significant decrease from >80% in the 1980’s. The reduced incidence of HBV-related HCC (HBV-HCC) with NAs with lamivudine, entecavir, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is well documented.
Commentary on: Echocardiography in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Is It Time to Reconsider Its Prognostic Utility?
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) represents a rare but devastating disease due to small pulmonary arterial vessels remodelling and increased pulmonary vascular resistance leading to right ventricular dysfunction, right heart failure and death.
The Inappropriate Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors: An Internal Medicine Residency Clinics Effort to Deprescribe
Since 1989, PPIs have become among the top-selling drug classes in the country. It is estimated that in the United States alone, about a quarter of the country suffers from acid related conditions. Their versatility and popularity have prompted the World Health Organization to add PPIs to their list of essential medications. The low cost of PPIs and over the counter (OTC) availability of these medications have made their use ubiquitous in outpatient care.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
