Loading
Archives of Gastroenterology Research
ISSN: 2692-5427
2021
Volume 2, Issue 1, p1-47
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
Gastrointestinal Manifestations of COVID-19: An Overview
Ronaldo Teixeira da Silva Jr, Glauber Rocha Lima Araújo, Hanna Santos Marques, Jéssica Oliveira de Souza Nascimento, Fernanda de Santana Rabelo, Ângela Reis Teixeira, Thanilly Silveira Macedo, Daniel Bastos Alves Lima, Fernanda Santos Mota, Raíssa Frazão Campos, Isabella Oliveira Bezerra, Railan Pessoa Silva, Larissa Alves Fernandes, Maria Luísa Cordeiro Santos, Fabrício Freire de Melo
The Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the new coronavirus of severe acute respiratory syndrome 2 (SARS-CoV-2), single-stranded, positive sense, spherical RNA virus with spikes protein that protrude on its surface giving the appearance of a crown, from the Latin corona. It belongs to the large family of coronaviruses (CoVs) and the genus β-coronavirus. COVID-19 can involve manifestations in the respiratory system, as well as other biological systems, as a intestinal.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p1-8 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.2.021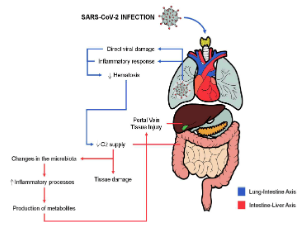
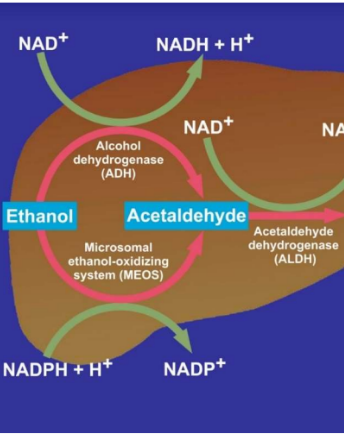
Alcoholic Liver Disease and the co-triggering Role of MEOS with Its CYP 2E1 Catalytic Cycle and ROS
Rolf Teschke, Manuela G. Neuman, Suthat Liangpunsakul, Helmut-Karl Seitz
Until the early sixties, the concept prevailed that alcoholic liver disease (ALD), also termed alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), results from malnutrition commonly observed among individuals consuming chronically high amounts of alcohol rather than being causally related to the use of alcoholic beverages. However, the malnutrition concept became a matter of debate because of the clinical observation that humans, even on a normal diet and without signs of underweight or malnutrition
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p9-25 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.2.022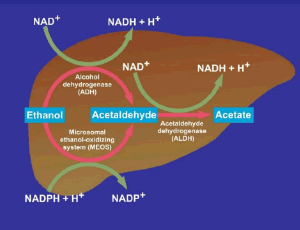
Updates in the Treatment of Superficial Gastric Neoplasms by Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Josue Aliaga Ramos, Vitor N. Arantes
Gastric cancer is one of the neoplasms with the highest degree of mortality worldwide, responsible for more than 780,000 deaths in 2018 and whose incidence has been increasing over the last few years, mainly in Asian and Latin American countries. The technological imaging advances in digestive endoscopy such as virtual chromoendoscopy and magnification associated with a systematic and comprehensive endoscopic examination of the entire gastric mucosa by a trained operator have optimized the early detection of pre-malignant and malignant lesions, which have favoured the high rate of curability through the use of endoscopic resection techniques such as endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD).
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p26-30 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.2.023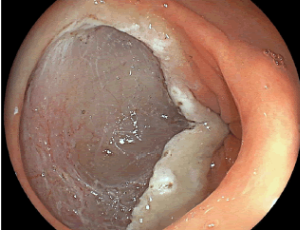
Importance of Autopsy from a Gastrointestinal Pathology Perspective: A Ten-year Review of 891 Autopsies
Ayesha S Siddique
There has been a decline in autopsy rates by 58% from 1972-2007. The major reason for this decline is the ability to diagnose diseases and disorders that result in mortality with greater accuracy. Additionally, the Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations dropped the standard practice of requiring a 20-25% autopsy rate for in-hospital deaths. The perception or attitude towards autopsies from both family members and clinicians is changing leading to a further decrease in the autopsy numbers.
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p31-34 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.2.024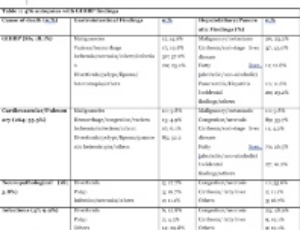
Advances in Functionalized Hybrid Biopolymer Augmented Lipid-based Systems: A Spotlight on Their Role in Design of Gastro Retentive Delivery Systems
Pratap Basim, Shashank Gorityala, Mallesh Kurakula
Biopolymers have earmarked their importance in the biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. Researchers are still working for the facilitation of better therapeutic effects and medical benefits. In this context, several strategies are on a play like functionalization of biopolymers with physicochemical modification, functionalization of lipids with biopolymers, development of composites or hybrid systems for bringing together the benefits of individual moieties/systems
Arch Gastroenterol Res, 2021, Volume 2, Issue 1, p35-47 | DOI: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.2.025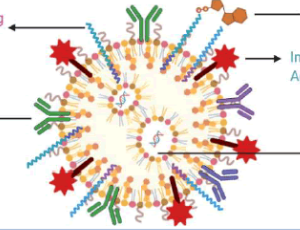
Recommended Articles
COVID-19 Clinical Research
While the global COVID-19 pandemic has challenged the entire humanity and health systems, it also triggered researchers to urgently perform clinical trials to assess the safety and efficacy of many agents and modalities to combat COVID-19. As of April 22, over 650 clinical studies have been registered both in USA and internationally. Results from these studies are also coming at a brisk pace in this unprecedented emergency.
Spontaneous Resolution of Infected Pancreatic Necrosis after Fistulization into Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
A 67-year-old female with a history of arterial hypertension and previous hysterectomy, was recovered, in July 2019, for moderately-severe acute biliary pancreatitis with evidence of stones in gallbladder and bile duct and pancreatic necrosis on imaging (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography. A contrast enhanced CT, a week after the admission, showed necrotic areas in the pancreas and a large peripancreatic fluid collection (60 mm long) with air pockets within (acute necrotic collection, with signs of infection. Since she was haemodynamically stable and there was no evidence of organ failure, according to “step-up approach”, she was managed medically with antibiotics (piperacillin-tazobactam + metronidazole) and fluids.
Role of the Gut Microbiome in the Modulation of Cancer Immunotherapy Response
The gut microbiome or gut flora is a vast community of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and fungi that inhabit the digestive tract of the human and other animals [1,2]. In the human body, bacterial species colonize into the oral cavity, skin, vagina, and placenta, however, the largest population of microorganisms resides in the intestine.
Evolution of Endoscopic Ampullectomy and Considerations for a Contemporary Approach
Endoscopic ampullectomy (or endoscopic resection of lesions associated with the ampulla of Vater) has now been performed for more than 25 years and has been supported by the literature, however, since its inception, the efficacy of this approach is still somewhat underappreciated. In our recent publication, despite its high success rate for clearance of ampullary adenomas, even with quite an extensive lateral spreading tumour component (LST-P), we wished to re-iterate and even celebrate the value of endoscopic ampullectomy, discuss our technique, highlight the risk of post procedural haemorrhage, discuss the adenoma recurrence rate and the need for a commitment to surveillance.
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer worldwide, affecting nearly one in eight women. Accurate cancer staging is essential for determining the patient’s prognosis and for choosing the appropriate treatment.
Gastric Cancer: A Brief Review, from Risk Factors to Treatment
Gastric cancer (GC), also known as stomach cancer, is a worldwide health problem. Anatomically, it can occur from the gastroesophageal junction to distal portions of the stomach. Considering both sexes, worldwide, it is the 5th most common neoplasm (5.7%) and the 3rd cause of mortality among malignancies, leading to approximately 782,000 deaths in 2018. The incidence varies geographically but 50% of new cases are diagnosed in developed countries. High incidence is observed in Asia, Latin America, and in the central and eastern parts of Europe. There are several ways to classify GC, but the most used is Lauren’s Classification, which proposes two main histological groups: intestinal and diffuse. This classification is important because there are marked etiological, pathological, and epidemiological differences between the subgroups, guiding the clinical approach for each patient.
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Liver Biopsy, Is It Ready for Prime Time?
Liver biopsy continues to be the gold-standard with regards to diagnosis and staging of the majority of liver diseases. Serologic markers certainly have helped in diagnosing various autoimmune and viral-related liver diseases. Furthermore, laboratory testing and imaging studies such as liver elastography have allowed us to non-invasively assess fibrosis. Unfortunately, there are shortcomings with these forms of testing. False positives or laboratory errors will lead to misleading diagnoses. Situations can also arise during which there are diagnostic dilemmas, such as an obese patient with positive autoimmune serology and elevated liver chemistries.
The Consideration of Endometriosis in Women with Persistent Gastrointestinal Symptoms and a Novel Neuromusculoskeletal Treatment Approach
Endometriosis is a chronic, hormone-dependent, inflammatory disease, characterized by the presence and growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterine cavity and it is associated with chronic pelvic pain and infertility. Worldwide, approximately 176 million women between the ages of 15 and 49 are affected by endometriosis. Endometriosis is a complex disease that induces a chronic inflammatory process and can be challenging to treat. Chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS) is defined as pelvic pain lasting greater than three to six months that is not solely related to menstruation, sexual activity or bowel movements.
Pharmacologic Therapy with Niacin for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Emerging Evidence
In pharmacologic doses niacin (nicotinic acid) has been used clinically for over six decades for atherogenic dyslipidemia and reduction of cardiovascular event risk. In combination with statin therapy, it effects regression of coronary atherosclerosis. Emerging evidence indicates a new potential use for niacin for the treatment of NAFLD and its complications. Despite this enormous amount of data on niacin, there is confusion and misconceptions about its use of a drug rather than as a vitamin, its formulations, and how it can be used in clinical practice. The purpose of this invited brief communication is to update and summarize this emerging evidence. We comment on how it may be valuable in the context of other drugs-in-development for NAFLD, especially for combination therapy for synergistic efficacy.
The Dual Role of Macrophages during Hepatitis B Infection
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) chronically infects more than 250 million individuals worldwide and is responsible for more than 800,000 deaths per year by promoting end-stage liver diseases, among which decompensated cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (WHO, July 2020) are prominent. Studies performed in chimpanzees or in animalversion of HBV (woodchuck HBV: WHBV) highlighted the lack of immune responses against the virus upon primary infection. Thus, HBV has been described as a “stealth” virus (i.e. a virus that does not modify/induce immune response in the cell). However, a growing number of studies describe that HBV is able to rapidly and efficiently counteract the innate immune response in a large variety of cells (hepatocytes, macrophages, Natural Killer cell…). Hereby, we focus on the role of macrophages (Mφ) during HBV infection.
What Can Go Wrong When Applying Immune Modulation Therapies to Target Persistent Bacterial Infections
Persistence is a transient phenotypic adaptation that confers survival to a small percentage of cells (between 0.01 and 10%) in genetically identical bacterial populations. Nevertheless, persistence greatly affects the evolution of acquired drug resistance mutations by decreasing antibiotic efficacy and generating a reservoir of surviving cells that can contribute to the onset of chronic infectious disease.
Refractory Gastro-oesophageal Reflux Disease and Laryngopharyngeal Reflux - Use the Bottom up Approach
The pathophysiology of typical gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) symptoms and reflux oesophagitis is associated with excess acid reflux, but both refractory GORD and laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) have strong links with functional gut disorders. Oesophageal pH impedance monitoring, our accepted gold standard for diagnosing GORD, has significant shortcomings when assessing proximal oesophageal and in particular pharyngeal reflux. In addition, identifying potential contamination of other parts of the respiratory tract such as lungs or sinuses is not possible. The association between irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and both refractory GORD and LPR suggests a common pathogenesis.
COVID-19 Disease and SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Patients with Cancer
Since the declaration of COVID-19 as a pandemic in March 2020 [1], there have been more than 100 million reported cases of COVID-19 worldwide and more than 2.1 million deaths [2].
COVID-19 and the Health of Illicit Substance Users: Preliminary Analysis from Illicit Drug Transaction Data
While much attention has been given to how COVID-19 patients are treated (or fail to be treated), the impact of the pandemic on illicit drug users remains largely undiscussed
Tenofovir at the Crossroad of the Therapy and Prophylaxis of HIV and HBV Infections
Tenofovir, alias (R)-PMPA, was first divulged as an anti- HIV agent in 1993 [1]. That it would in 2012, become the first antiretroviral agent, approved by the US FDA (Food and Drug Administration) to prevent HIV infection, could have been predicted from the findings of Tsai et al.
Gastrointestinal Manifestations of COVID-19: An Overview
The Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the new coronavirus of severe acute respiratory syndrome 2 (SARS-CoV-2), single-stranded, positive sense, spherical RNA virus with spikes protein that protrude on its surface giving the appearance of a crown, from the Latin corona. It belongs to the large family of coronaviruses (CoVs) and the genus β-coronavirus. COVID-19 can involve manifestations in the respiratory system, as well as other biological systems, as a intestinal.
COVID-19 Rapid Diagnostic Test Results and their Associations with Certain Factors Among the Residents of Balochistan
This paper analyses any possible association of various factors like gender, last COVID-19 PCR test results, BCG Vaccination, Seasonal Flu vaccination, occupation and confirmed case contact history with COVID-19 RDT results of the participants.
Alcoholic Liver Disease and the co-triggering Role of MEOS with Its CYP 2E1 Catalytic Cycle and ROS
Until the early sixties, the concept prevailed that alcoholic liver disease (ALD), also termed alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), results from malnutrition commonly observed among individuals consuming chronically high amounts of alcohol rather than being causally related to the use of alcoholic beverages. However, the malnutrition concept became a matter of debate because of the clinical observation that humans, even on a normal diet and without signs of underweight or malnutrition
Updates in the Treatment of Superficial Gastric Neoplasms by Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Gastric cancer is one of the neoplasms with the highest degree of mortality worldwide, responsible for more than 780,000 deaths in 2018 and whose incidence has been increasing over the last few years, mainly in Asian and Latin American countries. The technological imaging advances in digestive endoscopy such as virtual chromoendoscopy and magnification associated with a systematic and comprehensive endoscopic examination of the entire gastric mucosa by a trained operator have optimized the early detection of pre-malignant and malignant lesions, which have favoured the high rate of curability through the use of endoscopic resection techniques such as endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD).
Importance of Autopsy from a Gastrointestinal Pathology Perspective: A Ten-year Review of 891 Autopsies
There has been a decline in autopsy rates by 58% from 1972-2007. The major reason for this decline is the ability to diagnose diseases and disorders that result in mortality with greater accuracy. Additionally, the Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations dropped the standard practice of requiring a 20-25% autopsy rate for in-hospital deaths. The perception or attitude towards autopsies from both family members and clinicians is changing leading to a further decrease in the autopsy numbers.
About Scientific Archives
Scientific Archives is a global publisher initiated with the mission of ensuring equal opportunity for accessing science to research community all over the world. Spreading research findings with great relevance to all channels without any barrier is our goal. We want to overcome the challenges of Open Access with ensured quality and transparency.
