Loading
Archives of Clinical Ophthalmology
ISSN: 2771-7925
2021
Volume 1, Issue 1, p1-29
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Macular Microcirculation after Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment Repair Evaluated by OCT-Angiography
Evita Evangelia Christou, Maria Stefaniotou
In the process of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD), retinal homeostasis may be adversely affected with resultant modifications in retinal and choroidal tissue. Hypoxia and nutrient deprivation along with inflammation at the detached retina may lead to morphological and microvascularity alterations. These changes imply that the functional status of the macula may not be entirely restored despite anatomical repair.
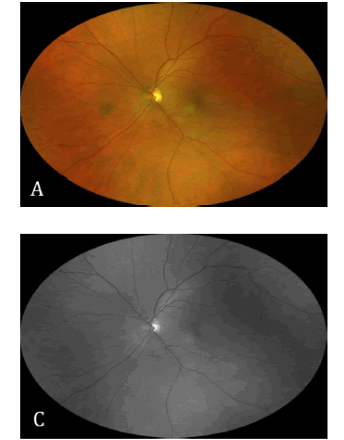
Arch Clin Ophthalmol, 2021, Volume 1, Issue 1, p1-7 | DOI: 10.33696/Ophthalmology.1.001
Focal Aggregates of Normal or Near Normal Uveal Melanocytes (FANNUMs) in the Choroid. A Practical Clinical Category of Small Ophthalmoscopically Evident Discrete Melanocytic Choroidal Lesions
James J. Augsburger
Multiple types of discrete melanocytic choroidal lesions are currently recognized, including benign choroidal nevi, choroidal malignant melanomas, patches of choroidal melanocytosis, and foci of choroidal melanocytes stimulated paraneoplastically by a systemic nonmelanoma malignant neoplasm.
Arch Clin Ophthalmol, 2021, Volume 1, Issue 1, p8-19 | DOI: 10.33696/Ophthalmology.1.002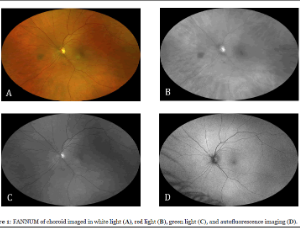
Mega-Dose Dietary Riboflavin in Treatment in Keratoconus, Post-Refractive Cornea Ectasia and Migraine. Has Its Time Arrived?
John Steven Jarstad
Recently, several studies and investigators have shown the beneficial effects of high dose dietary riboflavin (vitamin B2) in the treatment of keratoconus, post-refractive (LASIK, PRK & Radial Keratotomy) ectasia (with sunlight exposure) and patients treated with our own protocol (NIH Clinical Study – www.clinicaltrials.gov - # NCT 03095235) discovered significant relief for intractable migraine headaches and/or ophthalmic migraine (classic migraine visual symptoms without headache).
Arch Clin Ophthalmol, 2021, Volume 1, Issue 1, p20-20 | DOI: 10.33696/Ophthalmology.1.003
Multidisciplinary Acute Care of Central Retinal Artery Occlusion with a Stroke Paradigm: A Call to Action
Stacey Q. Wolfe, Stephanie A. Coffman, Mark Perez, Katriel Lee, Bartlett H.Hayes, Tamra Ranasinghe, Patrick A. Brown, Kyle M. Fargen
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is a painless ophthalmologic emergency with potential for irreversible vision loss. Similar to ischemic stroke, CRAO occurs when there is sudden obstruction of the central retinal artery, leading to ischemic injury to the retina and subsequent cell death. Continuous occlusion and ischemia of the retina progresses to permanent damage to retinal cells and loss of vision.
Arch Clin Ophthalmol, 2021, Volume 1, Issue 1, p20-26 | DOI: 10.33696/Ophthalmology.1.004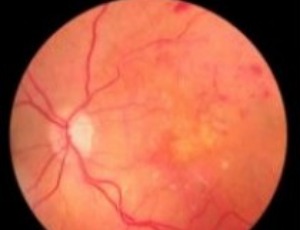
Generating Awareness and a Planned Multidisciplinary Treatment Approach Can Save Both the Sight and Life in Retinoblastoma in Developing Countries
Soma Rani Roy
While rare, retinoblastoma is the most common (1:16000 – 18000 live births) intraocular and life threatening tumor of childhood [1,2]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 66% of children present with symptoms before 2 years of age and 95% before 5 years of age. About 8000 new cases are detected annually with the highest incidence in Africa and India. In fact, more than 1400 cases each year are from India [3].
Arch Clin Ophthalmol, 2021, Volume 1, Issue 1, p27-29 | DOI: 10.33696/Ophthalmology.1.005
Recommended Articles
The Nature of Radiation-induced Inherited Recessive Gene Mutations in Drosophila Melanogaster
The nature of gene mutations induced by ionizing radiation in germ cells and transmitted to offspring remains one of the most important problems in radiation genetics of higher eukaryotes. The data accumulated in this field were obtained by different authors under different experimental conditions which does not give a complete insight about the nature of radiation-induced inherited mutations at different genome levels (chromosome, gene, DNA).
Macular Microcirculation after Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment Repair Evaluated by OCT-Angiography
In the process of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD), retinal homeostasis may be adversely affected with resultant modifications in retinal and choroidal tissue. Hypoxia and nutrient deprivation along with inflammation at the detached retina may lead to morphological and microvascularity alterations. These changes imply that the functional status of the macula may not be entirely restored despite anatomical repair.
Spontaneous Resolution of Infected Pancreatic Necrosis after Fistulization into Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
A 67-year-old female with a history of arterial hypertension and previous hysterectomy, was recovered, in July 2019, for moderately-severe acute biliary pancreatitis with evidence of stones in gallbladder and bile duct and pancreatic necrosis on imaging (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography. A contrast enhanced CT, a week after the admission, showed necrotic areas in the pancreas and a large peripancreatic fluid collection (60 mm long) with air pockets within (acute necrotic collection, with signs of infection. Since she was haemodynamically stable and there was no evidence of organ failure, according to “step-up approach”, she was managed medically with antibiotics (piperacillin-tazobactam + metronidazole) and fluids.
Gastric Cancer: A Brief Review, from Risk Factors to Treatment
Gastric cancer (GC), also known as stomach cancer, is a worldwide health problem. Anatomically, it can occur from the gastroesophageal junction to distal portions of the stomach. Considering both sexes, worldwide, it is the 5th most common neoplasm (5.7%) and the 3rd cause of mortality among malignancies, leading to approximately 782,000 deaths in 2018. The incidence varies geographically but 50% of new cases are diagnosed in developed countries. High incidence is observed in Asia, Latin America, and in the central and eastern parts of Europe. There are several ways to classify GC, but the most used is Lauren’s Classification, which proposes two main histological groups: intestinal and diffuse. This classification is important because there are marked etiological, pathological, and epidemiological differences between the subgroups, guiding the clinical approach for each patient.
The Consideration of Endometriosis in Women with Persistent Gastrointestinal Symptoms and a Novel Neuromusculoskeletal Treatment Approach
Endometriosis is a chronic, hormone-dependent, inflammatory disease, characterized by the presence and growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterine cavity and it is associated with chronic pelvic pain and infertility. Worldwide, approximately 176 million women between the ages of 15 and 49 are affected by endometriosis. Endometriosis is a complex disease that induces a chronic inflammatory process and can be challenging to treat. Chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS) is defined as pelvic pain lasting greater than three to six months that is not solely related to menstruation, sexual activity or bowel movements.
Refractory Gastro-oesophageal Reflux Disease and Laryngopharyngeal Reflux - Use the Bottom up Approach
The pathophysiology of typical gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) symptoms and reflux oesophagitis is associated with excess acid reflux, but both refractory GORD and laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) have strong links with functional gut disorders. Oesophageal pH impedance monitoring, our accepted gold standard for diagnosing GORD, has significant shortcomings when assessing proximal oesophageal and in particular pharyngeal reflux. In addition, identifying potential contamination of other parts of the respiratory tract such as lungs or sinuses is not possible. The association between irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and both refractory GORD and LPR suggests a common pathogenesis.
Gastrointestinal Manifestations of COVID-19: An Overview
The Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the new coronavirus of severe acute respiratory syndrome 2 (SARS-CoV-2), single-stranded, positive sense, spherical RNA virus with spikes protein that protrude on its surface giving the appearance of a crown, from the Latin corona. It belongs to the large family of coronaviruses (CoVs) and the genus β-coronavirus. COVID-19 can involve manifestations in the respiratory system, as well as other biological systems, as a intestinal.
Updates in the Treatment of Superficial Gastric Neoplasms by Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Gastric cancer is one of the neoplasms with the highest degree of mortality worldwide, responsible for more than 780,000 deaths in 2018 and whose incidence has been increasing over the last few years, mainly in Asian and Latin American countries. The technological imaging advances in digestive endoscopy such as virtual chromoendoscopy and magnification associated with a systematic and comprehensive endoscopic examination of the entire gastric mucosa by a trained operator have optimized the early detection of pre-malignant and malignant lesions, which have favoured the high rate of curability through the use of endoscopic resection techniques such as endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD).
Importance of Autopsy from a Gastrointestinal Pathology Perspective: A Ten-year Review of 891 Autopsies
There has been a decline in autopsy rates by 58% from 1972-2007. The major reason for this decline is the ability to diagnose diseases and disorders that result in mortality with greater accuracy. Additionally, the Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations dropped the standard practice of requiring a 20-25% autopsy rate for in-hospital deaths. The perception or attitude towards autopsies from both family members and clinicians is changing leading to a further decrease in the autopsy numbers.
Advances in Functionalized Hybrid Biopolymer Augmented Lipid-based Systems: A Spotlight on Their Role in Design of Gastro Retentive Delivery Systems
Biopolymers have earmarked their importance in the biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. Researchers are still working for the facilitation of better therapeutic effects and medical benefits. In this context, several strategies are on a play like functionalization of biopolymers with physicochemical modification, functionalization of lipids with biopolymers, development of composites or hybrid systems for bringing together the benefits of individual moieties/systems
Viable but Nonculturable Gastrointestinal Bacteria and Their Resuscitation
Viable but nonculturable (VBNC) bacteria are deeply dormant phenotypic variants that are characterized by a loss of culturability in conventional culture media, yet retain some viability markers. Thus, low metabolic activity, nutrient uptake, membrane integrity, and respiration are all detectable in these dormant cells. In 1982, the VBNC state was first described for Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. Shortly afterwards, VBNC Salmonella enteriditis were found to regain culturability
Archives of Gastroenterology Research: A Message from Prof. Dr. Rolf Teschke (Editor-in-Chief)
As the new editor-in-chief of Archives of Gastroenterology Research (AGR) I cordially welcome all current readers of AGR and future contributors to AGR. Together with my editorial team of AGR we encourage scientists and clinicians involved in the care of patients with gastrointestinal diseases to submit their interesting reports to AGR with the aim to be published following fair evaluation by external peer reviewers
Extragastric Manifestations of Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Commentary
Helicobacter pylori (Hp) is characterized as a gram-negative bacterium with microaerophilic metabolism, flagellated and helix-shaped that affects approximately 50% of the world population and, in some regions, this rate can exceed 80%. Hp infection is well known to infect the epithelial tissue of the stomach, being involved with development of many stomach diseases, including gastric carcinoma.
Gastric GIST with 13 kg in Asymptomatic Patient: A Rare Case of Giant GIST and Literature Review
Although gastrointestinal stromal tumors, GISTs, are the most common neoplasms arising from the gastrointestinal mesenchyme, they represent less than 1% of all digestive tumors. Its incidence has increased in recent years, probably due to improved diagnostic methods. It is currently known that GIST is the most common sarcoma. It originates from interstitial cells of Cajal and depends on the transcription factor ETV-1. These are neoplasms associated with molecular alterations and some mutations.
Elucidating the Role of Chemokines in Infectious Diseases and Gastric Cancer
Although the prevalence of gastric cancer is decreasing in many developed nations, it is the fourth most prevalent cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally. Around 8 percent of recently diagnosed malignant tumors are stomach cancer, more than 7,00,000 individuals die from gastric cancer yearly. Despite extensive research into new diagnostic and therapeutic methods, the prognosis for individuals with advanced stomach cancer remains dismal, and survival rates have hardly improved. In recent years, many latest innovations have improved our understanding of the molecular mechanisms and modifications that contribute to gastric cancer’s beginning and progression, including several genetic and molecular modifications and mutations.
Repurposing of an Antifungal Drug against Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
Molecular docking approaches explore the receptor-ligand conformations within the binding sites of macromolecular targets [1]. Structure-based drug discovery is widely used by the scientific community in Medicinal Chemistry to estimate the ligand-receptor binding free energy by evaluating critical phenomena involved in the intermolecular recognition process [2,3].
Targeting Cullin-RING E3 Ubiquitin Ligase 4 by Small Molecule Modulators
Cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase 4 (CRL4) plays an essential role in cell cycle progression. Recent efforts using high throughput screening and follow up hit-to-lead studies have led to identification of small molecules 33-11 and KH-4-43 that inhibit E3 CRL4’s core ligase complex and exhibit anticancer potential.
LncZFAS1 Inhibit MPP+-Induced Neuroinflammation Through TXNIP/MIB1 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase/NLRP3 Axis
Recently researchers have focused on the role of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, atrophic lateral sclerosis, Huntington’s disease, Multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease (PD). PD is one of the leading neurodegenerative diseases in developed countries and the complete etiological scenario remains unknown. A-synuclein misfolding and aggregation, mitochondrial dysfunction, dysfunctional protein clearance and ubiquitin/proteasome systems, and neuroinflammation have been associated with PD.
Body Iron Overload is a Determining Factor in Brain Damage in Acute Ischemic Stroke
Stroke is the second largest cause of death worldwide, with a world annual mortality incidence of about 5.5 million people, and it is also the leading cause of disability worldwide with 50% of survivors being chronically disabled.
Biomedical Gastronomy in the Management of Smell and Taste Disorders
Whether one lives to eat or just eats to live, the consumption, ingestion and digestion of foods and beverages comprise a complex system of intertwined signals and rituals.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
